In the competitive landscape of tire inflation, understanding the nuances between nitrogen and air is crucial for international B2B buyers. As businesses seek reliable and cost-effective solutions for tire maintenance, sourcing the right inflation method can significantly impact operational efficiency, safety, and overall vehicle performance. This guide delves deep into the advantages and disadvantages of nitrogen versus air in tire inflation, providing a comprehensive overview that spans various applications—from commercial fleets in Africa to automotive industries in Europe and South America.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the types of gases used in tire inflation, their respective benefits, and the contexts in which each may be preferable. Additionally, we will address critical factors such as supplier vetting, cost implications, and availability in different regions, ensuring that B2B buyers are equipped with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. With a focus on practical insights and actionable strategies, this resource empowers businesses from the Middle East to Germany to optimize their tire maintenance practices, enhancing both performance and cost-efficiency. By navigating the complexities of tire inflation with nitrogen versus air, buyers can confidently choose the best solution tailored to their unique operational needs.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Air Inflation | Utilizes atmospheric air; widely available and cost-effective | General vehicle fleets, light-duty vehicles | Pros: Cost-effective, easy access; Cons: Loses pressure faster, more frequent maintenance needed. |
| Nitrogen Inflation | Uses pure nitrogen; larger molecules minimize air loss | Heavy-duty vehicles, racing, aviation | Pros: Better pressure retention, improved performance; Cons: Higher initial cost, limited availability. |
| Hybrid Inflation | Combination of air and nitrogen; offers a balance | Mixed-use fleets, emergency scenarios | Pros: Cost-effective with some benefits of nitrogen; Cons: Reduced effectiveness of nitrogen properties. |
| High-Performance Inflation | Specialized nitrogen blends for racing and performance | Motorsports, high-performance vehicles | Pros: Optimal tire performance and durability; Cons: Expensive, requires specialized service. |
| Inflation with Additives | Uses nitrogen with tire sealants or additives | Commercial vehicles, off-road applications | Pros: Enhanced durability and puncture resistance; Cons: Increased complexity and potential for compatibility issues. |
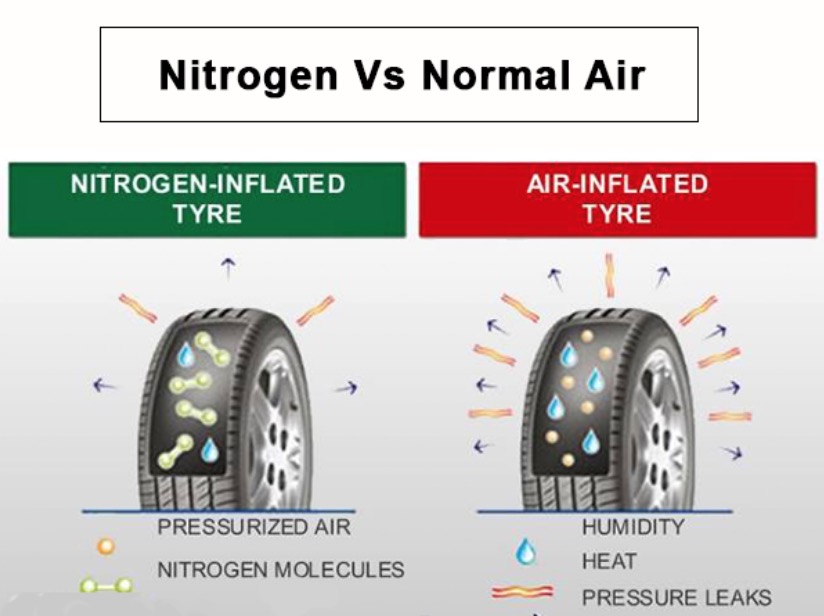
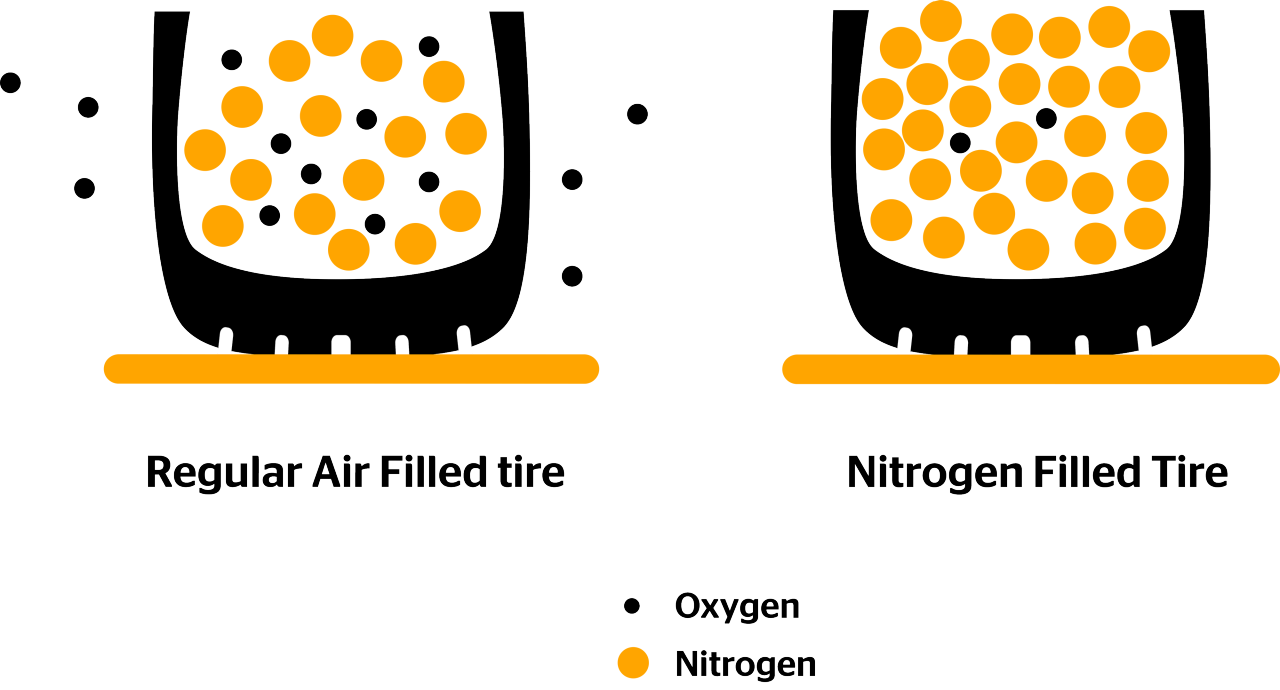
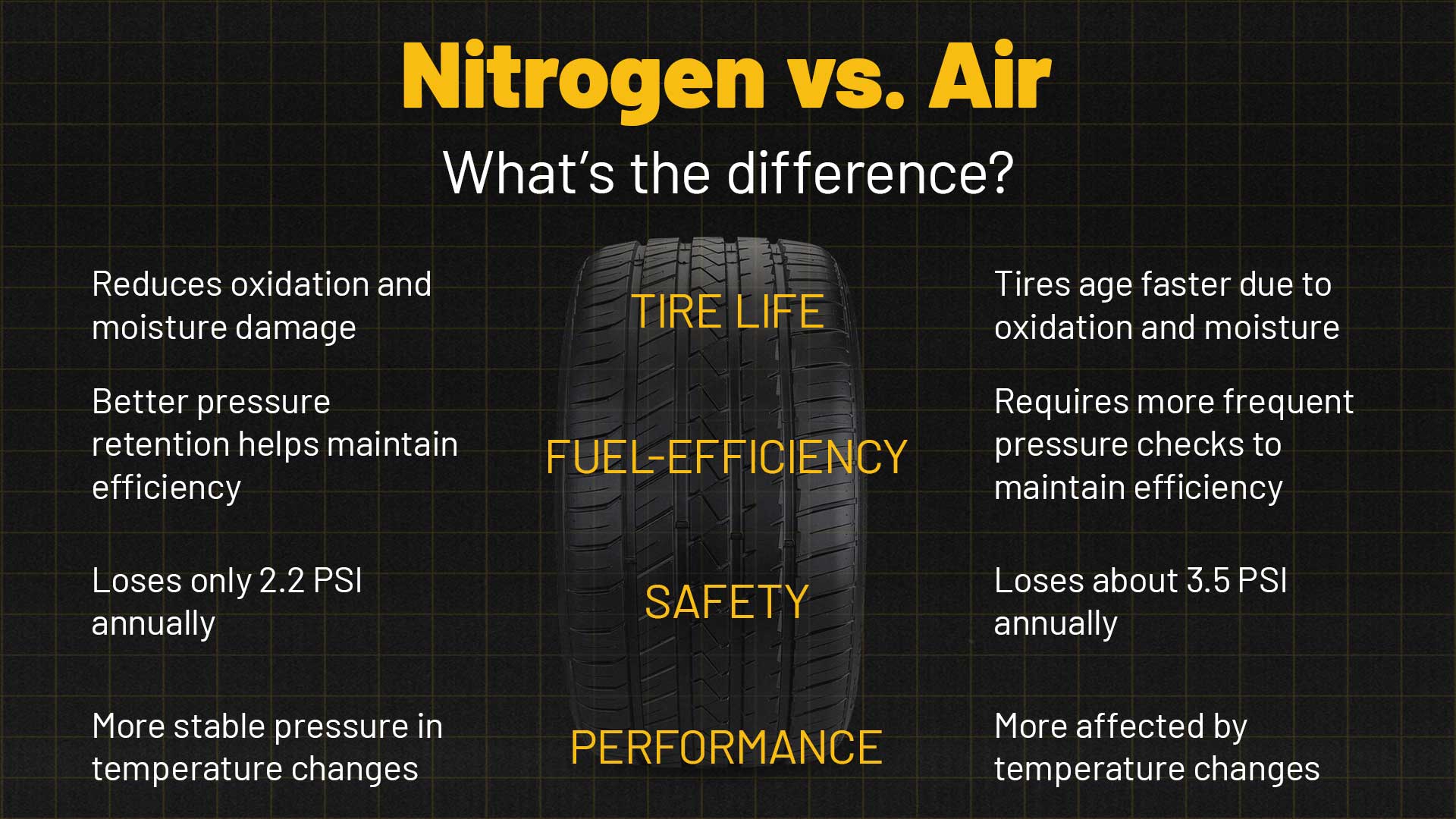
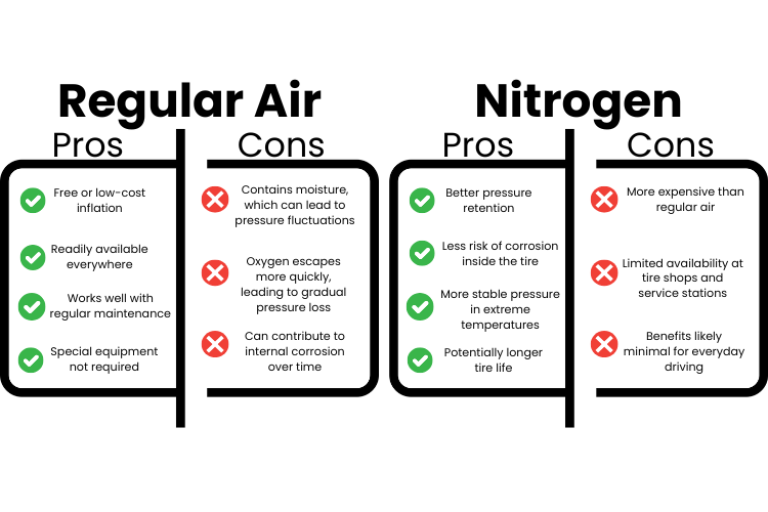
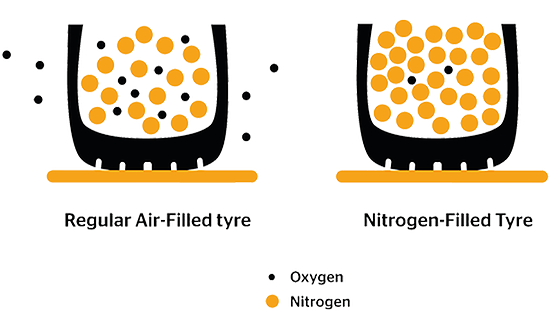
