In an increasingly interconnected global market, the ability to effectively inflate tires at a gas station is a critical skill that directly impacts vehicle performance, safety, and operational efficiency. Many B2B buyers, especially those sourcing automotive services or products in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in ensuring tire maintenance is both cost-effective and reliable. This guide addresses these challenges by offering a comprehensive overview of tire inflation processes, essential tools, and best practices tailored for various environments and vehicle types.
Within this guide, we delve into the specifics of tire inflation, exploring different types of air compressors available at gas stations, the varying applications based on vehicle specifications, and the crucial aspects of supplier vetting. Additionally, we provide insights into cost considerations, enabling businesses to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals. By empowering international B2B buyers with actionable knowledge, this resource not only enhances their understanding of tire maintenance but also contributes to improved fleet safety and longevity.
As you navigate the nuances of tire inflation, this guide serves as a valuable tool to streamline your purchasing decisions and ensure that your tire maintenance practices meet industry standards while maximizing efficiency and safety across your operations.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Air Pump | Requires physical effort to operate; often portable and compact | Small fleet operations, workshops | Pros: Low cost, no power needed. Cons: Labor-intensive, time-consuming. |
| Digital Air Compressor | Automatically inflates tires to set PSI; often includes pressure gauge | Automotive service centers, rentals | Pros: Precision, ease of use. Cons: Higher initial investment, potential maintenance required. |
| Coin-Operated Air Station | Typically found at gas stations; requires payment to operate | Public service stations, gas stations | Pros: Accessibility, no upfront investment. Cons: Ongoing costs, limited control over air quality. |
| Mobile Tire Inflation Service | On-site service using a truck-mounted compressor | Roadside assistance, fleet management | Pros: Convenience, saves time. Cons: Higher service fees, dependency on service availability. |
| Self-Service Tire Inflation Machine | Automated stations with user-friendly interfaces | Convenience stores, large parking lots | Pros: User-friendly, quick service. Cons: May be less reliable than manual checks, limited to set inflation rates. |
Manual air pumps are often compact and portable, making them suitable for small fleet operations or individual workshops. They require physical effort to operate, which may deter some users but can be advantageous for those looking to minimize costs. B2B buyers should consider the labor intensity and time involved in using these pumps, as they can be more time-consuming than automated options. However, their low cost and independence from power sources make them appealing for businesses with limited budgets.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
Digital air compressors are designed for precision, automatically inflating tires to a set PSI. This feature is particularly beneficial in automotive service centers and rental businesses where accuracy is paramount. The ease of use and time-saving nature of these devices can significantly enhance operational efficiency. However, B2B buyers should weigh the higher initial investment against the potential for reduced labor costs and improved customer satisfaction due to reliable tire maintenance.
Coin-operated air stations are commonly found at gas stations and offer a convenient solution for tire inflation without upfront costs. These stations provide accessibility for various users, including fleet drivers and the general public. However, buyers should consider the ongoing costs associated with using these machines and the limited control over the quality of air supplied. The potential for mechanical issues or outages at these stations could also disrupt operations, making alternative solutions worth exploring.
Mobile tire inflation services utilize truck-mounted compressors to provide on-site tire inflation, which is ideal for roadside assistance and fleet management. This service offers unparalleled convenience and can save valuable time, particularly in emergency situations. However, B2B buyers should assess the higher service fees associated with this option and consider the reliability of service availability, especially in remote areas.
Self-service tire inflation machines provide an automated, user-friendly interface for quick tire inflation. These machines are often located in convenience stores and large parking lots, making them accessible to a wide audience. While they can streamline the tire inflation process, buyers should be aware of potential reliability issues and the fact that they may not allow for precise adjustments compared to manual checks. The ease of use and speed can, however, enhance customer satisfaction and retention.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to inflate tires at a gas station | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics & Transport | Regular tire inflation for delivery vehicles | Enhances safety and efficiency, reducing downtime and fuel costs | Reliability of air compressors, accessibility, and maintenance support |
| Automotive Services | Tire inflation services offered at repair shops | Attracts customers, increases service revenue, and promotes safety | Quality of equipment, ease of use, and availability of parts |
| Agriculture | Inflation of agricultural vehicle tires at fueling stations | Ensures optimal performance of farming equipment, minimizing crop loss | Compatibility with various tire sizes and pressure specifications |
| Tourism & Hospitality | Tire inflation stations at tourist hotspots | Provides convenience for travelers, enhancing customer satisfaction | Location accessibility, operational hours, and service reliability |
| Construction | Tire inflation for construction machinery | Reduces equipment failure and maintenance costs, improving project timelines | Durability of inflators, ease of use in rugged environments |
In the logistics and transport sector, maintaining optimal tire pressure is critical for delivery vehicles. Gas stations equipped with air compressors allow drivers to easily inflate tires, ensuring safety and efficiency. Properly inflated tires improve fuel economy and reduce the risk of blowouts, which can lead to costly delays. For international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable and durable air compressors that can withstand varying environmental conditions is essential.
