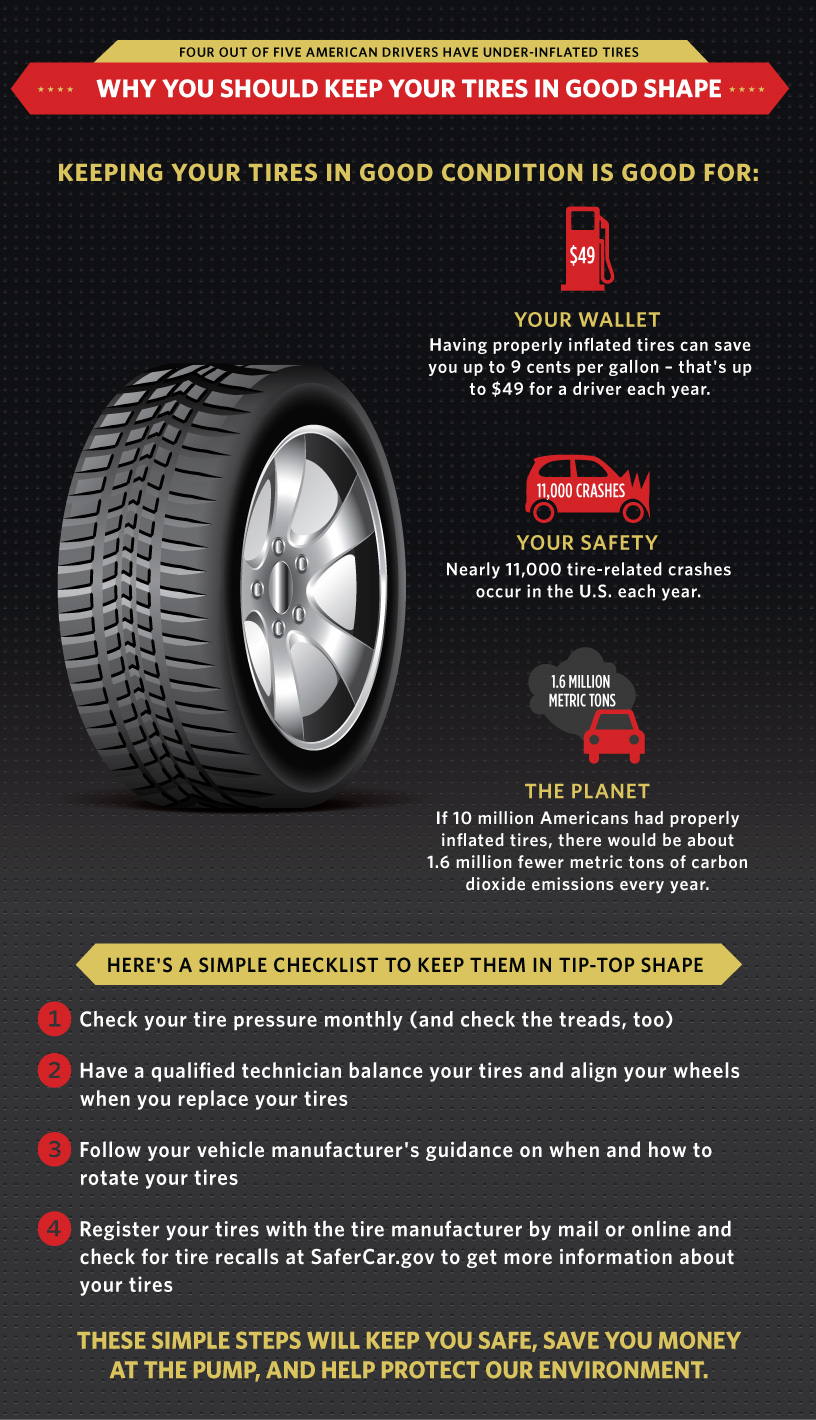
Navigating the global market for tires poses unique challenges, particularly when considering the critical safety implications of overinflated and underinflated tires. As B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these risks is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Tires that are improperly inflated can lead to significant issues, including increased wear and tear, compromised vehicle control, and heightened safety hazards that can result in costly accidents and liability concerns.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of tires available, their specific applications across different industries, and the importance of supplier vetting to ensure quality and compliance with international safety standards. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations, helping buyers assess the long-term value of their investments. By equipping stakeholders with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of tire procurement effectively.
In a market where safety and efficiency are paramount, understanding the nuances of tire inflation is not merely an operational concern; it is a strategic imperative. The knowledge gained from this guide will enable businesses to optimize their fleet performance, reduce operational costs, and enhance overall safety—factors that are critical to maintaining a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace.
