In an ever-evolving global market, sourcing tire inflaters that meet diverse industry needs can present significant challenges for B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for reliable and efficient tire inflation solutions, understanding the various types of inflators available—ranging from handheld and portable models to advanced automatic systems—is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the key applications of tire inflaters, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, providing valuable insights tailored for international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil.
Navigating the complexities of tire inflators involves more than just selecting a product; it requires a strategic approach to ensure that the chosen solutions align with operational requirements and regional standards. This guide empowers B2B buyers by equipping them with essential knowledge about performance metrics, compatibility with various tire types, and the latest technological advancements in inflator designs. By addressing the unique challenges faced by businesses in different geographical contexts, we aim to facilitate smarter procurement strategies that enhance operational efficiency and drive value. Whether you are looking to optimize your fleet maintenance or enhance customer service offerings, this guide serves as a critical resource for making effective purchasing decisions in the tire inflator market.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Tire Inflators | Compact, battery-operated or plug-in, often with built-in gauges | Automotive repair shops, roadside assistance | Pros: Easy to store, versatile; Cons: Limited power for larger tires. |
| Automatic Tire Inflators | Wall-mounted, programmable settings, digital gauges | Fleet maintenance, service stations | Pros: High efficiency, consistent results; Cons: Requires installation and may be costly. |
| Heavy-Duty Tire Inflators | High PSI capabilities, robust design, often battery-operated | Construction, agricultural machinery | Pros: Fast inflation for large tires; Cons: Bulky and expensive. |
