In the ever-expanding global market, understanding how to inflate a bike tire efficiently is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Sourcing high-quality bike maintenance supplies, including pumps and accessories, can be a challenge, especially when considering the diverse types of valves and pressure requirements. This guide aims to equip international buyers with the knowledge to navigate these complexities, ensuring they can make informed purchasing decisions that meet the specific needs of their markets.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will cover essential topics such as the various types of bike tire valves, the advantages of different pump types, and guidelines for optimal tire pressure. By delving into supplier vetting processes and cost considerations, this resource is designed to empower businesses to not only enhance their product offerings but also improve customer satisfaction and safety on the roads.
Understanding the nuances of tire inflation can significantly impact the performance and longevity of bicycles, making this guide an invaluable tool for any B2B buyer looking to make strategic investments in the cycling industry. With actionable insights and authoritative information, you will be well-prepared to meet the demands of your clientele while fostering a sustainable business model in an increasingly competitive landscape.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Track Pump | Floor-based, high volume, features a pressure gauge | Bicycle shops, rental services, workshops | Pros: Fast inflation, accurate pressure measurement. Cons: Bulky for transport. |
| Mini Pump | Portable, lightweight, often includes a hose for valve protection | Mobile bike repair, cycling events | Pros: Compact, easy to carry. Cons: Slower inflation, less accurate. |
| CO2 Inflator | Uses compressed gas cartridges for quick inflation | Emergency repairs, racing teams | Pros: Extremely fast inflation. Cons: Disposable cartridges, less sustainable. |
| Electric Pump | Battery-operated, automatic pressure settings | High-end bike retailers, service stations | Pros: Minimal effort, consistent pressure. Cons: Requires charging, heavier. |
| Hand Pump | Manual operation, simple mechanism, often lightweight | Casual cyclists, budget-friendly options | Pros: Affordable, easy to use. Cons: Requires physical effort, slower. |
Track pumps are designed for home use, ideal for high-volume inflation of bicycle tires. They feature a long hose and a sturdy base, allowing users to apply their body weight for efficient pumping. Equipped with a built-in pressure gauge, these pumps ensure precise inflation, making them suitable for bike shops and rental services where accuracy is crucial. For B2B buyers, investing in quality track pumps can enhance customer service by providing quick and reliable tire inflation for clients.
Mini pumps are essential for cyclists who need a portable solution for on-the-go repairs. Their lightweight design allows for easy transport, fitting into jersey pockets or attaching to bike frames. Many models include a hose to minimize stress on the valve during inflation. These pumps are particularly beneficial for mobile bike repair businesses and cycling events, where quick fixes are necessary. Buyers should consider durability and ease of use when selecting mini pumps for their inventory.
CO2 inflators offer a rapid solution for tire inflation, making them popular among racing teams and cyclists who prioritize speed. Utilizing compressed gas cartridges, they can inflate a tire in seconds, ideal for emergency situations. However, the disposable nature of cartridges raises sustainability concerns, which B2B buyers should weigh against the convenience factor. For businesses catering to competitive cyclists, including CO2 inflators in their product lineup can enhance service offerings.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
Electric pumps represent a modern solution for tire inflation, featuring automatic pressure settings that eliminate guesswork. They are particularly advantageous for high-end bike retailers and service stations, where efficiency and ease of use are paramount. While they provide consistent results with minimal physical effort, B2B buyers must consider the need for charging and the higher initial investment. These pumps can significantly enhance customer satisfaction in environments where time and precision are critical.
Hand pumps are a cost-effective choice for casual cyclists and budget-conscious buyers. They operate on a simple manual mechanism, making them easy to use without the need for electricity or cartridges. While they may require more effort and time for inflation, their affordability and reliability make them attractive for smaller shops and individual sellers. B2B buyers should focus on the balance between price and performance when selecting hand pumps to meet diverse customer needs.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to inflate a bike tire | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bicycle Manufacturing | Quality control during production | Ensures consistent performance and safety of bikes | Reliable inflating equipment, compatible with various valves |
| Rental Bike Services | Routine maintenance and customer service | Enhances customer experience and safety | Efficient pumps for quick service turnaround |
| Sports and Recreation | Event management for cycling competitions | Ensures optimal bike performance for athletes | Portable inflating solutions for on-the-spot needs |
| Logistics and Delivery | Delivery of bikes or bicycle parts | Reduces damage during transit due to proper inflation | Durable and lightweight pumping solutions |
| Urban Mobility Solutions | Integration in bike-sharing programs | Promotes sustainability and convenience for users | Multi-functional pumps adaptable to various bike types |
In the bicycle manufacturing sector, inflating bike tires is crucial during quality control processes. Manufacturers need to ensure that each tire meets safety and performance standards before leaving the production line. Proper inflation helps identify defects, ensuring that tires are neither over nor under-inflated, which could lead to safety issues. Suppliers must consider sourcing reliable pumps that can accommodate different valve types to cater to a range of bicycle models produced.