Standard air inflation is the most common method used for tire inflation, utilizing atmospheric air composed of approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace gases. It is readily available at virtually every service station, making it a cost-effective solution for general vehicle fleets and light-duty vehicles. However, tires inflated with air tend to lose pressure more quickly, necessitating frequent maintenance checks, which can be a drawback for businesses looking to minimize downtime.
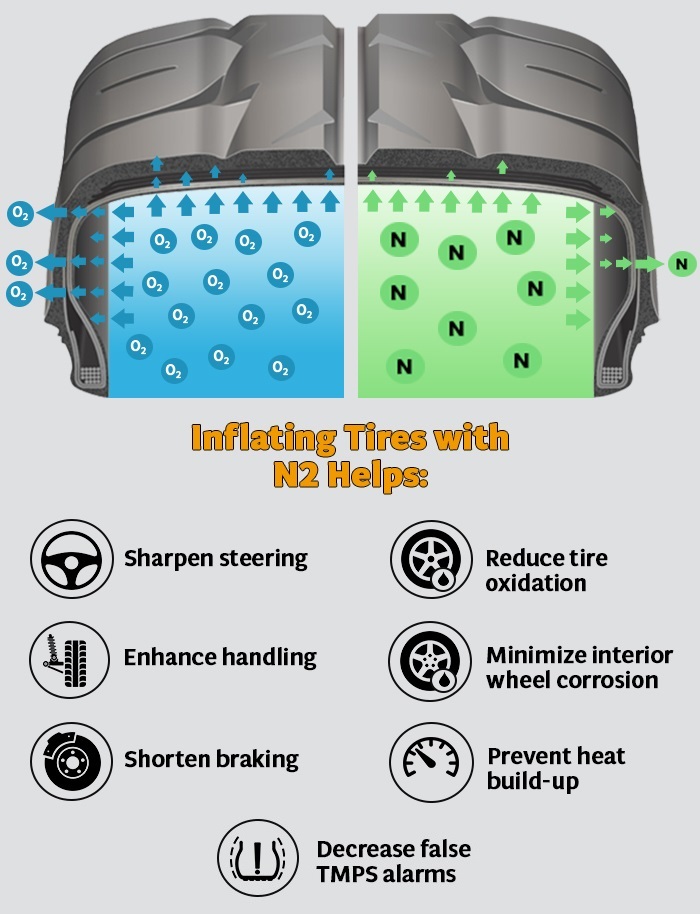
Nitrogen inflation is increasingly popular in heavy-duty vehicles, racing, and aviation due to its unique properties. Nitrogen molecules are larger than oxygen, allowing them to permeate through tire walls more slowly, resulting in better pressure retention. This inflation method is particularly beneficial for companies managing fleets that require optimal tire performance and fuel efficiency. Although the initial cost is higher and nitrogen filling stations may be less accessible, the long-term benefits often justify the investment.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
Hybrid inflation combines both air and nitrogen, creating a middle ground that offers some advantages of nitrogen while maintaining cost-effectiveness. This method can be particularly suitable for mixed-use fleets that may not require the full benefits of nitrogen inflation but want to reduce pressure loss compared to standard air. However, businesses must be aware that mixing the two gases diminishes the nitrogen’s effectiveness, so careful management is essential.