| Digital Tire Inflators | Digital pressure readouts, preset PSI settings | Automotive shops, personal vehicles | Pros: Accurate, user-friendly; Cons: May require batteries or charging. |
| Handheld Tire Inflators | Lightweight, manual operation, usually portable | Emergency kits, personal vehicles | Pros: Very portable, easy to use; Cons: Slower inflation rate. |
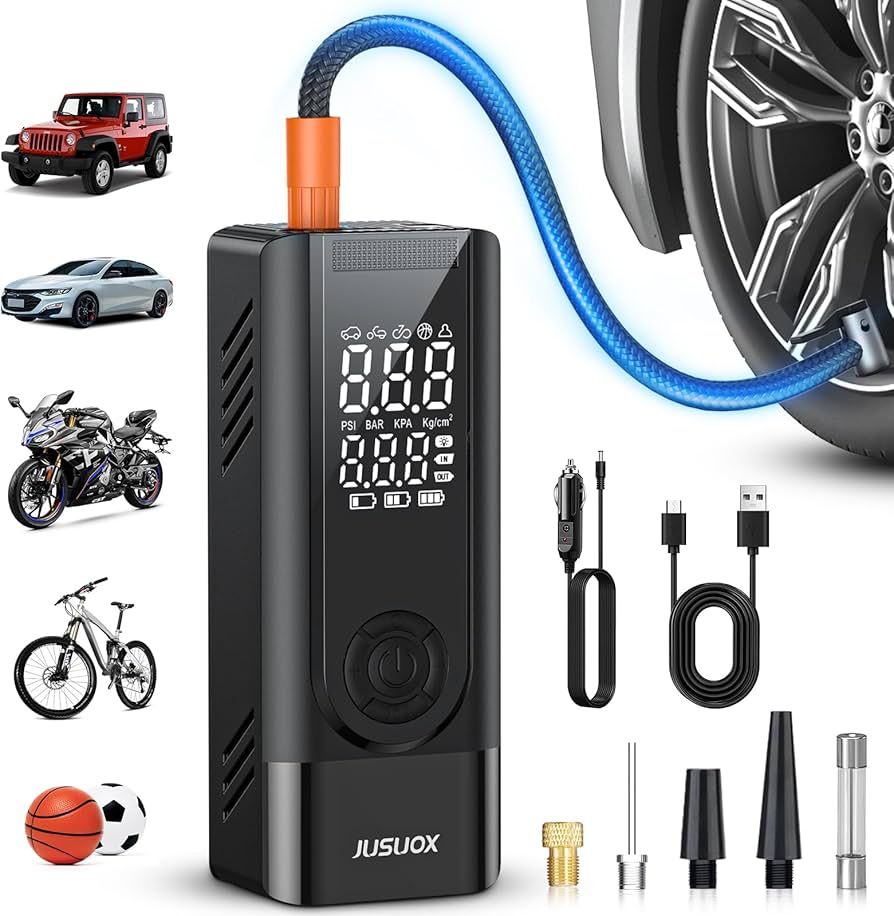
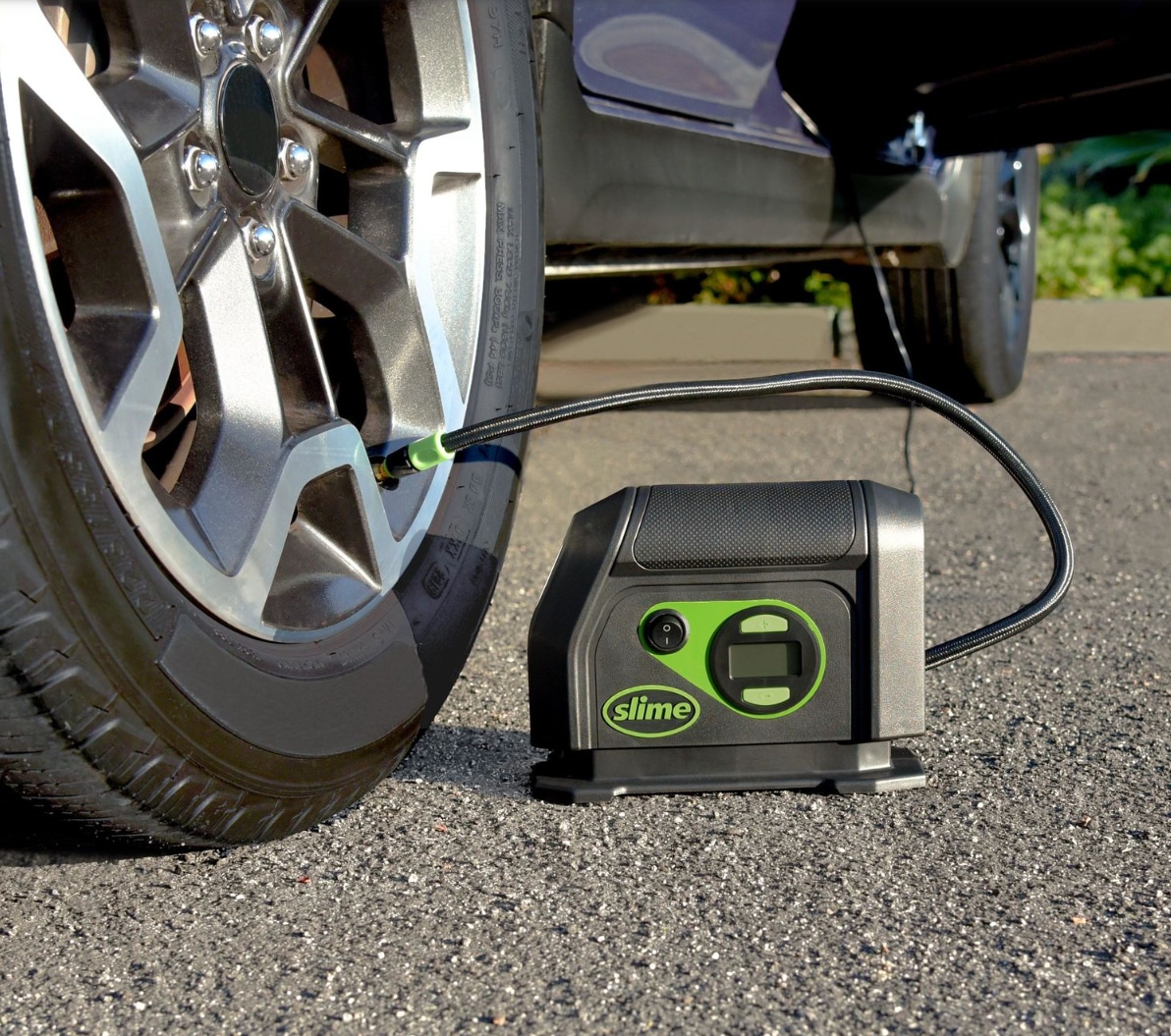
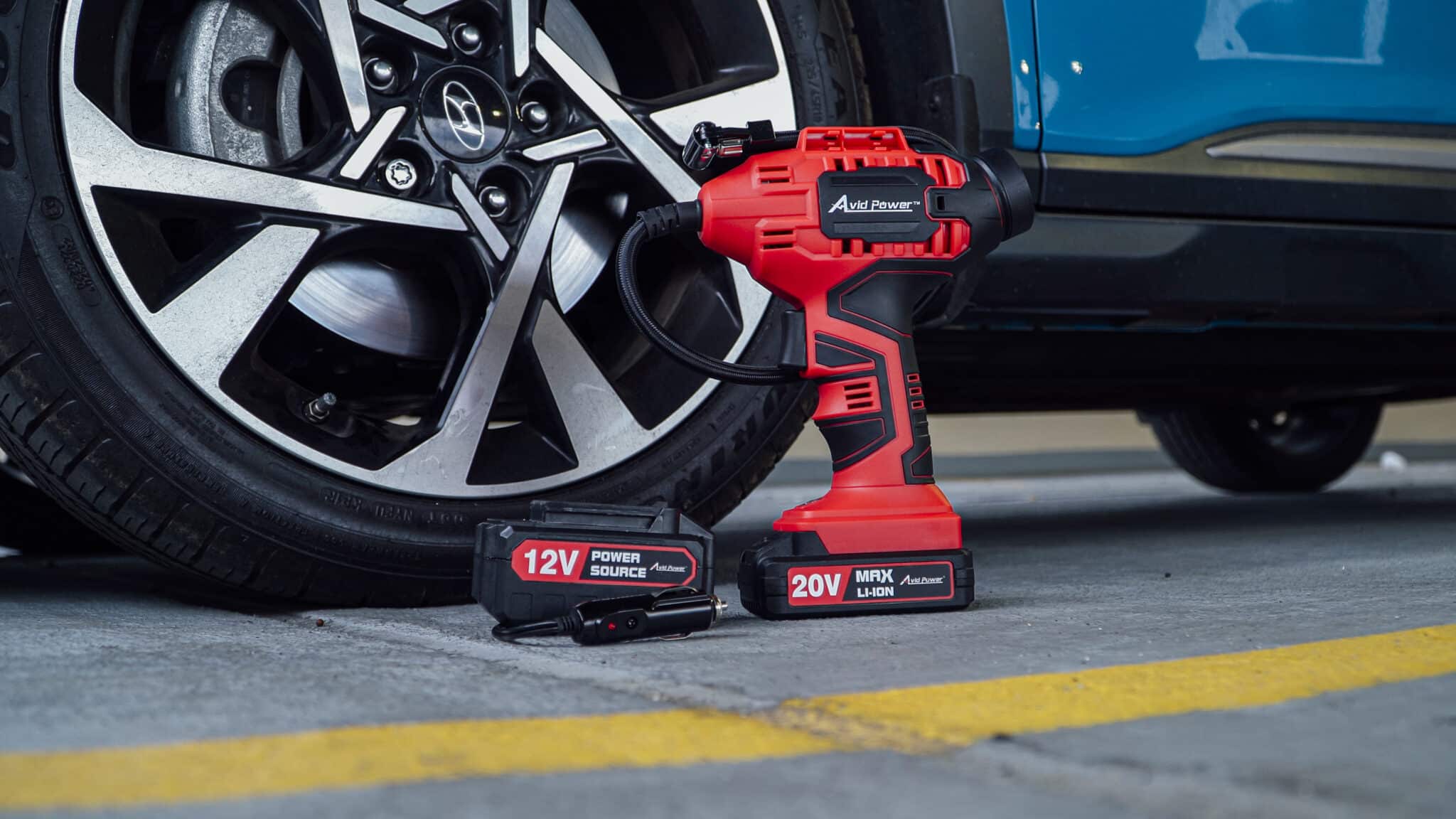
Portable tire inflators are designed for ease of use and convenience, making them ideal for automotive repair shops and roadside assistance services. These inflators are typically compact, often battery-operated or powered through a vehicle’s 12V outlet. They feature built-in pressure gauges for monitoring inflation levels. When purchasing, consider the inflator’s battery life, maximum PSI, and ease of storage, as these factors influence operational efficiency in various settings.
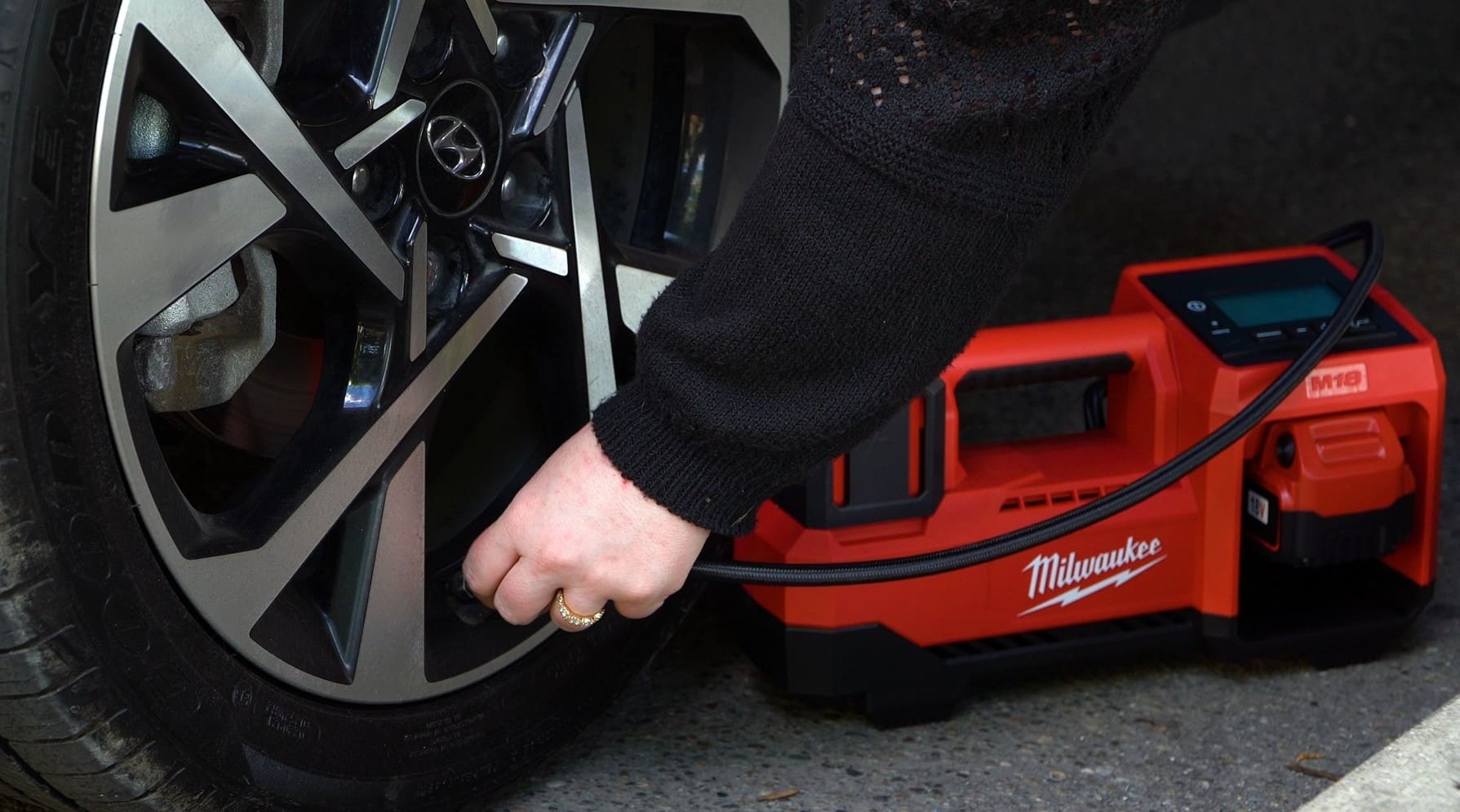
Automatic tire inflators are essential for businesses managing fleets, service stations, or high-volume tire services. These inflators can be wall-mounted and programmed to deliver precise air pressure, significantly enhancing productivity. Their digital gauges provide real-time monitoring, ensuring tires are inflated correctly every time. B2B buyers should assess installation requirements, upfront costs, and maintenance needs when considering these systems, as they can represent a significant investment.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Heavy-duty tire inflators are specifically designed for high-pressure applications, making them suitable for industries that deal with larger tires, such as construction and agriculture. These inflators can quickly inflate tires to high PSI levels, reducing downtime for heavy machinery. When evaluating options, B2B buyers should focus on the inflator’s build quality, power source, and inflation speed, as these factors are critical for operational efficiency in demanding environments.