| Typ Name | Wichtigste Unterscheidungsmerkmale | Primäre B2B-Anwendungen | Kurze Vor- und Nachteile für Käufer |
|---|---|---|---|
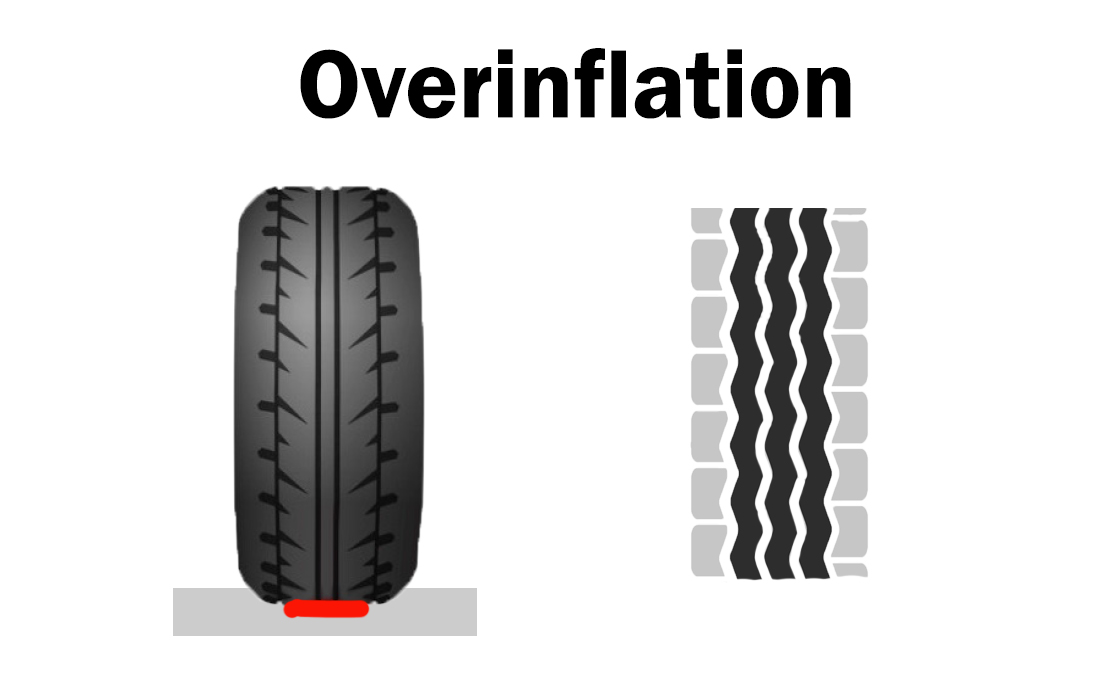
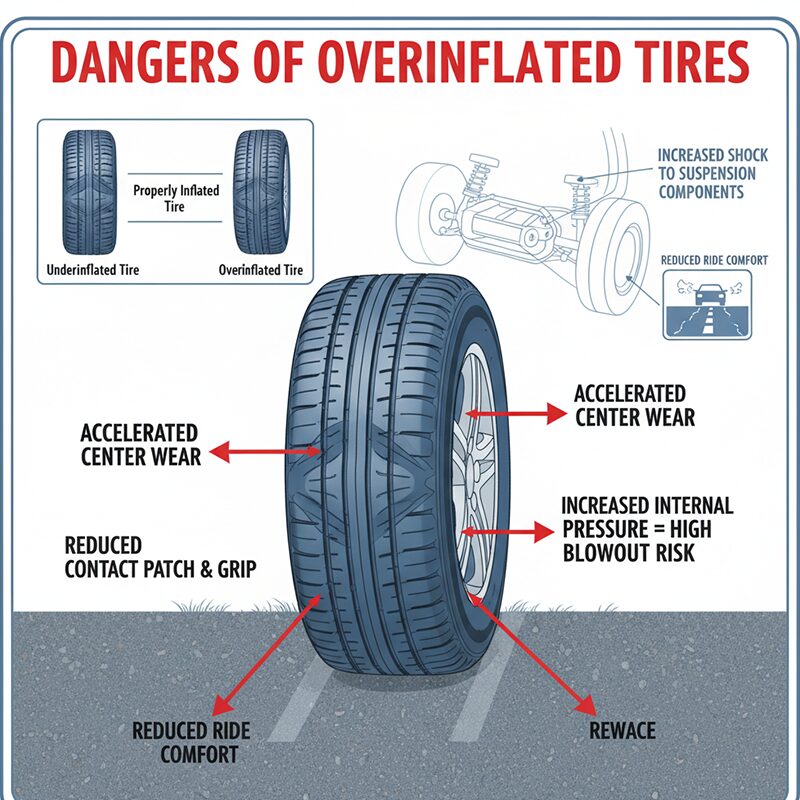
| Overinflated Tires | Increased air pressure leading to reduced contact area | Logistics, Transportation Services | Vorteile: Enhanced fuel efficiency; Nachteile: Higher risk of blowouts, uneven wear, and compromised handling. |
| Underinflated Tires | Decreased air pressure causing excessive flexing | Fleet Management, Delivery Services | Vorteile: Lower initial costs; Nachteile: Increased tire wear, poor fuel efficiency, and reduced control. |
| All-Season Tires | Versatile design suitable for varied conditions | General Fleet Operations | Vorteile: Year-round usability; Nachteile: Compromised performance in extreme conditions. |
| Performance Tires | Designed for high-speed stability and handling | Sports Car Rentals, Performance Fleets | Vorteile: Superior handling and traction; Nachteile: Increased wear and higher costs. |
| Off-Road Tires | Robust tread patterns designed for rugged terrains | Construction, Agriculture Equipment | Vorteile: Exceptional grip in rough conditions; Nachteile: Poor performance on paved roads and higher noise levels. |
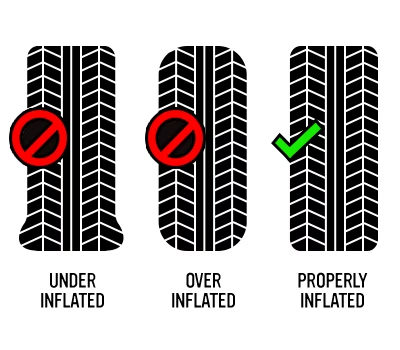
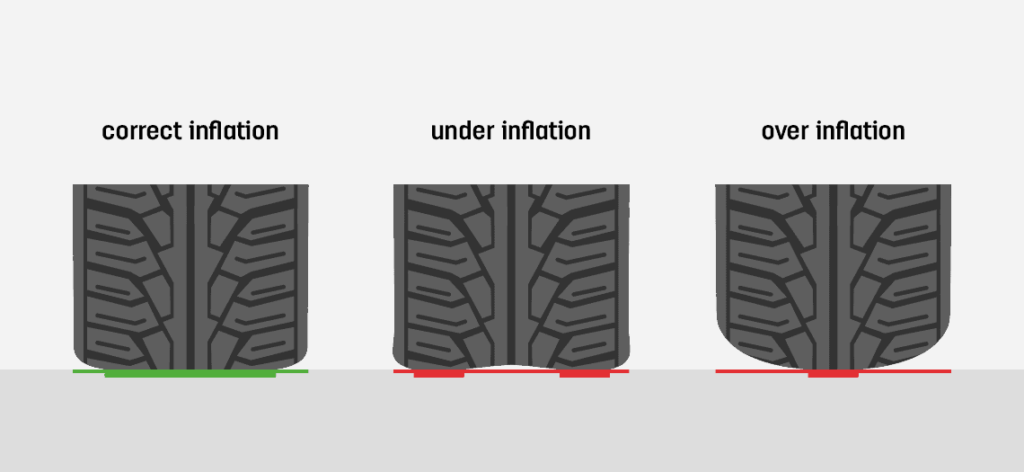
Overinflated tires are those filled beyond the manufacturer’s recommended pressure, resulting in a smaller contact patch with the road. This can lead to diminished traction and increased risk of blowouts, particularly in commercial fleets operating in diverse terrains. For businesses, the implications can be severe, including increased maintenance costs and potential liability issues from accidents. B2B buyers should prioritize regular tire pressure checks and invest in monitoring systems to mitigate these risks.
