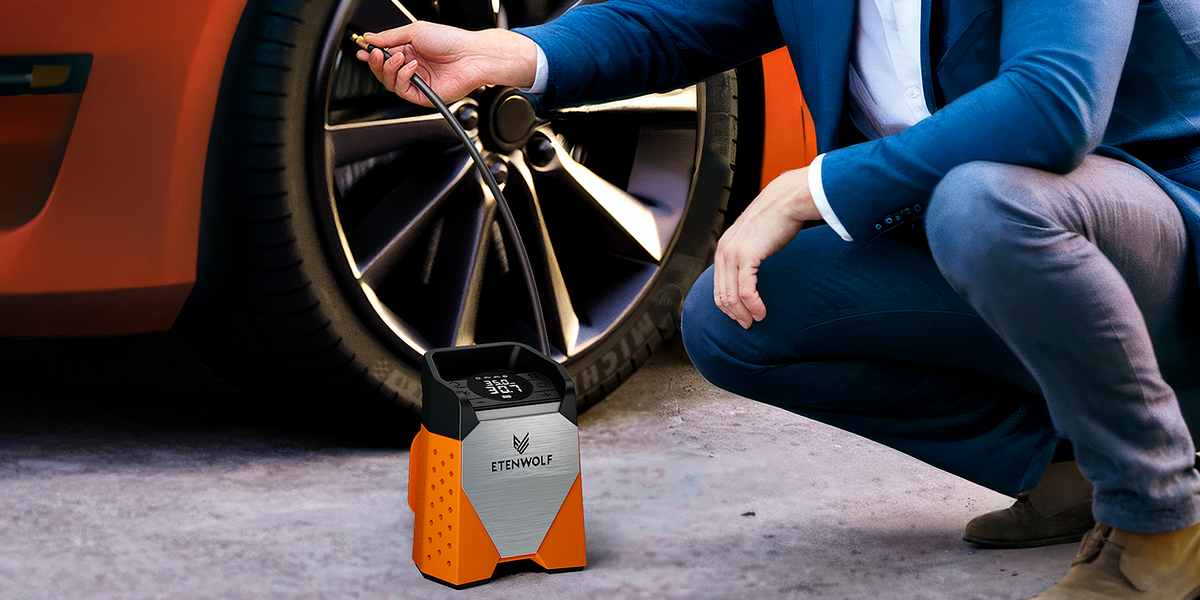
In the fast-paced world of automotive maintenance, knowing how to effectively use a tire inflator is crucial for businesses that rely on vehicle performance. Flat tires can disrupt operations, leading to costly delays and potential safety hazards. This comprehensive guide aims to equip international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Vietnam and Nigeria), with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about tire inflator products.
Our guide covers various types of tire inflators, including 12-volt and battery-powered options, and their specific applications across different vehicles and scenarios. It delves into essential features to consider, such as pressure accuracy, portability, and ease of use, which are critical for efficient tire maintenance. Additionally, we provide insights on supplier vetting processes to ensure you partner with reputable manufacturers, as well as a detailed overview of cost considerations that can influence your purchasing strategy.
By understanding the nuances of tire inflators and their applications, B2B buyers can enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime associated with tire issues. This guide serves as a valuable resource to empower your purchasing decisions, ensuring that you select the right tire inflator solutions to meet your business needs effectively.
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12-Volt Tire Inflators | Connects to vehicle’s power outlet; compact and portable | Automotive repair shops, fleet management | Vorteile: Affordable, easy to use. Nachteile: Limited power, may not handle larger tires. |
| Battery-Powered Tire Inflators | Self-contained power source; can double as a power bank | Roadside assistance, emergency kits | Vorteile: Versatile, no need for external power. Nachteile: Heavier, may require recharging. |
| Tire Inflator and Sealant Kits | Includes sealant for temporary fixes; often vehicle-specific | Automotive manufacturers, service centers | Vorteile: Quick temporary repair. Nachteile: Not a permanent solution, limited to small punctures. |
| High-Pressure Tire Inflators | Designed for larger tires; higher PSI capacity | Heavy-duty vehicle maintenance, construction | Vorteile: Efficient for large tires. Nachteile: Bulkier, typically more expensive. |
| Digital Tire Inflators | Features digital gauges and automatic shut-off | Tire retail shops, consumer automotive | Vorteile: Accurate readings, user-friendly. Nachteile: Higher cost, may require more maintenance. |
12-volt tire inflators are compact devices that connect directly to a vehicle’s power outlet, making them ideal for on-the-go tire inflation. Their portability makes them a popular choice for automotive repair shops and fleet management companies, where quick tire maintenance can minimize downtime. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the inflator’s power output and compatibility with various vehicle types, as some models may struggle with larger tires or require extended use.