For rental bike services, maintaining proper tire pressure is essential for customer satisfaction and safety. Regular tire inflation checks ensure that bikes are ready for use, enhancing the overall customer experience. This routine maintenance helps prevent issues such as flats or poor handling, which can result in negative reviews. Businesses should invest in efficient, easy-to-use pumps that allow quick service turnaround, ensuring bikes are always in optimal condition.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
In the realm of sports and recreation, particularly during cycling competitions, the ability to inflate bike tires quickly and accurately is vital. Athletes rely on optimal tire pressure for performance, grip, and comfort during races. Event organizers must ensure that portable inflating solutions are available on-site to assist cyclists with any tire issues. Sourcing high-quality, portable inflators can facilitate quick adjustments, thereby minimizing downtime and enhancing athlete performance.
In logistics and delivery services, particularly those involving bicycles or bicycle parts, proper tire inflation is critical to prevent damage during transit. Inflated tires can absorb shocks and reduce the risk of punctures, ensuring that deliveries arrive safely and in good condition. Businesses should look for durable and lightweight pumping solutions that can be easily integrated into their delivery processes, allowing for efficient pre-delivery checks.
Urban mobility solutions, including bike-sharing programs, depend on well-maintained bikes to promote sustainability and convenience. Regular tire inflation checks are necessary to ensure that bikes are always ready for users, enhancing the reliability of the service. Companies should consider multi-functional pumps that can adapt to various bike types, ensuring that they can efficiently manage their fleet and provide a seamless user experience.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when their bike fleet features a mix of valve types, such as Schrader and Presta. This can lead to confusion and inefficiency, especially when preparing a fleet of bikes for rental or delivery. If the pump does not match the valve type, employees may struggle to inflate tires properly, causing delays and potentially impacting customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To tackle this issue, businesses should invest in versatile pumps that can accommodate both Schrader and Presta valves. When sourcing pumps, look for models that feature dual-head designs or an adjustable chuck, which allows for seamless transitions between valve types. Additionally, training staff on how to identify valve types quickly can save time during tire inflation. Consider providing an easy reference guide or visual aids in the workspace to help employees recognize valve types at a glance. This proactive approach ensures that your team is always prepared, reducing downtime and improving the overall efficiency of your operations.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in bike rental and repair services, encounter the challenge of achieving the correct tire pressure for various bike models. Each bike may have different pressure requirements, and inflating tires to incorrect pressures can lead to poor riding experiences, increased wear on tires, and higher rates of punctures.
The Solution: Establishing a standardized pressure-checking protocol is essential. Equip your service area with reliable pressure gauges and ensure that all staff members are trained on how to use them effectively. To streamline this process, create a database or chart that lists the recommended tire pressures for each bike model in your fleet. This information can be easily accessed digitally or in print, allowing staff to inflate tires quickly and accurately. Regularly check and calibrate your pressure gauges to maintain accuracy, and consider implementing a routine maintenance schedule to ensure tire pressure is checked before each rental or use.
The Problem: A common issue among businesses that manage bike fleets is the lack of knowledge regarding proper pumping techniques. Employees may struggle with how to effectively use different types of pumps, leading to inefficient inflation processes and potential damage to the bike valves. This can result in frustration and reduced operational productivity.
The Solution: To mitigate this pain point, conduct regular training sessions focused on the proper use of bike pumps. These sessions should cover the mechanics of different pump types (track pumps, mini pumps, CO2 inflators) and demonstrate the best practices for inflating tires without damaging valves. Additionally, develop instructional materials such as videos, step-by-step guides, or infographics that employees can reference as needed. By equipping your staff with the knowledge and skills to inflate tires correctly, you enhance not only the efficiency of your operations but also the safety and satisfaction of your customers, ultimately leading to a better overall business performance.
When selecting materials for bike tire inflation equipment, it is essential to consider the properties and applications of various materials. The following analysis covers four common materials used in pumps and valves, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum is widely used in bike pumps and valve components due to its favorable properties. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it lightweight yet durable. Aluminum can withstand high pressures, typically rated up to 200 psi, and offers good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
Pros and Cons:
Aluminum is durable and resistant to rust, making it suitable for various climates. However, it can be more expensive than other materials like plastic, and manufacturing processes may require specialized equipment, increasing costs. Additionally, while it is lightweight, it may not be as robust as steel in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum’s compatibility with both Presta and Schrader valves makes it versatile for different bike types. However, it may not perform well in extremely high-temperature environments, which could affect the integrity of the pump seals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM for materials. The lightweight nature of aluminum is advantageous for shipping, but buyers should also consider the impact of local climate on material longevity.
Steel is another common material, especially for pump frames and components. It offers excellent strength and durability, with pressure ratings often exceeding 300 psi. Steel is also resistant to deformation under stress, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of steel is its robustness, which translates to longevity and reliability. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which can be a drawback for portable pumps. Steel is also prone to rust if not properly coated, which may necessitate additional maintenance.
Impact on Application:
Steel’s strength allows for effective inflation in high-pressure situations, making it suitable for performance-oriented bikes. However, its weight can be a disadvantage for users seeking lightweight solutions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel products must comply with corrosion resistance standards, particularly in humid or coastal regions. Buyers should also consider the ease of repair and availability of parts in their region, as steel pumps may require more maintenance.
Plastic is often used for pump bodies and valve components due to its lightweight and cost-effective nature. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene are common choices, with pressure ratings typically around 50-100 psi.
