In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality tire pressure gauges and fillers is essential for businesses aiming to maintain optimal vehicle performance and safety. However, international buyers often face challenges in identifying reliable suppliers, understanding varying product specifications, and navigating regional market dynamics. This guide serves as a vital resource for B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Nigeria—by providing comprehensive insights into the tire pressure gauge and filler market.
Within this guide, we delve into various types of tire pressure gauges and fillers, their specific applications, and the latest technological advancements that enhance their functionality. Additionally, we offer strategies for effective supplier vetting, ensuring you partner with manufacturers who meet stringent quality standards. Cost analysis is another critical component, as it equips buyers with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their budgetary constraints.
By addressing these key areas, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of the global market confidently. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, you will be well-equipped to select the best tire pressure gauges and fillers that not only meet your operational needs but also contribute to your bottom line.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Tire Pressure Gauge | High accuracy, digital display, often with memory feature | Automotive workshops, fleet maintenance | Pros: Easy to read, precise measurements. Cons: Requires batteries, may be more expensive. |
| Analog Tire Pressure Gauge | Mechanical dial or stick design, no power needed | General automotive services, tire shops | Pros: Durable, no battery dependency. Cons: Less precise, harder to read in low light. |
| Portable Tire Inflator | Combines gauge and inflator in one unit, often battery-operated | Roadside assistance, small repair shops | Pros: Convenient, versatile for various tires. Cons: Limited power for larger vehicles. |
| Inline Tire Inflator with Gauge | Connects directly to air compressor, provides real-time reading | Heavy-duty vehicle maintenance, garages | Pros: Fast inflation, real-time pressure monitoring. Cons: Requires an air compressor setup. |
| Multi-Tire Inflation System | Capable of inflating multiple tires simultaneously | Commercial fleets, racing teams | Pros: Saves time, efficient for large operations. Cons: Higher initial investment, requires space. |
Digital tire pressure gauges are known for their high accuracy and user-friendly digital displays. Many models come equipped with features such as memory settings to store previous readings, making them ideal for automotive workshops and fleet maintenance operations. When considering a digital gauge, businesses should evaluate battery life, display clarity, and potential calibration needs to ensure consistent performance.
Analog tire pressure gauges utilize a mechanical dial or stick design, which does not require any power source. This makes them exceptionally durable and reliable, particularly in environments where electronic devices may be susceptible to damage. While they are suitable for general automotive services and tire shops, buyers should be aware that analog gauges may be less precise than their digital counterparts and can be challenging to read in low-light conditions.
Portable tire inflators combine the functions of a gauge and inflator into a single, compact unit, often powered by batteries or vehicle power outlets. They are particularly advantageous for roadside assistance and small repair shops where convenience is paramount. Buyers should consider the inflator’s pressure capacity and ease of use, as well as whether it can accommodate various tire types, including those of motorcycles and smaller vehicles.
Inline tire inflators connect directly to an air compressor and provide real-time pressure readings during inflation. This setup is commonly used in heavy-duty vehicle maintenance and garages, where speed and efficiency are critical. Buyers should assess the compatibility of the inflator with their existing air compressor systems and ensure the gauge is calibrated for accuracy, as any discrepancies can lead to improper tire inflation.
Multi-tire inflation systems are designed for inflating multiple tires at once, making them particularly useful for commercial fleets and racing teams. These systems save considerable time and labor, which can significantly enhance operational efficiency. However, they require a higher initial investment and more space than traditional inflators. Buyers should weigh the long-term savings against the upfront costs and consider the system’s compatibility with their fleet’s tire types.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tire pressure gauge and filler | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Routine tire pressure checks and inflation | Enhances safety, improves fuel efficiency, and prolongs tire life | Durability, accuracy, ease of use, and compatibility with various tire types |
| Logistics and Transportation | Fleet tire maintenance and management | Reduces operational costs, minimizes downtime, and ensures compliance with safety regulations | High PSI capacity, portability, and robust construction for heavy use |
| Agriculture | Tire pressure management for farm equipment | Increases productivity, reduces soil compaction, and enhances equipment longevity | Weather resistance, ease of calibration, and versatility for different equipment |
| Construction | Tire pressure monitoring for heavy machinery | Ensures operational efficiency, reduces the risk of tire blowouts, and enhances safety on job sites | High durability, resistance to harsh conditions, and compatibility with air compressors |
| Aviation | Tire pressure calibration for aircraft | Enhances safety, ensures compliance with aviation standards, and improves fuel efficiency | Precision measurement, lightweight design, and certification for aviation use |
In automotive repair shops, tire pressure gauges and fillers are essential tools for conducting routine tire maintenance. Regularly checking and adjusting tire pressure not only enhances vehicle safety but also improves fuel efficiency and extends tire life. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable and accurate gauges that can withstand diverse weather conditions and varying tire types is crucial. Additionally, ease of use and the ability to quickly connect to existing air compressor systems are important considerations.
For logistics and transportation companies, maintaining proper tire pressure across fleet vehicles is vital for operational efficiency. Tire pressure gauges and fillers help prevent costly breakdowns and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Properly inflated tires reduce fuel consumption and extend tire lifespan, directly impacting operational costs. Buyers in this sector should prioritize equipment with high PSI capacity and robust construction to withstand frequent use in demanding environments.
In the agriculture sector, managing tire pressure on farm equipment is critical for optimizing performance and minimizing soil compaction. Proper tire inflation allows for better traction and reduced wear on tires, which translates to increased productivity during planting and harvesting seasons. When sourcing tire pressure gauges and fillers, agricultural buyers should look for weather-resistant options that are easy to calibrate and versatile enough to accommodate various types of equipment, from tractors to harvesters.
Construction sites often utilize heavy machinery that requires precise tire pressure management to ensure safety and operational efficiency. Tire pressure gauges and fillers help prevent tire blowouts and enhance the overall safety of job sites. For buyers in the construction industry, sourcing durable tools that can withstand harsh conditions is essential. Features such as high durability, resistance to dirt and moisture, and compatibility with air compressors are key factors to consider.
In aviation, tire pressure calibration is critical for ensuring safety and compliance with strict aviation standards. Accurate tire pressure measurements contribute to optimal aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. Buyers in this sector must prioritize precision measurement tools that are lightweight yet robust, with certification for aviation use. The ability to quickly and reliably check tire pressure is essential for maintaining operational safety in this highly regulated industry.
