Navigating the complexities of tire inflation in today’s global market poses significant challenges for B2B buyers. Understanding the intricacies of tire pressure management is crucial for businesses across various sectors, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The importance of sourcing reliable tire inflation solutions cannot be overstated, as improper tire pressure can lead to increased fuel consumption, reduced tire lifespan, and safety hazards. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international buyers, detailing the different types of tire inflation systems, their applications in diverse industries, and critical supplier vetting processes.
Within these pages, you will discover actionable insights on cost considerations, maintenance best practices, and the latest innovations in tire inflation technology. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can make informed purchasing decisions that not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to sustainability goals. Whether you’re looking to optimize fleet performance or ensure the safety of your logistics operations, this guide provides the tools necessary to navigate the tire inflation market effectively. With a focus on quality and reliability, you will be empowered to select the best solutions tailored to your specific needs, ultimately driving success in your business endeavors.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Inflation | Standard method using compressed air | Passenger vehicles, light trucks | Pros: Widely available, cost-effective. Cons: Requires regular monitoring for pressure loss. |
| Nitrogen Inflation | Uses nitrogen gas instead of regular air | Commercial fleets, aviation | Pros: Reduces pressure loss, enhances tire life. Cons: Higher initial cost, limited availability. |
| Foam-filled Tires | Tires filled with a solid foam material | Construction, military vehicles | Pros: Puncture-proof, no air pressure issues. Cons: Heavier, limited flexibility in tire design. |
| Self-Sealing Tires | Incorporate sealant to automatically seal punctures | Delivery vehicles, emergency services | Pros: Reduces downtime, enhances safety. Cons: Potentially higher cost, may not seal larger punctures. |
| Adjustable Pressure | Allows for on-the-fly inflation adjustments | Off-road vehicles, specialized transport | Pros: Optimizes performance for varying conditions. Cons: More complex systems, requires training for use. |
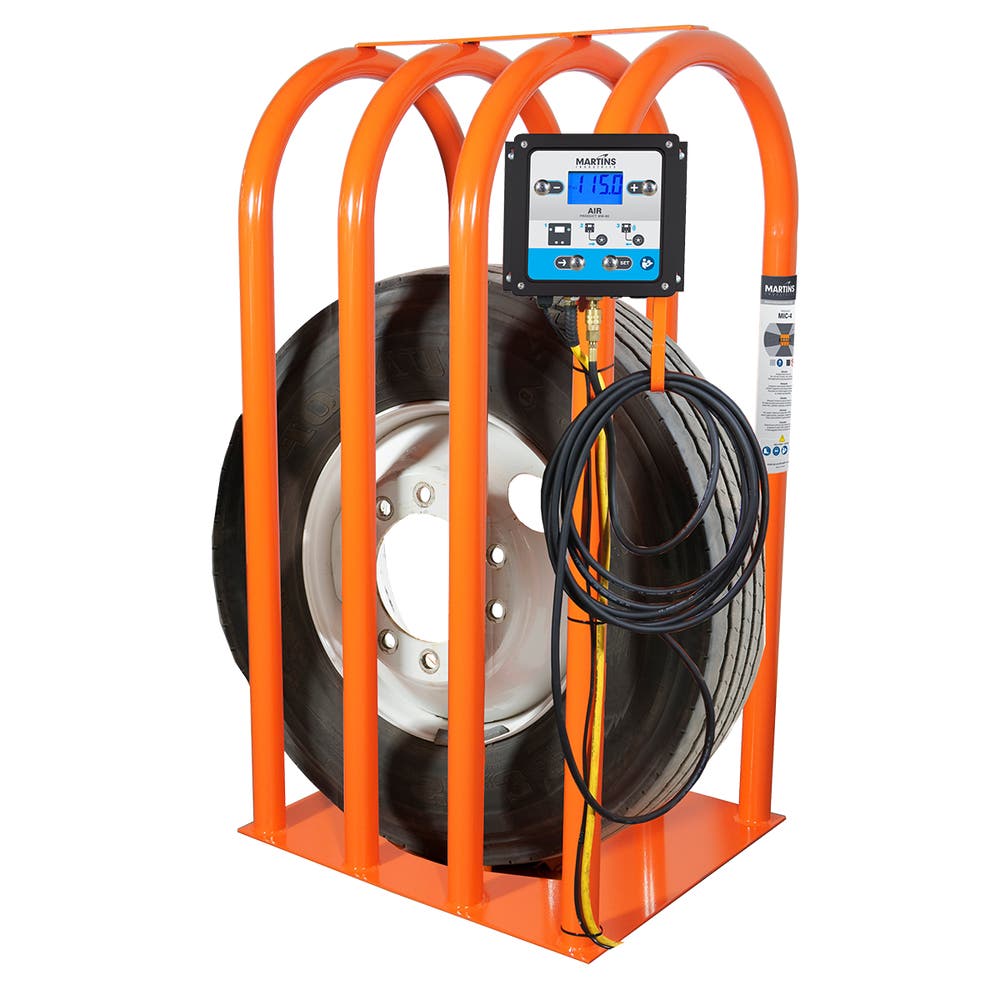
Air inflation is the most common method used for tires, employing compressed air to achieve the desired pressure. This method is readily available and cost-effective, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including passenger vehicles and light trucks. B2B buyers should consider the need for regular pressure checks, as tires naturally lose air over time, which can lead to performance issues and increased fuel consumption if not monitored.