Automotive service providers can enhance their offerings by including tire inflation services at gas stations. This not only attracts customers but also increases overall service revenue. By ensuring that vehicles leave with properly inflated tires, service centers can promote safety and customer satisfaction. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, investing in high-quality, user-friendly inflators can streamline operations and enhance service delivery.
In agriculture, maintaining tire pressure on farming equipment is vital for optimal performance. Access to tire inflation services at gas stations can help farmers quickly address pressure issues, reducing the risk of equipment failure during critical planting or harvesting periods. International buyers need to consider inflators that can accommodate the larger tire sizes common in agricultural machinery and ensure they meet local pressure specifications.
Gas stations located near tourist attractions can significantly enhance visitor experience by providing convenient tire inflation stations. This service allows travelers to maintain their vehicles easily, contributing to road safety and customer satisfaction. For B2B buyers in the hospitality sector, the strategic placement of inflation stations and the reliability of the equipment are key factors that can influence customer loyalty and repeat business.
In the construction industry, ensuring that machinery operates at optimal tire pressure is crucial for avoiding equipment failures that can derail project timelines. Access to tire inflation services at gas stations helps construction teams maintain their vehicles and machinery efficiently. Buyers in this sector should focus on durable inflators that can withstand harsh working conditions and ensure quick inflation to minimize downtime on construction sites.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly fleet managers and logistics companies, often face challenges in ensuring that their drivers know the correct tire pressure specifications for different vehicles. This lack of knowledge can lead to improper inflation, resulting in decreased fuel efficiency, increased tire wear, and ultimately, higher operational costs. In regions where tire pressure variations are common due to environmental conditions, this issue can become even more pronounced, leading to safety risks and unexpected breakdowns.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, businesses should invest in comprehensive training programs for their drivers that emphasize the importance of tire maintenance, specifically tire pressure management. This training should include the location of tire pressure specifications, which are typically found in the vehicle’s manual and on a sticker inside the driver’s door. Additionally, companies can provide easy-to-read reference guides or QR codes linking to digital resources on tire maintenance. Regular workshops or refreshers can keep this knowledge top-of-mind, ensuring that all drivers are equipped to check and inflate their tires accurately, thereby enhancing fleet safety and efficiency.
The Problem: B2B buyers in regions where gas stations may not consistently offer functional air compressors face significant logistical challenges. This inconsistency can lead to delays in delivery schedules if drivers are unable to inflate tires when needed. Such situations can be particularly problematic for companies operating in remote areas or regions with limited infrastructure, where alternatives may not be readily available.
The Solution: To address this challenge, businesses should establish partnerships with reliable fuel suppliers or invest in portable air compressors for their fleet. Portable air compressors can be compact and easily stored in company vehicles, allowing drivers to inflate tires regardless of gas station availability. Furthermore, companies can maintain a directory of gas stations with verified working air compressors, shared through a mobile app or printed resource. This proactive approach ensures that drivers are well-prepared for tire maintenance, regardless of their location, thereby minimizing downtime and ensuring efficient operations.
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers, especially in industries involving new or less experienced drivers, is the difficulty in properly using air inflation equipment at gas stations. Misuse of these machines can lead to under-inflation or over-inflation of tires, both of which pose safety risks and could result in costly repairs or accidents.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
The Solution: To combat this problem, businesses should implement hands-on training sessions focusing on the proper use of air inflation equipment. These sessions should cover how to read tire pressure gauges, the importance of checking tire pressure before and after inflation, and the steps to take when using gas station air compressors. Additionally, instructional videos can be created and shared with drivers, allowing them to refer back to the content as needed. Creating a culture of safety and proper maintenance will empower drivers to take responsibility for their vehicles, ultimately enhancing fleet reliability and reducing the risk of accidents.