Digital tire inflators have become popular in automotive shops and personal vehicle maintenance due to their accuracy and user-friendly features. They often include preset PSI settings, allowing users to inflate tires to the desired pressure without manual adjustments. B2B buyers should prioritize models with reliable digital readouts and consider battery or power source requirements, as these can affect the inflator’s usability in various settings.
Handheld tire inflators are lightweight and portable, making them ideal for personal vehicles and emergency kits. These inflators are easy to operate and can be quickly deployed in case of a flat tire. However, they generally have a slower inflation rate compared to other types. When purchasing, consider the inflator’s weight, ease of use, and whether it meets the PSI requirements for the vehicles in your fleet or personal use.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Tire Inflaters | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Service stations and garages for tire maintenance | Ensures quick service turnaround and customer satisfaction | Durability, ease of use, compatibility with various tire types |
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet maintenance for trucks and buses | Reduces downtime and enhances operational efficiency | High PSI capability, speed of inflation, robust design |
| Agriculture | Tire inflation for agricultural machinery | Optimizes machinery performance and reduces tire wear | Portability, compatibility with nitrogen, ruggedness |
| Construction | Tire inflation for heavy equipment | Minimizes project delays and ensures safety compliance | High durability, ease of transport, precise pressure control |
| Retail & E-commerce | Retail outlets for consumer tire inflators | Expands product offering and enhances customer service | Compact design, multiple power sources, affordability |
In automotive repair services, tire inflaters are essential tools for maintaining optimal tire pressure. Service stations utilize these devices to quickly inflate tires, ensuring customer vehicles are safe and roadworthy. The ability to provide rapid service enhances customer satisfaction and reduces wait times. Buyers in this sector should consider inflators that are durable, easy to operate, and compatible with various tire types, including those used in passenger vehicles and light trucks.
In the transportation and logistics sector, tire inflaters are crucial for maintaining the tires of fleets, including trucks and buses. Proper tire pressure is vital for fuel efficiency and safety, directly impacting operational costs. Quick inflation capabilities minimize vehicle downtime, allowing for timely deliveries. Buyers should prioritize inflators with high PSI capabilities and fast inflation speeds, ensuring they can handle the demands of heavy-duty vehicles effectively.
Agricultural machinery often operates in rugged environments, making tire maintenance essential for optimal performance. Tire inflaters are used to ensure that tractors and other farm equipment maintain proper tire pressure, which can significantly affect fuel efficiency and tire longevity. For buyers in this industry, portability and compatibility with nitrogen are important features, as they need reliable equipment that can withstand harsh working conditions.
In construction, tire inflaters are vital for ensuring that heavy equipment, such as excavators and bulldozers, operates safely and efficiently. Maintaining the correct tire pressure prevents accidents and project delays caused by equipment failure. Buyers in this sector should look for inflators that are robust, easy to transport, and capable of precise pressure control to meet the demanding requirements of construction sites.
Retail outlets that sell consumer tire inflators can enhance their product offerings by including high-quality inflators that cater to various customer needs. Providing tire inflators not only meets consumer demand but also improves customer service by allowing drivers to maintain their vehicles easily. Buyers in this sector should focus on compact designs with multiple power sources to appeal to a broad range of customers, while affordability remains a key consideration to ensure competitive pricing.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those managing fleets or automotive services, face the challenge of inconsistent tire pressure monitoring. Tires that are under or over-inflated can lead to increased fuel consumption, higher operational costs, and frequent tire replacements. This not only impacts the bottom line but can also compromise safety and vehicle performance. For businesses in regions with extreme temperatures, the risk of tire pressure fluctuations is even more pronounced, further complicating the management process.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should invest in high-quality, digital tire inflators equipped with accurate pressure gauges and automatic shut-off features. These inflators can provide precise inflation to the desired PSI, ensuring tires are consistently at the optimal pressure. Additionally, integrating a regular maintenance schedule that includes tire pressure checks can help mitigate these issues. Buyers should consider purchasing inflators that are compatible with their fleet’s specific tire requirements, and training staff on the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure can foster a culture of safety and cost-efficiency.
The Problem: Businesses operating in construction, agriculture, or heavy-duty transport often deal with large or specialized tires that require specific inflation tools. Standard tire inflators may not deliver the necessary pressure or volume to effectively inflate these tires, leading to delays and potential downtime. This situation can be particularly frustrating for companies that rely on heavy machinery for their operations, as any delay can result in significant financial losses.
The Solution: B2B buyers should look for tire inflators specifically designed for heavy-duty applications. These models typically offer higher PSI ratings and greater airflow capacities, ensuring they can handle the demands of larger tires. It is advisable to source inflators with robust features such as dual power sources (e.g., AC and DC) and compatibility with nitrogen inflation, which is often preferred for high-performance tires. Furthermore, establishing a relationship with suppliers who specialize in industrial-grade tire inflators can provide buyers with insights into the best options for their specific needs, ensuring operational efficiency.
The Problem: For businesses operating in remote areas, having access to reliable tire inflators can be challenging. Traditional inflators may not be portable enough for fieldwork, and relying on external service providers can lead to delays and increased costs. This is particularly relevant in regions such as Africa or South America, where infrastructure may be limited, and quick access to maintenance services is crucial for minimizing downtime.
The Solution: Investing in portable, battery-operated tire inflators can significantly enhance operational flexibility. B2B buyers should prioritize lightweight, compact inflators that can easily be transported to various job sites. Models that offer multiple charging options, such as solar power or vehicle charging, can be especially beneficial in remote locations. Additionally, providing training for staff on using these portable units can empower teams to address tire issues immediately, reducing reliance on external services and minimizing downtime. By equipping their teams with the right tools, businesses can maintain productivity, even in challenging environments.
When selecting materials for tire inflators, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations from a B2B perspective. The choice of materials can significantly impact the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the final product. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, steel, plastic, and rubber.
Aluminum is a popular choice for various components of tire inflators due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. With a temperature rating that can withstand high pressures, aluminum is suitable for both portable and stationary inflators.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it easy to handle, which is particularly advantageous for portable inflators. Additionally, its resistance to corrosion ensures longevity, especially in humid or saline environments, which is vital for buyers in coastal regions or areas with high humidity.
Cons: The primary drawback of aluminum is its cost, which is generally higher than that of plastic. Manufacturing processes can also be complex, especially for intricate designs, potentially leading to longer lead times.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and nitrogen, making it versatile for different tire types.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers in Africa and South America should ensure that aluminum components meet local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact.