Pros and Cons:
Plastic is inexpensive and lightweight, making it ideal for budget-friendly options. However, it lacks the durability of metal and may not withstand high pressures or extreme temperatures. Additionally, plastic components can degrade over time, particularly with exposure to UV light.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
Impact on Application:
Plastic is suitable for casual cyclists who prioritize convenience and cost over performance. However, it may not be suitable for high-performance applications where reliability is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with safety standards and are free from harmful chemicals. In regions with high UV exposure, selecting UV-resistant plastics is crucial for longevity.
Rubber is primarily used for seals and gaskets in pumps and valves. It offers excellent flexibility and can withstand a range of temperatures and pressures, typically rated up to 150 psi.
Pros and Cons:
Rubber seals provide an airtight connection, which is essential for effective inflation. However, they can wear out over time and may require replacement, adding to maintenance costs. Additionally, rubber can degrade in extreme temperatures or with prolonged exposure to certain chemicals.
Impact on Application:
Rubber seals are critical for ensuring no air leaks during inflation, thus enhancing the overall performance of the pump. However, the lifespan of rubber components can be a limiting factor in high-use scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should look for rubber products that meet international standards for durability and chemical resistance. In regions with extreme temperatures, selecting high-grade rubber can prevent premature failure.
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to inflate a bike tire | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Pump bodies and valve components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and potential for deformation | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty pump frames and components | Excellent strength and durability | Heavier and prone to rust | High |
| Plastic | Budget-friendly pumps and valve parts | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable and lower pressure rating | Low |
| Rubber | Seals and gaskets in pumps and valves | Provides airtight connections | Wears out over time and temperature sensitive | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for bike tire inflation equipment, considering performance, cost, and regional compliance.
The manufacturing process for bike tire inflation tools involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and functionality of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
The first stage is material preparation, where raw materials such as metals, plastics, and rubber are sourced. Common materials include aluminum or steel for pumps, rubber for seals, and plastics for the pump body.
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming, where they are shaped into various components.
The assembly stage involves bringing together all the individual components to create a fully functional bike tire inflation tool.
The finishing stage includes processes that enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of the product.
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that bike tire inflation tools meet industry standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be aware of both international and industry-specific standards that govern the manufacturing process.
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards like ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. This certification ensures that a company has a robust QA process in place.
In addition to international standards, industry-specific certifications can provide further assurance of product quality.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet established specifications.
IQC focuses on the materials received from suppliers. This stage involves testing materials for quality before they are used in production.
IPQC involves monitoring production processes and conducting inspections at various stages.
FQC is the last line of defense before products are shipped to customers.
B2B buyers should actively verify a supplier’s QC practices to ensure they are sourcing reliable products.
Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
Regular audits of suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing and QC processes.
Quality reports from suppliers can provide a snapshot of their QC processes and product performance.
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance.
B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific QC nuances when sourcing bike tire inflation tools.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in producing bike tire inflation tools, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and quality expectations. This diligence not only ensures the procurement of high-quality products but also fosters long-term supplier relationships built on trust and accountability.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
This practical sourcing guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for procuring the necessary equipment and knowledge for effectively inflating bike tires. Understanding the process and ensuring access to quality tools can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce maintenance issues.
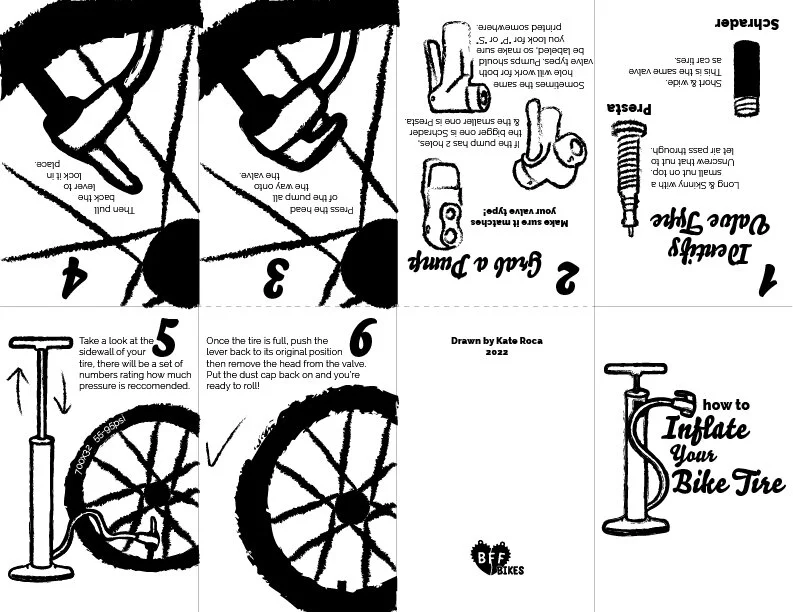
Before sourcing any inflation equipment, confirm the types of valves used on your bicycles—Presta, Schrader, or Dunlop/Woods. Each valve requires a specific type of pump or adapter, so understanding this detail is crucial for ensuring compatibility and avoiding unnecessary purchases.
Choose between various pump types based on your operational needs. A track pump is ideal for workshop settings due to its efficiency, while a mini pump is essential for on-the-go repairs.
When sourcing pumps and accessories, assess potential suppliers for reliability and quality. Look for suppliers with proven track records in the bicycle industry to ensure you receive durable and effective products.
Ensure the products you consider are made from high-quality materials and designed for longevity. This step is vital to minimize future replacement costs and maintain operational efficiency.