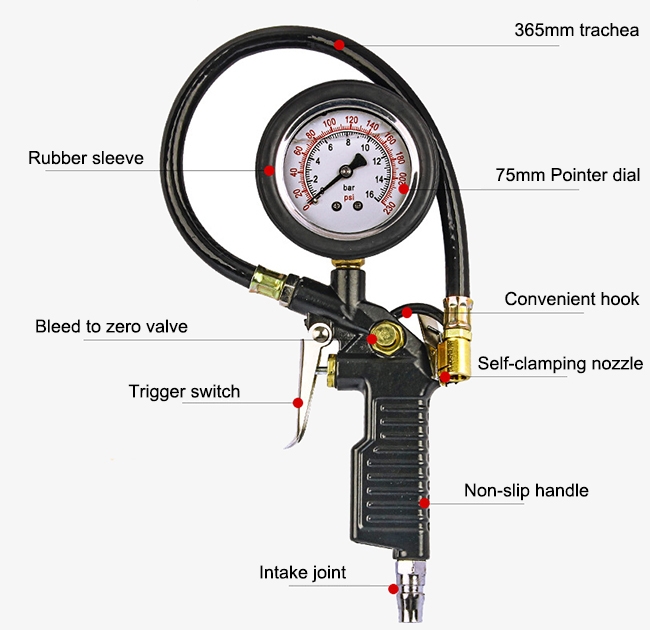
Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with the accuracy of tire pressure gauges and fillers, which can lead to operational inefficiencies. For instance, a logistics company in Brazil might rely on inaccurate tire pressure readings, resulting in over-inflation or under-inflation of tires. This not only affects fuel efficiency and tire longevity but can also compromise safety and increase the risk of tire blowouts during transportation. The challenge is heightened in regions with varying temperatures, where temperature fluctuations can further affect tire pressure readings.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest in high-quality digital tire pressure gauges that offer precise readings and temperature compensation features. When sourcing these products, prioritize gauges with calibration certifications and user-friendly interfaces for ease of operation. Additionally, implementing a regular maintenance schedule to check and calibrate gauges can ensure ongoing accuracy. Training staff on the importance of accurate readings and the correct usage of the gauges can also enhance tire management practices. By choosing reliable products and fostering a culture of accuracy, businesses can significantly improve their tire maintenance protocols.
The Problem: In fast-paced industries such as construction or agriculture, where time is a critical factor, the speed and efficiency of tire inflation can pose significant challenges. A company in Nigeria might find that their current tire inflator is too slow, leading to delays in operations, especially when dealing with heavy machinery that requires frequent tire adjustments. This inefficiency can result in increased downtime and lost revenue.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should consider investing in high-capacity tire inflators equipped with rapid inflation technology. Products that offer dual functionality—both inflating and deflating tires quickly—can be particularly beneficial. Additionally, choosing portable units with long hoses can enhance accessibility in tight spaces. Suppliers should be consulted to determine the best specifications based on the equipment being used, as different inflators may be suited for varying PSI requirements. Regular training for operators on how to use these inflators efficiently can also maximize productivity and minimize downtime.
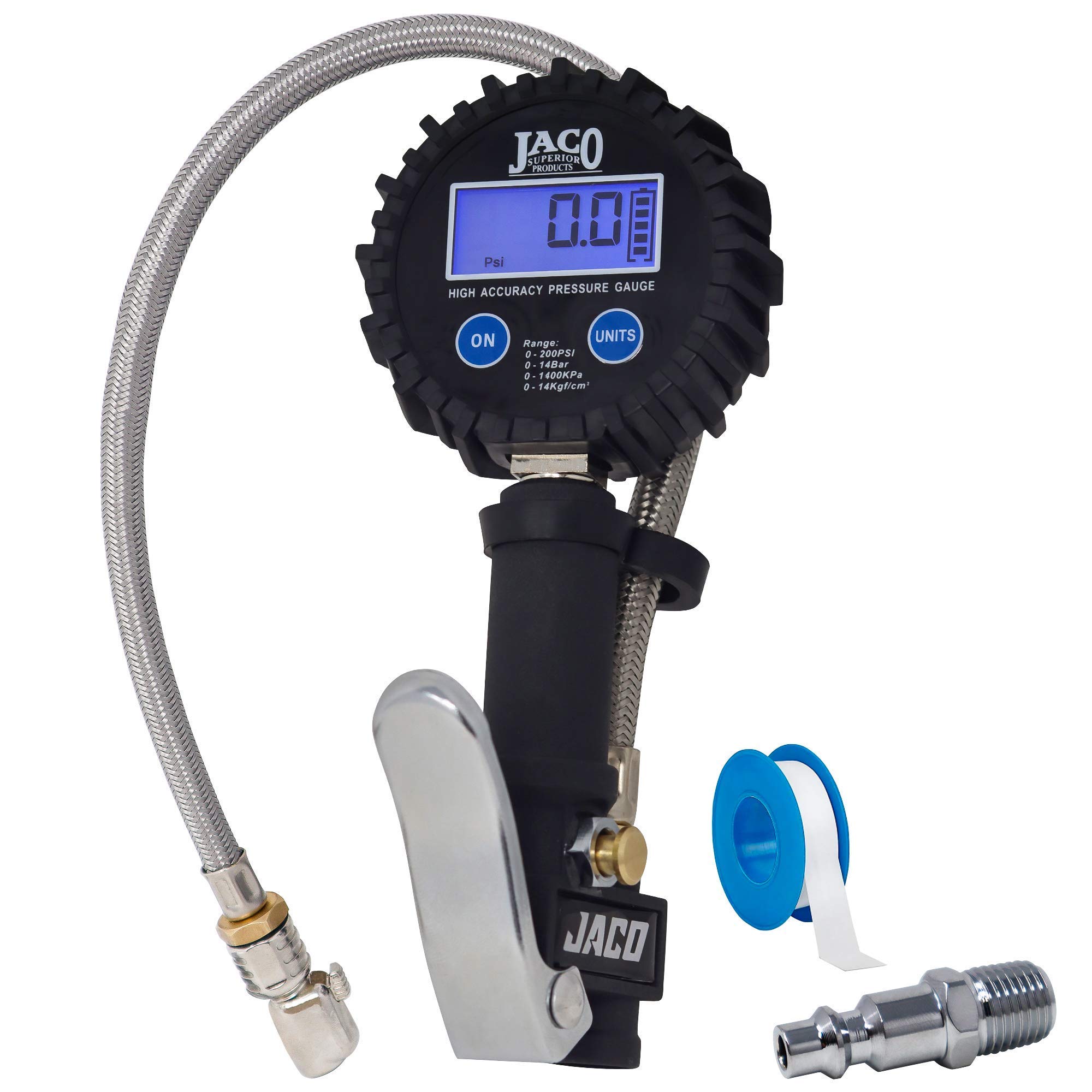

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
The Problem: Many businesses operate in harsh environments where tire pressure gauges and fillers are subject to extreme conditions, such as dust, moisture, and temperature variations. A mining company in South Africa, for instance, may find that their gauges frequently malfunction due to exposure to abrasive materials and extreme temperatures. This not only affects the reliability of the equipment but can also lead to costly repairs and replacements.