Battery-powered tire inflators are versatile tools that come with their own power source, allowing them to be used anywhere without needing to connect to a vehicle. This makes them particularly useful for roadside assistance teams or as part of emergency kits for businesses. When purchasing, buyers should consider the battery life and whether the inflator can also function as a power bank for other devices, adding to its utility.
Tire inflator and sealant kits are designed for quick, temporary fixes for flat tires. They often come with a sealant that can patch small punctures while inflating the tire. These kits are commonly used by automotive manufacturers and service centers, especially for vehicles that do not come with spare tires. B2B buyers should assess the sealant’s effectiveness and the kit’s ease of use, as well as any limitations regarding tire size and puncture type.
High-pressure tire inflators are specifically designed to handle larger tires, making them suitable for heavy-duty vehicles and construction equipment. Their ability to deliver higher PSI levels ensures efficient inflation, which is crucial for businesses that rely on large vehicles. Buyers should consider the inflator’s build quality, pressure capacity, and any additional features that enhance performance, such as extended hoses or quick-connect fittings.
Digital tire inflators come equipped with advanced features like digital pressure gauges and automatic shut-off capabilities, making them user-friendly and precise. They are frequently used in tire retail shops and consumer automotive applications, where accurate tire pressure is essential for safety and performance. When investing in a digital tire inflator, B2B buyers should evaluate the accuracy of the gauge, the ease of reading measurements, and overall durability, as these factors contribute to long-term value.
| Industrie/Sektor | Specific Application of how to use tire inflator | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Fleet maintenance for commercial vehicles | Reduces downtime and enhances operational efficiency | Ensure inflators can handle various tire sizes and pressures; consider durability and portability. |
| Landwirtschaft | Tire inflation for agricultural machinery | Improves productivity and reduces tire-related delays | Look for heavy-duty inflators that can withstand outdoor conditions; assess power options for remote locations. |
| Bauwesen | Tire management for construction vehicles and equipment | Enhances safety and minimizes project delays | Source robust inflators with high-pressure capacity; consider ease of use and maintenance requirements. |
| Automotive Services | Mobile tire repair services | Increases customer satisfaction and service speed | Choose portable inflators with reliable power sources and quick inflation times; assess compatibility with various tire types. |
| Logistics and Shipping | On-site tire inflation for delivery and transport vehicles | Ensures timely deliveries and reduces roadside incidents | Consider inflators that are compact and easy to transport; assess the need for multiple power options for versatility. |
In the transportation industry, tire inflators play a crucial role in maintaining the fleet of commercial vehicles. Regular tire pressure checks and inflation prevent premature tire wear and improve fuel efficiency. Businesses can minimize vehicle downtime by equipping their fleets with portable tire inflators, allowing quick tire repairs on-site rather than relying on roadside assistance. When sourcing, companies should prioritize inflators that can accommodate various tire sizes and pressures, ensuring they are built for durability and ease of use.
Agricultural operations often depend on heavy machinery, where tire maintenance is vital for productivity. A tire inflator allows farmers to quickly address tire pressure issues, ensuring that machinery like tractors and harvesters remain operational during critical times. This capability can significantly reduce delays caused by flat tires. Buyers in the agricultural sector should look for heavy-duty inflators capable of functioning in rugged outdoor conditions and consider the power options available for use in remote locations.
In construction, proper tire management for vehicles and equipment is essential to maintain safety standards on-site. A tire inflator enables quick inflation of tires, thus reducing the risk of accidents related to under-inflated tires. This proactive approach minimizes project delays and enhances overall site safety. When sourcing tire inflators for construction purposes, businesses should focus on models with high-pressure capacity and robust build quality to withstand the demanding environment.
For mobile tire repair services, having a reliable tire inflator is essential for customer satisfaction. Quick and efficient tire inflation can significantly reduce wait times for customers, making the service more appealing. These inflators should be portable and equipped with a reliable power source for convenience. Automotive service providers should evaluate inflators based on their inflation speed and compatibility with various tire types to ensure they can meet diverse customer needs.
In logistics and shipping, on-site tire inflation for delivery vehicles is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. Quick access to tire inflators allows drivers to address issues promptly, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing the likelihood of roadside incidents. When sourcing tire inflators for logistics, companies should consider compact designs for easy transport and assess the need for multiple power options to cater to different vehicle types.
Das Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when selecting the appropriate tire inflator for their fleet or equipment. With a plethora of options available, distinguishing between models that suit different vehicle types—such as light-duty trucks, passenger cars, or heavy machinery—can be overwhelming. Additionally, considerations like power source (12V vs. battery-operated), inflation speed, and maximum pressure capacity complicate the decision-making process. Buyers may worry about investing in a product that doesn’t meet their operational requirements, leading to inefficiencies or downtime.
Die Lösung: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their specific needs before purchasing a tire inflator. Begin by cataloging the types of vehicles in your fleet and their respective tire specifications, including recommended tire pressures. Based on this data, prioritize features that align with those requirements—such as a portable 12V inflator for passenger vehicles or a heavy-duty model for commercial trucks. Consulting product reviews, user testimonials, and manufacturer specifications can provide additional insights. Buyers may also consider investing in multi-functional inflators that can handle various applications, ensuring versatility and long-term value.