Create a maintenance schedule for your pumps to ensure they remain in optimal working condition. Regular checks and servicing can prevent breakdowns during critical times.
Different types of bicycles and riding conditions require specific tire pressures for optimal performance. Establish guidelines for inflating tires based on manufacturer recommendations.
Keep track of your inventory levels for pumps, adapters, and other accessories to avoid shortages. Implement a systematic approach to inventory management to ensure that all necessary tools are readily available.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source the tools and knowledge necessary to ensure proper bike tire inflation, enhancing overall service and customer satisfaction.
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing solutions related to inflating bike tires, several critical components come into play.
Materials: The primary materials include the pump body (often made from plastic or metal), hoses, valves (Schrader or Presta), and seals. The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost; for instance, high-quality aluminum or reinforced plastics can drive up expenses but offer durability and performance benefits.
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, these expenses can be substantial. Conversely, countries with lower labor costs may present more cost-effective options, albeit potentially with varying quality standards.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate overhead costs, making it essential for suppliers to adopt lean manufacturing techniques.
Tooling: Initial investment in tooling for production (molds for plastic components, machining tools for metal parts) can be significant. However, once amortized over large production runs, this cost per unit decreases, making volume purchases more attractive.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC measures ensures product reliability, which is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction. However, thorough QC processes can add to the overall cost structure, especially if third-party certifications (like ISO) are involved.
Logistics: Transportation costs, warehousing, and handling fees are essential considerations. For international buyers, logistics can represent a significant portion of the total cost due to tariffs, shipping rates, and delays at customs.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market demand, competitive pressures, and supplier reputation.
Several factors can influence the pricing dynamics of bike tire inflation solutions:
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Negotiating favorable MOQs can be beneficial for buyers looking to optimize their costs.
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specifications can increase costs due to the need for unique tooling or materials. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for increased expenses.
Material Selection: Higher-quality materials may increase initial costs but can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement needs, ultimately providing long-term savings.
Quality Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards can command higher prices. However, they may also ensure compliance with safety regulations, appealing to buyers in regions with strict quality expectations.
Supplier Factors: The reliability, reputation, and service level of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better support and quality assurance.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for pricing transparency. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, directly impacting total costs.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
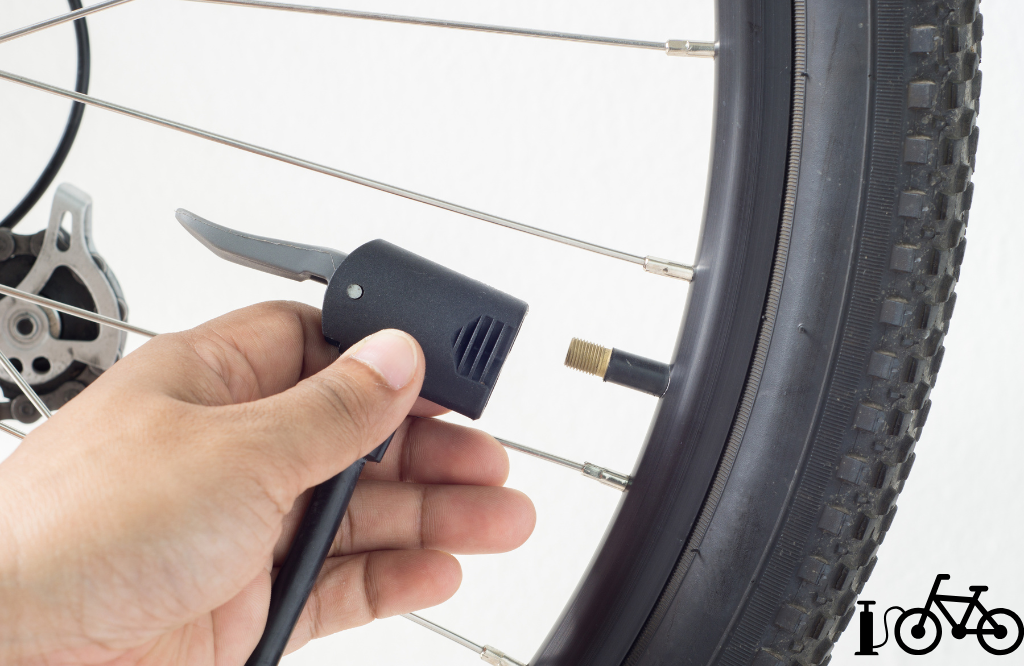

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially regarding bulk orders. Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than solely considering purchase price, assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, durability, and replacement frequency. This holistic view can lead to better long-term decisions.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences influenced by local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and market demand. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed sourcing decisions.
Evaluate Supplier Networks: Build relationships with multiple suppliers to enhance negotiation leverage and ensure competitive pricing. A diversified supplier base can also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly review market conditions and emerging technologies in the bike tire industry. Staying informed can lead to timely purchasing decisions that capitalize on cost-saving opportunities.
In conclusion, understanding the cost components and price influencers, along with implementing strategic sourcing tips, can significantly enhance the purchasing process for bike tire inflation solutions in the international B2B market.