Underinflated tires contain less air than recommended, causing them to flex excessively and wear unevenly. This can lead to compromised vehicle control, increased fuel consumption, and a higher frequency of tire replacements. For organizations with large vehicle fleets, such inefficiencies can translate into significant operational costs. Buyers should consider investing in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) to ensure optimal inflation levels and enhance overall vehicle safety.
All-season tires are engineered to perform adequately in various weather conditions, making them a practical choice for general fleet operations. Their design allows for reasonable performance in rain and light snow, which is advantageous for businesses that operate year-round. However, while they offer versatility, they may not perform as well in extreme weather conditions compared to specialized tires. B2B buyers should assess their operational environments to determine the suitability of all-season tires for their fleets.
Performance tires are crafted for superior handling and stability, ideal for high-speed applications and performance-oriented vehicles. They provide excellent grip, which can enhance safety and responsiveness during critical driving conditions. However, these tires tend to wear out more quickly and can be more expensive. Businesses in sectors like sports car rentals or performance vehicle fleets should weigh the benefits of enhanced performance against the potential for increased operating costs.
Off-road tires are specifically designed to navigate rugged terrains, making them indispensable for industries such as construction and agriculture. Their aggressive tread patterns provide exceptional traction on loose surfaces, ensuring that vehicles maintain mobility in challenging conditions. However, these tires can be less effective on paved roads and may produce higher noise levels. B2B buyers should consider the specific operational needs of their equipment when selecting off-road tires to ensure optimal performance and safety.

Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
| Industrie/Sektor | Specific Application of tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated. | Wert/Nutzen für das Unternehmen | Wichtige Überlegungen zur Beschaffung für diese Anwendung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport und Logistik | Fleet management relies on tire performance for safety and efficiency. | Improved safety, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced fuel efficiency. | Supplier reliability, adherence to safety standards, and local support services. |
| Landwirtschaft | Agricultural machinery requires optimal tire performance for heavy loads. | Increased operational efficiency and reduced risk of accidents. | Durability, load capacity, and compatibility with local terrain. |
| Bauwesen | Heavy construction vehicles need properly inflated tires for safety and stability. | Enhanced safety, reduced downtime, and lower operational costs. | Tire specifications for load ratings and local environmental conditions. |
| Mining | Mining operations depend on tire integrity to handle rough terrains and heavy loads. | Minimizing operational disruptions and enhancing worker safety. | Availability of specialized tires for extreme conditions and local service options. |
| Automotive Retail | Tire retailers must educate customers on the dangers of improper tire inflation. | Increased customer safety and loyalty through informed purchasing decisions. | Training for staff on tire safety, and sourcing high-quality, reliable products. |
In the transportation and logistics sector, fleet management is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Proper tire inflation directly impacts vehicle performance, affecting braking distance, fuel efficiency, and handling. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local road conditions and the specific tire requirements for different vehicles is essential. Regular tire pressure checks can significantly reduce maintenance costs and enhance safety, making it a top priority for fleet operators.
In agriculture, machinery such as tractors and harvesters relies heavily on tire performance to manage heavy loads across various terrains. Over-inflated or under-inflated tires can lead to poor traction and increased wear, which can disrupt operations and compromise safety. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing durable tires that can withstand local soil conditions and load capacities. Regular monitoring of tire pressure can enhance operational efficiency and minimize the risk of accidents.
The construction industry faces unique challenges regarding tire safety due to the weight and size of heavy equipment. Proper tire inflation ensures stability and safety on uneven surfaces, reducing the likelihood of accidents and operational downtime. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing tires that meet specific load ratings and can endure the harsh conditions typical of construction sites. Understanding the local environment is critical to selecting the right tire specifications.
In mining operations, the integrity of tires is paramount due to the extreme conditions and heavy loads involved. Over-inflated or under-inflated tires can lead to blowouts or loss of control, posing significant safety risks. Buyers in the mining industry must consider sourcing specialized tires designed for rugged terrains and high-stress environments. Regular maintenance and pressure checks are essential to minimize operational disruptions and ensure worker safety.
Tire retailers play a vital role in educating consumers about the hazards of improper tire inflation. By informing customers about the risks associated with over-inflated and under-inflated tires, retailers can enhance customer safety and foster loyalty. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on training staff on tire safety protocols and sourcing high-quality products that meet safety standards. This proactive approach can lead to informed purchasing decisions and ultimately contribute to safer driving experiences for consumers.
Das Problem: A fleet manager oversees multiple vehicles and faces the challenge of maintaining cost-effectiveness while ensuring safety. They notice that some tires are wearing unevenly, leading to more frequent replacements and increased maintenance costs. This uneven wear is often a result of improper tire inflation, which not only shortens tire life but also impacts vehicle performance and safety. The financial implications are significant, especially for businesses that rely on their vehicles for transportation and logistics.
Die Lösung: To combat uneven tire wear, fleet managers should implement a routine tire maintenance program that includes regular checks of tire pressure. Establish a standardized schedule for pressure checks, ideally bi-weekly or monthly, depending on usage. Utilize digital tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) that alert managers to any significant deviations in tire pressure. Additionally, provide training for drivers on the importance of maintaining proper tire inflation and recognizing signs of wear. This proactive approach can extend tire life, reduce costs, and improve overall vehicle safety, which is essential for operational efficiency.