High-performance inflation typically involves specialized nitrogen blends designed for racing and performance vehicles. This method maximizes tire performance, providing better grip, handling, and durability under extreme conditions. While this method is ideal for motorsports teams and high-performance vehicle manufacturers, it comes with a higher price tag and requires access to specialized filling equipment. Businesses in this sector should weigh the performance benefits against the associated costs.
Inflation with additives, such as tire sealants or puncture-resistant materials, can be advantageous for commercial vehicles operating in challenging environments. This method enhances tire durability and resistance to punctures, making it suitable for off-road applications. While the added complexity and potential compatibility issues can be a concern, the benefits of reduced maintenance and improved safety often make this an attractive option for B2B buyers in sectors like logistics and construction.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tire inflation with nitrogen vs air | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aviation | Tire inflation for commercial aircraft | Enhanced safety and performance due to stable pressure | Availability of nitrogen filling stations at airports |
| Construction | Tires for heavy construction machinery | Reduced downtime and maintenance costs | Reliable nitrogen supply for tire maintenance |
| Automotive Racing | Tire inflation for race cars | Improved handling and tire longevity | Access to specialized nitrogen filling equipment |
| Transportation & Logistics | Tires for freight and delivery trucks | Improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear | Cost-effective nitrogen filling options for fleets |
| Mining | Tires for mining vehicles | Enhanced durability and safety in extreme conditions | Access to nitrogen fill stations in remote locations |
In the aviation industry, tire inflation with nitrogen is critical for commercial aircraft. Nitrogen’s larger molecular structure minimizes pressure loss, ensuring optimal tire performance during takeoff and landing. This stability enhances safety and reduces the risk of tire blowouts, which can be catastrophic. For international buyers in this sector, sourcing nitrogen must consider the availability of filling stations at airports and compliance with aviation safety regulations.
Heavy construction machinery often operates in demanding environments where tire performance is crucial. Filling tires with nitrogen can significantly reduce the frequency of pressure loss, leading to lower maintenance costs and decreased downtime. This is particularly beneficial for construction firms in regions like Africa and South America, where machinery reliability is essential. Buyers should focus on suppliers that can provide consistent nitrogen availability to meet their operational needs.
In automotive racing, tire inflation with nitrogen is preferred for its ability to maintain consistent tire pressure under extreme conditions. This results in better handling, improved grip, and longer tire life, which are vital for competitive performance. Racing teams in Europe and the Middle East must ensure they have access to specialized nitrogen filling equipment and services to maintain their competitive edge.
For freight and delivery trucks, nitrogen inflation can lead to improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear. This is particularly advantageous for logistics companies operating across vast distances in regions like Europe and South America, where fuel costs are a significant operational expense. Buyers should seek cost-effective nitrogen filling solutions that can support large fleets while ensuring minimal disruption to operations.
Mining vehicles operate in some of the harshest conditions, making tire integrity paramount. Nitrogen inflation helps maintain tire pressure and durability, which is essential for safety and efficiency in mining operations. International buyers in the mining sector must consider the logistical challenges of accessing nitrogen in remote locations and partner with suppliers who can meet these demands reliably.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those managing fleets in regions like Africa and South America, often face challenges in sourcing reliable nitrogen inflation services. Many local service providers focus solely on traditional air inflation, leaving businesses with limited options for nitrogen. This can lead to inconsistent tire performance and higher operational costs due to fluctuating tire pressures, especially in extreme weather conditions.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this issue, B2B buyers should proactively establish relationships with specialized tire service providers that offer nitrogen inflation. Conduct market research to identify suppliers who specialize in nitrogen filling and have a proven track record. Additionally, consider leveraging technology by implementing a centralized management system for fleet maintenance that includes monitoring tire pressure and scheduling regular nitrogen inflation sessions. This not only ensures optimal tire performance but also promotes safety and efficiency across the fleet.
The Problem: Many businesses are hesitant to adopt nitrogen inflation due to perceived high costs compared to traditional air inflation. For companies operating on tight margins, the additional expense of nitrogen can seem unjustifiable, particularly if the benefits are not clearly communicated or understood. This hesitance can lead to missed opportunities for improved vehicle performance and reduced fuel consumption.
The Solution: B2B buyers should conduct a cost-benefit analysis that weighs the initial expenses of nitrogen inflation against the long-term savings it can generate. Highlight the potential for improved fuel efficiency, reduced tire wear, and lower maintenance costs. Furthermore, consider negotiating bulk pricing with nitrogen suppliers or exploring partnership options that may offer reduced rates for long-term contracts. By quantifying the benefits and aligning them with the company’s financial goals, buyers can make a more informed decision that justifies the upfront investment.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are unsure about the tangible performance benefits of using nitrogen versus air in tires. This uncertainty often stems from a lack of awareness or understanding of how nitrogen can impact tire pressure stability, fuel efficiency, and overall vehicle handling. Without clear insights, decision-makers may stick to conventional air inflation out of habit rather than exploring innovative solutions.