Das Problem: User error is a common concern when operating tire inflators, particularly among staff who may not be familiar with the equipment. Missteps, such as over-inflating tires or failing to check for visible damage, can lead to dangerous situations and costly repairs. Employees may also struggle with the setup process, leading to wasted time and resources, especially in a busy operational environment. This issue is exacerbated in regions where user training is minimal, resulting in inconsistent practices across the workforce.
Die Lösung: Implementing a structured training program is essential to mitigate user errors. This program should cover the proper usage of tire inflators, including pre-inflation checks, correct setup procedures, and safety precautions. Visual aids, such as instructional videos or step-by-step guides, can enhance understanding and retention. Additionally, consider establishing a checklist for employees to follow before using the inflator, ensuring that critical steps—such as verifying tire condition and setting the correct pressure—are not overlooked. Regular refresher courses can help maintain skills and awareness among staff, ultimately promoting a safer and more efficient operation.
Das Problem: When tire inflators malfunction or fail to deliver the expected performance, B2B buyers often find themselves without adequate support or troubleshooting resources. This lack of information can lead to frustration, as employees may be unsure how to address issues like insufficient power supply, overheating, or compatibility problems. In regions with limited access to customer service, this can result in prolonged downtime and increased operational costs.
Die Lösung: To address this pain point, businesses should proactively seek inflators that come with comprehensive user manuals and access to reliable customer support. Before making a purchase, buyers should inquire about warranty options and the availability of replacement parts. Additionally, creating an internal knowledge base with troubleshooting tips and common issues can empower employees to resolve minor problems independently. Regular maintenance checks and an inventory of commonly needed accessories—such as replacement hoses or connectors—can also prevent operational disruptions. By fostering a culture of preparedness and education around tire maintenance, businesses can enhance their operational resilience and efficiency.

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
When selecting materials for tire inflators, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, and cost. The following analysis discusses four common materials used in tire inflators: plastic, aluminum, rubber, and steel. Each material has unique properties that influence its suitability for different applications.
Plastic is often used in the housing and components of portable tire inflators due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. Key properties include a temperature rating that can typically withstand moderate heat and pressure, making it suitable for most tire inflation tasks.
Profis: Plastic is generally low-cost, lightweight, and can be molded into complex shapes, which enhances manufacturing efficiency. It is also resistant to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for use in various environments.
Nachteile: However, plastic can be less durable than metals, particularly under high-stress conditions or extreme temperatures. Over time, it may become brittle, especially if exposed to UV light or harsh chemicals.

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Plastic components are often used in the casing and some internal parts of inflators, where they protect sensitive electronics and mechanisms from external damage.
Überlegungen für internationale Einkäufer: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM for plastics is crucial, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where environmental factors can affect material longevity.
Aluminum is frequently chosen for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is particularly useful for components that require both durability and lightweight characteristics.
Profis: Aluminum is highly durable and can withstand high pressures, making it suitable for the high-performance demands of tire inflators. It also has good thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat generated during operation.

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Nachteile: The cost of aluminum is generally higher than plastic, and its manufacturing process can be more complex, which may lead to increased production costs.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Aluminum is often used in the body of the inflator and in high-stress components like the air hose connectors, enhancing the overall reliability of the product.
Überlegungen für internationale Einkäufer: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards such as DIN or JIS, particularly in Europe and Asia, where material specifications are strictly enforced.
Rubber is primarily used for seals and hoses in tire inflators due to its flexibility and resilience. It can handle a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making it a reliable choice for pneumatic applications.
Profis: Rubber is highly elastic and can create airtight seals, which is critical for maintaining pressure in tire inflators. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture.