When it comes to inflating tires at gas stations, the materials involved in the construction of air compressors, hoses, and fittings play a critical role in ensuring efficient and safe operation. Below, we analyze four common materials used in these applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Rubber is a widely used material in tire inflation hoses and seals due to its excellent elasticity and flexibility. It can withstand a temperature range of -40°F to 200°F (-40°C to 93°C) and has good pressure ratings, typically handling up to 150 psi. Its inherent corrosion resistance makes it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber hoses are durable and resistant to wear, but they can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and ozone. While rubber is generally cost-effective, the manufacturing complexity can increase with the need for specialized compounds to enhance durability.
Impact on Application:
Rubber hoses are compatible with air and nitrogen but may not be suitable for corrosive gases.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that rubber products meet local compliance standards, such as ASTM or ISO certifications, to guarantee safety and performance.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
Aluminum is often used in the construction of air compressor bodies and fittings due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It can handle high pressures, typically up to 300 psi, and operates efficiently in a wide temperature range.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation, but the cost can be higher than steel. Additionally, aluminum components may require more careful handling to avoid dents and deformation.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with air and non-corrosive gases, making it a reliable choice for tire inflation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should verify that aluminum components comply with relevant standards, such as DIN or JIS, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where such certifications are critical for market entry.
Steel is commonly used for air compressor frames and heavy-duty fittings due to its strength and durability. It can handle high pressures, often exceeding 300 psi, and performs well in various temperature conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Steel’s primary advantage is its robustness, making it suitable for high-demand environments. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, which can limit its lifespan unless treated. The manufacturing process can also be more complex, leading to higher costs.
Impact on Application:
Steel components are generally compatible with air and can withstand significant mechanical stress, making them ideal for commercial tire inflation stations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, such as parts of Africa and South America, should prioritize galvanized or stainless steel options to enhance longevity and comply with local standards.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is often utilized for lightweight hoses and fittings in tire inflation systems. It can handle pressures up to 150 psi and operates effectively in temperatures ranging from -10°F to 140°F (-23°C to 60°C).
Pros & Cons:
PVC is cost-effective and resistant to many chemicals, but it lacks the durability of rubber and steel. Its flexibility can also decrease at lower temperatures, which might impact usability in colder climates.
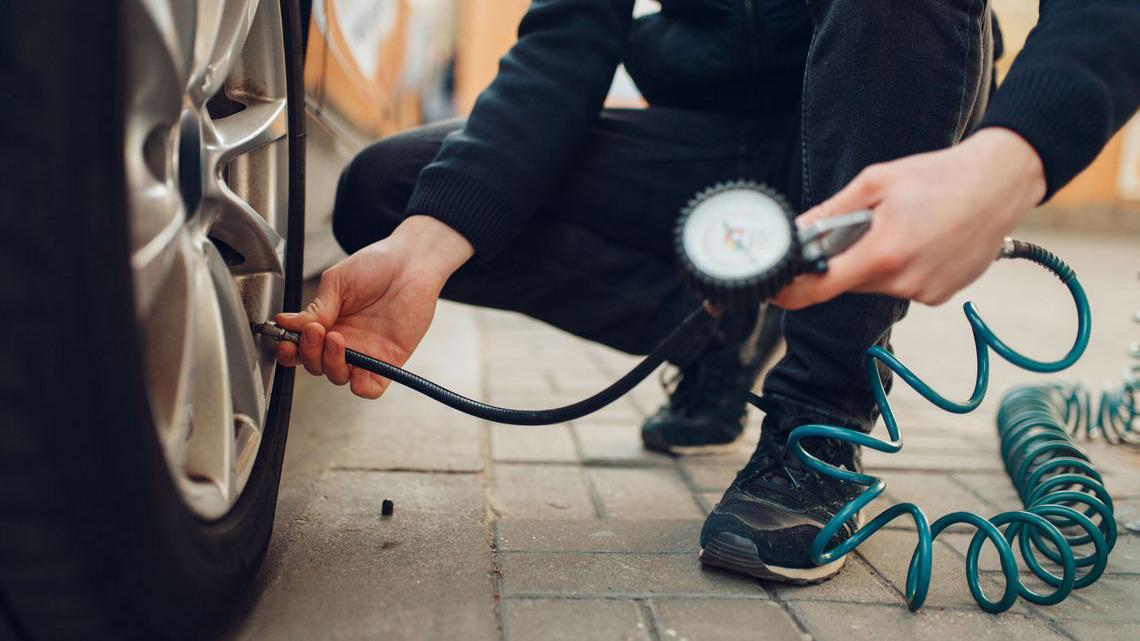

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
Impact on Application:
PVC hoses are suitable for air and non-corrosive gases but may not be ideal for high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should ensure that PVC products meet local safety standards and are appropriate for the climatic conditions of their operating regions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to inflate tires at a gas station | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Hoses and seals for air compressors | Excellent elasticity and flexibility | Degrades over time with UV exposure | Low |
| Aluminum | Compressor bodies and fittings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and requires careful handling | Med |
| Steel | Heavy-duty fittings and compressor frames | Robust and strong | Susceptible to corrosion without treatment | Med to High |
| PVC | Lightweight hoses and fittings | Cost-effective and chemical-resistant | Less durable and flexible in cold | Low |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for tire inflation systems, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
The manufacturing process for tire inflation equipment, commonly found at gas stations, involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of the equipment. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing equipment for their own operations.