The Solution: To address this knowledge gap, B2B buyers should invest in training and informational resources for their teams. Organize workshops or webinars featuring tire experts who can explain the science behind nitrogen inflation and its benefits in detail. Additionally, implementing a pilot program that allows a select number of vehicles to be fitted with nitrogen-filled tires can provide firsthand data and performance metrics. Collect and analyze this data to build a compelling case for wider adoption, showcasing the real-world advantages of nitrogen inflation in terms of safety, efficiency, and cost savings.
When considering tire inflation options, particularly nitrogen versus air, various materials play a crucial role in the overall performance and suitability of the application. Below, we analyze three common materials associated with tire inflation systems, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
Key Properties: Rubber is flexible, durable, and has good pressure retention capabilities. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically from -40°C to 100°C, and is resistant to wear and tear.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of rubber is its ability to maintain elasticity and flexibility under varying conditions. However, it can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and ozone, leading to potential leaks. The cost of rubber is generally low, but manufacturing complexity can increase depending on the specific formulation and additives used.
Impact on Application: Rubber’s compatibility with both nitrogen and air makes it suitable for various tire applications. However, the longevity of nitrogen-filled tires may be enhanced due to reduced oxidation and moisture.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for rubber quality. Additionally, local climatic conditions can affect rubber performance, necessitating region-specific formulations.
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can withstand high pressures. It is commonly used in tire valve stems and fittings, which are crucial for maintaining tire integrity.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its resistance to corrosion, particularly in humid or saline environments, making it ideal for regions like coastal areas in South America. However, aluminum can be more expensive than other metals and may require specific machining processes, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum valves are compatible with both nitrogen and air, providing reliable sealing capabilities. Their lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regional standards for aluminum quality and corrosion resistance, particularly in environments with high humidity or salt exposure. Compliance with local regulations is essential to ensure product longevity.
Key Properties: Steel is known for its strength and durability, with a high resistance to deformation under pressure. It typically has a higher weight compared to aluminum but offers excellent structural integrity.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its cost-effectiveness and robustness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, steel is prone to rust and corrosion, especially in humid environments, which can compromise tire integrity over time.
Impact on Application: Steel rims can effectively support both nitrogen and air-filled tires, but the risk of corrosion may be heightened in regions with high moisture levels. Regular maintenance and protective coatings can mitigate this issue.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should consider the local climate when selecting steel rims. Compliance with standards such as JIS and ASTM is crucial to ensure quality and safety.
| Material | Typical Use Case for tire inflation with nitrogen vs air | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Tire construction for both nitrogen and air inflation | Excellent elasticity and pressure retention | Degrades over time due to UV exposure | Low |
| Aluminum | Valve components for tire inflation systems | Corrosion-resistant and lightweight | Higher cost and machining complexity | Med |
| Steel | Rims for supporting tires filled with nitrogen or air | Cost-effective and robust | Prone to rust and corrosion | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in tire inflation with nitrogen versus air, offering actionable insights for B2B buyers across various international markets. Understanding these materials and their properties can help businesses make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
The manufacturing process for tire inflation systems, whether using nitrogen or air, involves a series of well-defined stages. Each stage requires precision and adherence to stringent quality standards to ensure the reliability and performance of the final product.
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves sourcing high-quality raw materials. For tire inflation systems, this includes the rubber compounds for tire construction, metal for valve stems, and the gases themselves—nitrogen and air.
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This process involves shaping the rubber compounds into tire forms.
Following the forming process, the assembly stage begins, where all components are brought together.
The finishing stage involves final inspections and preparations for the tires to be ready for distribution.
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the tire manufacturing process, especially given the safety implications of tire performance.
Adhering to international standards ensures that products meet safety and performance benchmarks. Notable standards include:
Quality control checkpoints are critical in maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. These checkpoints include:
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential to ensure that the products meet required standards.
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of confidence. These inspectors can perform unbiased assessments of the manufacturing processes and final products, ensuring compliance with agreed-upon specifications.
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification can be particularly important for international buyers.
In the competitive landscape of tire manufacturing, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers. By ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality controls and international standards, buyers can secure reliable, high-performance tire inflation systems that meet their operational needs. This diligence not only enhances safety but also fosters long-term partnerships and trust in supplier relationships.
This guide provides B2B buyers with a structured approach to sourcing tire inflation solutions, specifically comparing nitrogen and air. Understanding the nuances between these two options is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that can impact vehicle performance, safety, and overall operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
Start by clarifying the requirements for your tire inflation needs. Consider factors such as the types of vehicles in your fleet, operating conditions, and expected tire performance.
– Weight Capacity: Heavier vehicles may benefit more from nitrogen, which maintains tire pressure better under load.