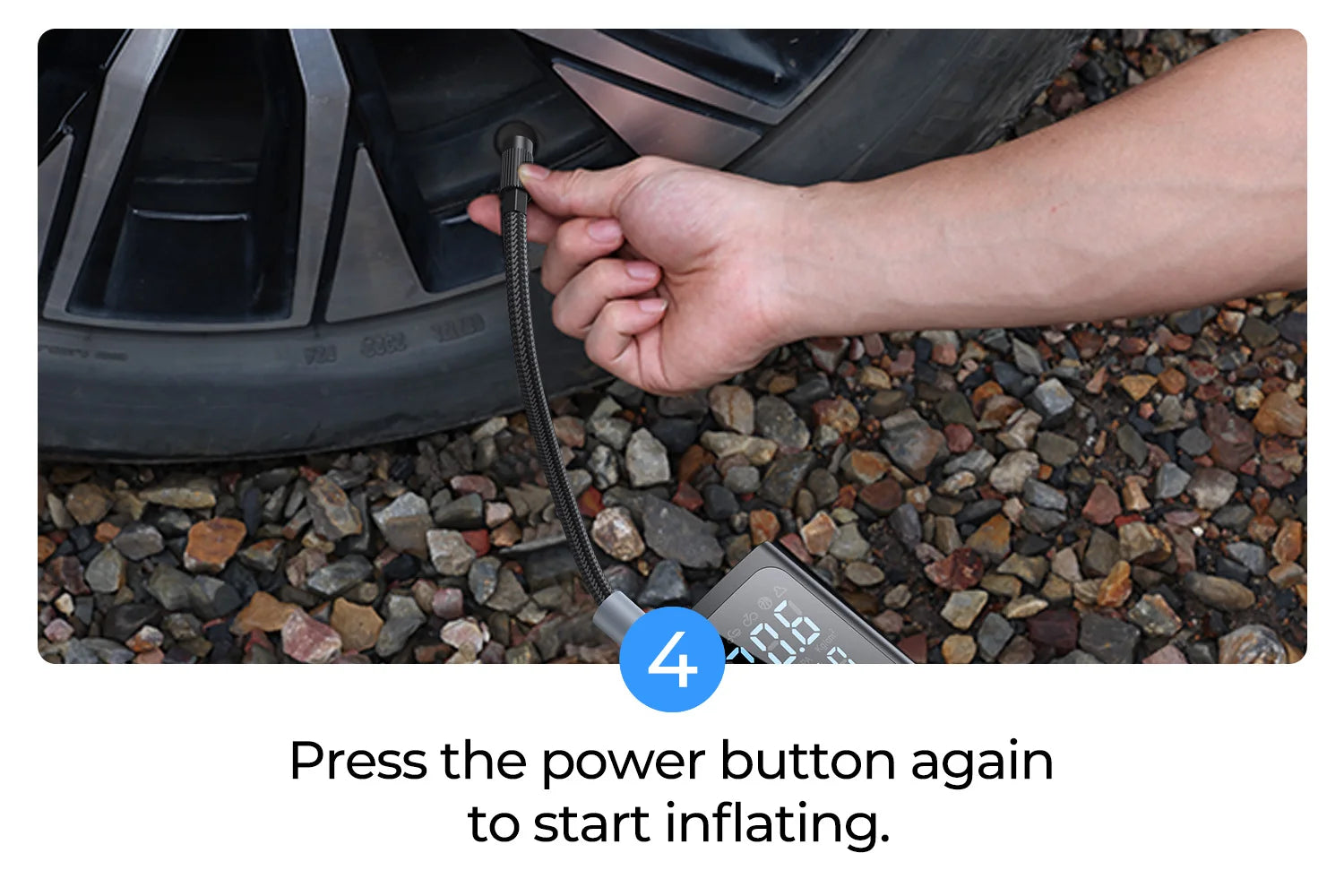
Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Nachteile: However, rubber can degrade over time due to exposure to ozone, UV light, and certain chemicals, which may limit its lifespan in outdoor applications.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Rubber components are essential for ensuring that the inflator maintains proper pressure and does not leak air during operation.
Überlegungen für internationale Einkäufer: Buyers should look for rubber materials that comply with international standards for automotive applications, particularly in regions with varying climatic conditions.
Steel is less commonly used in portable tire inflators but is sometimes employed in high-pressure applications or heavy-duty models due to its strength and durability.
Profis: Steel is incredibly strong and can withstand high pressures, making it ideal for heavy-duty inflators. It is also resistant to wear and tear.
Nachteile: The main drawback is that steel is heavier and more prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can affect portability and longevity.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Steel components may be used in the internal structure or high-stress areas of the inflator, ensuring robustness.
Überlegungen für internationale Einkäufer: Compliance with corrosion resistance standards is essential, especially in humid or coastal regions in Africa and South America.
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to use tire inflator | Hauptvorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Beschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kunststoff | Gehäuse und nicht-strukturelle Komponenten | Leicht und korrosionsbeständig | Less durable under stress | Niedrig |
| Aluminium | Body and high-stress components | Hohes Verhältnis von Festigkeit zu Gewicht | Höhere Kosten und komplexe Herstellung | Med |
| Gummi | Dichtungen und Schläuche | Excellent elasticity and airtight sealing | Verschlechtert sich im Laufe der Zeit durch Exposition | Niedrig |
| Stahl | Heavy-duty applications | Extremely strong and durable | Schwerer und korrosionsanfälliger | Hoch |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and considerations for various materials used in tire inflators, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional standards.
The manufacturing process of a tire inflator involves several key stages that ensure the final product is both functional and reliable. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
The first step in manufacturing a tire inflator is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials used in tire inflators include durable plastics for the casing, metal components for the internal mechanisms, and rubber for hoses and seals. Quality assurance begins at this stage, where suppliers must meet specific material standards to ensure durability and safety. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers utilize high-grade materials by requesting material certification documents.