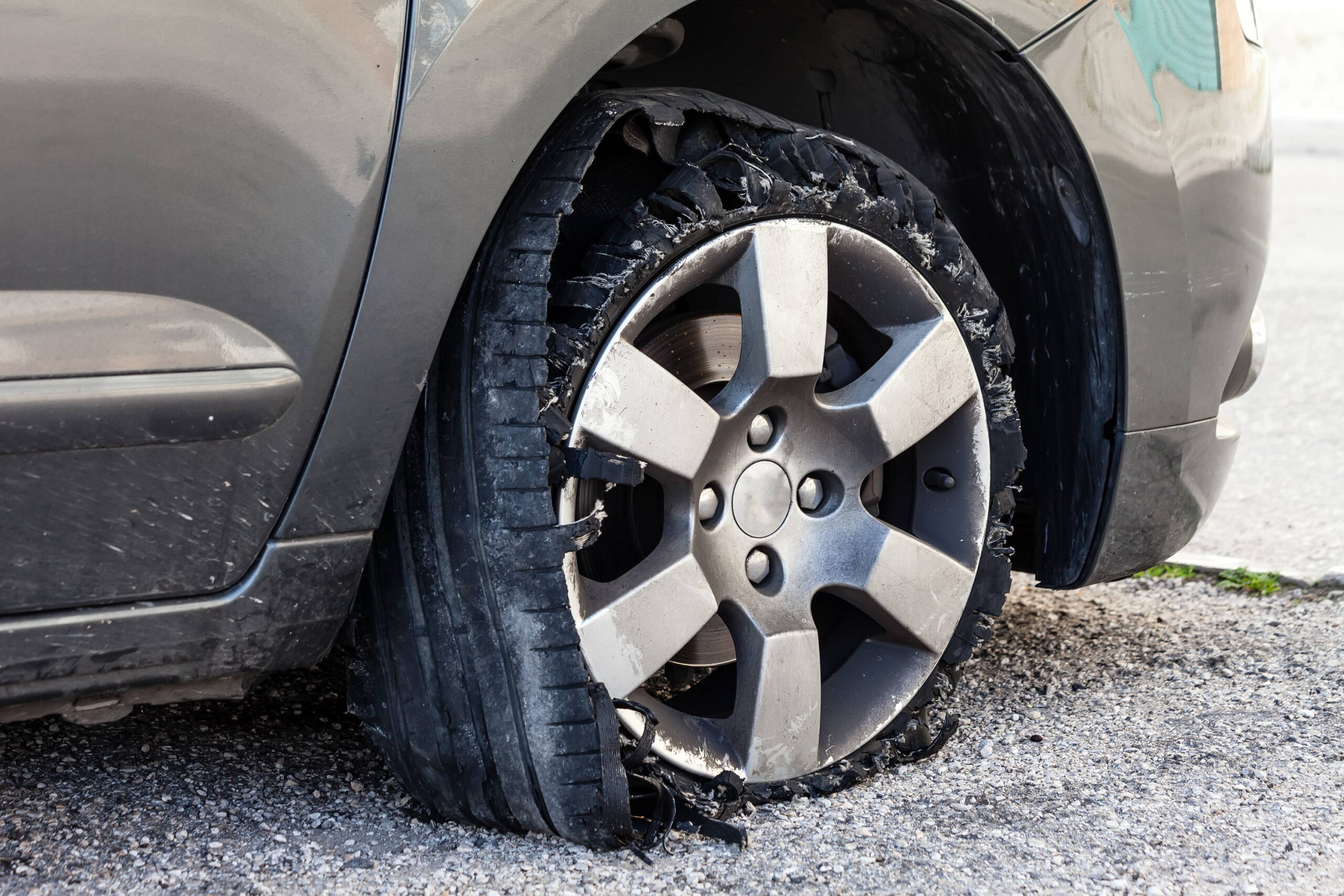
Das Problem: A logistics company operating in regions with poor road conditions is particularly vulnerable to tire blowouts caused by overinflation or underinflation. The risk of blowouts not only endangers the drivers but also leads to costly downtime and damaged goods. A single blowout can result in a significant delay, affecting delivery schedules and customer satisfaction, which can be detrimental to the company’s reputation.
Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
Die Lösung: To mitigate the risk of tire blowouts, companies should invest in high-quality, durable tires that are designed to withstand the specific conditions they operate in. Additionally, establish a comprehensive training program that educates drivers about proper inflation techniques and the dangers of both overinflation and underinflation. Implementing a regular inspection schedule, where tires are checked for proper inflation and any visible signs of damage, is crucial. Furthermore, consider integrating predictive maintenance technologies that analyze tire data and provide alerts before issues escalate, thereby enhancing safety and operational reliability.
Das Problem: A transportation company is experiencing rising fuel costs, which eat into their profit margins. Upon investigation, they discover that many of their vehicles are equipped with underinflated tires, causing increased rolling resistance. This not only leads to higher fuel consumption but also contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the fleet, which is a growing concern for many businesses aiming for sustainability.
Die Lösung: To improve fuel efficiency, transportation companies should prioritize tire maintenance by implementing a tire inflation management system. This system can automate the monitoring of tire pressure and provide real-time data to fleet managers. In addition, educating drivers on the correlation between tire pressure and fuel consumption can foster a culture of accountability. Encouraging drivers to conduct pre-trip inspections that include checking tire pressure can make a significant difference. Moreover, consider adopting fuel-efficient tire models that are specifically designed to minimize rolling resistance, ultimately leading to reduced fuel costs and a more sustainable operation.
By addressing these common pain points with practical solutions, B2B buyers can enhance safety, reduce costs, and improve overall operational efficiency when dealing with tires that can be hazardous if improperly inflated.
When addressing the hazards associated with over-inflated or under-inflated tires, it’s crucial to understand the materials used in tire manufacturing. The choice of materials can significantly influence tire performance, safety, and longevity. Below, we analyze four common materials used in tire production, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
Rubber compounds are the backbone of tire manufacturing, offering flexibility and resilience. They are designed to withstand varying temperatures and pressures, critical for maintaining tire integrity under different driving conditions.
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Rubber compounds have excellent elasticity, enabling them to absorb shocks and provide traction. They can be formulated to meet specific temperature and pressure ratings, ensuring performance in extreme conditions.
Pro und Kontra: The durability of rubber compounds is a significant advantage, but they can degrade over time due to environmental factors like UV exposure. While rubber is generally cost-effective, high-performance compounds can be more expensive and complex to manufacture.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: The choice of rubber compound directly affects a tire’s grip and handling characteristics, particularly in wet conditions. This is vital for safety, especially in regions prone to heavy rainfall.