– Climate Considerations: In regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, nitrogen can provide more stable pressure retention.
Investigate current market trends regarding nitrogen versus air tire inflation. This includes understanding user experiences and preferences in your target regions.
– Regional Preferences: Different areas may have varying opinions on the effectiveness of nitrogen versus air, influenced by climate and road conditions.
– Industry Insights: Look for case studies or surveys from industries similar to yours to gauge the effectiveness of nitrogen inflation in real-world applications.
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality.
– Company Profiles: Request detailed company information, including years in business, and expertise in tire inflation solutions.
– Client References: Ask for testimonials or case studies from other businesses in your industry to validate their claims.
Ensure that your suppliers possess the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. This step is vital for maintaining quality and safety.
– Quality Assurance: Look for ISO certifications or similar standards that indicate a commitment to quality control.
– Safety Compliance: Ensure that the supplier adheres to safety regulations relevant to tire inflation systems, especially if nitrogen is involved.
Conduct a comprehensive cost analysis comparing nitrogen and air inflation solutions. While nitrogen may have higher initial costs, consider the long-term benefits.
– Operational Efficiency: Calculate potential savings from improved fuel economy and reduced tire wear associated with nitrogen use.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in maintenance and re-inflation costs over time to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Establish a maintenance plan to ensure the longevity of your tire inflation system. This includes regular pressure checks and supplier support.
– Supplier Support Services: Evaluate the level of technical support and training provided by the supplier to your staff.
– Maintenance Schedule: Develop a routine maintenance plan to monitor tire pressure and performance, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Finally, compile all gathered information to make a well-informed decision on your tire inflation solution.
– Decision Matrix: Create a matrix to compare suppliers based on criteria such as cost, reliability, and customer service.
– Trial Period: Consider negotiating a trial period with the selected supplier to assess the performance of nitrogen versus air in your specific applications before making a long-term commitment.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of tire inflation solutions, ensuring they choose the best option for their operational needs.
When analyzing the cost structure for tire inflation with nitrogen versus air, several key components must be considered. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The primary material difference lies in the gas used for inflation. Nitrogen is typically more expensive due to the purification process required to extract it from the atmosphere. In contrast, air, which is composed of approximately 78% nitrogen, is readily available and incurs minimal costs.
Labor: Labor costs will vary based on the complexity of the tire inflation process. Filling tires with nitrogen often requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, potentially increasing labor costs compared to standard air filling, which can be performed quickly at gas stations.
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs can be higher for nitrogen filling due to the need for dedicated nitrogen storage and inflation equipment. In contrast, air inflation requires less specialized equipment, resulting in lower overhead.
Tooling and QC: The investment in tooling for nitrogen inflation systems can be significant. Additionally, quality control measures must ensure that the nitrogen purity levels meet industry standards, further adding to costs.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
Logistics: The logistics of sourcing nitrogen, including storage and distribution, can be more complex than for air. The need for specialized tanks and transportation for nitrogen can drive up logistics costs.
Margin: Suppliers may charge a premium for nitrogen inflation services due to the perceived benefits and the increased costs associated with providing this service.
Several factors can influence the pricing of tire inflation services, particularly for B2B buyers looking to optimize their purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchasing of nitrogen can lead to significant cost savings. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, making it essential for buyers to negotiate favorable terms.
Specs and Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific operational needs may incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of custom inflation solutions versus standard offerings to manage expenses effectively.
Materials: The choice of inflation gas can significantly impact costs. While nitrogen is more expensive, it may offer long-term savings through enhanced tire performance and longevity, which can justify the initial investment.
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with quality certifications and proven track records may charge higher prices. However, investing in quality can lead to reduced maintenance costs and improved safety.
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Buyers should conduct due diligence to ensure they are partnering with reputable providers who can deliver consistent quality and service.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery can also influence costs. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize logistics costs while ensuring timely delivery.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when procuring tire inflation services.
Negotiation: Always engage in negotiations with suppliers. Leverage volume purchases and long-term contracts to secure better pricing and terms.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial inflation costs. Factors such as fuel efficiency, tire lifespan, and maintenance costs should be included in your analysis.
Pricing Nuances: Understand the pricing nuances specific to your region. For example, in Europe, regulatory compliance may add to costs, while in developing markets, availability of nitrogen inflation services may be limited, affecting pricing.
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better service and pricing. Regular communication can also help buyers stay informed about market trends and pricing changes.
Prices for tire inflation services can vary widely based on geographic location, market conditions, and specific supplier offerings. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing that aligns with their operational needs.