Once materials are prepared, the forming process begins. This may involve injection molding for plastic parts, which allows for precise shapes and designs. Metal components are often produced through stamping or machining processes. The forming techniques used can greatly affect the durability and performance of the inflator. Buyers should consider suppliers who employ advanced technologies, such as CNC machining, to ensure consistent quality and precision.
The assembly of tire inflators requires skilled labor and precise machinery. This stage involves integrating various components, such as motors, hoses, and digital displays. Automated assembly lines are increasingly common, as they enhance efficiency and reduce human error. During this phase, it is crucial to implement rigorous checks to ensure that each unit meets performance specifications. B2B buyers can inquire about the assembly process and workforce training to gauge the supplier’s commitment to quality.

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Finishing touches on tire inflators can include surface treatments, painting, and final inspections. Surface treatments may enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors, such as moisture and UV light. Painting not only improves aesthetics but also provides additional protection. A comprehensive final inspection (FQC) is conducted to confirm that each inflator meets the required specifications and is free from defects. B2B buyers should ask for samples or view production videos to understand the finishing quality.
Quality assurance in tire inflator manufacturing is guided by several international standards. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Other relevant standards may include CE marking for safety compliance in Europe and specific industry certifications like the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards for inflators used in specialized applications.
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process. These checkpoints typically include:

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
B2B buyers should request detailed reports on these QC checkpoints from potential suppliers to assess their quality assurance practices.
Testing methods for tire inflators may include:
These tests help identify potential failures and ensure that the inflator will perform reliably in real-world situations. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing protocols used by suppliers and request access to test results.
To ensure that a supplier adheres to robust quality control measures, B2B buyers can take several steps:

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality control. Variations in regional standards and regulations can complicate procurement processes. Buyers should be aware of local compliance requirements and ensure that suppliers are equipped to meet these standards. Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may affect communication regarding quality expectations, necessitating clear and concise documentation.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with tire inflators is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material quality, assembly techniques, and rigorous testing methods, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source reliable and effective tire inflators for their business needs.
This practical guide serves as a checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure and effectively use tire inflators. Understanding how to utilize these devices efficiently can lead to improved vehicle maintenance, reduced downtime, and enhanced operational efficiency, particularly in industries reliant on transportation.
Before purchasing a tire inflator, assess the specific requirements of your fleet or operation. Consider the types of vehicles you manage, the frequency of tire maintenance, and the typical environments in which your vehicles operate.
– Wichtige Überlegungen:
– Vehicle types: Cars, trucks, or heavy machinery?
– Usage frequency: Daily operations or occasional emergencies?
Establish the technical parameters that your chosen inflator must meet. This includes maximum pressure capacity, hose length, and power source compatibility (12V, battery-operated, etc.).
– Specifications to Review:
– Maximum PSI: Ensure it meets the needs of your vehicle types.
– Hose length: Consider accessibility for various tire positions.
Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your operational demands. Look for suppliers with a proven track record and reliability in your region.
– Actions to Take:
– Request company profiles and product samples.
– Review customer testimonials and case studies relevant to your industry.
Investigate the features of the tire inflators you are considering. Look for models that offer essential functions such as automatic shut-off, digital pressure gauges, and additional attachments for diverse applications.
– Essential Features:
– Automatic stop function: Prevents over-inflation.
– Built-in LED lights: Useful for roadside assistance at night.
Ensure that the tire inflators comply with local and international safety standards. This is particularly critical in regions with stringent regulations.
– Überprüfung der Einhaltung der Vorschriften:
– Verify certifications: ISO, CE, or other relevant standards.
– Review safety features: Check for overheating protection and robust construction.
Perform a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to understand the financial implications of your purchase. Factor in not only the initial cost but also long-term maintenance and operational savings.
– Erwägungen:
– Purchase price vs. operational efficiency: How will the inflator reduce downtime?
– Warranty and support: What after-sales service is provided?

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Develop a strategy for training your team on the proper use of tire inflators. Effective training ensures that staff can utilize the equipment safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of accidents.
– Training Focus Areas:
– Safe operation protocols: Emphasize tire inspection and inflation techniques.
– Troubleshooting common issues: Equip staff with knowledge to handle minor problems.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding tire inflators that enhance their operational efficiency and ensure vehicle safety.
When sourcing tire inflators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
Materialien: This includes the cost of raw materials such as plastic, metal components, and electronic parts. The quality and type of materials directly impact durability and performance. For example, a tire inflator made with higher-grade materials may have a higher upfront cost but can offer better longevity and reliability.
Arbeit: Labor costs vary significantly based on geographic location. Manufacturers in regions with lower wage standards may offer more competitive pricing. However, it’s essential to consider the skill level of workers, as more experienced labor can result in higher-quality products.
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: This encompasses costs related to factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and salaries of managerial staff. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, leading to more favorable pricing for buyers.