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. Typically, components such as steel for the frame, rubber for the hoses, and electronic parts for pressure gauges are sourced from trusted suppliers. Manufacturers conduct stringent assessments to ensure materials meet specific standards for durability and performance.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo a series of pre-processing steps, including cutting, shaping, and surface treatment, which prepare them for assembly. This phase may also involve the application of protective coatings to prevent corrosion, particularly for equipment intended for use in harsh environmental conditions.
In the forming stage, manufacturers employ various techniques to create the individual components of the tire inflation systems. Common methods include stamping, welding, and molding. For example, the metal frames are often welded together using advanced robotic welding techniques to ensure precision and strength.
For components like hoses, rubber molding techniques are utilized to create flexible yet durable parts that can withstand high pressure and frequent use. The choice of technique depends on the design specifications and the required performance characteristics of the final product.
The assembly process is where the individual components come together to form the complete tire inflation unit. This stage typically involves both manual labor and automated machinery. Workers assemble parts such as the air compressor, pressure gauge, and inflation nozzle, while robotic systems may be used for tasks that require high precision.
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the assembly line to ensure that each component meets the required standards. This includes verifying the proper alignment of parts and testing the functionality of electronic components before moving on to the finishing stage.
Once assembled, the tire inflation units undergo finishing processes designed to enhance their performance and aesthetic appeal. This may include painting, coating, and final inspections. The painting process not only provides a visually appealing finish but also protects the equipment from environmental factors such as moisture and UV exposure.
Final inspections are crucial to ensure that all components function correctly and meet safety standards. This is where manufacturers may employ testing methods such as pressure tests and performance evaluations to confirm that the units can reliably inflate tires to specified pressures.
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of the manufacturing process, particularly for equipment that will be used in safety-critical applications like tire inflation. Adhering to international standards ensures that products meet safety and reliability expectations.
For tire inflation equipment, adherence to ISO 9001 standards is fundamental. This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, compliance with CE (Conformité Européenne) marking is essential for equipment sold within the European market, indicating that it meets safety and health requirements.
In some regions, particularly in the Middle East and Africa, manufacturers may also need to comply with local regulations and standards, which can vary significantly. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications for their target markets.
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process. The primary QC checkpoints include:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or returned to the supplier.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly and manufacturing stages, regular inspections are conducted to monitor production processes. This includes checking for proper assembly, alignment, and functionality of components.
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the tire inflation units are assembled, they undergo rigorous testing to ensure they function correctly and meet performance specifications. This often includes pressure tests and operational checks.
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring the reliability of the products they purchase. Here are some strategies to consider:
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can help assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. These audits can be performed by the buyer or through third-party inspection services.
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including reports from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. This documentation can offer insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance practices. This can be particularly beneficial for international buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers.
International B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Factors such as local regulations, varying quality standards, and cultural differences in business practices can all impact supplier relationships.
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with both international and local standards applicable to their markets. Additionally, establishing clear communication channels and expectations regarding quality can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that both parties are aligned on quality objectives.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for tire inflation equipment is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on manufacturing stages, adhering to international standards, and implementing robust quality control measures, businesses can ensure they source reliable and effective tire inflation solutions for their operations.