In the world of tire inflation, the debate between using nitrogen and air has garnered considerable attention. However, there are alternative solutions that B2B buyers might consider when evaluating the best approach for their fleets or operations. This analysis will compare tire inflation using nitrogen versus air against two viable alternatives: tire inflation with compressed air and the use of tire sealants.
| Comparison Aspect | Tire Inflation With Nitrogen Vs Air | Compressed Air Inflation | Tire Sealants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Maintains pressure longer; better handling | Sufficient for daily use; pressure drops faster | Prevents leaks; can seal punctures |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; $20/tire average | Lower cost; typically free at gas stations | Moderate cost; $10-$30 per tire |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment; less available | Widely available at gas stations | Easy to apply; DIY options available |
| Maintenance | Low; check pressure regularly | Regular checks needed; more frequent inflation | Minimal; seals punctures automatically |
| Best Use Case | High-performance vehicles; extreme conditions | Everyday vehicles; general use | Off-road vehicles; emergency kits |
Compressed air is the traditional method for inflating tires, consisting primarily of oxygen and nitrogen. While it is cost-effective and readily available at most gas stations, its performance may not match that of nitrogen inflation. Tires inflated with air tend to lose pressure more quickly due to the smaller size of oxygen molecules, which can lead to more frequent maintenance. Despite these drawbacks, compressed air is suitable for everyday vehicles where high performance is not a critical concern.
Tire sealants present an innovative solution for maintaining tire integrity. These products are designed to seal punctures as they occur, reducing the need for frequent inflation and tire replacements. Sealants are easy to apply, often coming in a DIY format, making them a practical choice for off-road vehicles or emergency situations. However, the effectiveness of sealants can vary based on the size and location of the puncture, and they may not restore full tire pressure, which can affect handling. Despite these limitations, they offer a compelling option for those seeking to minimize downtime and maintenance.
When selecting the best tire inflation solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and vehicle types. Nitrogen inflation is ideal for high-performance or specialized vehicles requiring consistent pressure and handling, while compressed air is a cost-effective choice for everyday applications. Tire sealants can be beneficial for emergency preparedness and off-road scenarios but may not replace the need for regular maintenance. Ultimately, the right solution will align with the buyer’s performance goals, operational costs, and ease of implementation. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can optimize their tire management strategies and enhance vehicle performance.
When considering tire inflation methods, understanding specific technical properties can significantly impact decision-making for B2B buyers. Here are critical specifications that should be evaluated:
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms associated with tire inflation:
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of tire inflation with nitrogen versus air more effectively, ensuring they make informed choices that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
The global tire inflation market is witnessing a significant shift due to increasing awareness of tire maintenance and performance enhancement. Nitrogen inflation is gaining traction, particularly in sectors involving heavy-duty vehicles, such as logistics and aviation, where tire pressure stability is crucial. In regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can be challenging, the ability of nitrogen to maintain tire pressure longer than regular air can be a game-changer for fleet operators. Emerging technologies, such as smart tire monitoring systems that leverage IoT (Internet of Things), are also influencing purchasing decisions, allowing businesses to optimize tire performance and monitor inflation levels in real-time.
Moreover, regulatory pressures in Europe and the Middle East are pushing companies to adopt more efficient tire management practices. Germany, known for its automotive innovation, is seeing increased investments in nitrogen inflation systems, driven by a focus on performance and safety. Similarly, in Saudi Arabia, the combination of extreme temperatures and demanding road conditions creates a favorable environment for nitrogen use, as it mitigates the risks associated with tire pressure fluctuations. As international B2B buyers consider their options, understanding these regional dynamics and technological advancements is critical for making informed sourcing decisions.
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the tire inflation sector, with businesses increasingly seeking environmentally friendly practices. Nitrogen inflation offers a distinct advantage in this context; it reduces the need for frequent refilling, thereby minimizing waste and resource consumption. Furthermore, the production of nitrogen can be achieved through sustainable methods, making it a more eco-friendly option compared to traditional air, which is often compressed from natural gas.
Ethical sourcing is also paramount for B2B buyers. Companies are now expected to ensure that their suppliers adhere to responsible practices throughout the supply chain. This involves selecting partners who prioritize environmental certifications and use sustainable materials in their tire products. As a result, buyers should look for suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing practices and can provide certifications that confirm their commitment to sustainability. By aligning with such suppliers, businesses can not only enhance their corporate responsibility image but also appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation with nitrogen vs air
The evolution of tire inflation technologies has been marked by a transition from simple air inflation to the more advanced use of nitrogen. Initially, air was the only option available, primarily due to its accessibility and cost-effectiveness. However, as industries recognized the benefits of nitrogen, particularly in high-performance applications like racing and aviation, its use began to spread to everyday vehicles.
In recent years, advancements in tire technology, such as improved rubber compounds and construction methods, have complemented the benefits of nitrogen inflation, leading to better fuel efficiency and tire longevity. This progression has been particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as the focus on total cost of ownership has increased. As businesses seek to optimize their fleets and reduce operational costs, understanding the historical context of tire inflation technologies is crucial for making strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
How do I determine if nitrogen or air is better for my fleet tires?
When deciding between nitrogen and air for tire inflation, consider your operational needs and the environment in which your vehicles operate. Nitrogen-filled tires maintain pressure longer and reduce moisture, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and tire longevity. If your fleet operates in extreme temperatures or demanding conditions, nitrogen may provide a more stable performance. However, if cost is a significant concern, standard air is more readily available and cost-effective. Evaluate your fleet’s specific usage patterns to make the best choice.
What is the best inflation method for heavy-duty vehicles?