Internationale Erwägungen: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that rubber compounds comply with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, to guarantee safety and performance.
Steel belts are often incorporated into tires to enhance strength and reduce the risk of punctures. They provide additional support to the tire structure, improving stability during operation.
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Steel belts have high tensile strength and excellent resistance to deformation, making them ideal for high-performance tires that experience significant stress.
Pro und Kontra: The inclusion of steel belts significantly improves tire durability and performance. However, they can increase the overall weight of the tire, potentially affecting fuel efficiency.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: Steel belts contribute to better handling and control, particularly at higher speeds. This is crucial for commercial vehicles operating in demanding environments.
Internationale Erwägungen: Compliance with international standards for steel quality is essential, especially in regions like Europe, where regulations may be stricter.
Fabric reinforcements, such as polyester or nylon, are used in tire construction to provide flexibility and reduce weight. These materials help in maintaining the tire’s shape while allowing for some degree of flex.
Wichtige Eigenschaften: Fabrics are lightweight and can be engineered to provide varying levels of strength and flexibility, which is essential for performance in diverse conditions.
Pro und Kontra: Fabric reinforcements enhance ride comfort and reduce rolling resistance, improving fuel efficiency. However, they may not offer the same level of puncture resistance as steel belts.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: The choice of fabric can influence tire performance, particularly in terms of comfort and handling. This is especially important for passenger vehicles.
Internationale Erwägungen: Buyers should consider the availability and quality of fabric materials in their region, as well as any applicable safety standards.
Additives and fillers are used to enhance the properties of rubber compounds, improving performance characteristics such as wear resistance and heat dissipation.
Wichtige Eigenschaften: These materials can be tailored to achieve specific performance metrics, including temperature stability and abrasion resistance.

Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
Pro und Kontra: While additives can significantly enhance tire performance, they may increase production costs and complexity. The selection of the right additives is critical to achieving the desired balance between performance and cost.
Auswirkungen auf die Anwendung: The right combination of additives can improve tire longevity and safety, particularly in harsh operating conditions.
Internationale Erwägungen: Buyers must be aware of local regulations regarding chemical additives in tire manufacturing, especially in markets with stringent environmental standards.
| Material | Typical Use Case for tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated. | Hauptvorteil | Wesentlicher Nachteil/Beschränkung | Relative Kosten (niedrig/mittel/hoch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Compounds | Main material for tire construction, ensuring flexibility and traction. | Excellent durability and elasticity. | Degrades over time due to UV exposure. | Mittel |
| Steel Belts | Provides structural integrity and puncture resistance in tires. | Enhances strength and stability. | Increases tire weight, affecting efficiency. | Hoch |
| Fabric Reinforcements | Used to balance weight and flexibility in tire construction. | Improves ride comfort and reduces rolling resistance. | Lower puncture resistance compared to steel. | Mittel |
| Additives and Fillers | Enhances rubber properties for improved performance and longevity. | Optimizes performance characteristics. | Increases production complexity and cost. | Mittel bis Hoch |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a vital resource for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions regarding tire materials that mitigate hazards associated with improper inflation.
The tire manufacturing process is a complex series of steps that require precision and quality control to ensure safety and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the reliability of potential suppliers.
The first stage involves the preparation of raw materials, which typically includes natural and synthetic rubber, carbon black, fabric (like polyester, nylon, or steel), and various chemicals. These materials are carefully sourced and tested for quality, as they play a critical role in tire performance. The quality of the rubber, for instance, affects the tire’s durability and traction.
In the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into tire components. This includes the tread, sidewalls, and inner linings. The process often employs advanced machinery for mixing and extruding rubber into specific shapes. Precision is vital here, as any inconsistencies can lead to performance issues, such as uneven wear or susceptibility to blowouts.
Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
Once the components are formed, they are assembled into a complete tire. This stage involves layering the components in a specific order, followed by molding. The assembly must be executed under strict quality control to ensure that the tires meet performance specifications. Any defects at this stage can compromise the tire’s integrity.
The finishing stage includes curing the tires in a heated mold, which solidifies their shape and enhances their strength. After curing, tires undergo a visual inspection and may be subjected to additional tests. This ensures that they meet both manufacturer and international safety standards.
Quality assurance is critical in the tire manufacturing process, as it directly impacts safety and performance. B2B buyers must be familiar with various international and industry-specific standards.

Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has a systematic approach to managing quality, which is essential for producing safe and reliable tires.
In addition to ISO standards, certain products may require compliance with regional regulations, such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
In the tire industry, specific certifications such as the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards are also relevant. These standards focus on materials and products used in tire manufacturing, ensuring they meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the tire manufacturing process, with several checkpoints established to ensure that standards are met.
Eingehende Qualitätskontrolle (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival. This ensures that only high-quality materials proceed to the manufacturing stages.
Prozessbegleitende Qualitätskontrolle (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks are performed to monitor the process and ensure that components are being produced to specifications. This includes monitoring material properties and dimensions.
Endgültige Qualitätskontrolle (FQC): After tires are fully assembled and cured, they undergo a final inspection. This includes visual checks and performance tests to ensure they meet all safety standards.
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of tires at different stages of production.
Establishing a reliable supply chain is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in markets with varying regulations and standards.
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a manufacturer’s quality control processes. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not be able to visit suppliers in person.

Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of QC and certification can be complex, particularly in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Different regions may have specific regulations regarding tire manufacturing and safety standards. For example, the European Union has stringent requirements for tire labeling and performance, while regulations in the Middle East may differ significantly. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with the relevant regulations in their target markets.
The implications of over-inflated or under-inflated tires extend far beyond performance; they directly impact safety on the road. By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting tire suppliers, ensuring they provide products that meet safety and performance standards. Investing in quality assurance not only protects your business but also enhances customer satisfaction and safety.
This practical sourcing guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with essential steps to ensure they procure tires safely and efficiently, considering the hazards associated with both over-inflation and under-inflation. Proper tire management is vital for vehicle performance, safety, and cost efficiency.
Begin by defining the specifications required for your operations. Consider the vehicle types, load capacities, and the terrain where the tires will be used. This step is crucial as different tires are engineered for specific purposes, and selecting the wrong type can lead to performance issues and safety hazards.