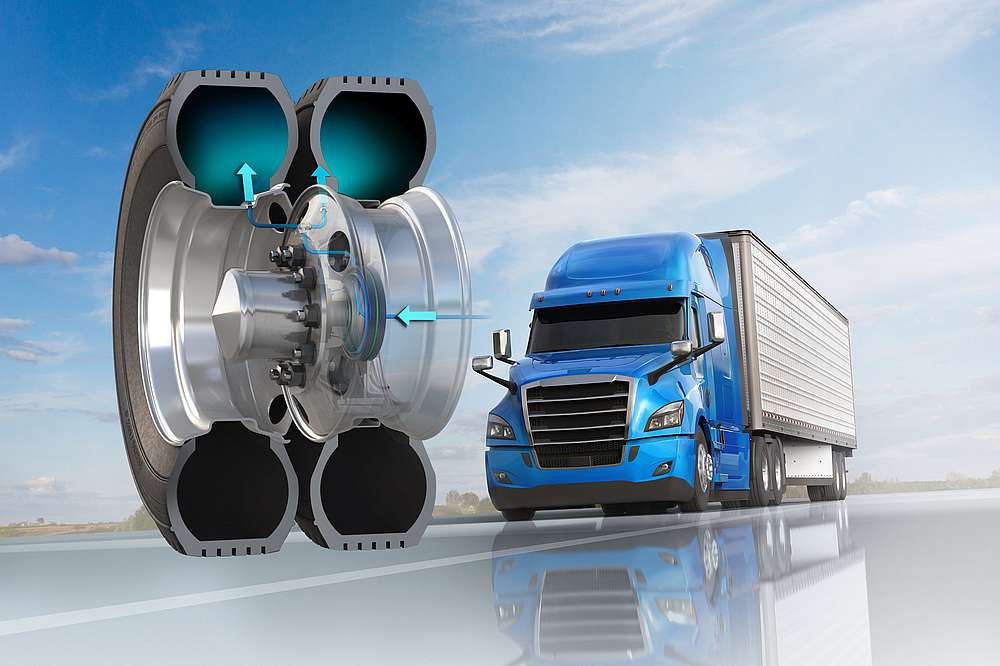
Nitrogen inflation involves filling tires with nitrogen gas instead of regular air, which can significantly reduce pressure loss and improve tire longevity. This method is particularly beneficial for commercial fleets and aviation, where tire performance is critical for safety and efficiency. While the initial costs may be higher, the long-term savings on tire replacements and fuel efficiency make it an attractive option for businesses focused on operational efficiency.
Foam-filled tires are designed to be puncture-proof by replacing air with a solid foam material. This makes them ideal for use in construction and military vehicles, where reliability is paramount. The key consideration for B2B buyers is the trade-off between the added weight of foam-filled tires and the elimination of air pressure concerns, which can impact overall vehicle performance.
Self-sealing tires are equipped with a built-in sealant that automatically seals punctures, making them particularly advantageous for delivery vehicles and emergency services. These tires can minimize downtime and enhance safety, as drivers can continue operating even after sustaining a puncture. However, buyers should weigh the benefits against the potentially higher costs and limitations in sealing larger punctures.
Adjustable pressure systems allow for dynamic inflation adjustments based on varying road conditions, making them popular in off-road vehicles and specialized transport applications. This flexibility can optimize tire performance, improving traction and handling. However, the complexity of these systems may require additional training for personnel, which is an important consideration for B2B buyers looking to implement such technologies in their fleets.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tire inflation | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Fleet Management | Enhances safety and reduces operational costs | Need for reliable inflation systems and monitoring tools |
| Agriculture | Agricultural Machinery | Improves efficiency and reduces downtime | Durable inflation solutions suitable for rugged conditions |
| Construction | Heavy Equipment | Ensures optimal performance and extends equipment life | Robust inflation systems that can handle varying pressures |
| Logistics & Warehousing | Material Handling Equipment | Increases productivity and minimizes tire-related issues | Availability of portable inflation solutions for flexibility |
| Automotive Services | Tire Maintenance Services | Enhances customer satisfaction and safety | Access to accurate tire pressure gauges and inflation tools |
In transportation, maintaining proper tire inflation is critical for fleet management. Companies often utilize centralized tire inflation systems that monitor and adjust tire pressure automatically, ensuring safety and reducing fuel consumption. Properly inflated tires can lead to a 3% improvement in fuel efficiency, which is significant for fleet operators facing rising fuel costs. International buyers should consider sourcing high-quality, reliable inflation systems that can withstand various environmental conditions, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East where temperatures can fluctuate dramatically.