Steel is often used for the structural components of tire inflators, such as frames and support brackets. Its high tensile strength and durability make it an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Steel’s robustness ensures that inflators can withstand rigorous use, particularly in industrial settings. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to aluminum, making it appealing for budget-conscious buyers.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Cons: However, steel is prone to corrosion, especially if not treated or coated properly. This can lead to decreased lifespan and increased maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is generally suitable for high-pressure applications, but it may require protective coatings to ensure compatibility with various media, particularly in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should be aware of the specific corrosion resistance standards applicable in their regions, as well as any environmental regulations regarding steel manufacturing and disposal.
Plastic is commonly used for housing and non-structural components of tire inflators. Its lightweight and moldable characteristics make it an attractive option for manufacturers.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastic is its low cost and ease of manufacturing. It can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs that enhance user experience.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Cons: The downside is that plastic may not withstand high temperatures and pressures as effectively as metals. This limits its application in high-performance inflators.
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for low-pressure applications and is often used in consumer-grade inflators.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards is essential, especially regarding the use of BPA-free materials in consumer products. Buyers in Europe may have specific regulations regarding the types of plastics that can be used.
Rubber is primarily used in seals and hoses within tire inflators. Its flexibility and resilience make it ideal for creating airtight connections.
Pros: Rubber’s excellent sealing properties ensure that air does not leak during inflation, which is critical for maintaining accurate pressure levels. It is also resistant to wear and tear, enhancing the durability of the inflator.
Cons: The main limitation of rubber is its susceptibility to degradation from UV light and extreme temperatures, which can reduce its lifespan.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Impact on Application: Rubber is compatible with various gases, including air and nitrogen, making it versatile for different applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that rubber components meet international standards for durability and safety, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for tire inflaters | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable inflator bodies | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Structural components | High durability and cost-effective | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Plastic | Housing and non-structural parts | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Limited high-pressure performance | Low |
| Rubber | Seals and hoses | Excellent sealing properties | Susceptible to UV and temperature degradation | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for tire inflaters, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
The manufacturing of tire inflaters involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring that the final product meets quality and performance standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. Manufacturers typically source high-quality raw materials such as plastic, metal, and rubber. These materials are often subjected to rigorous quality checks upon arrival at the factory, ensuring they meet specific industry standards.
After inspection, materials are sorted and prepared for the next stage. For example, plastics may be granulated and then melted for molding, while metals might be cut or rolled to specific dimensions. This initial quality control (IQC) step is crucial for identifying any defects early in the process.
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will make up the tire inflater. Common techniques include injection molding for plastic parts, die casting for metal components, and extrusion for rubber hoses. Each method is chosen based on the required specifications and volume of production.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Injection molding, for instance, allows for high precision and repeatability, crucial for parts like pressure gauges and housing. Advanced CNC machining may also be employed for metal parts, ensuring tight tolerances that are vital for performance and safety.
Assembly is where the individual components come together to form the final product. This stage can vary significantly between manufacturers, depending on the complexity of the tire inflater design. Automated assembly lines are often utilized for high-volume production, allowing for efficient and consistent assembly.
In manual assembly processes, skilled technicians may perform critical tasks such as installing electronic components, connecting hoses, and affixing pressure gauges. Quality checks during assembly (in-process quality control or IPQC) are vital to ensure that each unit meets specifications before moving to the next stage.
Finishing processes enhance the appearance and functionality of tire inflaters. These may include painting, coating, or applying labels and decals. Additionally, final quality control checks (FQC) are conducted to verify that all components are correctly assembled and that the inflator operates as intended.
Some manufacturers may also conduct aesthetic inspections to ensure that the product meets branding requirements. This attention to detail can significantly influence customer satisfaction, particularly for B2B buyers looking to maintain a strong brand image.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
B2B buyers should be aware of various international and industry-specific standards that govern the manufacturing and quality assurance of tire inflaters. ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established a robust quality management framework, ensuring consistency in product quality and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, tire inflaters may also need to comply with specific regional regulations, such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For products intended for certain markets, additional certifications may be required, such as American Petroleum Institute (API) standards for inflators designed for use in industrial applications.
Quality control checkpoints are integral to ensuring that tire inflaters meet specified standards throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
Common testing methods used in quality control include pressure testing, electrical safety testing, and performance evaluations under various conditions. These tests help ensure that the inflaters are reliable and safe for consumer use.
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. One effective method is to conduct supplier audits, which involve visiting the manufacturing facility to assess compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes.
Buyers should also request quality assurance reports that document the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. These reports provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality and any issues that may have been encountered during production.
Additionally, third-party inspections can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures. Engaging with third-party organizations that specialize in product testing and certification can help ensure that the inflaters meet international standards and buyer requirements.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification. Different markets may have varying regulatory requirements, which can affect product acceptance.
For instance, while CE marking is crucial for products sold in Europe, other regions may have their own certification processes. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that suppliers can provide the necessary documentation for compliance.
Furthermore, cultural differences in business practices may affect communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear and consistent communication channels with suppliers can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that quality standards are maintained throughout the supply chain.
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for tire inflaters is essential for B2B buyers. By being informed about the various stages of production, relevant standards, and quality control checkpoints, buyers can make educated decisions when selecting suppliers. Additionally, verifying supplier practices through audits and third-party inspections can further ensure that the products meet the required quality standards, ultimately enhancing buyer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring tire inflaters, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful procurement process. By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget.
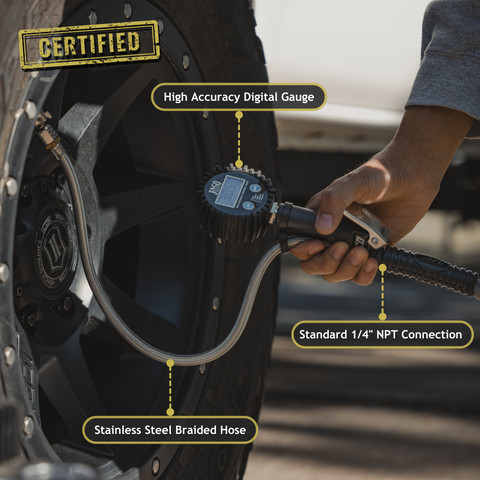
Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Understanding the specific requirements for tire inflaters is crucial. Consider the types of vehicles you will service—passenger cars, trucks, or heavy machinery—and their corresponding tire pressure needs. Look for features such as maximum psi, inflation speed, and compatibility with different inflation mediums (air, nitrogen).
Stay updated on the latest tire inflator technologies and market trends. Innovations such as automatic shutoff features, digital pressure displays, and compact designs can enhance efficiency and user experience. Understanding these trends will help you identify products that offer the best value for your investment.
Before committing to a supplier, thorough vetting is essential. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients, especially those in similar industries or geographic regions. This step ensures that the supplier has a proven track record of reliability and quality.
Ensure that the tire inflators meet relevant quality standards and certifications. This can significantly impact performance, safety, and durability, particularly in demanding environments. Products that have undergone third-party testing or certification can provide additional assurance of quality.
After narrowing down your list of potential suppliers, request detailed quotations. Compare not just the price but also the terms of service, warranty periods, and after-sales support. Look for value-added services such as training or maintenance packages that can enhance the overall value of your purchase.
Strong after-sales support can save time and costs in the long run. Evaluate the warranty offered on the tire inflators and the supplier’s responsiveness to service inquiries. A reliable support system is essential for addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase.
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that the contract clearly outlines all terms, including delivery timelines, payment schedules, and service agreements. Double-check all details to avoid any misunderstandings later. This final step solidifies your procurement and sets the stage for a successful partnership.
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process and secure tire inflaters that meet their operational demands while ensuring quality and reliability.