Inflating tires at a gas station is a critical maintenance task that ensures vehicle safety, enhances fuel efficiency, and prolongs tire lifespan. This guide outlines a practical checklist for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to streamline their sourcing process for tire inflation services and equipment.
Understanding the specific tire pressure requirements for your vehicles is essential. Each vehicle has a recommended PSI (pounds per square inch) that can be found in the owner’s manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. Knowing this ensures that you can communicate effectively with suppliers about the necessary equipment and services.
Start by compiling a list of nearby gas stations that offer air inflation services. Evaluate their reputation through customer reviews and testimonials, particularly focusing on their reliability and accessibility. Look for providers that have modern, well-maintained air compressors to ensure efficient service.
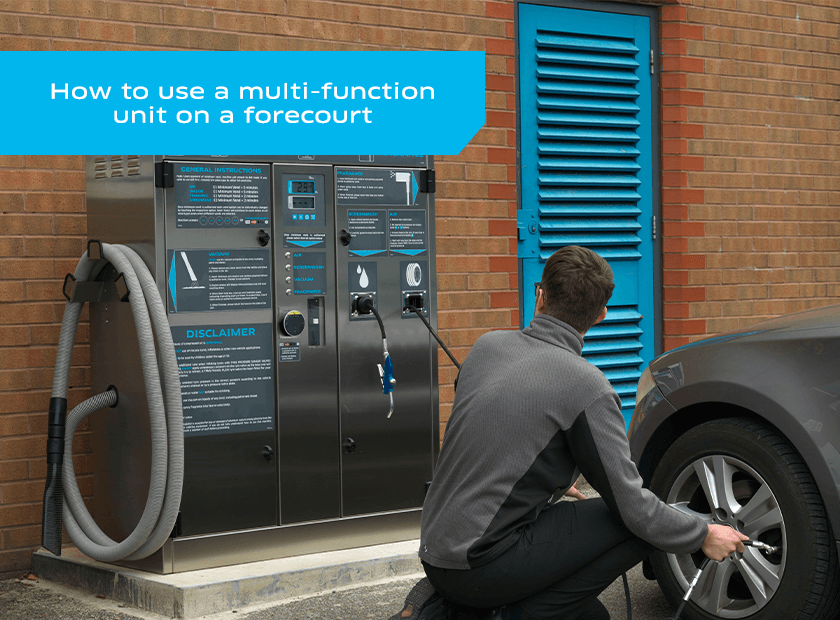
Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
When sourcing air inflation equipment, prioritize stations that use high-quality, calibrated air compressors. Check for features such as digital pressure gauges and automatic shut-off mechanisms to prevent over-inflation. These factors enhance safety and efficiency, reducing the risk of tire damage.
Compare the costs associated with using air inflation services at different gas stations. Some may offer free air, while others charge a fee. Understanding the pricing structure is crucial for budgeting, especially for businesses with multiple vehicles requiring regular maintenance.
Ensure that the gas stations and service providers comply with local and international safety standards. This may include checking for certifications or endorsements from relevant automotive authorities. Compliance not only guarantees safety but also reflects the professionalism of the service provider.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
Look for gas stations that provide complementary services, such as tire pressure monitoring and maintenance checks. This can be beneficial for businesses that want a one-stop solution for vehicle care. Additional services can also enhance the value of your procurement, leading to better overall vehicle performance.
Once you identify reliable gas stations and service providers, consider establishing a partnership. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better service agreements, discounted rates, and improved responsiveness to your needs. Regular communication can also help in staying updated on any changes in services or pricing.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the process of sourcing tire inflation services at gas stations, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Proper tire maintenance is not just about convenience; it’s a strategic investment in vehicle safety and efficiency.
When evaluating the cost structure for inflating tires at a gas station, several essential components come into play. Understanding these elements allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
Materials: The primary material cost is the air compressor, which includes components such as hoses, gauges, and nozzles. The initial investment in high-quality air compressors can significantly impact long-term operational costs. Additionally, costs related to maintenance and potential replacement parts should be factored in.
Labor: While self-service air stations require minimal direct labor, the operational costs associated with maintenance personnel should be considered. In regions with varying labor costs, it is crucial to assess local wage rates and the availability of skilled labor for equipment upkeep.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with the production of air compressors and related equipment. Factors such as factory rent, utilities, and administrative expenses contribute to the overall overhead and should be included in the pricing models.