The Solution: To overcome these durability challenges, B2B buyers should focus on sourcing industrial-grade tire pressure gauges and inflators designed specifically for rugged environments. Look for products that feature reinforced housings, weatherproof components, and protective casings to withstand harsh conditions. Additionally, establishing a routine for inspecting and maintaining equipment can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Engaging with suppliers who understand the unique demands of your industry can also ensure that you are equipped with the best tools for the job. By prioritizing durability and reliability in product selection, companies can enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
When selecting materials for tire pressure gauges and fillers, it is essential to consider various properties and how they align with the specific needs of international B2B buyers. The following analysis covers four common materials used in the manufacturing of these devices, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for different markets.
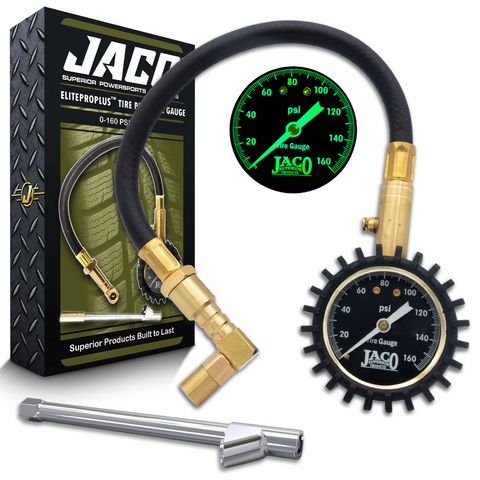

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
Brass is a widely used material in tire pressure gauges and fillers due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for automotive applications. The alloy’s malleability allows for easy machining, which is advantageous during manufacturing.
Pros: Brass is durable, relatively inexpensive, and easy to work with, making it a popular choice for both manufacturers and end-users. It also provides good thermal conductivity, which can be beneficial in applications where heat dissipation is required.
Cons: While brass is resistant to corrosion, it can still tarnish over time, especially in harsh environments. Additionally, its mechanical properties may not be as robust as some alternatives, which could limit its use in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with various media, including air and nitrogen, which are commonly used in tire inflation. However, it may not be suitable for aggressive chemicals, which could corrode the material.
Stainless steel is another popular choice for tire pressure gauges and fillers, known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength. It can handle high-pressure applications and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for heavy-duty use.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel ensures a long lifespan, which is particularly appealing to B2B buyers focused on reducing maintenance costs. Its resistance to rust and corrosion makes it suitable for various environments, including those with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than brass, which could impact the overall cost of the product. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex, requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including air, nitrogen, and even some aggressive chemicals. This versatility makes it suitable for various applications across different industries.
Aluminum is a lightweight material that offers good corrosion resistance and is often used in portable tire inflators and gauges. Its low density makes it easy to handle and transport, which is particularly beneficial for mobile applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which enhances portability. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to stainless steel, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers.
Cons: Aluminum is less durable than brass or stainless steel and may not withstand extreme pressures or temperatures as effectively. It is also more prone to denting and scratching, which could affect the aesthetic and functional aspects of the product.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for air and nitrogen but may not be appropriate for applications involving aggressive chemicals, which can lead to corrosion over time.
Plastic is increasingly being used in tire pressure gauges and fillers, especially in consumer-grade products. It offers a range of properties that can be beneficial in specific applications.
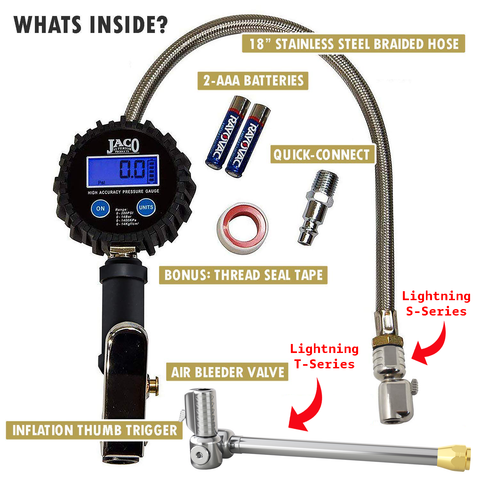

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
Pros: Plastic is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion. It can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs that may enhance user experience.
Cons: The primary drawback of plastic is its lower durability and strength compared to metals. It may not withstand high pressures or extreme temperatures, limiting its use in professional or heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic is typically suitable for air and nitrogen but may not hold up well in environments with extreme temperatures or exposure to chemicals, which could lead to degradation over time.