In agriculture, tire inflation is vital for agricultural machinery such as tractors and harvesters. Properly inflated tires enhance traction and reduce soil compaction, which can improve crop yields. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased fuel consumption and accelerated wear, leading to costly downtimes. Buyers in South America, where agriculture is a major industry, should seek durable inflation solutions that can operate effectively in rugged terrain and varying weather conditions, ensuring optimal performance year-round.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Construction companies rely on heavy equipment that requires precise tire inflation to function optimally. Proper tire pressure ensures that machinery operates efficiently, reducing the risk of breakdowns that can delay projects. Over-inflated or under-inflated tires can lead to uneven wear and decreased stability, posing safety risks. Buyers in Europe should focus on sourcing robust inflation systems that can accommodate the high demands of construction sites, including those that can handle varying pressures and provide real-time monitoring capabilities.
In logistics and warehousing, proper tire inflation is crucial for material handling equipment such as forklifts and pallet jacks. Ensuring optimal tire pressure can significantly increase productivity by minimizing tire-related issues that can lead to operational delays. Companies should consider portable tire inflation solutions that allow for quick adjustments on the go, especially in fast-paced environments. For international buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating temperatures, sourcing reliable and easy-to-use inflation tools is essential to maintain operational efficiency.
For automotive service providers, maintaining correct tire pressure is vital for customer safety and satisfaction. Offering tire inflation services can enhance the overall service experience, as properly inflated tires improve vehicle handling and fuel efficiency. This not only leads to happier customers but also reduces the risk of tire-related accidents. Automotive service businesses in the Middle East and Europe should invest in accurate tire pressure gauges and reliable inflation equipment to ensure they can meet customer needs effectively.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those managing fleets, face significant challenges due to underinflated tires. When tires are not properly inflated, they wear out faster, leading to increased replacement costs and reduced vehicle efficiency. This problem is exacerbated in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, such as the Middle East and South America, where tire pressure can drop significantly with temperature changes. The result is not only financial strain but also compromised safety, as underinflated tires can lead to blowouts and accidents.
The Solution: To combat the issue of underinflation, businesses should implement a proactive tire maintenance program. This includes regular tire pressure checks, ideally once a month or before long trips, using calibrated gauges. Businesses can invest in digital tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) that provide real-time data on tire pressure, alerting managers when levels fall below recommended thresholds. Additionally, creating a comprehensive training program for drivers on the importance of tire maintenance and how to check tire pressure can foster a culture of safety and efficiency. This proactive approach not only extends tire life but also enhances overall fleet safety and performance.
The Problem: Overinflation is another prevalent issue faced by B2B buyers, particularly in environments where drivers may not be aware of the correct tire pressure specifications. Overinflated tires can lead to uneven tread wear and a harsher ride, negatively impacting vehicle control and safety. In Europe, where regulatory compliance is strict, businesses risk penalties if their vehicles are found to be in poor condition due to overinflated tires.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with overinflation, businesses should ensure that all employees are educated on how to read the tire pressure recommendations, which are typically found on the driver’s side door jamb or in the vehicle manual, rather than relying on the maximum pressure listed on the tire sidewall. Implementing a routine check before vehicles are dispatched, paired with the use of portable tire inflators equipped with accurate gauges, can help maintain the correct pressure. Additionally, creating a checklist for pre-trip inspections can ensure that tire pressure is consistently monitored, fostering a safer driving environment and reducing the likelihood of tire-related incidents.
The Problem: Businesses in regions with distinct seasonal changes, such as those in Africa and parts of Europe, often switch between summer and winter tires. However, this transition can lead to inconsistent tire pressure management. Tires naturally lose pressure over time, and the change in temperature from summer to winter can exacerbate this issue. Without proper monitoring, businesses may find themselves with poorly inflated tires, leading to safety hazards and increased operational costs.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
The Solution: To tackle the challenges of seasonal tire changes, businesses should establish a seasonal tire management protocol. This involves a thorough inspection and pressure check when switching tires. Using a portable tire inflation compressor can make this process efficient and ensures that all tires are inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended PSI. Furthermore, businesses can invest in training sessions that educate staff about the importance of seasonal tire maintenance, including the need to check pressure more frequently during the transition periods. By implementing these strategies, businesses can enhance safety and performance while minimizing costs associated with tire wear and potential accidents.