When sourcing tire inflaters, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
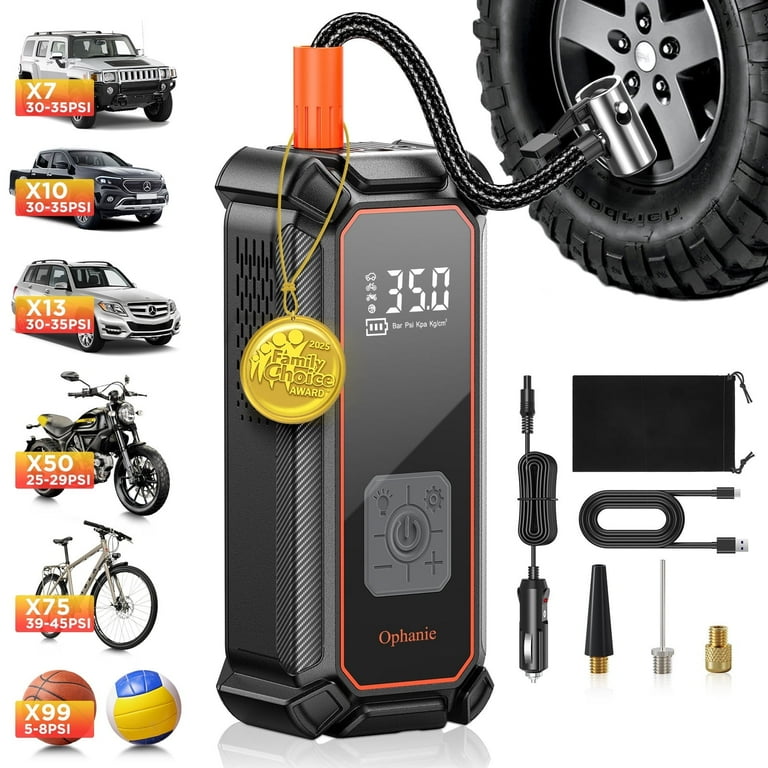

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality components, such as durable plastics, metals, and electronic parts, typically elevate the price. For instance, inflators designed for high-pressure applications or those featuring advanced technology (like digital gauges) may require more expensive materials.
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturing processes. Countries with lower labor costs, such as Vietnam or Brazil, may offer competitive pricing. However, it’s essential to consider the skill level required for assembly and quality checks, as this can affect overall product quality and reliability.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and administrative expenses related to production. Manufacturers with efficient operations may pass savings onto buyers, while those with higher overhead costs may reflect this in their pricing.
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom inflators. Buyers should inquire about these costs if they require unique designs or functionalities, as they can be amortized over larger production runs.
Quality Control (QC): Investments in QC processes ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. Certifications (such as ISO) may add to costs but can enhance marketability and buyer confidence.
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, the shipping method, and any applicable tariffs. International buyers should be aware of these factors, especially when sourcing from regions like Asia or Europe.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary widely based on market demand and competition. Understanding typical margins in the tire inflator market can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
Several factors influence the pricing of tire inflaters, including volume or minimum order quantity (MOQ), specifications and customization, materials, quality certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to reduced unit prices. Suppliers are more willing to negotiate on pricing for bulk purchases, making it beneficial for businesses with high turnover.
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specific PSI ratings or unique designs, can increase costs. Standard models are generally more affordable, so buyers should assess whether customization is necessary for their needs.
Materials: As mentioned earlier, the choice of materials directly impacts cost. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between material quality and price to ensure they receive adequate performance without overspending.
Quality and Certifications: Products with recognized certifications may command higher prices but can assure buyers of their reliability and safety. This is particularly relevant in regions where compliance with local regulations is critical.
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and geographic location can influence pricing. A well-established supplier may offer better service and product quality, justifying a higher price point.
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms can significantly affect total costs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears shipping and insurance costs, impacting the final price a buyer pays.
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing tire inflaters, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume discounts and be prepared to negotiate terms with suppliers. A clear understanding of market prices and competitor offerings can strengthen your bargaining position.
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase costs, consider maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. Selecting high-quality inflators may reduce TCO over time, despite a higher upfront investment.
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Be aware of regional pricing differences and currency fluctuations. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s vital to factor in local market conditions and demands.
Assess Supplier Reliability: Choose suppliers with proven track records for quality and service. Engaging with established manufacturers can minimize risks associated with defects and delays.
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping up-to-date with industry developments can provide insights into pricing fluctuations and emerging technologies, enabling better strategic sourcing decisions.
The prices and cost structures discussed are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific product requirements. Always conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes before finalizing any purchasing decisions.
When it comes to maintaining vehicle performance and safety, ensuring proper tire pressure is crucial. While tire inflaters are a widely recognized solution, several alternative methods can achieve similar outcomes. This analysis provides a comparative overview of tire inflaters against two viable alternatives: portable air compressors and nitrogen inflation systems. Each method has its unique benefits and drawbacks, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand their options.

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
| Comparison Aspect | Tire Inflaters | Portable Air Compressors | Nitrogen Inflation Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Quick inflation; compact design | High pressure; versatile applications | Stable pressure; slower inflation |
| Cost | Moderate ($30 – $100) | Higher initial investment ($100 – $300) | Higher ongoing costs (equipment + nitrogen) |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly; minimal setup | Requires more setup; needs power source | Requires specialized equipment and training |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate; oil changes and filter replacements | Low; periodic nitrogen supply refills |
| Best Use Case | Personal vehicles; emergencies | Workshops; multi-vehicle operations | Fleet management; performance vehicles |
Portable Air Compressors
Portable air compressors are versatile tools that can be used for a wide range of inflation tasks beyond tires, such as powering pneumatic tools or inflating sports equipment. Their performance is generally superior, allowing for higher pressure and faster inflation times. However, they typically require a more significant initial investment and may necessitate a power source, which can limit their portability. Maintenance is moderate, as they may require oil changes and filter replacements over time. They are best suited for businesses with multiple vehicles or those needing robust inflation solutions.
Nitrogen Inflation Systems
Nitrogen inflation systems offer a specialized approach, utilizing nitrogen instead of regular air to inflate tires. The primary advantage of nitrogen is its ability to maintain tire pressure longer and reduce oxidation inside the tire, leading to enhanced tire lifespan and fuel efficiency. However, the initial setup costs can be high, and ongoing expenses include nitrogen refills. Moreover, implementing this system requires specialized equipment and knowledge, which may not be feasible for all businesses. These systems are ideal for fleet operations or performance vehicles where optimal tire performance is crucial.
Selecting the right tire inflation solution depends on various factors, including budget, operational requirements, and specific use cases. For businesses focused on cost-effectiveness and ease of use, tire inflaters present a practical choice, especially for personal vehicles or emergency situations. On the other hand, if your operations involve multiple vehicles or require high-pressure applications, investing in a portable air compressor may yield better long-term value. For those looking to maximize tire performance and longevity, nitrogen inflation systems are worth considering despite their higher costs and complexity. Evaluating these aspects will help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
When selecting tire inflaters for commercial purposes, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial. Here are several critical specifications that buyers should consider:
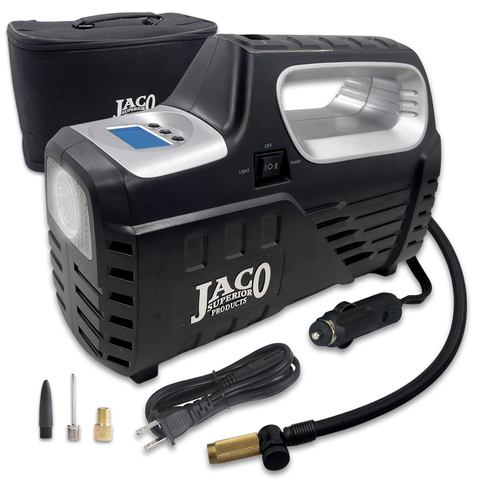

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
The maximum pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates how much air pressure the inflator can produce. For commercial applications, inflators capable of reaching higher PSI are essential, particularly for larger vehicles such as trucks and SUVs, which may require pressures of up to 80 PSI. A higher max pressure ensures versatility across different tire types and sizes.