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): Investment in tooling for manufacturing quality air compressors is critical. Moreover, ensuring that the equipment meets safety standards and performs reliably requires a robust QC process, which also adds to the cost structure.
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering air compressor units to gas stations can vary widely based on geographic location. International shipping considerations, including customs and duties, are particularly important for buyers in regions like Africa and South America.
Margin: Finally, suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and supplier reputation.
Several factors influence the pricing structure for tire inflation services at gas stations. Understanding these influencers can help international buyers negotiate better terms.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchasing often results in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should inquire about MOQs and how they can leverage larger orders to achieve cost savings.
Specifications and Customization: Tailoring equipment to meet specific needs, such as high-capacity compressors or integrated payment systems, can increase initial costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price hikes.
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials typically lead to increased pricing. Certifications that meet international safety and performance standards can also add to costs but provide assurance of reliability.
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and financial stability can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
Incoterms: Understanding the delivery terms is crucial for international buyers. Incoterms dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, influencing total costs and pricing negotiations.
For B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management strategies are vital.
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing flexibility, especially for bulk purchases. Highlighting long-term partnerships may also yield better terms.
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over the equipment’s lifespan. This holistic view can lead to smarter purchasing decisions.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand regional market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and local economic conditions that could affect pricing. Building relationships with local distributors can also provide insights into pricing trends and potential discounts.
Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding tire inflation services. Compliance can affect equipment choices and operational costs.
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier agreements, and geographical factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations before making purchasing decisions.
In today’s automotive landscape, ensuring proper tire inflation is critical for safety, efficiency, and longevity of vehicle performance. While inflating tires at gas stations remains a common practice, various alternative methods and technologies are available. This analysis compares the traditional approach of using gas station air compressors with other viable solutions, such as portable air compressors and tire inflation monitoring systems.
| Comparison Aspect | How To Inflate Tires At A Gas Station | Portable Air Compressor | Tire Inflation Monitoring System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable but can be inconsistent due to varying station quality | High performance; provides precise control | Automatically maintains optimal pressure |
| Cost | Typically low cost; may require coins or tokens | Initial investment required; varies by brand | Higher upfront cost; potential savings on tire wear |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple; requires minimal setup | Moderate; requires familiarity with the device | Requires installation; user-friendly apps available |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; depends on station upkeep | Moderate; requires occasional checks | Low; generally self-sufficient once installed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for quick, on-the-go inflation | Best for frequent travelers or those with multiple vehicles | Excellent for fleet management or high-usage vehicles |
Portable air compressors offer an effective alternative to gas station inflation. These compact devices are designed for on-the-go use, allowing vehicle owners to inflate tires anytime, anywhere. Their performance is generally superior, providing precise control over tire pressure. However, they require an initial investment, which can vary significantly based on brand and features. While they are user-friendly, individuals must familiarize themselves with the operation of the device. Maintenance is moderate, as users should periodically check the compressor for functionality, but overall, they provide a reliable option for those who travel frequently or manage multiple vehicles.
Tire inflation monitoring systems represent a technological advancement in tire care. These systems automatically monitor tire pressure and adjust it as needed, ensuring optimal performance without requiring manual intervention. The primary advantage is the constant oversight of tire health, which can lead to significant savings in fuel efficiency and tire longevity. However, the initial cost can be higher than other methods, and installation may require professional assistance. Once set up, these systems are generally low maintenance, offering peace of mind for fleet managers or individuals who prioritize vehicle performance.
Choosing the right tire inflation method depends on specific business needs and operational contexts. For companies that require quick, cost-effective solutions, inflating tires at gas stations may suffice. However, businesses that prioritize efficiency and tire longevity might find portable air compressors or tire inflation monitoring systems to be more beneficial in the long run. Ultimately, evaluating the performance, cost, and ease of implementation will guide B2B buyers in selecting the most suitable solution tailored to their operational demands.
When it comes to inflating tires at a gas station, understanding the technical properties involved is vital for ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity of tires. Here are some critical specifications:
Pressure Range (PSI)
– Definition: PSI (pounds per square inch) measures the air pressure within the tire.
– B2B Importance: Maintaining the correct PSI is crucial for vehicle safety and performance. Over-inflated or under-inflated tires can lead to accidents or increased fuel consumption, impacting the bottom line for businesses relying on vehicle fleets.
Tire Size Specifications
– Definition: Each tire has specific dimensions, usually represented as a combination of numbers (e.g., 205/55R16).
