In the quest for operational efficiency, sourcing the right air compressor can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of air compressor types, applications, and market dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The variety of options—from portable to stationary, oil-free to oil-lubricated—can be overwhelming, especially when considering factors such as power requirements, noise levels, and maintenance needs.
This comprehensive guide is designed to illuminate the global market for air compressors, providing insights into the diverse types available, their specific applications, and the critical considerations for supplier vetting. It delves into cost analysis, highlighting how to balance budget constraints with quality and performance. Additionally, the guide offers practical tips for navigating the complexities of international trade, ensuring that you can secure the best equipment for your business needs.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights, this resource aims to streamline your procurement process, ultimately enhancing productivity and reducing operational downtime. Whether you’re operating in the bustling markets of Nigeria or the dynamic industries of Vietnam, understanding the landscape of air compressor options will enable you to make strategic, value-driven decisions that align with your business goals.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
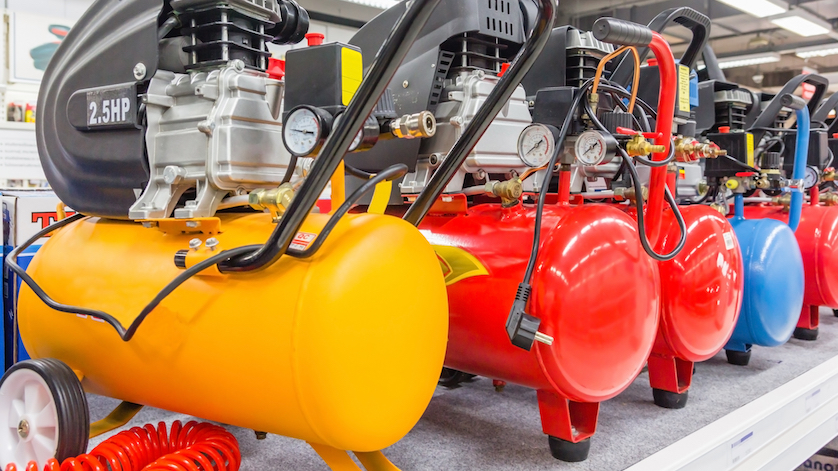
| Portable Air Compressors | Lightweight, compact, easy to transport | Construction sites, automotive repair, DIY projects | Pros: Easy to move; Cons: Limited power and tank size. |
| Stationary Air Compressors | Larger, fixed installations, higher capacity | Manufacturing, workshops, heavy-duty applications | Pros: Greater power and efficiency; Cons: Less flexible. |
| Oil-Free Air Compressors | Require no lubrication, cleaner air output | Painting, food processing, medical applications | Pros: Low maintenance; Cons: Generally less durable. |
| Oil-Lubricated Air Compressors | Uses oil for lubrication, durable and powerful | Industrial manufacturing, automotive service | Pros: High performance; Cons: Requires regular maintenance. |
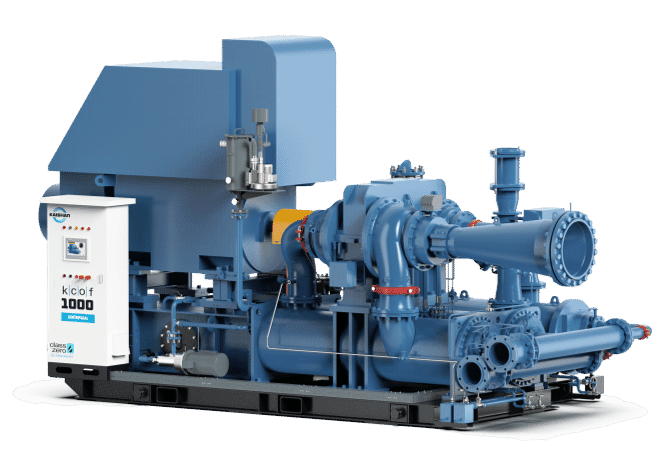
| Rotary Screw Compressors | Continuous operation, high efficiency | Large-scale industrial use, HVAC applications | Pros: Long lifespan; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
Portable air compressors are designed for mobility, making them ideal for various job sites, from construction to automotive repair. They typically feature a smaller tank size and lighter weight, allowing for easy transport. B2B buyers should consider the power output and tank size to ensure it meets their operational needs. While they are convenient for smaller tasks, their limited capacity may not support heavy-duty applications effectively.
Stationary air compressors are built for permanent installation, offering higher capacity and power for demanding tasks. They are commonly used in manufacturing and workshops, where continuous operation is essential. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate the compressor’s horsepower and tank size to ensure it aligns with their production requirements. Although they require a larger footprint, their efficiency and reliability make them a preferred choice for heavy-duty applications.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
Oil-free air compressors deliver clean air without the risk of oil contamination, making them suitable for sensitive applications like painting and food processing. These compressors are low maintenance and ideal for environments where air purity is critical. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced maintenance against potential limitations in durability and power. They are particularly advantageous for industries that prioritize hygiene and cleanliness.