Werkzeugbau: Customization of inflators may require specific tools and molds, which can increase initial costs. Bulk orders can help spread these costs over a larger volume, thus reducing the per-unit cost.
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Investing in stringent QC processes ensures that the tire inflators meet safety and performance standards. While this may raise costs initially, it can lead to fewer returns and warranty claims, ultimately reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Logistik: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the destination and volume. Factors like Incoterms, shipping methods, and freight charges can significantly influence the final price. For international buyers, understanding local regulations and duties is crucial for accurate cost forecasting.
Marge: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of their costs. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s position within the supply chain.
Several factors influence the pricing of tire inflators, particularly for international B2B buyers.
Volumen/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for minimum order quantities (MOQ), making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs against potential savings.
Spezifikationen und Anpassungen: Tailoring inflators to meet specific market needs or branding requirements can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against its impact on pricing.
Materialien und Qualitätszertifikate: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO standards) can enhance reliability but also increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these factors align with their operational needs and customer expectations.
Lieferanten-Faktoren: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven quality and service, while emerging suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market entry.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can help in negotiating better terms and avoiding unexpected costs.
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant savings.
Verstehen der Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO): When evaluating suppliers, consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, repairs, and potential downtime.
Beziehungen nutzen: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms and pricing. Engage with suppliers regularly to understand their challenges and capabilities.
Be Informed: Research market prices and trends to empower your negotiations. Knowledge of competitive pricing can help in securing better deals.
Flexibility: Being open to alternative products or specifications can lead to better pricing. Suppliers may be willing to negotiate on items that do not affect your core requirements.
Timing: Consider timing your purchases to coincide with off-peak seasons when suppliers may be more willing to negotiate on price.
By understanding the cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can navigate the tire inflator market more effectively, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their business objectives.

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
When faced with the challenge of flat or under-inflated tires, a portable tire inflator is a popular choice for many drivers. However, various alternatives exist that can also effectively address tire inflation needs. This analysis will compare the use of a tire inflator against two viable alternatives: a tire sealant kit and a traditional air compressor. Each solution presents unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential for B2B buyers to evaluate which method best meets their operational requirements.
| Vergleich Aspekt | How To Use Tire Inflator | Tire Sealant Kit | Traditional Air Compressor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | Quick inflation for minor punctures. | Seals small punctures but limited to certain sizes. | High-volume air delivery for rapid inflation. |
| Kosten | Typically ranges from $30 to $200. | Usually priced around $20 to $50. | Prices can vary widely; basic models start at $50. |
| Leichte Implementierung | Simple plug-and-play operation. | Requires minimal setup, but some knowledge needed. | More complex setup; may require additional equipment. |
| Wartung | Minimal; generally requires occasional checks. | Single-use; disposal needed after use. | Regular maintenance required for longevity. |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Ideal for emergency roadside assistance. | Suitable for temporary fixes on small punctures. | Best for regular use in workshops or garages. |
A tire sealant kit is designed to provide a quick and temporary solution for small tire punctures. It works by injecting a sealant into the tire, which fills the puncture as the tire rotates. The primary advantage of this method is its simplicity and speed, allowing drivers to quickly get back on the road without the need for a full tire replacement. However, tire sealants are limited in their effectiveness; they can only seal punctures of a certain size and are not suitable for sidewall damage. Furthermore, this solution is generally considered a temporary fix, necessitating a trip to a tire service provider for permanent repairs.
A traditional air compressor offers a more robust solution for tire inflation, especially in a workshop or garage setting. Unlike portable inflators, air compressors can deliver high volumes of air quickly, making them suitable for larger tires and multiple vehicles. They can also be used for various applications beyond tire inflation, such as powering pneumatic tools. However, traditional compressors can be bulkier and require more setup, including a power source and possibly additional hoses or fittings. Regular maintenance is also needed to ensure optimal performance, making them less practical for occasional use compared to portable inflators.
Selecting the right tire inflation method ultimately depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the buyer. For businesses focused on efficiency and rapid response, a portable tire inflator may be the best option due to its ease of use and compact design. Alternatively, for those seeking a more versatile and powerful solution, a traditional air compressor may be more appropriate, particularly in workshop settings. Meanwhile, tire sealant kits serve as a valuable tool for quick, temporary fixes but should be complemented with more permanent solutions for long-term tire health. By weighing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints.
Understanding the technical specifications of tire inflators is essential for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some critical specifications to consider:

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Power Source Type
– Definition: Tire inflators can be powered by a 12-volt outlet (car battery) or come with a built-in rechargeable battery.
– Bedeutung: Knowing the power source is crucial for compatibility with vehicles and equipment. In regions with frequent power outages, battery-powered models may be more reliable.
Maximum Pressure Capacity
– Definition: This indicates the highest pressure the inflator can achieve, usually measured in PSI (pounds per square inch).