The duty cycle refers to the amount of time an inflator can operate before it needs to cool down. This is often expressed in minutes (e.g., 20 minutes of continuous use followed by a 30-minute rest). A longer duty cycle is vital for businesses that require rapid turnaround on tire service, minimizing downtime and increasing productivity.
Tire inflaters can be powered by various sources, including AC power, DC power (from a car battery), or rechargeable batteries. The choice of power source affects portability and convenience. For businesses operating in remote areas or requiring mobility, battery-operated inflators are beneficial, whereas workshop settings may favor AC-powered models.
The accuracy of the pressure gauge is vital for ensuring that tires are inflated to the correct specifications. Digital gauges provide precise readings and often include preset options for common tire pressures. Analog gauges, while still effective, may require more manual adjustments. Choosing an inflator with a reliable gauge helps prevent under- or over-inflation, which can lead to tire damage and safety risks.
Inflation speed, measured in liters per minute (L/min), determines how quickly an inflator can fill a tire. Faster inflators save time, which is particularly important in high-volume tire service environments. Understanding the average inflation time for different tire sizes can help businesses optimize their service efficiency.
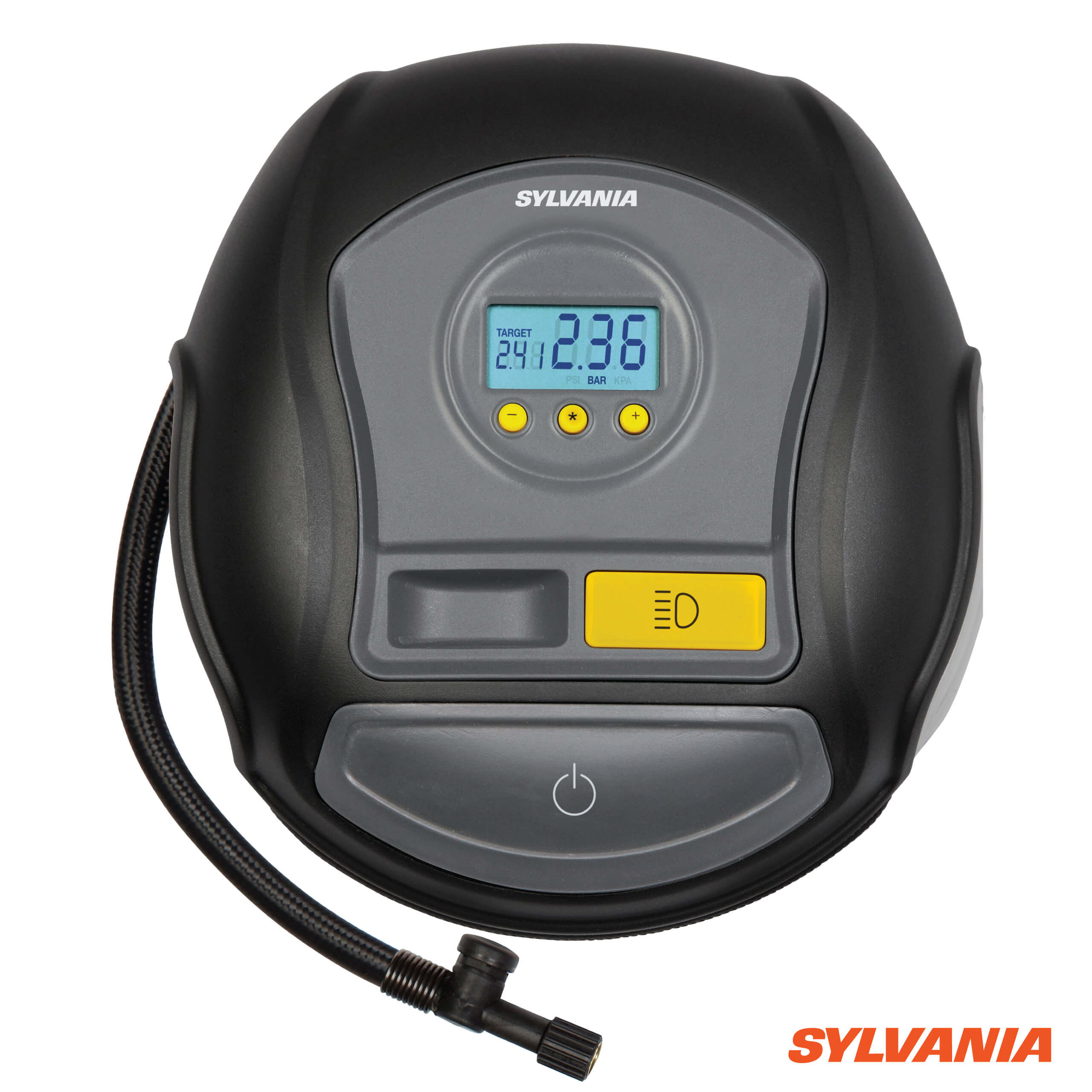

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiations with suppliers. Here are key terms to understand:
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are sold under another brand’s name. In the context of tire inflaters, knowing whether a product is OEM can indicate the quality and compatibility with specific tire models, which is essential for maintaining standards in service operations.
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for businesses looking to stock inventory without overcommitting financially. This is especially relevant for B2B buyers who may be managing cash flow while ensuring they have sufficient stock for customer demand.
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers. For tire inflaters, submitting an RFQ can lead to better pricing, especially when purchasing in bulk. This process helps businesses compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions.
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping costs and risk management. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers operating in global markets, ensuring clarity in logistics and delivery responsibilities.
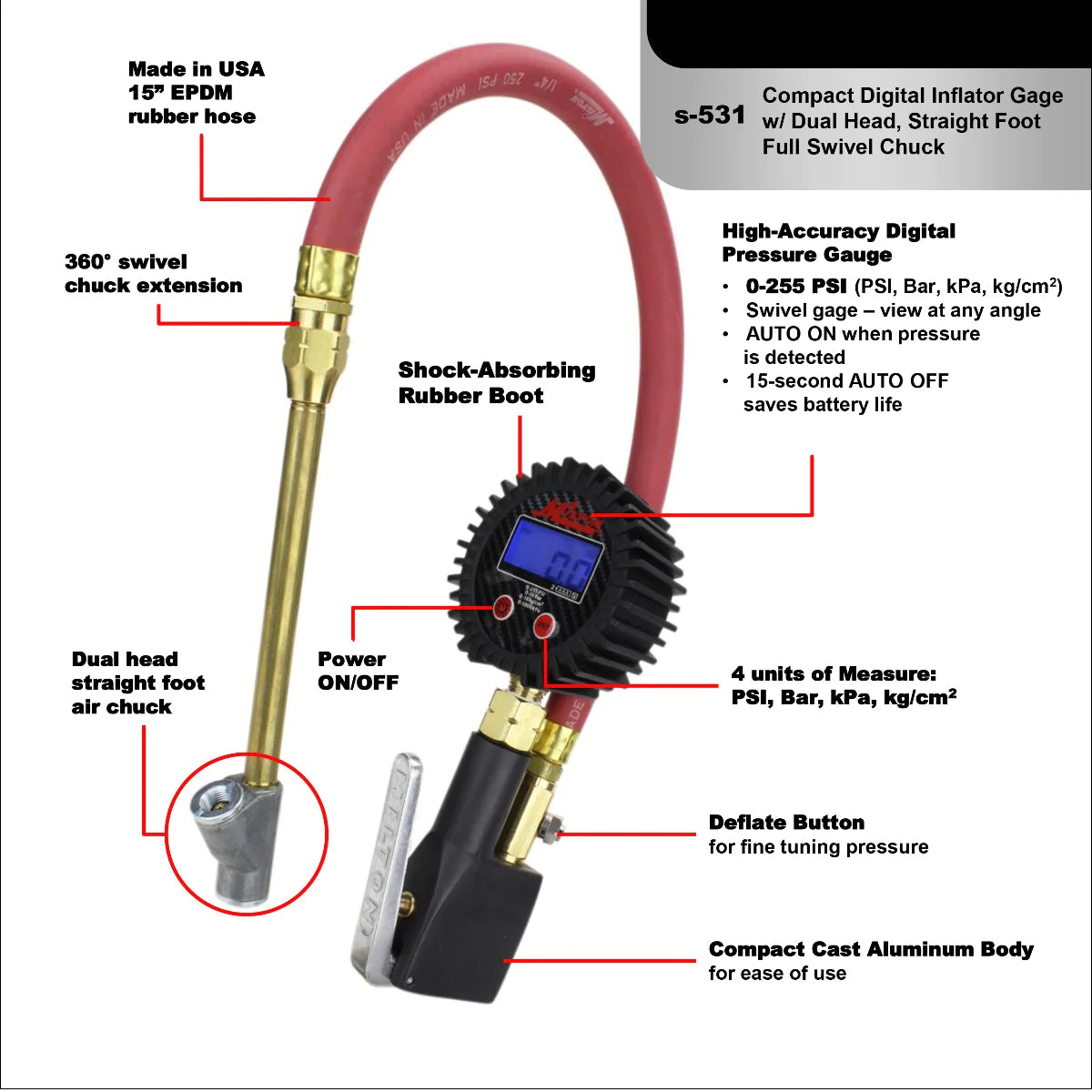
Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
The warranty period is the duration for which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects. A longer warranty period often reflects confidence in product quality and durability, providing peace of mind to businesses that rely on tire inflaters for their operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they choose the right tire inflaters that meet their operational needs and business goals.