| Material | Typical Use Case for tire pressure gauge and filler | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | General automotive applications | Good corrosion resistance and durability | Can tarnish over time | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty and industrial applications | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Portable tire inflators and consumer-grade gauges | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer-grade gauges and low-cost applications | Lightweight and moldable | Lower durability and pressure limits | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with crucial insights into the materials used in tire pressure gauges and fillers, allowing for informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
Manufacturing tire pressure gauges and fillers involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring product quality and reliability. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
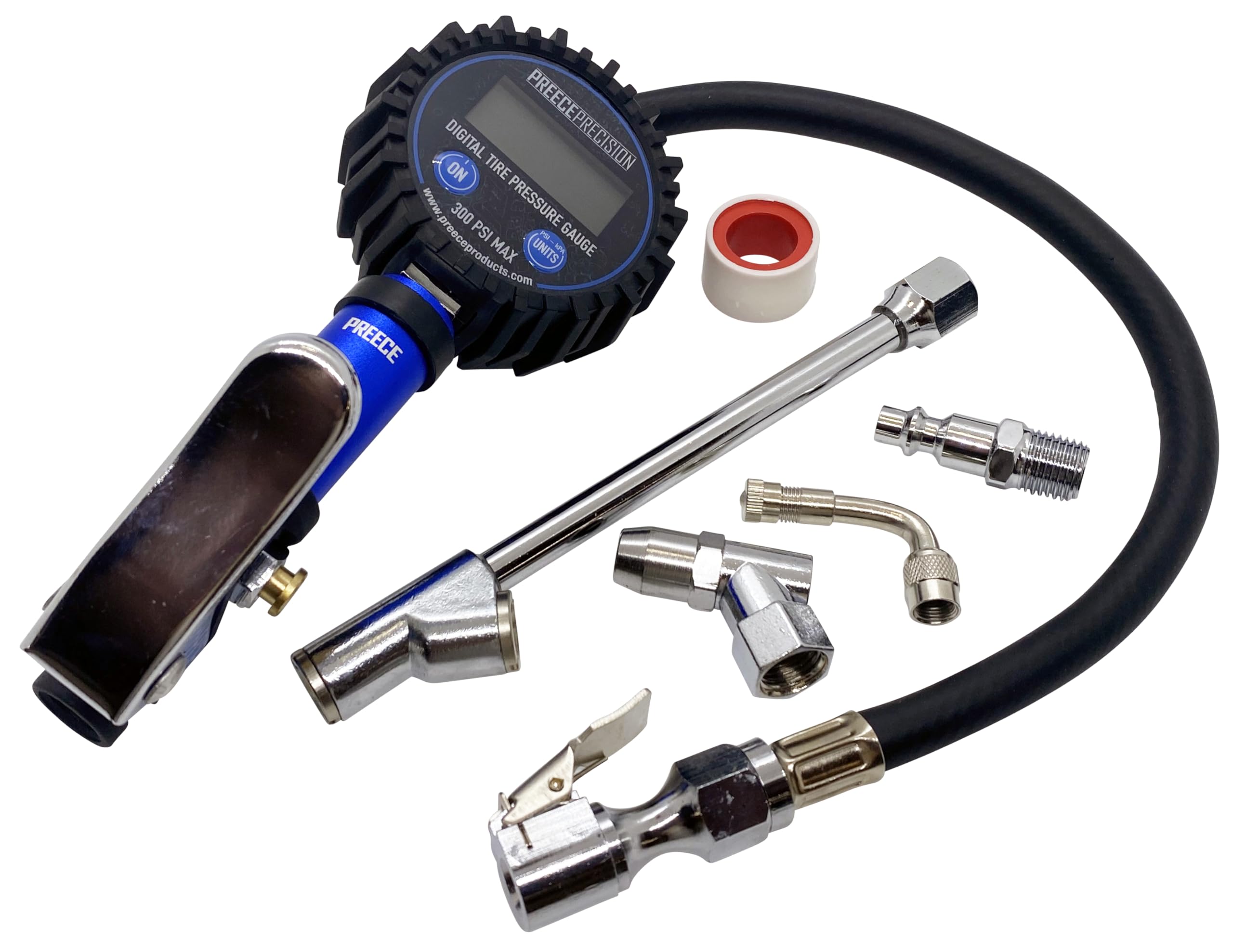

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing high-quality materials, typically metals like aluminum or stainless steel for durability, and plastic components for lightweight designs. Suppliers should ensure that materials meet international standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications. Rigorous checks during this stage can prevent defects that may arise from inferior materials.
Forming: In the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into the required components. Techniques such as precision machining, injection molding for plastic parts, and die-casting for metal components are commonly employed. The choice of technique depends on the complexity of the part and the desired precision. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often used to achieve high tolerances, ensuring that components fit together seamlessly.
Assembly: Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. Automated and manual assembly lines are utilized to put together various parts, including the gauge, hose, and connectors. This stage may involve the use of specialized tools to ensure that connections are secure and leak-proof. It is crucial to maintain cleanliness in the assembly area to avoid contamination that could affect the gauges’ performance.
Finishing: The final stage, finishing, includes processes such as surface treatment, painting, and quality checks. Surface treatments like anodizing or galvanizing enhance corrosion resistance, while painting may be used for aesthetic purposes or additional protection. This stage often incorporates final inspections to ensure that each product meets the required specifications.
Quality assurance (QA) is essential to guarantee that tire pressure gauges and fillers meet industry standards and customer expectations. Effective QA involves implementing relevant international standards and conducting multiple quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process.
Relevant International Standards: B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that comply with ISO 9001, which specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with CE marking is also important for products sold in the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For specific industrial applications, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may also be relevant.
Quality Control Checkpoints: Several checkpoints are integral to the QA process:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications. This is crucial for preventing defects from entering the production line.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor processes and identify any deviations from set standards. This includes monitoring machine settings, part dimensions, and assembly procedures.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each tire pressure gauge and filler undergoes a thorough inspection to verify its functionality, accuracy, and durability. This may include pressure tests, calibration checks, and visual inspections.
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that tire pressure gauges and fillers meet performance standards. These methods can include:
Functional Testing: This involves simulating real-world usage scenarios to verify that the gauges accurately measure pressure and that fillers operate effectively.
Calibration: Regular calibration against a standard reference gauge ensures accuracy. Manufacturers should provide calibration certificates to guarantee compliance with accuracy standards.
Durability Testing: Assessing the product’s resilience to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and physical stress is crucial, especially for products used in diverse climates across Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
Leak Testing: For inflators, leak tests are performed to ensure that air does not escape during operation, which is vital for performance and user safety.