– Bedeutung: Different vehicles and applications require varying tire pressures. Buyers must ensure the inflator can accommodate the pressures needed for their specific use cases, especially for heavy-duty vehicles.
Aufblasgeschwindigkeit
– Definition: The time it takes for the inflator to fully inflate a tire, typically expressed in minutes.
– Bedeutung: Time efficiency is critical in B2B operations, particularly in logistics and transportation. A faster inflator minimizes downtime, making it an attractive feature for businesses.
Schlauchlänge
– Definition: The length of the air hose that connects the inflator to the tire valve.
– Bedeutung: A longer hose provides more flexibility and ease of use, especially in tight spaces or for larger vehicles. This is particularly relevant for companies managing a fleet of vehicles with varying tire placements.
Digital Display
– Definition: Many modern tire inflators come with a digital pressure gauge.
– Bedeutung: A digital display offers precise pressure readings, reducing the risk of over-inflation or under-inflation. This feature is vital for maintaining vehicle safety and tire longevity.
Sicherheitsmerkmale
– Definition: Includes automatic shut-off mechanisms and thermal protection to prevent overheating.
– Bedeutung: Safety features are essential for preventing accidents and equipment failure, which can lead to costly downtime. B2B buyers should prioritize inflators that incorporate these features for safer operations.
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: Ein Unternehmen, das Teile und Geräte herstellt, die von einem anderen Hersteller vermarktet werden können.
– Bedeutung: Understanding whether a tire inflator is OEM or aftermarket can influence quality and warranty considerations, affecting long-term operational costs.
MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Bedeutung: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to stock up on tire inflators for resale or fleet maintenance.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for a specific quantity of goods.
– Bedeutung: RFQs help buyers compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal for their needs.
Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Bedeutung: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, especially when importing tire inflators from different regions.
Gewährleistungsfrist
– Definition: The time frame during which the manufacturer guarantees the product will function as expected.
– Bedeutung: A robust warranty period can indicate product quality and reliability, reducing long-term maintenance costs for businesses.
Vorlaufzeit
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Bedeutung: Understanding lead times is crucial for planning inventory and ensuring that tire inflators are available when needed, especially in high-demand seasons.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability in tire maintenance.
The global tire inflator market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing vehicle ownership and the necessity for efficient tire maintenance. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for portable tire inflators is surging, as they offer practical solutions for roadside emergencies and regular vehicle upkeep. Technological advancements are shaping this market, with features like digital pressure gauges, automatic shut-off functions, and multi-purpose capabilities making inflators more user-friendly and efficient.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards smart inflators that integrate with mobile applications, allowing users to monitor tire pressure in real-time and receive alerts for maintenance. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms has transformed sourcing strategies for B2B buyers, enabling them to access a wider range of products at competitive prices. As international markets evolve, buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide reliable products with strong after-sales support, reflecting a growing emphasis on customer service and brand loyalty.

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
Sustainability is becoming a focal point for B2B buyers in the tire inflator sector, as companies increasingly recognize the environmental impact of their supply chains. The production of tire inflators often involves materials and processes that can contribute to pollution and waste. Therefore, buyers are seeking out suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing carbon footprints during manufacturing.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers keen to partner with manufacturers who adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade labels can enhance a brand’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. For B2B buyers in emerging markets, aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can also open doors to new customer segments and foster long-term relationships built on shared values.
The evolution of tire inflators has been marked by a transition from manual pumps to sophisticated electronic devices. Historically, tire maintenance relied on hand pumps and basic tools, which often required significant physical effort and time. As vehicle technology advanced, so did the need for more efficient solutions, leading to the introduction of electric and battery-powered inflators in the late 20th century.
Today, tire inflators are equipped with smart technology, allowing for precise pressure monitoring and ease of use. The integration of digital displays and automated features not only enhances user experience but also contributes to safer driving practices by ensuring optimal tire pressure. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial, as it highlights the importance of investing in modern, reliable inflators that meet the demands of contemporary vehicle maintenance.

Illustrative image related to how to use tire inflator
How do I solve a tire inflator that won’t power on?
To troubleshoot a tire inflator that won’t power on, start by checking the power source. Ensure the inflator is properly connected to a functional 12-volt outlet or that its internal battery is charged if it’s a battery-operated model. Inspect the power cable for any visible damage or loose connections. If the inflator is still unresponsive, consult the user manual for specific troubleshooting steps or consider contacting the manufacturer for support.
What is the best tire inflator for commercial vehicles?
For commercial vehicles, look for a tire inflator that offers high PSI capabilities, durability, and fast inflation times. Models with a pressure range of at least 150 PSI are ideal, as they can accommodate larger tires. Additionally, features such as a long air hose, multiple nozzle attachments, and an automatic shut-off function enhance usability. Brands known for their reliability in commercial applications include DEWALT and Viair, which provide robust options suitable for frequent use.
How can I ensure the tire inflator I source meets quality standards?