The tire inflators market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increased vehicle ownership globally, particularly in emerging economies such as Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia. Factors such as rising awareness of vehicle maintenance, the importance of tire pressure in fuel efficiency, and the growing trend of DIY vehicle care are propelling demand. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of smart tire inflators equipped with digital pressure gauges and automatic shutoff features, enhancing user convenience and safety.
International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide innovative and reliable products. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology is becoming a significant trend, with features like mobile app connectivity for tire pressure monitoring and alerts. Moreover, the demand for portable and battery-operated inflators is rising as consumers prioritize convenience and ease of use. Buyers from regions like Brazil and Vietnam are particularly interested in compact models that offer versatility for various applications, from personal vehicles to commercial fleets.
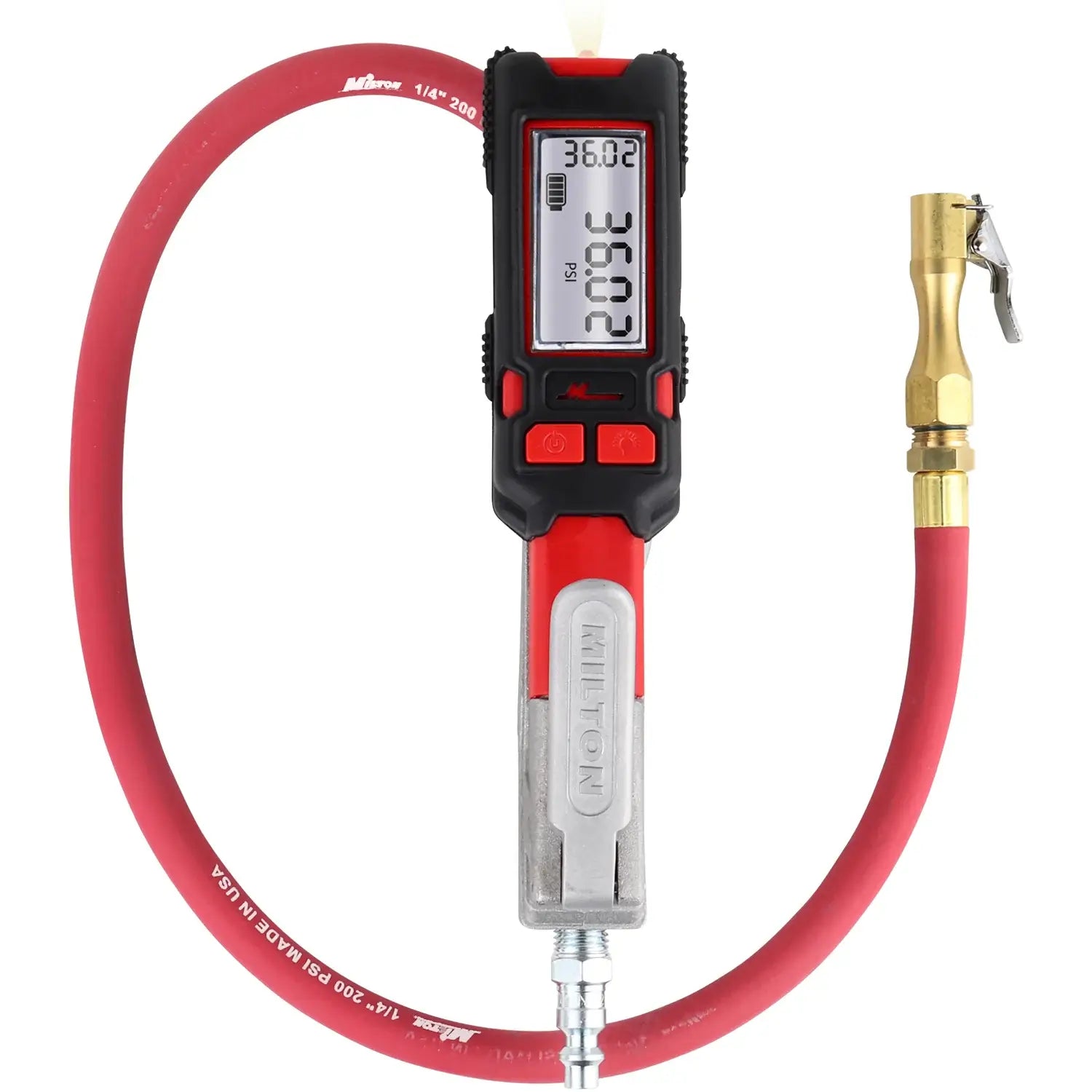

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Supply chain dynamics are also evolving, with manufacturers focusing on local sourcing to reduce lead times and costs. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where logistics can be challenging. As manufacturers adapt to these market demands, international partnerships and collaborations are becoming essential for competitive pricing and product availability.
The tire inflators sector is increasingly influenced by sustainability concerns, as B2B buyers are more conscious of the environmental impact of their purchases. The production and disposal of tire inflators can contribute to waste and pollution, prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing has become a priority, with businesses looking for suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and processes.
Green certifications are gaining traction, with manufacturers being encouraged to obtain certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, the use of recyclable materials in inflator construction is becoming a key differentiator in the market. Buyers are also interested in products that offer energy efficiency, as they align with broader sustainability goals.
Moreover, companies are increasingly focusing on transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that all components are sourced responsibly. This shift not only meets the demands of eco-conscious consumers but also enhances brand reputation and loyalty in competitive markets. As sustainability continues to shape the landscape, B2B buyers will benefit from aligning with suppliers who prioritize ethical practices and environmental stewardship.