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet industry standards and regulations. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 and other relevant quality assurance measures. This is critical because reputable suppliers are more likely to provide high-quality products that adhere to safety norms.
Assess the quality of the tires you plan to procure. Check for performance metrics, including tread wear ratings and fuel efficiency. Quality tires reduce the risk of hazards related to improper inflation, such as blowouts and uneven wear, ultimately leading to lower operational costs.
Create a comprehensive maintenance plan that includes regular inspections and inflation checks. This step is essential to prolong tire life and ensure safety. Regular maintenance minimizes the risk of accidents caused by improper tire pressure.
Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms and pricing. Understand the total cost of ownership, including potential discounts for bulk purchases and warranty options. This is important to ensure you are getting the best value for your investment.
Develop a tracking system to monitor tire performance over time. This helps identify any recurring issues related to inflation and wear patterns, allowing for timely interventions. Implementing this system is vital to maintaining optimal vehicle safety and performance.
Conduct training sessions for your team focusing on the importance of proper tire inflation and the risks associated with neglecting tire maintenance. This step enhances safety awareness and promotes a culture of proactive maintenance within your organization.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of tire procurement, ensuring they prioritize safety and efficiency in their operations.

Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
When analyzing the cost structure of tires, particularly in the context of the hazards associated with over-inflation and under-inflation, several cost components come into play:
Materialien: The quality of rubber, steel belts, and other materials significantly affects the tire’s performance and safety. Premium materials may raise upfront costs but can reduce the risk of blowouts and extend tire lifespan, ultimately saving costs over time.
Arbeit: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing and quality control. Skilled labor may demand higher wages but can lead to better craftsmanship and adherence to safety standards.
Fertigungsgemeinkosten: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient production processes can lower these expenses, contributing to a more competitive pricing structure.
Werkzeugbau: The initial investment in specialized molds and machinery can be substantial. However, effective tooling design can enhance production efficiency and product quality, ensuring that tires meet safety regulations.
Qualitätskontrolle (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is essential, especially for tires, as they directly impact vehicle safety. While these measures may increase costs, they mitigate risks associated with defective products.
Logistik: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on geographic location and distribution methods. Efficient logistics strategies can minimize expenses and ensure timely delivery, which is crucial for maintaining supply chain integrity.
Marge: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the cost structure allows buyers to negotiate better margins without compromising on quality.
Several factors influence pricing dynamics in the tire market:
Volumen/MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge): Bulk purchasing often leads to price reductions. Buyers can negotiate better deals by consolidating orders, which is especially beneficial for businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where logistics can be more complex.
Spezifikationen und Anpassungen: Customized tires tailored to specific vehicle types or conditions (e.g., off-road vs. highway) can significantly impact pricing. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to ensure they receive appropriate quotes.
Materialien und Qualitätszertifikate: Tires that meet international safety standards and certifications (such as ISO or DOT) typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the cost against the potential risks of purchasing lower-quality options.
Lieferanten-Faktoren: Supplier reputation, reliability, and financial stability can influence pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers can lead to more favorable terms and consistent quality.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international buyers. They define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total landed cost of the tires.
International B2B buyers should consider several strategies to enhance their sourcing efficiency:
Negotiation Skills: Strong negotiation capabilities can lead to better pricing and terms. Buyers should be prepared to discuss volume discounts and payment terms to maximize cost efficiency.
Gesamtbetriebskosten (TCO): Buyers must evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with tire performance, maintenance, and safety. Investing in higher-quality tires may offer savings through reduced replacements and improved fuel efficiency.
Nuancen in der Preisgestaltung für internationale Käufer: Currency fluctuations, tariffs, and regional market conditions can affect pricing. Buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe should stay informed about economic trends to make strategic purchasing decisions.
Supplier Evaluation: Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Assess their quality control processes, certifications, and customer reviews to ensure they align with your safety and performance expectations.
Regular Market Research: The tire market is dynamic, with pricing influenced by raw material costs and technological advancements. Staying updated on industry trends can provide buyers with insights for timely purchasing decisions.
Pricing in the tire industry can vary widely based on numerous factors, including geographic location, market conditions, and specific tire specifications. The insights provided in this analysis are intended to guide B2B buyers in their sourcing decisions but should not be interpreted as definitive price quotations. Always conduct thorough market research and consult with suppliers for the most accurate pricing information.
When considering the hazards associated with improperly inflated tires, it’s essential to explore alternative solutions that can enhance safety and performance. This analysis compares traditional tire management against innovative technologies that address the risks of over-inflation and under-inflation.
| Vergleich Aspekt | Tires Can Be Hazardous If Over Inflated Or Under Inflated | Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) | Automatic Tire Inflation Systems (ATIS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leistung | High risk of blowouts, reduced traction, and uneven wear. | Provides real-time tire pressure data, enhancing safety. | Maintains optimal pressure automatically, improving performance. |
| Kosten | Low initial cost, but frequent replacements can add up. | Moderate initial investment; cost-effective over time. | Higher installation cost, but long-term savings on tire wear and fuel efficiency. |
| Leichte Implementierung | Requires regular manual checks; labor-intensive. | Easy to install, integrates with existing systems. | More complex installation; may require specialized equipment. |
| Wartung | Regular checks needed; often neglected. | Minimal maintenance; alerts for issues. | Low maintenance; system monitors itself. |
| Bester Anwendungsfall | Basic vehicle maintenance for cost-conscious operators. | Ideal for fleet management and safety-conscious businesses. | Best for high-usage vehicles needing consistent performance. |
TPMS is an advanced technology that continuously monitors tire pressure and alerts drivers of any deviations from the recommended levels. The primary advantage of TPMS is its ability to provide real-time data, which can significantly enhance safety by preventing issues before they escalate. However, the initial investment for TPMS can be moderate, and while it requires minimal maintenance, it still necessitates regular system checks to ensure functionality. This system is particularly beneficial for fleet operators who prioritize safety and need to monitor multiple vehicles effectively.
Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
ATIS represents a more sophisticated solution that automatically maintains tire pressure within optimal ranges, eliminating the risks associated with human error. The main benefit of ATIS is its ability to enhance vehicle performance and safety without the need for manual intervention. While the upfront installation costs are higher compared to traditional tire management methods, the long-term savings on tire wear and improved fuel efficiency can offset these costs. This system is ideal for high-usage vehicles, such as those in logistics or transportation sectors, where consistent tire performance is crucial.
For B2B buyers, the decision to invest in tire management solutions should be based on specific operational requirements and budget considerations. Traditional tire management may suffice for smaller operations with limited vehicle use, while technologies like TPMS and ATIS offer significant safety and performance enhancements for larger fleets. Evaluating the cost-benefit ratio, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements will help businesses select the most appropriate solution to ensure safety, reduce operational costs, and extend tire lifespan.
Understanding the technical properties of tires, particularly in the context of inflation, is crucial for B2B buyers. Improper tire inflation can lead to significant safety hazards, increased costs, and operational inefficiencies. Here are critical specifications that should be considered:
Tire Pressure Rating (PSI)
– Definition: Pounds per square inch (PSI) is the unit that measures the inflation pressure of a tire. Each tire has a specific recommended PSI, which can be found in the owner’s manual or on the vehicle’s placard.
– Bedeutung: Adhering to the recommended PSI ensures optimal performance, safety, and longevity of the tire. Over or under-inflated tires can lead to blowouts, uneven wear, and reduced fuel efficiency, affecting operational costs and vehicle safety.
Tread Depth
– Definition: This measures the depth of the grooves in the tire tread, usually expressed in millimeters. It is essential for water drainage and traction.
– Bedeutung: Insufficient tread depth can lead to hydroplaning and loss of control, especially in wet conditions. Regularly checking tread depth can prevent costly accidents and enhance safety, making it a vital consideration for fleet management.
Load Index
– Definition: The load index is a numerical code that indicates the maximum weight a tire can safely carry at its recommended inflation pressure.
– Bedeutung: Selecting tires with an appropriate load index is critical for ensuring that they can handle the weight of the vehicle and any additional load. Underestimating this can lead to tire failure and significant safety risks.
Sidewall Flexibility
– Definition: This property refers to how much the sidewall of the tire can flex under load. It affects how the tire absorbs shocks from road irregularities.
– Bedeutung: Tires with optimal sidewall flexibility can better absorb impacts, reducing the risk of damage and improving ride comfort. In regions with poor road conditions, this property becomes even more significant for fleet operations.
Temperature Resistance
– Definition: This property indicates the tire’s ability to withstand heat generated during operation. It is often classified by a temperature rating (A, B, C).
– Bedeutung: Tires that overheat can lead to blowouts, particularly in hot climates. Understanding temperature resistance helps in selecting suitable tires for specific geographical conditions, enhancing safety and performance.
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and decision-making for B2B buyers. Here are some essential terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: OEM refers to the company that originally manufactures the tires or vehicles.
– Bedeutung: Buying OEM tires ensures that the products meet the manufacturer’s specifications, which is crucial for maintaining safety and performance standards.
MOQ (Mindestbestellmenge)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Bedeutung: Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan inventory levels and negotiate better pricing, ensuring that tire supplies are adequate without overstocking.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price for specific quantities of goods.
– Bedeutung: Using RFQs allows businesses to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive procurement of tires and related services.
Incoterms (Internationale Handelsklauseln)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods.
– Bedeutung: Familiarity with Incoterms can prevent misunderstandings regarding shipping costs and responsibilities, crucial for international tire procurement and logistics.
UTQG (Uniform Tire Quality Grading)
– Definition: A system that grades tires based on treadwear, traction, and temperature resistance.
– Bedeutung: Understanding UTQG ratings helps buyers make informed decisions about tire performance and longevity, ensuring they select products that meet their operational needs.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance safety, reduce costs, and optimize tire performance in their operations.
The global tire market is experiencing significant dynamics driven by factors such as increasing vehicle ownership, rising safety concerns, and advancements in technology. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-performance tires that mitigate the risks associated with over-inflation and under-inflation is growing. International B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing tires that not only meet safety standards but also enhance vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Emerging trends include the adoption of smart tire technology that monitors tire pressure in real-time, providing alerts for optimal inflation levels. This innovation is crucial in regions with varying road conditions, such as potholes or uneven surfaces, where tire performance can be severely compromised. Additionally, there is a noticeable shift towards digital platforms for procurement, enabling B2B buyers to access a wider range of suppliers, compare prices, and evaluate product specifications more effectively. Sustainability is also becoming a key consideration, with buyers looking for suppliers who prioritize environmentally friendly practices in tire production and sourcing.
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the tire industry, particularly given the environmental impact of tire production and disposal. Over-inflated and under-inflated tires not only pose safety risks but also contribute to increased fuel consumption and emissions. B2B buyers are now more aware of the environmental footprint of their purchases and are seeking suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices.
The demand for “green” certifications and materials is on the rise. Many manufacturers are now focusing on using renewable resources, such as natural rubber and recycled materials, in tire production. Furthermore, ethical supply chains that ensure fair labor practices and transparency are gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to partner with manufacturers who adhere to international environmental standards, as this not only enhances their corporate responsibility profile but also meets the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
The tire industry has undergone significant evolution over the decades, particularly in response to safety concerns related to tire inflation. Historically, tire technology focused primarily on durability and cost-effectiveness, often neglecting the critical aspect of tire pressure management. However, as automotive safety standards have evolved, so too has the industry’s approach to tire design and performance.
In recent years, the introduction of tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) has revolutionized how drivers and fleet operators manage tire inflation. These systems alert users to pressure deviations, reducing the risks associated with both over-inflated and under-inflated tires. Furthermore, the integration of advanced materials and manufacturing processes has led to the development of tires that are not only safer but also more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly. This historical shift reflects the industry’s growing recognition of the importance of tire performance in overall vehicle safety and efficiency, paving the way for a more responsible approach to tire sourcing and usage in the B2B landscape.
1. How do I solve the problem of uneven tire wear due to improper inflation?
To address uneven tire wear caused by over-inflation or under-inflation, regularly check and maintain tire pressure according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Implement a systematic tire maintenance schedule that includes pressure checks, visual inspections for wear patterns, and rotations every 5,000 to 7,500 miles. Additionally, consider investing in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) that provide real-time data, helping to prevent issues before they escalate. By ensuring proper inflation, you can extend tire life and improve overall vehicle performance, ultimately reducing replacement costs.