When it comes to maintaining optimal performance and safety in cycling, ensuring proper tire inflation is essential. While the traditional method of inflating a bike tire using a pump is widely recognized, several alternative solutions have emerged. This section compares the conventional tire inflation method against innovative alternatives, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | How To Inflate A Bike Tire | CO2 Inflators | Electric Air Pumps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for consistent pressure; requires manual effort. | Quick inflation; can over-inflate if not monitored. | Automated inflation; often equipped with digital pressure gauges. |
| Cost | Relatively low-cost (manual pumps range from $20-$100). | Moderate cost ($10-$50 for inflators and cartridges). | Higher initial investment ($50-$200), but long-term savings on labor. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple process; requires knowledge of valve types. | Very easy; minimal setup required, but requires cartridges. | User-friendly; often just plug and play with built-in features. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; requires occasional checking for wear. | Low; cartridges are disposable but need stock management. | Moderate; requires power source and occasional cleaning. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for regular bike maintenance in workshops. | Excellent for emergency situations on rides. | Best for home use with multiple bikes needing inflation. |
CO2 inflators are a popular alternative for cyclists who prioritize speed and convenience. These devices utilize compressed carbon dioxide cartridges to inflate tires quickly, making them ideal for emergency situations during rides. One significant advantage is their portability; they are lightweight and can easily fit into a jersey pocket or saddlebag. However, a notable downside is the potential for over-inflation if the user is not careful, as well as the fact that the cartridges are single-use, necessitating frequent replacements. This can become costly over time, especially for high-volume users.
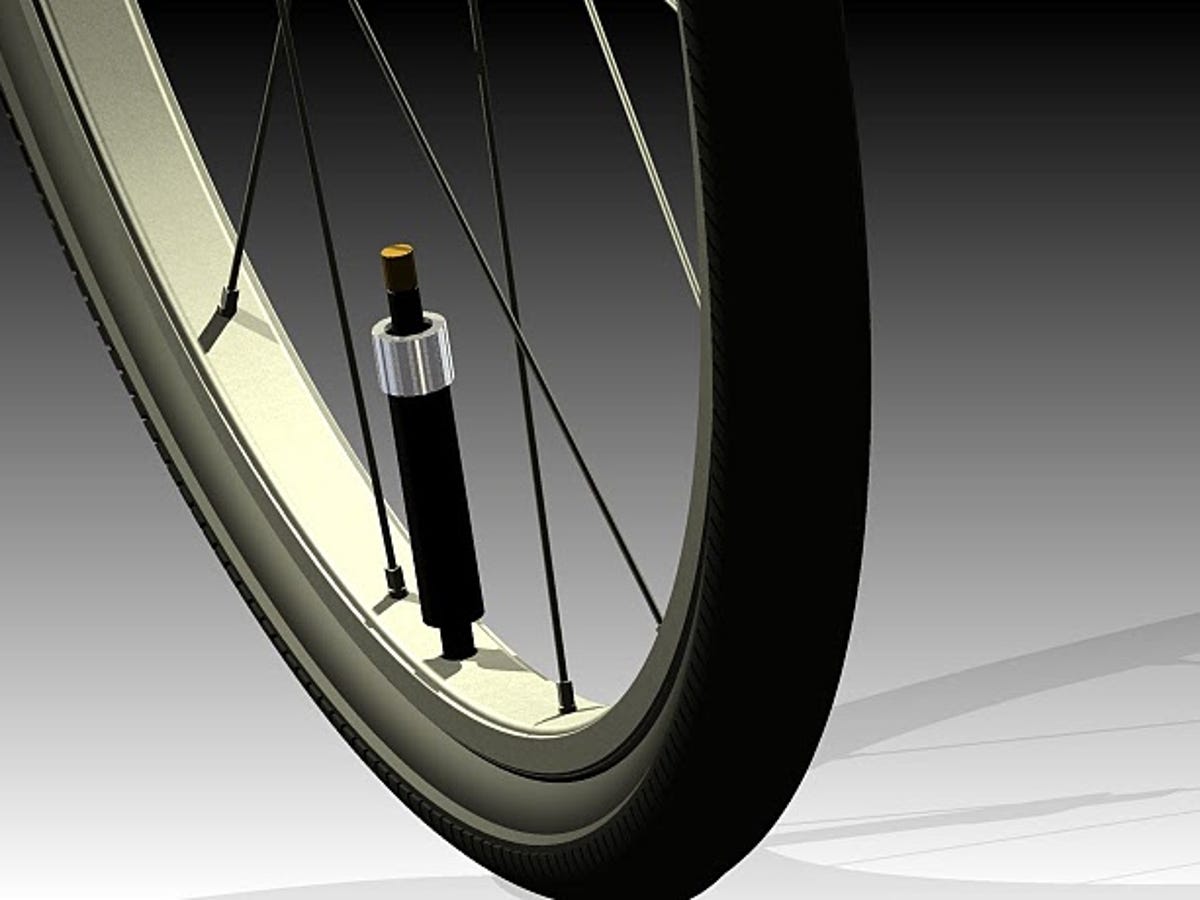

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
Electric air pumps represent a more advanced alternative, appealing to those who prefer automation in their maintenance tasks. These pumps typically come equipped with digital pressure gauges, allowing for precise inflation without the manual effort required by traditional pumps. Their ease of use makes them suitable for both professional and casual cyclists. However, the higher initial cost and the need for a power source can be barriers for some users. Additionally, these pumps may not be as portable as manual pumps, making them less ideal for on-the-go inflation.