B2B buyers must conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers to ensure adherence to quality standards. Here are some effective strategies:
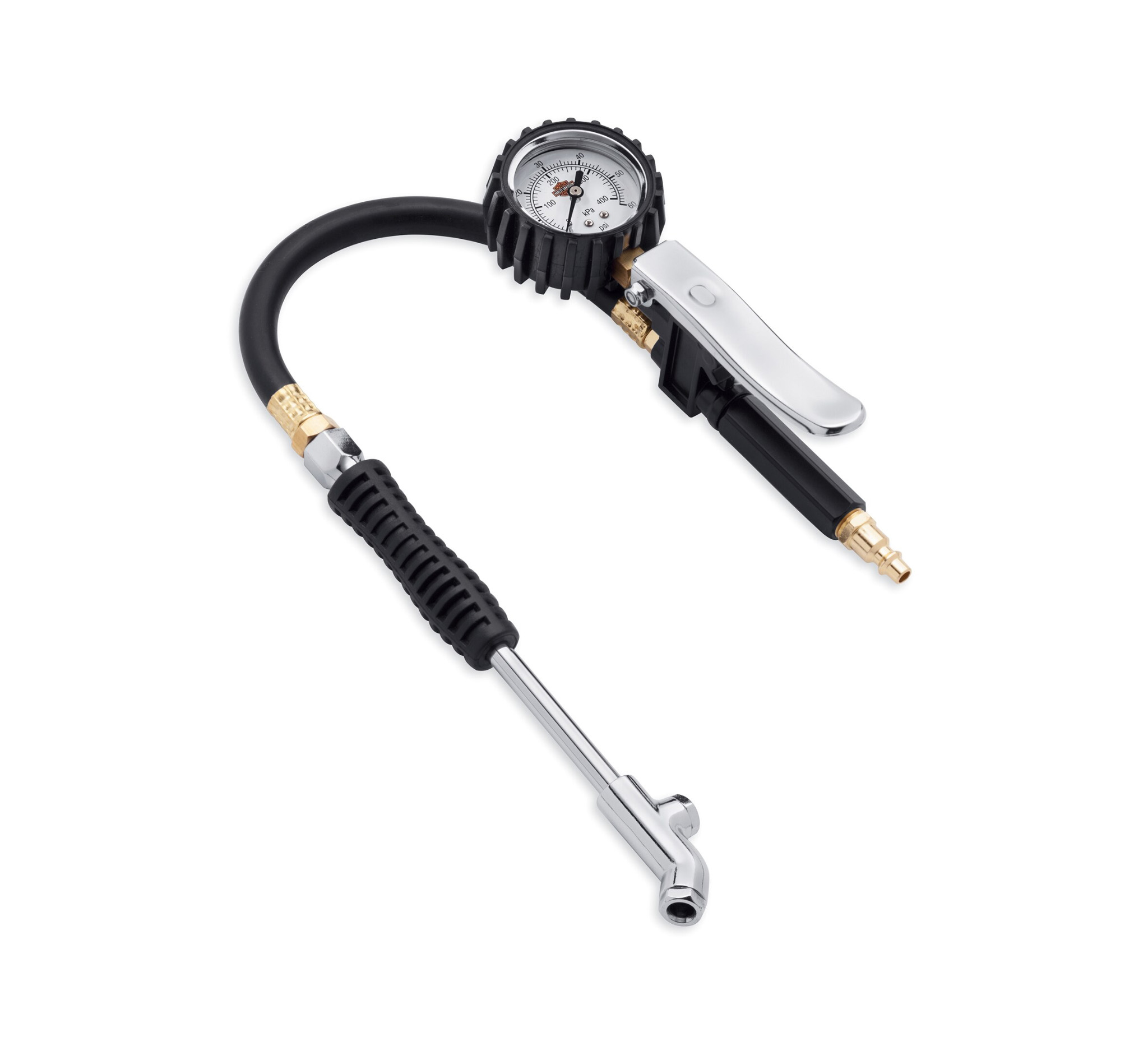

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. This can include on-site visits to observe operations firsthand.
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results, allows buyers to assess the supplier’s commitment to quality assurance.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can verify compliance with international standards and provide additional assurance of product quality.
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality control. It is essential to consider the following nuances:
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should be well-versed in local laws regarding product safety and quality standards to ensure compliance.
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and foster better relationships with suppliers. Buyers should be aware of how quality is perceived and prioritized in different markets.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: The supply chain’s complexity can impact product quality. Buyers should assess the logistics capabilities of suppliers, including their ability to manage quality throughout the supply chain.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes, ensuring that they select suppliers capable of delivering high-quality tire pressure gauges and fillers that meet their specific needs and expectations.
In today’s competitive market, sourcing the right tire pressure gauges and fillers is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers make informed decisions when procuring these essential tools.
Begin by determining the specific requirements for your tire pressure gauges and fillers. Consider the types of vehicles or equipment you will service, as this will dictate the necessary pressure range (e.g., 0-100 PSI or 0-150 PSI) and the gauge format (digital or analog). Additionally, evaluate the need for features such as temperature compensation or built-in hoses for ease of use.
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in tire pressure gauges and fillers. Look for manufacturers or distributors with a proven track record in your region. Utilize industry forums, trade shows, and online marketplaces to gather insights and reviews about supplier reliability and product quality.
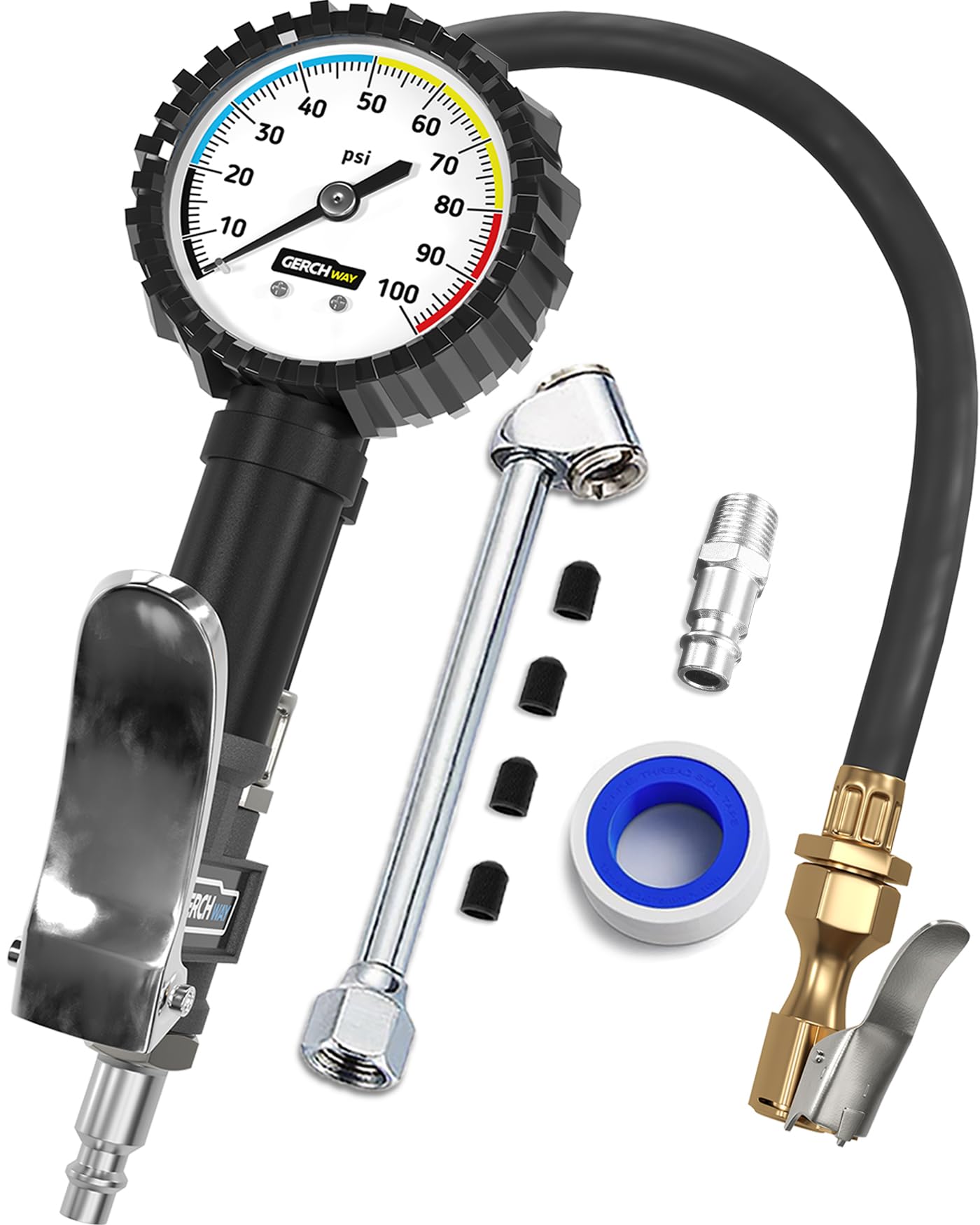

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses that have purchased similar products. This step helps ensure that the supplier is reputable and capable of meeting your quality and delivery expectations.