2. What is the best tire pressure for optimal vehicle safety?
The optimal tire pressure for safety varies by vehicle and tire type, but it is typically indicated on a label found inside the driver’s door or in the vehicle owner’s manual. Generally, most passenger vehicles require tire pressures between 30 to 35 PSI. For commercial vehicles, refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines, as they may have specific recommendations based on load and usage. Regularly checking tire pressure, especially before long trips or after significant changes in temperature, ensures that you maintain safety and efficiency on the road.
3. How can I identify reliable tire suppliers for my business needs?
To identify reliable tire suppliers, consider their reputation in the industry, customer reviews, and years of experience. Request references and check for certifications like ISO or local quality standards that validate their manufacturing processes. Additionally, assess their ability to provide consistent quality and timely deliveries, especially if you operate in regions with specific tire regulations, like those in Africa or South America. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers who prioritize customer service and transparency will enhance your procurement process.
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for tire purchases?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for tire purchases can vary significantly based on the supplier and type of tires. Many manufacturers set MOQs to cover production costs, often ranging from 50 to 500 units. It’s essential to communicate your business needs and negotiate MOQs that align with your inventory strategy. Some suppliers may be flexible, especially for long-term partnerships or bulk orders, allowing you to optimize your inventory while managing cash flow effectively.
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing tires internationally?
Payment terms for international tire sourcing typically range from upfront payment to net 30 or net 60 terms, depending on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, or payment through trade finance solutions. It’s crucial to establish clear terms before finalizing orders, including currency exchange considerations and any applicable taxes or tariffs. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in your contracts to avoid misunderstandings.
6. How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my tire procurement process?
To ensure quality assurance in tire procurement, develop a comprehensive QA plan that includes supplier audits, product testing, and performance evaluations. Specify quality standards in your purchase agreements and request samples before large orders. Establish a feedback loop with your suppliers to discuss any quality issues promptly and ensure that corrective actions are taken. Consider collaborating with third-party inspection services, especially when importing tires, to validate that they meet safety and performance requirements.
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing tires?
When importing tires, logistics considerations include understanding shipping regulations, customs clearance processes, and potential tariffs or duties applicable in your region. Choose reliable freight forwarders familiar with tire transportation to navigate these complexities efficiently. Additionally, consider lead times for production and shipping, and plan your inventory levels accordingly to avoid stockouts. It’s also wise to have contingency plans for potential delays, especially in regions with less predictable logistics infrastructure.
8. How do I handle tire disposal responsibly after use?
Responsible tire disposal involves adhering to local regulations regarding recycling and waste management. Many regions have specific guidelines for tire disposal to minimize environmental impact. Consider partnering with tire recycling companies that can repurpose old tires into new products or energy. Educating your team on proper disposal methods and including recycling options in your procurement contracts can enhance your company’s sustainability efforts while complying with environmental standards.
Bereich: eastcoasttoyota.com
Registriert: 2000 (25 Jahre)
Einleitung: The article discusses the hidden risks associated with overinflated and underinflated tires, emphasizing the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure for vehicle performance and safety. Key points include: 1. Uneven tread wear caused by incorrect inflation, leading to costly replacements and alignment issues. 2. Reduced vehicle control due to improper tire contact with the road. 3. Increased…
Bereich: guerrallp.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Einleitung: Driving on underinflated tires poses significant dangers, including increased likelihood of tire-related accidents, overheating, tire failure, longer stopping distances, and adverse effects on handling and tread life. A study by the NHTSA found that vehicles with tires under-inflated by at least 25% are three times more likely to be involved in accidents. Under-inflation causes tires to age 32% fa…
Bereich: grandprixperformance.com
Registriert: 2000 (25 Jahre)
Einleitung: Grand Prix Performance offers a range of tires suitable for all types of vehicles. They emphasize the importance of proper tire pressure for safety and vehicle performance, highlighting that underinflated tires can lead to premature wear, decreased fuel efficiency, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. They also provide car repair services, including alignments, brakes, suspensions, oil changes,…
In conclusion, the safety and performance of tires hinge critically on maintaining the correct inflation levels. Over-inflated tires can lead to reduced traction, increased wear, and a higher risk of blowouts, while under-inflated tires compromise handling and fuel efficiency. B2B buyers must recognize that investing in proper tire maintenance and sourcing reliable products can significantly enhance operational safety and reduce long-term costs.
Strategic sourcing becomes essential in this context, as it allows businesses to procure high-quality tires and related services that meet rigorous safety standards. By prioritizing partnerships with reputable manufacturers and service providers, companies can ensure the longevity and performance of their tire investments.

Illustrative image related to tires can be hazardous if over inflated or under inflated.
As we look to the future, it is vital for international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to prioritize tire safety in their procurement strategies. Regular inspections and adherence to manufacturer recommendations will not only safeguard vehicles but also enhance overall operational efficiency. Engage with suppliers today to ensure your fleet is equipped with the safest, most efficient tires available on the market.
Die in diesem Leitfaden enthaltenen Informationen, einschließlich der Angaben zu Herstellern, technischen Spezifikationen und Marktanalysen, dienen ausschließlich Informations- und Bildungszwecken. Sie stellen keine professionelle Kaufberatung, Finanzberatung oder Rechtsberatung dar.
Obwohl wir alle Anstrengungen unternommen haben, um die Richtigkeit und Aktualität der Informationen zu gewährleisten, übernehmen wir keine Verantwortung für etwaige Fehler, Auslassungen oder veraltete Informationen. Marktbedingungen, Unternehmensangaben und technische Standards können sich ändern.
B2B-Käufer müssen ihre eigene unabhängige und gründliche Due-Diligence-Prüfung durchführen bevor Sie eine Kaufentscheidung treffen. Dazu gehört, dass Sie sich direkt mit den Anbietern in Verbindung setzen, Zertifizierungen überprüfen, Muster anfordern und sich professionell beraten lassen. Das Risiko, sich auf die Informationen in diesem Leitfaden zu verlassen, trägt allein der Leser.