Oil-lubricated air compressors are known for their durability and high performance, making them suitable for industrial manufacturing and automotive services. They can handle heavier workloads and longer operational cycles but require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Businesses should consider the maintenance costs and frequency when investing in these compressors. Their robust construction often justifies the investment for companies with demanding air compression needs.
Rotary screw compressors are designed for continuous operation and are highly efficient, making them perfect for large-scale industrial applications and HVAC systems. They offer a longer lifespan and can operate at higher capacities compared to other types. However, the initial investment can be significant, so B2B buyers should evaluate their long-term operational needs and budget. These compressors are particularly valuable for businesses seeking reliability and efficiency in their air supply systems.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Air Compressor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Pneumatic Tool Operation | Increases efficiency and productivity in assembly lines | Reliability, maintenance requirements, and power output |
| Automotive Repair | Tire Inflation and Paint Spraying | Enhances service speed and quality of repairs | Portability, tank size, and pressure capacity |
| Construction | Heavy Equipment Operation | Powers tools like nail guns and impact wrenches | Durability, portability, and noise levels |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and Processing | Ensures hygiene and efficiency in production | Compliance with safety standards and air quality |
| Oil and Gas | Drilling and Production | Supports extraction processes and equipment operation | Energy efficiency, robustness, and local support |
In the manufacturing sector, air compressors are vital for operating pneumatic tools in assembly lines. These tools, which include drills, wrenches, and cutters, require a consistent air supply to function effectively. By utilizing air compressors, manufacturers can significantly enhance production efficiency and reduce downtime. International buyers must consider the reliability of compressors and their maintenance requirements, as well as the power output to ensure compatibility with their existing tools.
In automotive repair shops, air compressors are essential for tasks like tire inflation and paint spraying. They facilitate quick service turnaround, allowing mechanics to handle multiple vehicles efficiently. The ability to use air-powered tools enhances the quality of repairs, resulting in higher customer satisfaction. Buyers should focus on the portability and tank size of compressors, as well as their pressure capacity to meet diverse service demands.
Air compressors play a crucial role in the construction industry by powering various tools, including nail guns and impact wrenches. They streamline workflows on job sites, enabling workers to complete tasks more quickly and effectively. For B2B buyers in construction, key considerations include the durability of the compressor, its portability for on-site use, and acceptable noise levels to comply with local regulations.
In the food and beverage industry, air compressors are used for packaging and processing applications, ensuring that products are sealed and stored hygienically. The use of oil-free air compressors is particularly important in this sector to prevent contamination. Buyers must prioritize compliance with safety standards and air quality to maintain product integrity and meet regulatory requirements.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
Air compressors are critical in the oil and gas industry, supporting drilling and production operations. They provide the necessary power for various extraction processes and equipment. Buyers in this sector should look for energy-efficient models that can withstand harsh conditions and ensure robust local support for maintenance and repairs.
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in manufacturing and automotive sectors, often encounter the challenge of inconsistent air pressure from their compressors. This inconsistency can lead to subpar performance in pneumatic tools, resulting in incomplete tasks, increased downtime, and potential safety hazards. For example, a paint shop relying on an air compressor with fluctuating pressure may find that the finish on their products is uneven, leading to costly rework and dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize selecting air compressors with adequate pressure regulation features and capacity tailored to their specific application requirements. When sourcing a compressor, consider investing in models equipped with advanced pressure regulators and larger tanks that can sustain stable pressure during operation. Additionally, implementing regular maintenance schedules, including checking for leaks in hoses and fittings, can prevent pressure drops. Training personnel on optimal usage techniques will also help maintain consistent output, ensuring quality across production processes.
The Problem: Noise pollution is a significant concern for many B2B buyers, especially those operating in urban areas or enclosed spaces. Air compressors can produce high decibel levels, which may violate local noise regulations and create uncomfortable working environments. Employees exposed to loud machinery for prolonged periods may experience reduced productivity, increased stress levels, and potential hearing damage.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
The Solution: To mitigate noise issues, buyers should consider investing in quiet air compressors designed specifically for low-noise operation. Look for models with a decibel rating below 70 dB, which can significantly decrease workplace noise levels. Additionally, implementing soundproofing measures in compressor rooms or using acoustic enclosures can further reduce noise transmission. It’s also beneficial to train staff on proper operational techniques and scheduling compressor use during off-peak hours to minimize disruption.
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the right type of air compressor that meets diverse operational needs. Different applications, such as powering pneumatic tools, inflating tires, or painting, require specific types of compressors (e.g., oil-free vs. oil-lubricated). Making the wrong choice can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and equipment failures.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their operational needs before purchasing. Creating a detailed list of required applications will help identify the necessary specifications. For instance, if the primary use involves painting or food-grade applications, an oil-free compressor is essential for maintaining clean air quality. Engaging with suppliers who offer expert consultation can also provide invaluable insights. Additionally, consider modular compressor systems that allow for easy upgrades or adjustments based on changing operational demands, ensuring long-term flexibility and efficiency.
When selecting materials for air compressors, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. Different materials can significantly affect performance, durability, and cost. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in air compressor construction.