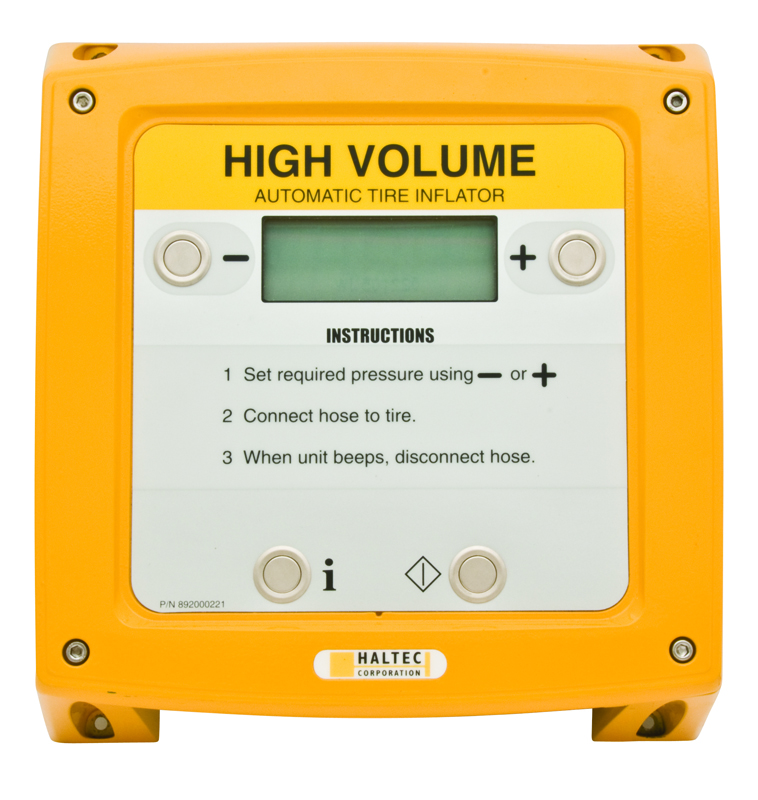

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
The evolution of tire inflators reflects the broader advancements in automotive technology and consumer needs. Initially, manual inflators were the norm, requiring significant physical effort and time. As automotive maintenance became more accessible, the introduction of electric and portable inflators revolutionized the market, allowing for quick and efficient tire inflation.
Over the past two decades, technological advancements have led to the development of automatic and smart inflators that not only inflate tires but also monitor pressure levels. Features such as built-in pressure gauges, programmable settings, and even smartphone connectivity have become standard, catering to a tech-savvy consumer base.
This evolution underscores the importance of innovation in the tire inflators sector, as manufacturers strive to meet the changing demands of B2B buyers. As the market continues to grow, the emphasis on performance, convenience, and sustainability will likely drive further advancements, shaping the future of tire inflators.
How do I solve issues with tire inflaters not reaching the desired pressure?
To address problems with tire inflaters failing to achieve the required pressure, first check if the inflator is compatible with the tire specifications. Ensure that the inflator’s maximum PSI rating meets or exceeds your tire’s requirements. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the nozzle and checking for leaks in hoses or connections, can also help. If the issue persists, consider investing in a higher-quality inflator known for its accuracy and reliability. Lastly, review the manufacturer’s guidelines for optimal usage practices to avoid miscalculations.
What is the best tire inflator for commercial use?
The best tire inflator for commercial use typically features a high PSI capacity, rapid inflation speed, and durability. For instance, models like the Viair 88P are highly regarded for their speed and efficiency, especially for larger tires on trucks and SUVs. Additionally, inflators with automatic shut-off features and digital pressure gauges enhance user convenience and safety. When selecting, consider the specific needs of your fleet or operations, such as power source and portability, to ensure it aligns with your business requirements.
What factors should I consider when sourcing tire inflators internationally?
When sourcing tire inflators internationally, consider several factors: supplier reliability, product quality, shipping logistics, and compliance with local regulations. Verify the manufacturer’s reputation through reviews and references. Assess the quality of materials and technology used in the inflators to ensure they meet your operational standards. Additionally, factor in shipping costs, lead times, and any import duties that may apply. It’s also beneficial to have clear communication regarding warranties and after-sales support to avoid complications.
How can I vet suppliers for tire inflaters?
To effectively vet suppliers for tire inflaters, begin by conducting thorough research on potential manufacturers. Request certifications, such as ISO or CE, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Engage in direct communication to gauge responsiveness and transparency. Consider visiting their facilities if possible, or request video tours to assess production capabilities. Additionally, seek out reviews or testimonials from other businesses that have purchased from them. Establishing a trial order can also provide insight into their reliability and product quality before committing to larger orders.
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for tire inflators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for tire inflators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of inflators. Typically, MOQs can range from as low as 50 units to several hundred. Suppliers may set higher MOQs for customized inflators or specialized features. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their flexibility on MOQs, especially if you are a smaller business. Some suppliers might offer reduced MOQs for first-time orders or during promotional periods, so it’s worth exploring these options.
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing tire inflaters?
Payment terms for purchasing tire inflaters can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers might offer letter of credit arrangements, particularly for larger orders. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, PayPal, or escrow services, which can provide additional security. It’s also advisable to establish a clear agreement on payment schedules and conditions to avoid misunderstandings during the transaction process.
How can I customize tire inflaters for my business needs?
Customizing tire inflaters involves discussing specific requirements with your supplier, including branding, color, and features. Many manufacturers offer options for custom logos or unique configurations tailored to your business needs. Be clear about the functionalities you require, such as digital gauges, automatic shut-off, or compatibility with nitrogen inflation. Additionally, inquire about the minimum order quantities for customized products and lead times for production, as these factors can influence your purchasing decision.
What quality assurance measures should I implement for tire inflaters?
Implementing quality assurance measures for tire inflaters includes establishing a comprehensive inspection process upon receipt of goods. This should involve checking for physical damages, verifying specifications, and conducting performance tests to ensure they meet the required standards. Collaborate with suppliers to understand their quality control processes and request documentation of compliance with international safety standards. Additionally, consider periodic audits of your suppliers to ensure ongoing adherence to quality benchmarks, which can help maintain product reliability in your operations.
Domain: martinsindustries.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Automatic Tire Inflators, Wall-mounted Tire Inflators, handheld or manual options, certified inflators for accurate inflation/deflation, digital gauge, nitrogen-inflation compatibility, various models including Handheld digital tire inflator (Flate Mate Handheld MH-30), Analog Handheld Tire Inflator (Flate Mate Analog Handheld MH-31-PSI), Automatic Tire Inflator (Flatematic Handheld MHA-100), Auto…
In the evolving landscape of tire inflaters, strategic sourcing is paramount for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. The diversity of products available—from automatic and wall-mounted inflators to portable options—offers tailored solutions for varying market needs across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the distinct features, such as digital gauges, compatibility with nitrogen inflation, and portability, empowers buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific requirements.
Moreover, as tire maintenance becomes increasingly vital for optimizing vehicle performance and safety, the demand for reliable inflators is set to grow. By prioritizing quality and cost-effectiveness in their sourcing strategies, buyers can position themselves competitively in their respective markets.
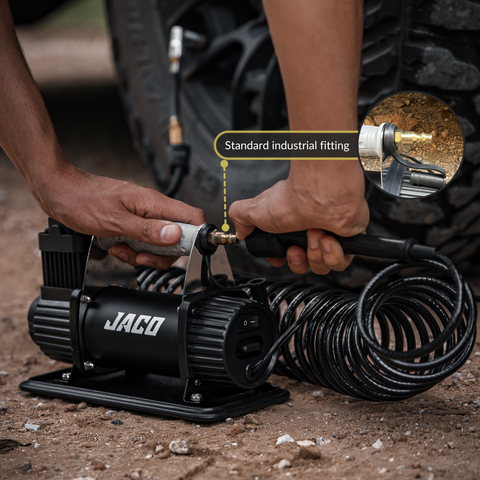

Illustrative image related to tire inflaters
Looking ahead, it is essential for businesses to engage with reputable suppliers who can provide innovative and efficient inflator solutions. As the market continues to expand, leveraging strategic partnerships will not only enhance product offerings but also drive long-term growth. Now is the time for international buyers to capitalize on these opportunities and secure a sustainable supply chain for tire inflaters that meets the demands of a dynamic automotive industry.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.