To ensure the tire inflator meets quality standards, verify that it complies with international safety and performance certifications, such as CE, ISO, or UL. Request product samples and conduct thorough testing before committing to a bulk order. Additionally, engage with suppliers who provide transparent documentation regarding their quality assurance processes and any relevant certifications. Regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can also help maintain quality control.
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for tire inflators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for tire inflators vary by supplier and can range from as low as 50 units to several hundred. To negotiate favorable terms, consider discussing your specific needs with potential suppliers, including volume discounts and potential for future orders. Some manufacturers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time buyers or long-term partnerships, so it’s beneficial to establish a good rapport with your supplier.
What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing tire inflators?
When negotiating payment terms for sourcing tire inflators, aim for conditions that balance risk and cash flow. Common terms include a 30% deposit upfront with the remaining 70% due upon delivery. You might also consider options like letter of credit or escrow services for larger transactions. Ensure the payment terms are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings and protect both parties.
How do I customize tire inflators for my brand?
To customize tire inflators for your brand, communicate your specific requirements to the supplier, including branding elements such as logos, colors, and packaging. Many manufacturers offer OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) services that allow for branding and design modifications. Be prepared to provide design files and discuss production timelines, as customizations may affect lead times and costs.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing tire inflators?
When importing tire inflators, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, costs, and delivery timelines. Evaluate whether to use air or sea freight based on urgency and budget. Be aware of customs regulations and duties applicable in your region, which can affect total landed costs. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the import process and help navigate any potential challenges.
How often should I check the tire inflators’ performance and reliability?
Regularly checking the performance and reliability of tire inflators is crucial, especially for businesses that rely on them for fleet maintenance. Conduct performance evaluations every three to six months, focusing on functionality, inflation speed, and accuracy of pressure readings. Additionally, inspect for any wear and tear or damage that could affect performance. Keeping a maintenance log can help track usage patterns and identify when replacements are necessary.
Bereich: reddit.de
Registriert: 2005 (20 Jahre)
Einleitung: Automatic air station for vehicle tires, typically found at locations like Wawa or Sheetz. Features include: setting tire pressure using up and down arrows (default is usually 32 PSI), nozzle attachment to tire valve, air pumping mechanism that checks tire pressure multiple times during the process, and an audible beep when the inflation is complete.
Bereich: lincoln.com
Registriert: 1997 (28 Jahre)
Einleitung: The Tire Inflator and Sealant Kit is designed to temporarily fix flat tires, allowing you to reach a Lincoln Retailer for service. It is an alternative to a spare tire and provides a temporary repair. The kit is equipped with sealant sufficient for one tire repair only. It is important to check the Owner’s Manual for speed and distance limitations after using the kit. The kit may be located in the…
Bereich: macheforum.com
Registriert: 2018 (7 Jahre)
Einleitung: 1) Remove the tire inflator and sealant from the plastic bag and read the instructions on pages 329-330 of the manual. 2) Perform a dry run of plugging it in, hooking it to the tire, checking the tire pressure with it off, and turning it on if necessary. Ensure the dial is set to ‘air only’. 3) Only use the sealant setting if critical and necessary, as sealant can gum up the tire and make it impos…
Bereich: wikihow.com
Registriert: 2004 (21 Jahre)
Einleitung: This company, WikiHow – Tire Inflation Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Bereich: kiaofmyrtlebeach.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Einleitung: Kia’s Tire Inflator Kit is a compact and convenient solution for inflating flat or low-pressure tires. It includes a small air compressor that plugs into the car’s 12-volt power outlet, a tire pressure gauge, and a sealant solution. The kit is designed to provide an easy-to-use alternative to traditional spare tires and is included with many Kia vehicles as standard equipment. To use the kit, the …
In conclusion, understanding how to effectively use tire inflators is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By strategically sourcing reliable tire inflators, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and provide essential support to their customers, minimizing downtime caused by flat tires. Key takeaways include the importance of choosing the right type of inflator—whether 12-volt or battery-powered—and ensuring that safety precautions are observed to avoid potential hazards.
Investing in high-quality tire inflators not only saves costs related to roadside assistance but also equips your teams with the tools needed for immediate tire repairs. By fostering relationships with reputable suppliers, businesses can ensure access to durable and efficient inflators tailored to various vehicle types and conditions.
As we look ahead, we encourage B2B buyers to explore partnerships that prioritize quality and reliability in tire maintenance solutions. The demand for portable tire inflators is only set to grow, and being proactive in sourcing these products will position your business as a leader in customer service and operational excellence. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your fleet management and customer satisfaction today.
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Kaufberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für etwaige Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensangaben und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due-Diligence-Prüfung durchführen bevor Sie eine Kaufentscheidung treffen. Dazu gehört, dass Sie sich direkt mit den Anbietern in Verbindung setzen, Zertifizierungen überprüfen, Muster anfordern und sich professionell beraten lassen. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt allein der Leser.