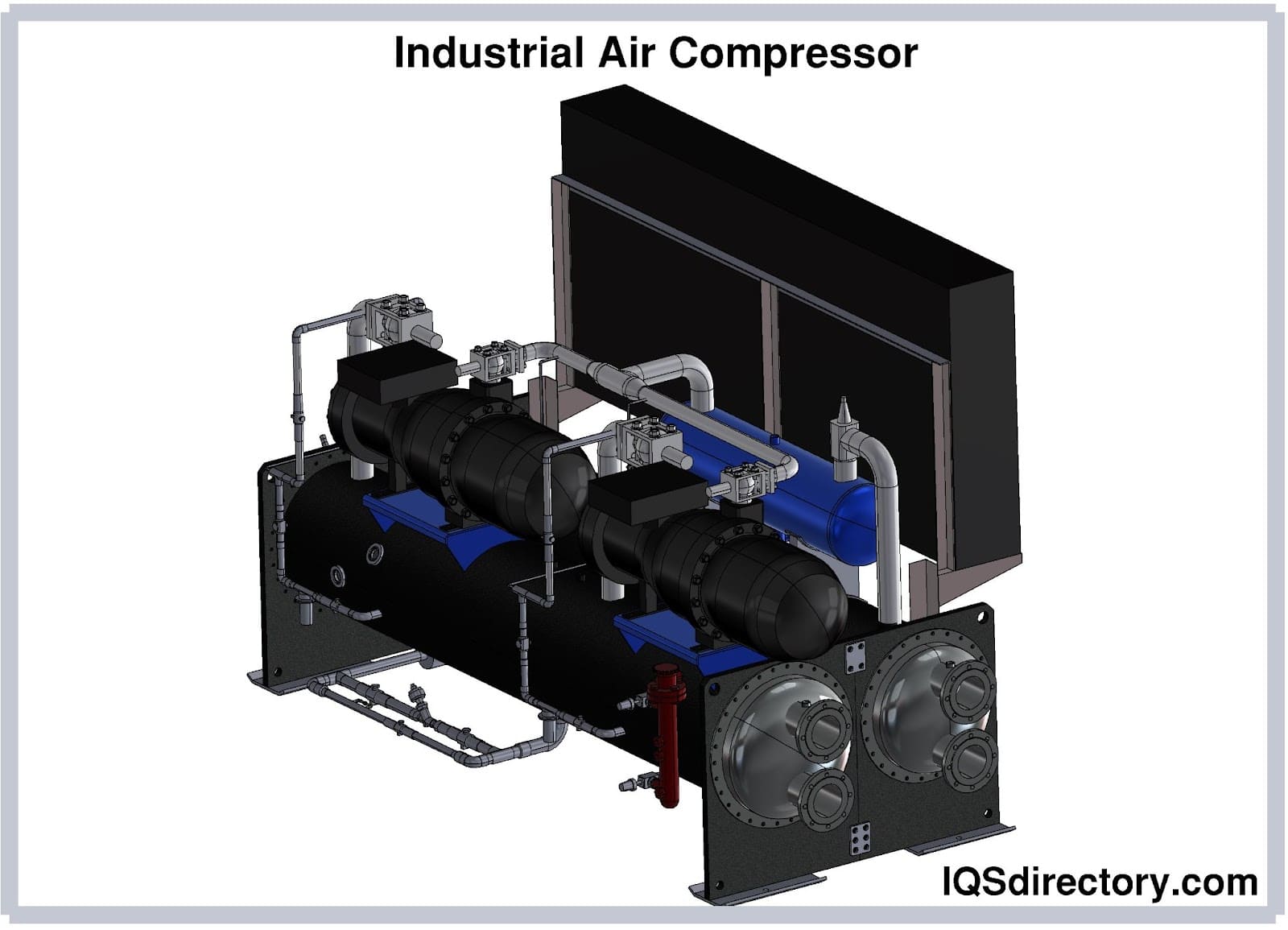
Illustrative image related to air compessor
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, typically up to 150 psi.
Pros & Cons: The main advantages of aluminum include its light weight, which enhances portability, and its resistance to rust and corrosion. However, it is less durable than steel and can be prone to deformation under extreme pressure or impact. Additionally, aluminum is generally more expensive than some alternatives.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for portable air compressors used in automotive and light industrial applications where weight and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that aluminum components meet local standards for pressure vessels, such as ASTM or DIN specifications.
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high strength and durability, capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures, often exceeding 200 psi.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
Pros & Cons: Steel’s primary advantage is its robustness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be susceptible to rust if not properly coated. The manufacturing complexity for steel components can also be higher, potentially increasing production costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in stationary air compressors and industrial applications where high pressure and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is crucial, especially for buyers in Europe, where stringent regulations may apply. Steel components should be sourced from certified suppliers to ensure quality and compliance.
Key Properties: Plastic materials, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene, are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They can handle moderate pressures but are generally not suitable for high-temperature applications.