– B2B Importance: Accurate knowledge of tire sizes is essential for businesses to ensure compatibility with their vehicles and avoid the costs associated with incorrect purchases or installations.
Material Composition
– Definition: Tires are made from various materials, including rubber, steel, and fabric, each affecting durability and performance.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the material properties helps businesses select tires that meet their operational requirements, balancing performance with cost-effectiveness.
Temperature Tolerance
– Definition: This refers to the maximum and minimum temperatures that tires can withstand without compromising performance.
– B2B Importance: Knowledge of temperature tolerance is critical for businesses operating in diverse climates. Tires that cannot handle extreme temperatures may lead to increased wear and tear, resulting in higher maintenance costs.
Valve Stem Type
– Definition: The valve stem is the part of the tire that allows for inflation and deflation. There are various types, including Schrader and Presta.
– B2B Importance: Ensuring compatibility with inflation equipment is crucial for operational efficiency. Misalignment can lead to delays and increased service time at gas stations.
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and improve operational efficiency. Here are some common trade terms relevant to tire inflation:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM specifications ensures that businesses purchase high-quality, compatible tire inflation systems, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: For businesses that rely on tire maintenance, knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management, avoiding overstock or stockouts.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Utilizing RFQs effectively can lead to better pricing and terms, ultimately lowering operational costs for tire management.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international rules governing commercial contracts for the sale of goods.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs when procuring tire inflation equipment from international suppliers.
Tread Depth
– Definition: The vertical measurement between the top of the tread rubber to the bottom of the tire’s deepest grooves.
– Relevance: Monitoring tread depth is vital for safety and regulatory compliance. Businesses must ensure that their vehicles meet legal requirements to avoid fines and enhance safety.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding tire inflation processes, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
The global tire inflation market, particularly at gas stations, is evolving rapidly due to various factors influencing consumer behavior and technological advancements. One of the primary drivers is the increasing awareness of vehicle safety and maintenance, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, where road safety remains a critical issue. As vehicle ownership rises in these regions, the demand for accessible tire maintenance solutions grows, prompting gas stations to enhance their tire inflation services.
Another key trend is the integration of digital technologies in tire inflation systems. Smart air compressors equipped with digital displays and automated pressure regulation features are becoming more prevalent. These innovations not only streamline the inflation process but also provide users with real-time data on tire pressure, enhancing safety and fuel efficiency. Furthermore, the adoption of mobile applications that guide users to the nearest gas station with air services is gaining traction, driven by the increasing use of smartphones in all regions.
For international B2B buyers, understanding local market dynamics is essential. In regions like the Middle East and Europe, regulatory frameworks around vehicle emissions and safety standards are becoming stricter. This creates opportunities for suppliers who can offer advanced tire inflation technologies that comply with these regulations. Additionally, partnerships with local gas stations and service centers can be a strategic advantage, facilitating smoother distribution channels and better customer outreach.
As environmental concerns gain prominence globally, sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the sourcing of tire inflation solutions. The tire industry has a significant environmental impact, particularly concerning the energy consumed during tire manufacturing and the waste generated from discarded tires. For B2B buyers, selecting suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices is not just a moral obligation but also a business imperative.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate tires at a gas station
Adopting sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials in air compressors or promoting tire maintenance that extends the lifespan of tires, can enhance a company’s brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, as regulations around waste management and emissions become stricter, buyers must ensure their partners comply with these standards to avoid potential legal repercussions.
In addition to compliance, offering services that promote ethical sourcing and sustainability can attract a broader customer base. Initiatives such as tire recycling programs and partnerships with organizations focused on environmental conservation can also enhance a company’s market position, particularly in regions where sustainability is increasingly valued.
Historically, tire inflation was a manual process, often requiring drivers to rely on handheld pumps or service personnel at gas stations. With the advent of automotive technology in the 20th century, tire inflation systems became more sophisticated. The introduction of automated air compressors in gas stations marked a significant milestone, making it easier for consumers to inflate their tires independently.
Over the past two decades, the focus has shifted towards digitalization and automation. Modern tire inflation stations are now equipped with digital pressure gauges and automatic shut-off features, ensuring that tires are inflated to the correct pressure without the risk of over-inflation. This evolution not only enhances user experience but also contributes to better fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle emissions.