When selecting the most suitable bike tire inflation method, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational contexts, such as the volume of bikes serviced, the frequency of use, and the environments in which the bikes will be used. For businesses focused on quick roadside assistance, CO2 inflators may be the most effective option. Conversely, for those managing a fleet of bikes requiring regular maintenance, investing in electric air pumps could yield better long-term efficiency and user satisfaction. By assessing these factors, buyers can align their choices with their operational goals and enhance their service offerings.
When it comes to inflating bike tires, several technical properties are critical for ensuring performance, safety, and compatibility with various products. Understanding these specifications is essential for B2B buyers in the cycling industry.
Pressure Rating (PSI/BAR)
This indicates the maximum and minimum air pressure that a tire can safely hold. It is crucial for optimizing performance and preventing blowouts. Tires inflated beyond their maximum rating can fail, leading to safety hazards. For B2B buyers, selecting tires with appropriate pressure ratings ensures compliance with safety regulations and enhances customer satisfaction.
Valve Type Compatibility
Most bicycles utilize either Presta or Schrader valves. Presta valves are thinner and typically found on higher-end bikes, while Schrader valves are broader and resemble those used in car tires. Understanding valve compatibility is essential for manufacturers and retailers to ensure that pumps and accessories meet the needs of their target markets.
Material Composition
The inner tubes and tires are often made from rubber compounds that affect flexibility, durability, and puncture resistance. For B2B buyers, sourcing high-quality materials can lead to better product performance and longevity, ultimately enhancing brand reputation in competitive markets.
Tire Size Specifications (ETRTO)
The European Tire and Rim Technical Organization (ETRTO) provides a standardized system for tire sizing, expressed in millimeters. Accurate sizing is vital for compatibility with bike frames and rims. B2B buyers must ensure that their products align with these specifications to avoid costly returns and enhance customer trust.
Weight Tolerance
Weight tolerance refers to the amount of weight a tire can support without compromising its integrity. This is particularly important for performance cycling where weight savings can lead to improved speed. Buyers in the cycling industry should consider weight tolerance when sourcing tires for specific cycling disciplines.
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms relevant to bike tire inflation and related products:
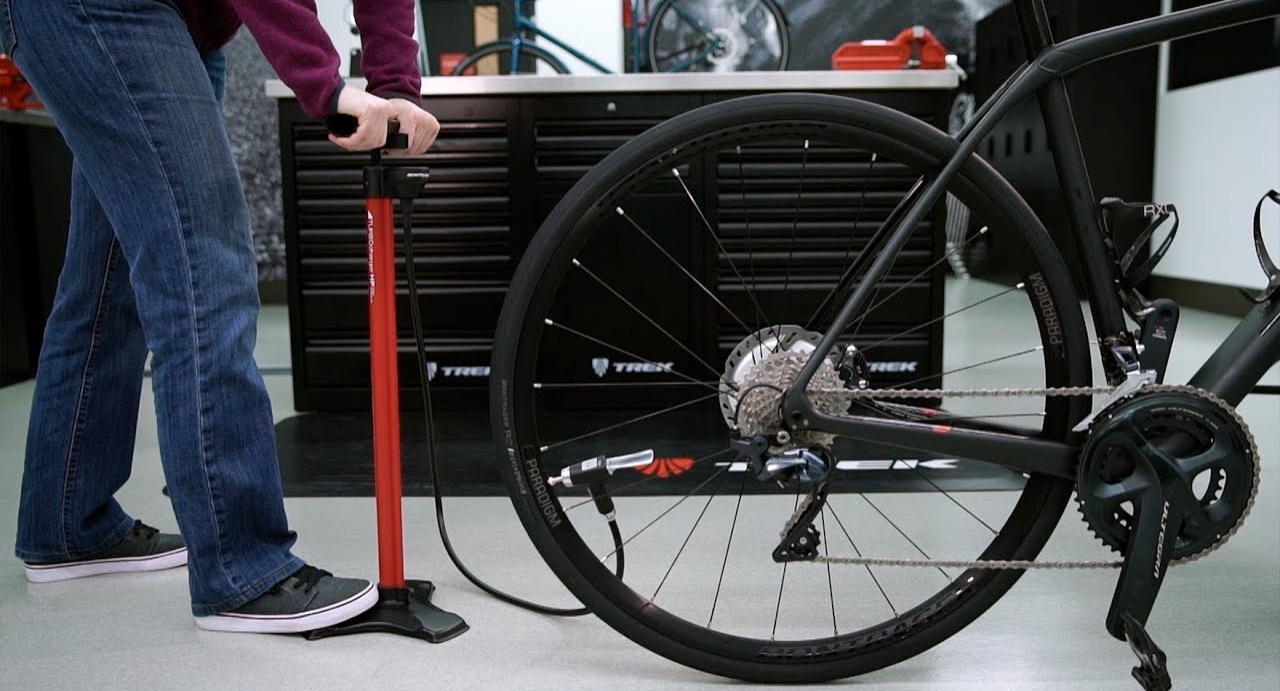

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are sold under another company’s brand name. For B2B buyers, partnering with OEMs can provide access to high-quality components that meet specific performance criteria, ensuring product reliability.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This is an essential consideration for B2B buyers, as it impacts inventory costs and cash flow. Understanding MOQ can help businesses manage their supply chain more effectively.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can facilitate price comparisons and help negotiate better terms with suppliers, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. For B2B buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing shipping costs and responsibilities effectively.