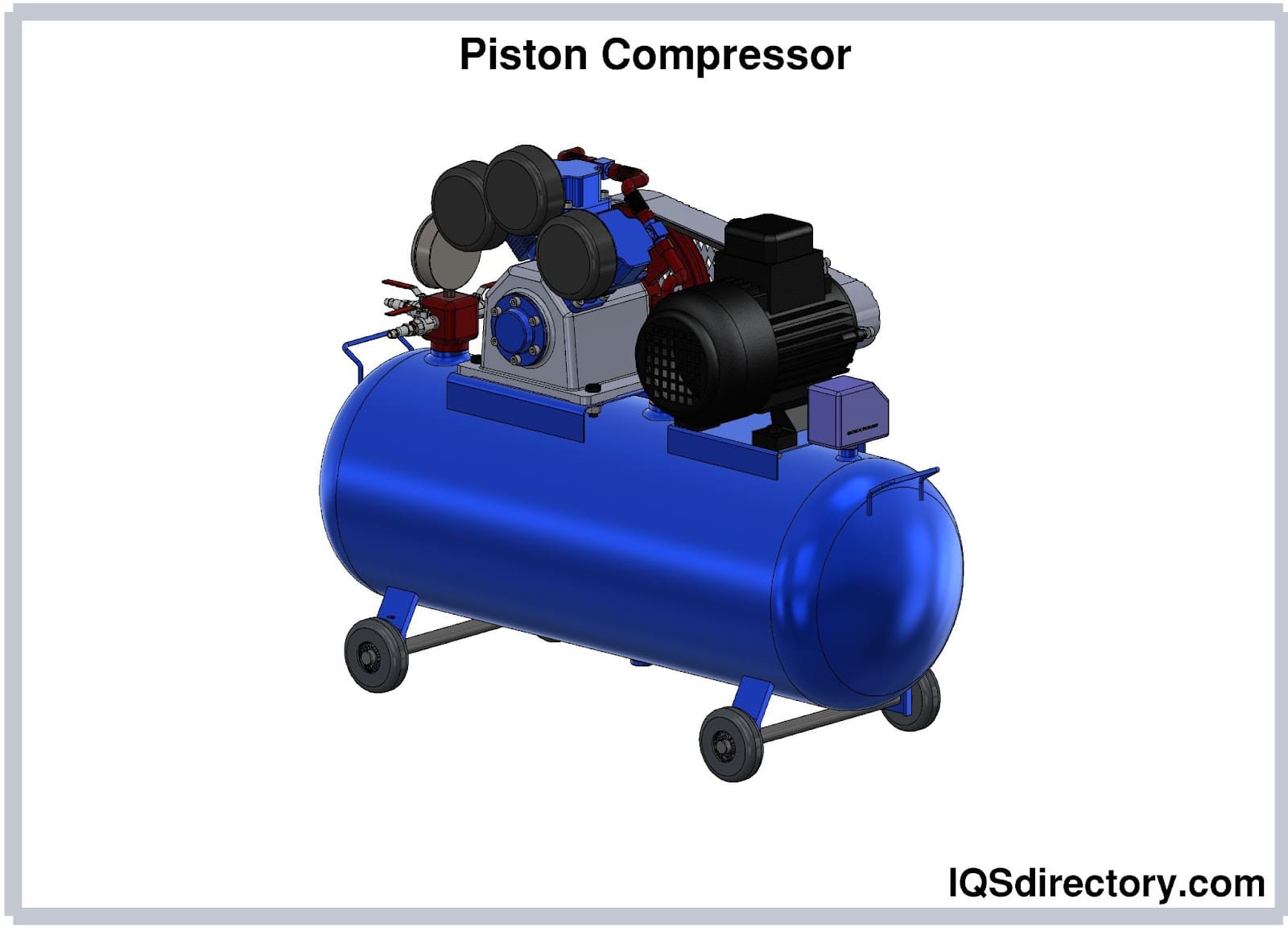
Illustrative image related to air compessor
Pros & Cons: The advantages of plastic include low cost and ease of manufacturing, allowing for complex shapes and designs. However, plastics may not withstand high pressures or extreme temperatures, limiting their application scope.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are often used in smaller, portable compressors for tasks like tire inflation and small pneumatic tools.
Considerations for International Buyers: When sourcing plastic components, buyers should verify that materials comply with local regulations regarding chemical resistance and safety standards, especially in regions like South America where regulations may vary.
Key Properties: Composite materials combine the benefits of different materials, often featuring a matrix of resin reinforced with fibers. They can be designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures while remaining lightweight.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for portable applications. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture, which may increase overall costs.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful in applications requiring both lightweight and high-strength components, such as in aerospace or specialized industrial compressors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that composite materials meet international standards for pressure vessels and durability, particularly in regions with harsh environmental conditions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for air compressor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable air compressors for automotive use | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| Steel | Industrial stationary air compressors | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to rust | High |
| Plastic | Small, portable compressors for tire inflation | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Limited pressure and temperature tolerance | Low |
| Composite | Specialized industrial compressors | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide serves as a foundational resource for B2B buyers in understanding the implications of material selection for air compressors. By considering these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
Manufacturing air compressors involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
The manufacturing process begins with material selection and preparation. Common materials used in air compressor production include aluminum, steel, and various polymers. The chosen materials undergo cutting, machining, and surface treatment to meet design specifications. For instance, steel components may be treated to enhance corrosion resistance, while aluminum parts are often anodized to improve durability.