For heavy-duty vehicles, nitrogen is often the superior choice due to its larger molecular structure, which minimizes pressure loss over time. This is particularly beneficial for trucks and machinery that endure heavy loads and varying temperatures. The stability of nitrogen can enhance tire performance, leading to better handling and safety. However, it’s essential to ensure that your local suppliers can provide nitrogen inflation services consistently to avoid operational disruptions.
Can I mix nitrogen and air in my tires, and what are the implications?
Yes, you can mix nitrogen and air in your tires, but it is not recommended if you want to reap the full benefits of nitrogen. Mixing reduces the effectiveness of nitrogen, as the presence of oxygen can lead to moisture buildup, which can compromise tire performance. If you find yourself needing to inflate a nitrogen-filled tire with air due to availability issues, be aware that this may necessitate more frequent monitoring and adjustments to tire pressure.
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing nitrogen tire inflation services?
When sourcing nitrogen tire inflation services, consider supplier reliability, equipment quality, and cost. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to provide consistent nitrogen purity, as lower purity can diminish performance benefits. Additionally, assess their logistics capabilities to ensure timely service, especially if you operate a large fleet. Finally, consider any local regulations that might affect the availability and pricing of nitrogen inflation services in your region.
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for nitrogen tire inflation equipment?
Minimum order quantities for nitrogen tire inflation equipment can vary widely based on the supplier and your specific needs. Typically, suppliers may require a minimum order of several units or a bulk purchase for installation in a commercial setting. It’s advisable to engage with multiple suppliers to compare MOQs and negotiate terms that fit your operational requirements, especially if you are looking to outfit multiple locations.
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my nitrogen tire inflation system?
To ensure quality assurance for your nitrogen tire inflation system, select suppliers who provide detailed specifications and testing certifications for their equipment. Regular maintenance and calibration of inflation systems are crucial; thus, choose suppliers that offer ongoing support and training. Implement a routine inspection schedule to monitor tire performance and pressure levels, ensuring that the system operates effectively and meets your fleet’s performance standards.
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing nitrogen inflation services internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of nitrogen inflation services can vary significantly. Common terms include upfront payment, net 30, or net 60 days post-delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront and consider using letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. Ensure that your agreements are detailed and transparent, covering potential additional costs such as shipping and customs fees.
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing nitrogen for tire inflation?
When sourcing nitrogen for tire inflation, logistics considerations include transportation, storage, and local regulations regarding gas handling. Ensure that the supplier has the capability to deliver nitrogen in a timely manner and that they comply with safety standards for gas transportation. Additionally, confirm that your facility has appropriate storage options for nitrogen tanks, and be aware of any local laws governing the use and storage of compressed gases to avoid potential legal issues.
Domain: principlevolvocarssanantonio.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Nitrogen-filled tires can hold their pressure longer, potentially improving comfort and fuel economy. Filling tires with air is less expensive and more commonly available. Both nitrogen and air have unique advantages and disadvantages. Nitrogen is preferred in heavy equipment and race cars due to its larger molecule size, which helps maintain tire pressure. However, nitrogen is more costly and les…
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Filling tires with nitrogen can provide several benefits compared to standard compressed air, which is mostly nitrogen (about 80%). Key advantages include: 1. Inert nature of nitrogen reduces oxidation on the inner rim surface, minimizing leakage at the tire bead. 2. Nitrogen lacks water molecules, which helps maintain consistent tire pressure during temperature fluctuations, preventing pressure d…
Domain: sunsationall.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Nitrogen Tire Inflation service offered by SUNSATIONall for $20.00. The service uses a state-of-the-art Branick® nitrogen inflation system that purges tires of 95-99% oxygen through a 3 purge cycle and inflates all 4 tires simultaneously in about 5 minutes. Benefits include: prevention of oxidation, moisture, and corrosion, better pressure retention (tires lose no pressure from permeation), increa…
Domain: continentaltire.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Nitrogen is offered as an alternative to air for tire inflation. It is an inert gas that does not support moisture or combustion, making it suitable for specialized applications like aircraft, mining, and professional auto racing. While nitrogen may reduce tire inflation loss by permeation, it does not prevent loss from punctures or leaks. Regular tire pressure checks are essential regardless of t…
In evaluating the strategic sourcing of tire inflation methods—nitrogen versus air—international B2B buyers must consider both the operational benefits and cost implications. Nitrogen-filled tires offer superior pressure retention, enhancing fuel efficiency and extending tire life, which can be particularly advantageous for businesses operating fleets or heavy machinery. Conversely, air remains a more accessible and cost-effective solution, particularly in regions where nitrogen filling stations are limited.
Strategic sourcing decisions should focus on the unique requirements of the business, including vehicle type, operational conditions, and long-term cost savings. Companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must weigh the initial investment in nitrogen against the potential for reduced maintenance and improved performance over time.
As the automotive landscape evolves, integrating advanced tire inflation technologies could position your business for greater efficiency and sustainability. Now is the time to evaluate your tire inflation strategy. Consider reaching out to suppliers and industry experts to explore the best options tailored to your operational needs, ensuring your fleet is both efficient and competitive in today’s market.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.