Supply Chain Management
This refers to the management of the flow of goods and services, including all processes that transform raw materials into final products. In the context of bike tires, effective supply chain management ensures that all components are available when needed, reducing downtime and enhancing customer service.
Aftermarket Products
These are products that are not sourced from the original manufacturer but are compatible with their products. For B2B buyers, understanding the aftermarket landscape can open up additional revenue streams through accessories and replacement parts, enhancing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their product offerings and improve customer satisfaction in the competitive cycling market.
The bike tire inflation sector is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing popularity of cycling as a sustainable mode of transportation and leisure activity. Urbanization in regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East is prompting governments to invest in cycling infrastructure, thus enhancing the demand for cycling accessories, including tire inflation solutions. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms facilitates the global distribution of pumps and related products, making it easier for B2B buyers to source high-quality items from various markets.
Emerging technologies are also transforming the bike tire inflation landscape. Innovations such as smart pumps equipped with digital pressure gauges and connectivity features are gaining traction. These devices offer real-time pressure monitoring and can be integrated with mobile applications, providing cyclists with enhanced control over their bike maintenance. Additionally, the trend toward tubeless tires is creating new opportunities for suppliers who can provide specialized inflation equipment tailored to this growing segment.
International B2B buyers must be aware of regional preferences and requirements when sourcing products. For instance, while Presta valves dominate in Europe, Schrader valves are more common in other regions. Understanding these dynamics will enable buyers to make informed decisions and cater to the specific needs of their markets.
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the bike tire inflation sector, as consumers increasingly prioritize environmentally friendly products. B2B buyers are now seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. This includes using recyclable materials, reducing carbon footprints during production, and ensuring fair labor practices throughout the supply chain.
The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes cannot be overlooked. Many companies are now exploring options such as biodegradable materials for pump components and eco-friendly packaging solutions. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and Fair Trade practices are gaining importance, as they assure buyers of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the promotion of cycling as a green transport alternative reinforces the need for sustainable practices in the industry. B2B buyers who align with suppliers that prioritize sustainability not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute to a more sustainable future for the cycling community.
The evolution of the bike tire inflation market mirrors the broader advancements in cycling technology. Initially, simple hand pumps dominated the market, requiring significant physical effort to inflate tires. As cycling gained popularity, particularly in urban settings, the demand for more efficient and user-friendly solutions led to the development of track pumps and mini-pumps.
The introduction of CO2 inflators further revolutionized the market, offering cyclists a rapid inflation option during rides. The shift towards tubeless tire systems has also necessitated specialized inflators, adapting to the changing needs of cyclists.
This evolution has been accompanied by an increasing focus on quality and reliability, with B2B buyers now more inclined to invest in durable, high-performance pumps. As cycling continues to grow as a lifestyle choice across various regions, the bike tire inflation market is poised for further innovation and development, presenting ample opportunities for international buyers to explore.
1. How do I choose the right pump for inflating bike tires?
Selecting the right pump is crucial for effective tire inflation. Identify whether your bike uses Presta or Schrader valves, as most pumps are compatible with one or both types. For regular use, a track pump is recommended for its efficiency and built-in pressure gauge, while a mini-pump is ideal for on-the-go repairs. Ensure the pump has a flexible hose to prevent valve damage during inflation. Additionally, consider the pump’s build quality and ease of use, especially if you plan to sell or distribute these to customers.
2. What is the recommended tire pressure for different types of bikes?
Tire pressure varies significantly based on bike type and tire specifications. Generally, road bikes require higher pressures (80-130 psi) for speed, while mountain bikes function better at lower pressures (30-50 psi) for traction and comfort. Check the sidewall of the tire for manufacturer-recommended pressure ranges. Ensuring the correct pressure not only enhances performance but also reduces the risk of punctures. Educating your customers about these specifics can lead to better customer satisfaction and reduced returns.
3. How can I identify if a bike tire is under-inflated?
An under-inflated tire often feels soft and squishy when squeezed. Additionally, a bike may feel sluggish, and the tires can appear bulging or squirmy during rides. Regularly checking tire pressure with a gauge is recommended, especially before rides. If a tire is consistently under-inflated, it may indicate a slow leak or puncture, which should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage. Providing guidance on tire maintenance can enhance customer loyalty and ensure they have a better riding experience.
4. What should I do if my bike tire won’t inflate?
If a tire fails to inflate, first check the pump attachment to ensure an airtight seal on the valve. If it’s secure and the tire still won’t inflate, inspect for a puncture or damage to the inner tube. A visible air leak or hissing sound indicates a puncture, which may require tube replacement. Educating your clients on troubleshooting techniques can empower them to handle basic maintenance, reducing reliance on professional services and enhancing their biking experience.
5. How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing bike pumps for resale?
To ensure quality assurance in bike pumps, conduct thorough supplier vetting, including checking certifications and product reviews. Request samples for testing before bulk purchases to evaluate performance and durability. Establish clear quality control standards and ensure compliance with international safety regulations. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and any potential issues that may arise during production or shipping.
6. What customization options should I consider when sourcing bike pumps?
Customization options can significantly enhance product appeal. Consider branding opportunities, such as custom colors, logos, or packaging. Additionally, explore variations in pump design to cater to specific markets, such as ergonomic handles or integrated pressure gauges. Discussing these options with suppliers early in the negotiation process can lead to unique offerings that differentiate your products in competitive markets, ultimately increasing sales potential.