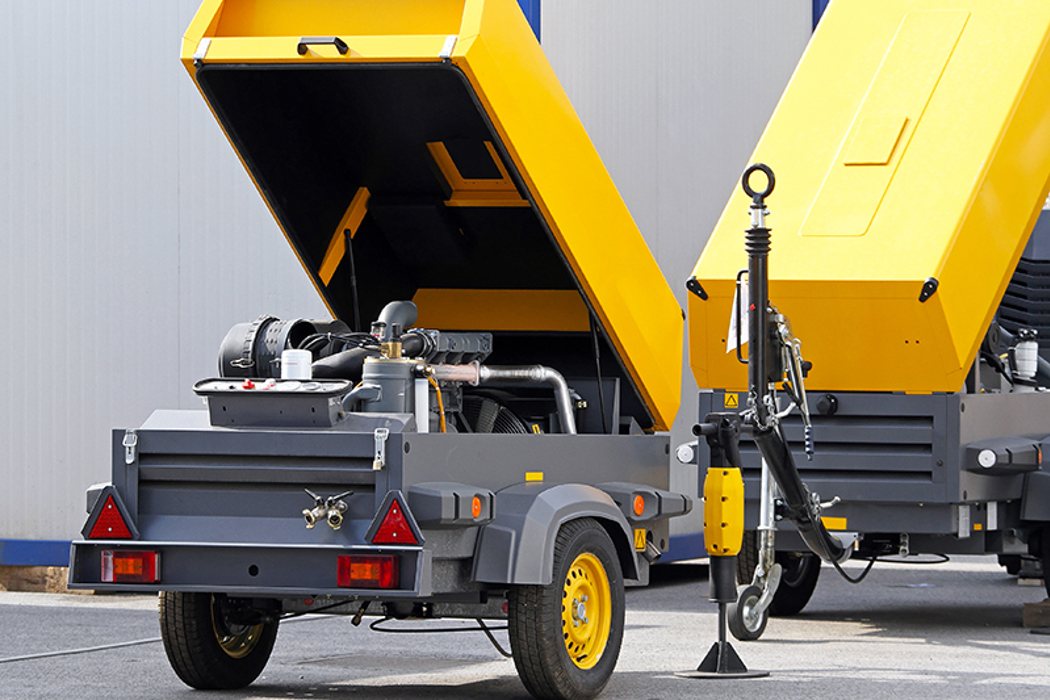

Illustrative image related to air compessor
After material preparation, the forming stage involves shaping these materials into the required components. Techniques such as stamping, casting, and forging are commonly employed. For instance, the compressor’s cylinder may be cast to achieve the desired strength and shape, while other components like brackets and housings might be stamped from sheets of metal. Precision is crucial in this stage, as even minor deviations can affect the overall performance of the compressor.
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form a complete air compressor. This process may involve both manual labor and automated systems, depending on the scale of production. Assembly typically follows a systematic approach, where components are first organized and then assembled in a specific sequence to ensure efficiency. Key components such as the motor, tank, and pressure switch are integrated, and all connections are meticulously checked to ensure they meet operational standards.
Finishing processes are vital for enhancing the appearance and functionality of the air compressor. These processes include painting, coating, and quality checks. A protective coating may be applied to prevent rust and enhance durability, while a final inspection ensures that all components are correctly assembled and functioning as intended. This stage is critical for identifying any defects that may have occurred during manufacturing.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of air compressors. International and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in maintaining quality throughout the production process.
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established a quality management system that ensures consistent quality in products and services. Additionally, certifications like CE mark signify that the product meets European safety, health, and environmental protection standards, while API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications are crucial for compressors used in oil and gas applications.
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated into the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure that the final product meets all quality standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
Illustrative image related to air compessor
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Ensuring that only materials that meet predefined standards are used is essential for maintaining product quality.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are performed to ensure that each stage of production adheres to quality standards. This may involve monitoring the precision of machining or the integrity of welds.
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the assembly is complete, the air compressor undergoes final testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This includes checking for leaks, testing pressure settings, and verifying noise levels.
A variety of testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and safety of air compressors. These may include:
Performance Testing: Assessing the compressor’s capacity to deliver air at specified pressures and flow rates.
Durability Testing: Subjecting the compressor to extended operational hours to identify potential failures under stress.
Safety Testing: Ensuring that all safety features, such as pressure relief valves, function correctly to prevent accidents.
Noise Level Testing: Measuring sound output to ensure compliance with local regulations, particularly important for indoor applications.
When sourcing air compressors, B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control practices. Here are several ways to verify supplier QC:
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturer’s production processes, quality control measures, and compliance with industry standards.
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insight into the supplier’s QC performance, including defect rates and results from previous inspections.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can help validate the manufacturer’s claims regarding quality and compliance with international standards.
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital. Compliance with local regulations and international standards is essential. Buyers should also consider potential language barriers and cultural differences that may impact communication regarding quality expectations.