Ask for samples of the tire pressure gauges and fillers you are considering. Testing these products firsthand allows you to evaluate their performance, accuracy, and usability. Look for features such as ease of reading the gauge, durability of materials, and overall build quality.
Once you have gathered all necessary information, compare pricing and terms from different suppliers. Look beyond the initial cost; consider warranty options, bulk purchase discounts, and after-sales support. Understanding the total cost of ownership is crucial for making a financially sound decision.
Engage in negotiations with your chosen supplier to finalize the terms of your purchase. Discuss lead times, payment terms, and delivery schedules to ensure they align with your business needs. Clear communication at this stage can prevent misunderstandings later on.
After procurement, establish a system for ongoing evaluation of the tire pressure gauges and fillers. Monitor their performance and reliability in your operations. Regular feedback can inform future purchases and help maintain a high standard of service for your customers.
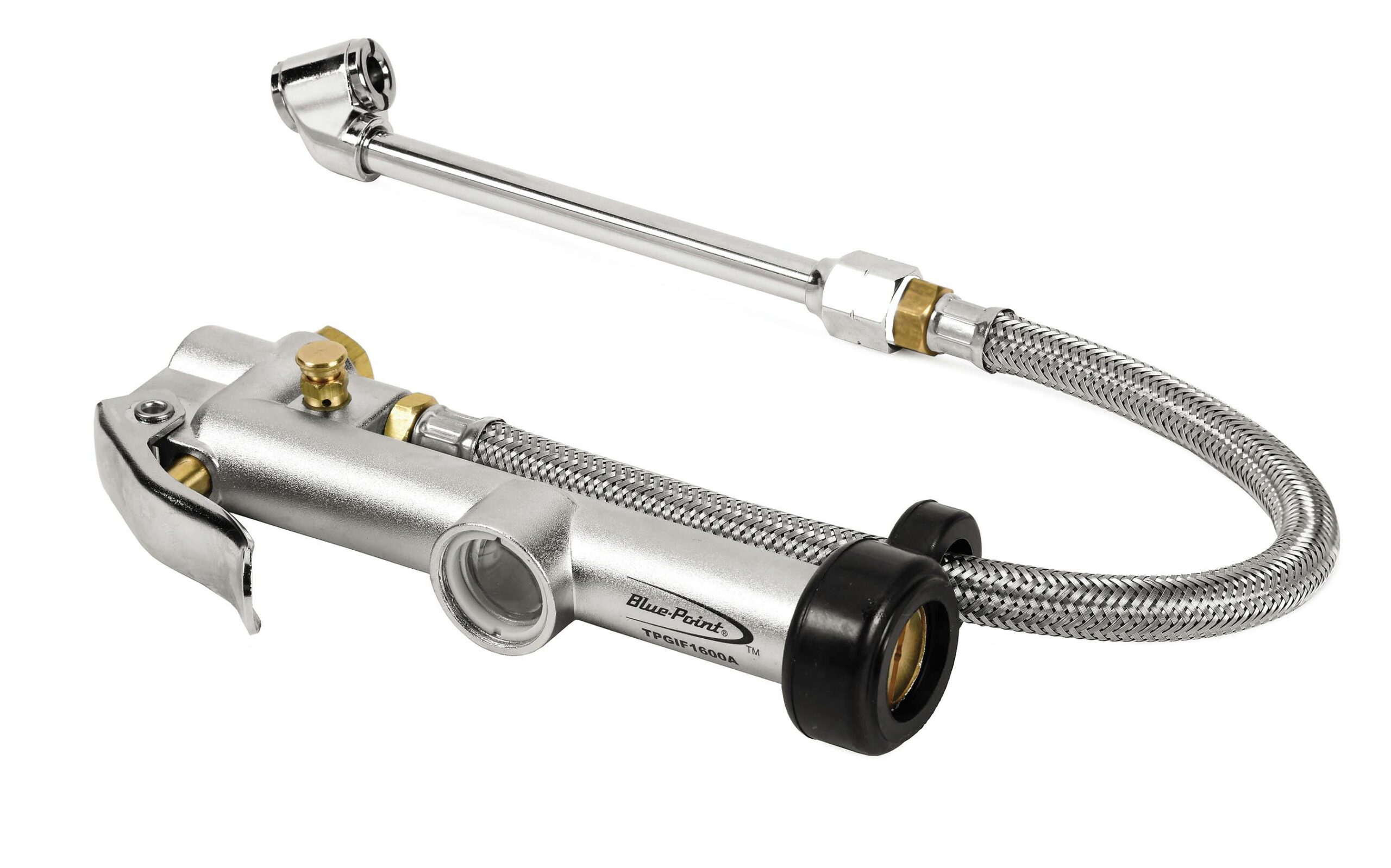

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for tire pressure gauges and fillers, ensuring they select the best products to meet their operational needs.
When sourcing tire pressure gauges and fillers, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The quality and type of materials significantly influence costs. For instance, digital gauges often use higher-grade electronics than analog models, which can increase the base price. Durable materials that withstand harsh environments, such as those found in Africa or South America, may also command a premium.
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the final pricing. Countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, may produce more expensive products. In contrast, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs might offer better margins but could lead to quality concerns.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting pricing positively.