Today, the tire inflation sector continues to innovate, with advancements such as mobile app integration and smart sensors that monitor tire pressure in real time. As this technology evolves, B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest trends and innovations to leverage opportunities in this growing market.
1. How do I solve low tire pressure issues at a gas station?
To address low tire pressure, first ensure you have the correct tire pressure gauge and know your vehicle’s recommended PSI, typically found in the owner’s manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. Park your vehicle near the air compressor at the gas station and turn off the engine. Remove the valve cap from the tire, attach the tire pressure gauge to get an accurate reading, and compare it to the recommended PSI. If the tire is under-inflated, connect the air hose to the valve stem, activate the compressor, and fill in short bursts, checking the pressure frequently to avoid over-inflation.
2. What is the best air compressor type for inflating tires at a gas station?
The best air compressor for inflating tires at a gas station is one that offers a reliable and consistent PSI output, typically ranging from 30 to 35 PSI for most vehicles. Look for a compressor with a built-in pressure gauge for accuracy and automatic shut-off features to prevent over-inflation. Gas stations often provide coin-operated air machines, but ensure they are well-maintained and calibrated for consistent performance. If you plan to establish a partnership with a supplier, consider those that offer durable, high-quality compressors suitable for frequent use in various climates.
3. How can I ensure the air compressor at the gas station is working properly?
Before using an air compressor, inspect it for any visible signs of wear or damage. Check if the pressure gauge is functional and displays readings correctly. It’s advisable to test the compressor with your own tire pressure gauge to verify its accuracy. If the compressor requires coins or tokens, ensure it accepts your currency, and confirm that it dispenses air correctly. If you experience issues, consider locating another gas station or contacting the service provider for maintenance.
4. What are the best practices for tire maintenance when sourcing tires internationally?
When sourcing tires internationally, best practices include verifying the quality and specifications of the tires against your regional standards. Ensure suppliers provide certifications and test results to confirm compliance with safety regulations. Establish clear communication regarding tire pressure recommendations and maintenance guidelines. Additionally, consider conducting on-site inspections and audits of the manufacturing facilities to ensure quality control processes are in place.
5. How do I vet suppliers for tire inflators and compressors?
To vet suppliers for tire inflators and compressors, start by researching their reputation through industry reviews and testimonials. Request references from other B2B clients, focusing on their experiences with product quality and customer service. Evaluate the supplier’s certifications and compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider their responsiveness to inquiries, willingness to provide samples, and ability to accommodate your specific needs, including customization options.
6. What are typical payment terms for international tire suppliers?
Payment terms for international tire suppliers can vary widely but often include options such as net 30, 60, or 90 days after receipt of goods. Some suppliers may request a deposit before production, especially for custom orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow and operational needs. Consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks associated with international transactions.
7. How can I ensure quality assurance when importing tires?
To ensure quality assurance when importing tires, implement a robust quality control process that includes pre-shipment inspections by a third-party agency. Define quality standards and specifications that the tires must meet before shipment. Request detailed documentation from the supplier, including certificates of compliance and test reports. Additionally, establish a clear return policy for defective products and maintain open communication with your supplier to address any quality concerns promptly.
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing tires internationally?
When sourcing tires internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Work with a reliable freight forwarder who understands the complexities of international shipping and can handle documentation efficiently. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs, to ensure profitability. Additionally, plan for potential delays in customs and ensure that your inventory management system can accommodate variations in delivery schedules.
Domain: acg.aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: Tire pressure gauge, air compressor, vehicle’s air pressure specifications (found in car manual and on sticker on driver’s door jamb).
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Social Networking Platform, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
In conclusion, the process of inflating tires at a gas station serves as an essential practice for maintaining vehicle safety and efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding the significance of proper tire inflation can translate into enhanced operational performance and reduced maintenance costs. Key takeaways include the importance of regular tire pressure checks, the accessibility of air compressors at gas stations, and the need for accurate pressure gauges to prevent over or under-inflation.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring that businesses have reliable access to quality tools and services for tire maintenance. By investing in partnerships with reputable gas station networks and equipment suppliers, companies can enhance their service offerings, ensuring that their fleets remain safe and efficient on the road.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to prioritize tire maintenance as part of their broader operational strategies. Embracing these best practices not only promotes vehicle longevity but also fosters a culture of safety and efficiency in transportation. Engage with local suppliers and service providers to establish a robust tire maintenance program that meets your business needs and drives future success.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.