Additionally, it’s crucial for buyers to be aware of the logistical aspects of quality assurance, such as shipping and handling practices, which can affect the integrity of the products during transit. Establishing a clear communication channel with suppliers regarding quality expectations can mitigate risks and ensure that the final products meet the required standards.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for air compressors are intricate and designed to meet high standards. By understanding these processes and the importance of quality control, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with manufacturers.
In the competitive landscape of industrial tools and equipment, sourcing the right air compressor is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process, ensuring that they make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Before exploring suppliers, establish the technical requirements of your air compressor. Consider factors such as tank size, horsepower, and the type of compressor (oil-free vs. oil-lubricated) that aligns with your operational needs. These specifications will guide your selection and help in comparing products across different manufacturers.
Different applications demand different air compressors. Understanding the specific tasks—such as tire inflation, powering pneumatic tools, or spray painting—will inform your choice. Each application has unique requirements regarding air pressure and flow rate.
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This diligence will help you gauge the reliability and reputation of potential suppliers.
Once you have a shortlist of compressors, compare pricing among suppliers. However, be wary of deals that seem too good to be true; they may compromise on quality. Additionally, review warranty options to understand the level of support you can expect after purchase.
After-sales support is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring your compressor runs smoothly. Inquire about the availability of service centers and the responsiveness of customer support.
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s time to negotiate the terms. Discuss payment options, delivery timelines, and installation services. Clear communication at this stage can help prevent misunderstandings later.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their air compressor procurement process, ensuring they select the right equipment from reputable suppliers while maximizing value and efficiency.
Illustrative image related to air compessor
Understanding the cost structure of air compressors is essential for B2B buyers looking to source efficiently. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The raw materials used, such as metals, plastics, and electrical components, constitute a significant portion of the total cost. High-quality materials often lead to higher prices but can enhance durability and performance.
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for assembly workers, engineers, and quality control personnel. Regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, which is particularly relevant for buyers from developing markets in Africa and South America.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the expenses related to running the production facility, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. These costs can vary widely depending on the location of the manufacturer.
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for molds and specialized equipment can be substantial. Buyers should consider these costs when ordering customized products or larger quantities.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that air compressors meet industry standards and certifications. While this adds to the cost, it can prevent costly returns and warranty claims.
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and customs duties, are critical for international buyers. The choice of Incoterms will significantly impact the final landed cost of the compressors.
Margin: Finally, suppliers will add their profit margin, which varies based on market competition, brand reputation, and perceived value.
Several factors influence the pricing of air compressors, and understanding these can aid buyers in making informed purchasing decisions:
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Negotiating favorable terms based on anticipated volume can yield significant savings.
Specifications and Customization: Custom features can increase costs, particularly if they require specialized tooling or materials. Clearly defining specifications upfront can help avoid unexpected price hikes.
Materials and Quality Certifications: Compressors made from premium materials or those that meet specific industry certifications will command higher prices. Buyers should balance quality with budget constraints.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better support and product reliability.
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. For example, CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) includes shipping costs in the price, while FOB (Free on Board) places responsibility on the buyer once the goods are on board. This distinction can affect cash flow and overall cost.
When sourcing air compressors, particularly in international markets, consider the following strategies:
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in open dialogue with suppliers about pricing. Leverage your understanding of cost components and market rates to negotiate better terms.
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. An air compressor that is slightly more expensive upfront may save money over its operational lifespan.
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions that may affect pricing. For buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, local suppliers may offer competitive pricing compared to international manufacturers.
Research and Compare Suppliers: Use online platforms to compare various suppliers and their offerings. Look for reviews, testimonials, and certifications to gauge reliability and quality.
Consider Local Partnerships: Establishing relationships with local distributors can simplify logistics and reduce costs, especially when navigating customs regulations.
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough research and obtain quotes tailored to your unique sourcing needs.
In the realm of industrial and commercial applications, air compressors have long been a staple for powering tools, inflating tires, and facilitating various pneumatic operations. However, as technology evolves, several alternative solutions have emerged that offer competitive performance and unique advantages. This analysis provides a comparative overview of air compressors against two viable alternatives: electric blowers and hydraulic systems.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
| Comparison Aspect | Air Compressor | Electric Blower | Hydraulic System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High air pressure; versatile for various tools | Moderate air flow; ideal for cleaning and drying | High force output; excellent for heavy lifting |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Low to moderate cost; affordable | High upfront cost; requires significant investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and maintenance | Simple plug-and-play operation | Complex installation; needs specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed (oil changes, filter checks) | Low maintenance; generally hassle-free | Regular checks and fluid changes required |
| Best Use Case | Painting, powering tools, inflating tires | Leaf blowing, cleaning debris, drying surfaces | Heavy machinery operations, lifting and moving loads |
Electric blowers are primarily designed for blowing air, making them ideal for tasks like cleaning debris from outdoor spaces or drying surfaces. They are typically less expensive than air compressors and require minimal maintenance. With a straightforward plug-and-play design, electric blowers can be easily deployed without extensive setup. However, their performance is limited when it comes to high-pressure applications, which may restrict their usability in industrial settings where power tools are involved.