Tooling: Custom tooling is necessary for specific designs or features. Buyers should consider these costs, especially when sourcing customized solutions that may require unique molds or machines.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to the overall cost. Certifications such as ISO or safety standards can also elevate pricing but assure buyers of product integrity.
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the origin and destination of the products. International shipping, particularly to regions like Africa or the Middle East, can be subject to tariffs and customs fees, which should be factored into the total cost.
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the pricing structure. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Several factors can influence pricing for tire pressure gauges and fillers:
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs. B2B buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchasing to leverage volume discounts.
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specific pressure ranges or digital displays, can drive up costs. Buyers should be clear on their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications can significantly affect the price. Higher-quality materials with certifications may be more expensive but often lead to better performance and longer product life.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a critical role in pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but the assurance of product performance can justify the expense.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the total landed cost.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
Negotiate Terms: Leverage your purchasing power. Discussing payment terms, delivery schedules, and after-sales support can yield more favorable conditions.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and operational efficiency. Investing in higher-quality products can reduce long-term expenses.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences and market conditions. Factors such as local demand, currency fluctuations, and economic stability can influence pricing strategies.
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, especially for future orders. Regular communication can also help in negotiating discounts or favorable terms.
By considering these insights and strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing tire pressure gauges and fillers, ensuring they achieve the best value for their investments.

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
In the realm of tire maintenance, a tire pressure gauge and filler are essential tools used to monitor and adjust tire pressure, ensuring safety and efficiency in vehicle operation. However, various alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar goals. This section provides a comparative analysis of tire pressure gauges and fillers against other viable options, enabling B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions based on their specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Tire Pressure Gauge And Filler | Portable Air Compressor | Digital Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Accurate pressure readings; manual filling | Fast inflation; can fill multiple tires quickly | Continuous monitoring; alerts for low pressure |
| Cost | Moderate ($30 – $100) | Higher initial investment ($50 – $200) | Varies widely ($40 – $300) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple setup; requires basic skills | Requires electrical source or battery | Complex installation; may need professional help |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional calibration needed | Moderate; requires regular checks and maintenance | Low; mostly software updates needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for individual users or small garages | Suitable for workshops or roadside assistance | Best for fleet management or high-volume users |
Portable air compressors are powerful alternatives to tire pressure gauges and fillers, primarily designed for quick tire inflation. They can fill multiple tires rapidly, making them ideal for busy workshops or roadside assistance scenarios. However, the initial investment is typically higher, and they require a power source, which may limit portability. Maintenance can also be moderate as they require regular checks to ensure functionality.
Digital Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) offer a high-tech alternative for tire pressure management. These systems continuously monitor tire pressure and provide real-time alerts, ensuring that drivers are informed before pressure drops to unsafe levels. While the investment can be significant, especially for advanced models, the benefits include increased safety and convenience. However, installation can be complex, often requiring professional assistance, which might not be feasible for all businesses.
Selecting the right solution for tire maintenance involves considering several factors such as performance, cost, and specific use cases. For businesses focused on individual tire maintenance or smaller operations, a tire pressure gauge and filler may suffice. In contrast, those with higher demands, such as workshops or fleet managers, might benefit more from portable air compressors or advanced TPMS. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs and operational context will guide B2B buyers toward the most effective tire maintenance solution for their requirements.
When selecting tire pressure gauges and fillers, understanding the technical specifications is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Here are critical properties to consider:
Pressure Range
This specification indicates the minimum and maximum pressure the gauge can measure, typically expressed in PSI (pounds per square inch). Common ranges include 0-100 PSI or 0-200 PSI. For B2B buyers, selecting a product with an appropriate pressure range ensures compatibility with various tire types, from passenger vehicles to heavy-duty trucks.
Accuracy
Accuracy is crucial in tire pressure management, often specified as a percentage (e.g., ±1% of full scale). High-accuracy gauges minimize the risk of under- or over-inflation, which can lead to tire wear, reduced fuel efficiency, and safety hazards. For businesses, investing in accurate gauges can enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs related to tire maintenance.
Material Grade
The materials used in manufacturing tire pressure gauges and fillers affect durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum, brass, and high-grade plastics. A robust material grade ensures resistance to corrosion and wear, especially in harsh environments. B2B buyers should prioritize products made from durable materials to ensure longevity and reduce replacement frequency.
Calibration
Calibration refers to the process of adjusting the gauge to ensure accurate readings. Many professional-grade gauges come pre-calibrated, but some may require periodic recalibration. Understanding calibration needs helps businesses maintain accuracy over time, which is critical for safety and compliance in commercial applications.
Connection Type
This specification details how the gauge or filler connects to air hoses or tire valves. Common connection types include Schrader and Presta valves. Knowing the correct connection type is essential for compatibility with the equipment used in various regions and types of vehicles, ensuring seamless operations.
Display Type
Tire pressure gauges may feature analog or digital displays. Digital displays often provide easier reading and can include additional features like backlighting or integrated temperature readings. Choosing the right display type can enhance user experience and efficiency, especially in low-light conditions or for less experienced users.
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in the tire pressure gauge and filler market. Here are some key terms to know:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products that may be sold under another brand name. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers seeking quality and reliability, as OEM products often meet stringent standards.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to scale operations without overcommitting resources.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price bids from suppliers. For buyers, issuing an RFQ can facilitate competitive pricing and ensure they receive comprehensive proposals from potential vendors.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and liabilities associated with their purchases.
Lead Time
This term refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times helps businesses plan their inventory and ensure timely delivery for operational needs.
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the product’s condition and longevity. Knowing the warranty terms is critical for buyers, as it provides assurance and recourse in case of defects or performance issues.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, fostering better partnerships and enhancing their operational efficiency in tire maintenance.
The tire pressure gauge and filler sector is experiencing notable growth driven by increasing vehicle ownership and a heightened focus on safety and fuel efficiency. Globally, the demand for accurate tire pressure monitoring is escalating, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where road conditions can vary significantly. Emerging technologies, such as digital gauges with Bluetooth connectivity, are revolutionizing the way businesses and consumers monitor tire pressure. These innovations not only improve accuracy but also enhance user convenience, catering to a tech-savvy market.

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
International B2B buyers are also witnessing a shift toward automation and smart solutions in tire inflators, which are designed for faster and more efficient tire maintenance. As electric vehicles gain traction, the need for compatible and efficient tire inflation solutions is set to rise. Moreover, the growing awareness of vehicle maintenance’s impact on fuel consumption is prompting businesses to invest in high-quality tire pressure monitoring equipment. In this competitive landscape, sourcing products that meet international standards while ensuring cost-effectiveness is crucial for buyers, particularly in emerging markets where price sensitivity is prevalent.