7. What are typical payment terms when sourcing bike accessories internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include a deposit (often 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. It’s crucial to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Consider using letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment. Establishing clear payment terms in your contracts can minimize disputes and ensure smoother transactions throughout the procurement process.
8. How can I manage logistics efficiently for importing bike pumps?
Efficient logistics management is key to successful international trade. Partner with reliable freight forwarders who understand the nuances of shipping bike accessories, including customs regulations and tariffs. Use trackable shipping methods to monitor your goods in transit, and prepare all necessary documentation in advance to avoid delays. Consider warehousing options closer to your target market to reduce shipping times and costs. Regularly reviewing your logistics strategy can help streamline operations and improve overall profitability.
Domain: bikeradar.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Track pump: A home essential for efficient and quick inflation, features a long flexible hose, large camber for quick air transfer, and a base for stability. Most include a pressure gauge. Mini pump: Recommended to have a hose for easier use, ideal for on-the-go inflation.
Domain: schwinnbikes.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: 1. Tire Inflation Pressure: Every tire has a maximum inflation recommendation (usually in PSI or bars) labeled on the side of the tire. It’s important to check this before pumping to avoid pinch flats or poor traction. 2. Valve Types: There are two styles of valves: Presta (found on higher-end and road bikes) and Schrader (used on cars and many bike tires). Most Schwinn pumps feature a dual head t…
Domain: bicycles.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Presta valve, floor pump, tire pressure of 110 psi (7.5 atm), pump gauge up to 100 psi, valve stem length issues, valve cap, valve adapter, jam nut for valve stability.
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This article provides a guide on how to inflate bike tires, focusing on two types of valves: Schrader and Presta. Key details include: 1. Schrader Valve: Also known as an American valve, typically found on cars and less expensive bikes. To inflate, unscrew the rubber cap, use a compatible pump, and monitor the PSI. 2. Presta Valve: Commonly found on high-end road bikes, it requires loosening a bra…
In conclusion, mastering the art of inflating bike tires is essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety in cycling. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of high-quality pumps and compatible accessories is crucial. By investing in reliable equipment—such as track pumps for home use and mini pumps for on-the-go repairs—businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce maintenance costs.
Moreover, understanding the different valve types and optimal pressure settings can significantly impact the riding experience, making it essential for suppliers to offer comprehensive product education. This knowledge not only fosters customer loyalty but also positions your business as a trusted authority in the cycling market.
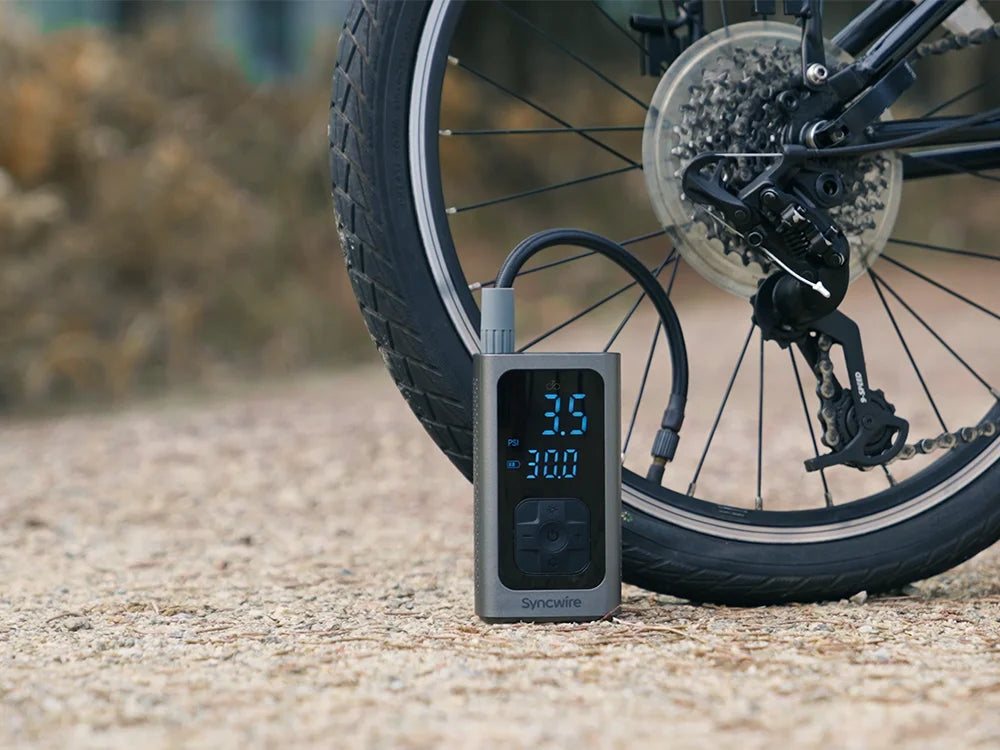

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a bike tire
As the cycling industry continues to grow, especially in emerging markets, the demand for efficient tire inflation solutions will rise. Now is the time to evaluate your supply chain and invest in quality products that meet the needs of your clientele. Embrace this opportunity to lead in the market by ensuring your offerings are equipped to support cyclists in achieving their best rides.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.