Hydraulic systems utilize pressurized fluid to transmit power, making them highly effective for heavy lifting and machinery operations. They deliver superior force compared to air compressors, making them ideal for tasks that involve significant weight or resistance. However, hydraulic systems come with a higher initial cost and require specialized installation and maintenance knowledge. While they excel in specific applications, their complexity may deter businesses looking for simpler, more versatile solutions.
When considering the right solution for your specific needs, it’s crucial to evaluate your operational requirements. Air compressors are often the go-to choice for versatility in powering various tools and tasks, especially in environments where high air pressure is essential. Conversely, if your needs lean more towards cleaning or surface drying, an electric blower could provide a cost-effective solution with less hassle. For operations that require heavy lifting, investing in a hydraulic system may be justified, despite its complexity and cost. By understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Air compressors are essential tools in various industries, serving diverse applications from powering pneumatic tools to inflating tires. Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with air compressors is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here’s an overview of key specifications and terms that will aid in your procurement process.
Tank Capacity (Gallons)
Tank capacity, measured in gallons, determines the volume of compressed air the unit can store. This specification is vital for understanding how long the compressor can operate before needing to refill. A larger tank capacity is beneficial for continuous use in industrial applications, while smaller tanks are suited for portable or DIY tasks.
Horsepower (HP)
The horsepower rating indicates the power output of the compressor’s motor. Higher horsepower typically translates to faster air delivery rates and the ability to power more demanding tools. For B2B buyers, selecting the right horsepower is essential to match the compressor with the intended applications, ensuring efficiency and productivity.
CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute)
CFM measures the airflow produced by the compressor. It is critical for determining whether the compressor can keep up with the air consumption of tools. Buyers should compare the CFM ratings of different models against the requirements of their tools to avoid performance issues.
PSI (Pounds per Square Inch)
PSI indicates the maximum pressure the compressor can generate. Different applications require varying pressure levels; for example, spray painting may require lower PSI, while nail guns typically require higher PSI. Understanding the PSI capability ensures that the compressor meets the specific needs of your operations.
Oil-Free vs. Oil-Lubricated
This specification refers to the type of compressor design. Oil-free compressors are designed for applications where air purity is critical, while oil-lubricated models are built for durability and heavy-duty tasks. B2B buyers must assess their requirements for air quality and maintenance to select the appropriate type.
Noise Level (Decibels)
Noise level is measured in decibels (dB) and is an important consideration for workplace comfort. Compressors with lower dB ratings are preferable for indoor use or environments where noise reduction is essential. Buyers should consider this factor, especially for operations in populated or sensitive areas.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking high-quality, compatible parts or equipment for their air compressors.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and determining the feasibility of purchasing from a supplier, especially when dealing with bulk orders.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. Buyers use RFQs to compare offers from different suppliers, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and favorable terms for air compressor procurement.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is vital for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations related to air compressors.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. This is a critical factor for B2B buyers to consider, as longer lead times can impact project schedules and operational efficiency.
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the time frame during which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects. Understanding warranty terms helps buyers assess the reliability of the compressor and the level of support they can expect post-purchase.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical specifications and trade terms, you can make more informed decisions when purchasing air compressors, ensuring that your business operations run smoothly and efficiently.
The air compressor market is experiencing robust growth driven by diverse global demands across various sectors, including manufacturing, construction, and automotive. As industries increasingly adopt automation and advanced manufacturing processes, the need for reliable air compression technology is paramount. The global market is projected to reach significant milestones, with emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East leading the charge. Factors such as urbanization, infrastructure development, and rising disposable incomes in these regions are propelling demand for air compressors.
In terms of technology, the sector is witnessing a shift towards smart air compressors integrated with IoT capabilities, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This trend enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, making it particularly appealing to B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions. Additionally, there is a growing preference for energy-efficient and quieter models, driven by regulatory pressures and the need for sustainable operations. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on designing compressors that comply with environmental standards while delivering high performance.
International B2B buyers, especially from Nigeria and Vietnam, should keep an eye on these emerging trends. Sourcing strategies that prioritize flexibility, adaptability, and technological advancements will be crucial in navigating the competitive landscape. Collaborating with suppliers who understand local market dynamics and regulatory requirements will also be beneficial.
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the air compressor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the operational lifecycle of air compressors are under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek sustainable alternatives. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable and have a lower carbon footprint, as well as adopting manufacturing practices that minimize waste and emissions.
Illustrative image related to air compessor
Moreover, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and energy efficiency labels can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability. Choosing air compressors with energy-efficient designs not only benefits the environment but also leads to significant cost savings over time, making it a win-win for businesses.
In regions like Europe, where stringent environmental regulations are in place, the emphasis on sustainability is even more pronounced. Buyers from Africa and South America are also starting to recognize the importance of ethical supply chains, aligning their procurement strategies with global sustainability goals. This shift towards green practices not only enhances brand reputation but also opens new market opportunities as consumers become increasingly eco-conscious.