The environmental impact of manufacturing tire pressure gauges and fillers is an increasingly critical concern for B2B buyers. Sustainable sourcing practices, such as utilizing recycled materials and minimizing carbon footprints during production, are becoming essential. Companies are encouraged to seek suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, not only for compliance but also for brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Ethical supply chains are paramount in today’s global market, particularly in regions with stringent regulations on labor and environmental practices. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that hold green certifications, such as ISO 14001, which indicate a commitment to environmental management. Additionally, sourcing products made from eco-friendly materials, like biodegradable plastics or sustainably sourced metals, can enhance a company’s marketability and align with consumer demand for responsible products. Emphasizing these factors not only contributes to a healthier planet but also fosters a more resilient and ethically sound supply chain.
Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
The tire pressure gauge and filler sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, manual gauges were the norm, requiring users to interpret readings from analog dials, which often led to inaccuracies. The introduction of digital technology in the late 20th century marked a turning point, offering precise measurements and ease of use.
As the automotive industry advanced, so too did the technology behind tire maintenance tools. Modern innovations, such as automatic inflators and smart gauges that connect with mobile devices, reflect the sector’s response to consumer needs for efficiency and accuracy. The historical progression from manual to digital solutions illustrates the industry’s adaptability and ongoing commitment to enhancing vehicle safety and performance, making it a critical area of focus for international B2B buyers today.
1. How do I choose the right tire pressure gauge and filler for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate tire pressure gauge and filler involves assessing the specific requirements of your operation. Consider factors such as the types of vehicles serviced, the range of tire pressures needed, and the frequency of use. For high-volume applications, digital gauges with quick inflation capabilities may be ideal, while portable options are suitable for mobile services. Additionally, evaluate durability and ease of use, ensuring the equipment can withstand the demands of your work environment.
2. What are the key features to look for in a tire pressure gauge and filler?
When sourcing tire pressure gauges and fillers, prioritize features such as accuracy, pressure range, and ease of readability. Digital gauges often provide precise readings and may include additional functionalities like temperature compensation. Ensure that the filler has a robust design, quick-connect fittings, and compatibility with various air compressor systems. A lock-on feature can also enhance usability by maintaining a secure connection during inflation.
3. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for tire pressure gauges and fillers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers based on production capabilities and inventory levels. Generally, MOQs may range from 50 to several hundred units. It is advisable to negotiate with suppliers to determine a reasonable MOQ that aligns with your business needs while ensuring you can maintain adequate stock levels. Consider discussing potential discounts for larger orders, as this can be beneficial for both parties.
4. How do I vet suppliers of tire pressure gauges and fillers?
Vetting suppliers is crucial for ensuring product quality and reliability. Start by researching potential suppliers’ backgrounds, including their production capabilities, certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples to assess product quality firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes and return policies. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness, which are essential for a successful partnership.
5. What are common payment terms for international purchases of tire pressure gauges and fillers?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the specifics of the transaction. Common terms include advance payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon shipment. For international transactions, using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services can mitigate risks. Always clarify payment terms in writing and ensure they align with your cash flow capabilities to facilitate smoother transactions.
6. How can I ensure the quality of tire pressure gauges and fillers during international trade?
To ensure quality, establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier. Request quality certifications and documentation that demonstrate compliance with international standards. Implementing an inspection process, either through third-party services or in-house checks, can help verify product quality before shipment. Additionally, consider building a relationship with suppliers who have a proven track record of quality assurance and customer satisfaction.
7. What logistical considerations should I be aware of when importing tire pressure gauges and fillers?
Logistical considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling your product type and destination. Understand the import regulations specific to your country, as these can affect delivery times and costs. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping to avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
8. Are there customization options available for tire pressure gauges and fillers?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including branding, packaging, and specific features tailored to your business needs. Customization can enhance brand recognition and provide a competitive edge. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options, such as specific colors, materials, or additional functionalities. Be aware that customization may affect pricing and lead times, so plan accordingly.
Domain: jacosuperiorproducts.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: – **Product Range**: Tire Inflator Gauges
– **Promotions**: Early Black Friday: Extra 15% Off Orders Over $50 (Ends 11/30) – Use Code: BF2025; 100% Free Shipping on all USA orders.
– **Featured Products**:
1. **FlowPro® Digital Tire Inflator with Pressure Gauge – 200 PSI**
– Price: $39.95 (originally $89.99)
– Rated “Best Inline Tire Pressure Gauge” by Car and Driver Magazine.
2. **F…
Domain: steelmantools.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘STEELMAN # 75052 Straight Chuck Tire Inflator with Built-In Gauge and Green 12-Inch Hose’, ‘price’: ‘$29.99’, ‘availability’: ‘In stock’}, {‘name’: ‘STEELMAN # 75051 Straight Chuck Tire Inflator with Built-In Gauge and 12-Inch Hose’, ‘price’: ‘$21.99’, ‘availability’: ‘In stock’}, {‘name’: ‘STEELMAN # 97977 High Accuracy Digital Gauge Tire Inflator with Temperature Compensation and 15-I…
Domain: longacreracing.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Collection: Tire Pressure Gauges
– High-quality components, calibrated for reliability and durability.
– Large face with easy-to-read numbers.
– 360-degree swivel chuck for viewing at any angle.
– Built-in air bleeder valves to reduce pressure in overinflated tires.
– Sturdy flexible hose included.
– Suitable for streetcars, race cars, trucks, motorcycles, and bikes.
– Helps maintain proper tire p…
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of tire pressure gauges and fillers is essential for international B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and safety across diverse markets. By understanding the latest advancements in technology, such as digital gauges with high accuracy and portable inflators, businesses can significantly improve their tire maintenance processes. This not only leads to enhanced vehicle performance but also contributes to cost savings through improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear.
Moreover, building strong relationships with reliable suppliers can ensure access to high-quality products that meet regional compliance standards and customer expectations. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for innovative and efficient tire maintenance solutions will only grow.

Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers to invest in strategic sourcing initiatives that prioritize quality, reliability, and technological advancement in tire pressure management. By doing so, businesses can position themselves as leaders in their respective markets, ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow. Embrace the future of tire maintenance and elevate your sourcing strategy today.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Illustrative image related to tire pressure gauge and filler