The evolution of air compressors dates back to the early 19th century, where they were primarily used in industrial applications. Over the decades, advancements in technology have transformed air compressors from basic pneumatic tools into sophisticated machines capable of meeting diverse operational needs. The introduction of electric and gas-powered models has expanded their usability across various environments, from workshops to large-scale industrial sites.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing energy efficiency and reducing noise levels, responding to both market demands and regulatory pressures. The integration of digital technologies has further revolutionized the sector, allowing for smarter, more efficient operations. As the industry continues to innovate, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these developments to leverage the full potential of modern air compressor technologies.
How do I select the right air compressor for my business needs?
Selecting the right air compressor involves assessing your specific applications and requirements. Consider the type of tasks you will perform (e.g., powering pneumatic tools, spray painting, or inflation), the required pressure (PSI), and the volume of air (CFM) needed. Additionally, evaluate the environment where the compressor will be used—portable models are suitable for mobile tasks, while stationary units provide more power for heavy-duty operations. Finally, consult with suppliers to understand the various types, such as oil-free versus oil-lubricated compressors, to find the best fit for your operational needs.
What are the essential factors to consider when sourcing air compressors internationally?
When sourcing air compressors internationally, consider factors such as supplier reliability, product quality, and compliance with local regulations. Assess the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and previous export experience. It’s crucial to review customer feedback and conduct due diligence through background checks. Additionally, understand the logistics involved, including shipping costs, delivery timelines, and any import duties or taxes that may apply. Establishing clear communication with suppliers can help mitigate risks and ensure alignment on product specifications and delivery expectations.
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for air compressors from suppliers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for air compressors can vary significantly between suppliers. Some manufacturers may have low MOQs, allowing you to order a small quantity for trial purposes, while others may require larger orders to optimize production efficiency and reduce costs. When negotiating with suppliers, be clear about your needs and inquire about flexible ordering options, especially if you are testing a new market or product line. Understanding the MOQ can help you manage your inventory effectively and align with your budget constraints.
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing air compressors internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of air compressors typically vary by supplier and may include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Common terms may involve a deposit (e.g., 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipment or upon receipt. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms that protect both parties, ensuring secure transactions while considering factors like currency fluctuations and international banking fees. Always review the supplier’s payment policies and negotiate terms that align with your financial processes.
How can I ensure the quality of air compressors before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of air compressors, request detailed product specifications, certifications, and testing standards from suppliers. Consider ordering samples or conducting factory visits to assess manufacturing practices firsthand. Implement a quality assurance (QA) process by setting up inspections at various stages of production, which can help identify potential issues before shipment. Additionally, consider partnering with third-party inspection services to conduct thorough checks on product quality and compliance with industry standards, ensuring that the compressors meet your operational requirements.
What types of air compressors are most suitable for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, rotary screw and reciprocating air compressors are popular choices due to their efficiency and ability to handle heavy workloads. Rotary screw compressors are ideal for continuous operation and provide a steady airflow, making them suitable for larger facilities with demanding air needs. Reciprocating compressors, on the other hand, offer versatility and are often used in smaller workshops. Evaluate your specific air demands, duty cycle, and available space to choose the most effective compressor type for your industrial operations.
What are the logistics considerations when importing air compressors?
Logistics considerations for importing air compressors include selecting the right shipping method, understanding customs regulations, and ensuring proper documentation. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments. Ensure compliance with local import regulations, including tariffs and taxes, and prepare necessary paperwork like commercial invoices and packing lists. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the logistics process, ensuring timely delivery while minimizing the risk of delays or additional costs.
Can I customize air compressors to meet specific operational needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for air compressors to suit specific operational requirements. Customization may include modifications to tank size, pressure settings, or the inclusion of specific features like noise reduction or advanced control systems. When discussing customization with suppliers, clearly outline your needs and desired specifications. Keep in mind that custom orders may require longer lead times and may have higher MOQs, so plan accordingly to align with your operational timelines.
Domain: usaircompressor.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: US Air Center Compressors: Compressor-Dryer-Tank-Filters in One Box, 19 CFM to 140 CFM, 80 PSI to 200 PSI, 5 Hp | 208-230V 1 Phz, 5 Hp to 30 Hp | 208-230V 3 Phz. Fixed Speed Compressors: For Continuous High-Duty Cycle Applications, 19 CFM to 750 CFM, 80 PSI to 200 PSI, 10 Hp to 50 Hp | 220-600V 3 Phz. Variable Speed Drive Compressors: For Variable Duty Cycles, up to 35% Energy Savings, 19 CFM to 2…
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of air compressors presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse range of air compressor types—such as portable, stationary, oil-free, and oil-lubricated—enables buyers to select the right equipment tailored to their specific industrial needs. The importance of sourcing from reputable suppliers cannot be overstated, as it ensures not only product quality but also reliable after-sales support and maintenance services.

Illustrative image related to air compessor
Furthermore, as industries worldwide shift towards sustainability, the demand for energy-efficient and low-noise compressors is on the rise. By prioritizing these factors in their purchasing decisions, buyers can enhance operational efficiency and reduce overall costs.
Looking ahead, the global air compressor market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing industrialization. As an international buyer, aligning your sourcing strategy with these trends will position your business for success. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore innovative solutions, and make informed decisions to capitalize on this evolving landscape. Your proactive approach today will lead to enhanced productivity and competitive advantage tomorrow.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.