When selecting materials for tire inflation systems, several options are commonly utilized, each with distinct properties and implications for performance, durability, and cost. Understanding these materials can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
Key Properties: Rubber is the primary material used in tire construction, offering excellent elasticity and resilience under varying pressure and temperature conditions. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C and pressures up to 44 PSI, making it suitable for diverse climates.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Pros & Cons: Rubber is durable and provides good traction and flexibility, essential for optimal tire performance. However, it can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and ozone, leading to cracking and loss of elasticity. The manufacturing process can also be complex, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Impact on Application: Rubber’s compatibility with air makes it ideal for tire inflation. However, its performance can be affected by environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, which are more prevalent in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials. In regions with high UV exposure, selecting UV-resistant rubber compounds can enhance longevity.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Key Properties: Steel is often used in tire rims and valves, providing high strength and resistance to deformation. It typically has a tensile strength of around 370 MPa and can handle high pressures without significant risk of failure.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s durability and strength make it an excellent choice for structural components. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, particularly in humid or saline environments, which can lead to premature failure. The cost of steel can also be higher compared to alternatives like aluminum.
Impact on Application: Steel components are critical for maintaining tire integrity under high pressure. However, the presence of corrosion can compromise the sealing capabilities of valves, leading to air loss.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in coastal regions or areas with high humidity should consider corrosion-resistant coatings or stainless steel options. Compliance with standards like ISO 9001 for quality management can also be beneficial.
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly thermoplastics, are used in tire valves and inflation systems. They offer lightweight properties and can withstand pressures up to 30 PSI, depending on the type used.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of plastics can improve fuel efficiency by reducing overall vehicle weight. However, they may not offer the same durability as metals, and their performance can degrade under extreme temperatures or UV exposure.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for low-pressure applications and are often used in consumer vehicles. Their compatibility with air makes them useful in tire inflation systems, but they may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the plastics used meet relevant safety standards, such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding plastic use can help in compliance.
Key Properties: Composites combine materials such as carbon fiber and resin, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to environmental degradation. They can handle pressures similar to steel and are often used in high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and offer excellent resistance to corrosion and UV degradation. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and require specialized processes, which may not be feasible for all manufacturers.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for high-performance vehicles where weight reduction is critical. Their ability to maintain structural integrity under pressure enhances tire performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the cost-benefit ratio of composites, especially in regions where budget constraints are significant. Compliance with advanced material standards such as ISO 14001 for environmental management may also be relevant.
| Material | Typical Use Case for tire inflation | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Tire construction | Excellent elasticity and resilience | Degrades under UV exposure | Medium |
| Steel | Rims and valves | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Plastics | Tire valves and inflation systems | Lightweight, improves fuel efficiency | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Composites | High-performance tire applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in tire inflation systems, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
The manufacturing process for tire inflation equipment involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Common materials for tire inflation systems include high-grade rubber, metal alloys, and plastics. Each material is chosen for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear and tear. Suppliers often source these materials from certified vendors to ensure quality.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
In this phase, raw materials undergo rigorous testing to check for defects or impurities. For instance, rubber compounds may be tested for elasticity and tensile strength, while metals are assessed for corrosion resistance. Ensuring that these materials meet quality standards is crucial, as they directly impact the performance and lifespan of the tire inflation equipment.
The forming stage involves transforming raw materials into usable components. Techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, and die-casting are commonly employed. For instance, rubber components are often created through injection molding, where heated rubber is injected into molds to create specific shapes.
Metal parts are typically formed through processes like stamping or machining, which allow for precise dimensions and tolerances. Each method has its advantages, depending on the complexity and volume of production. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific forming techniques used by suppliers to understand the potential impact on product quality.
Once individual components are formed, they proceed to the assembly stage. This stage requires careful attention to detail, as the effectiveness of tire inflation systems depends on the proper integration of various parts. Automated assembly lines are often used to enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
During assembly, components such as pressure gauges, hoses, and valves are combined to create a complete tire inflation system. Quality checks are performed at this stage to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended. B2B buyers should ask suppliers about their assembly processes and any specific machinery or technology employed to guarantee precision.
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the product’s aesthetic and functional qualities. This may involve surface treatments, painting, or applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear. Finishing processes are essential for ensuring the durability and longevity of tire inflation equipment, especially in harsh environments.
Quality control checkpoints during this stage include visual inspections and functionality tests. B2B buyers should consider asking for documentation regarding the finishing processes to verify that they align with international quality standards.
Quality assurance in tire inflation manufacturing is critical for ensuring safety and performance. Various international standards, such as ISO 9001, outline the requirements for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for compliance with EU regulations and API standards for petroleum equipment can be crucial indicators of quality. These certifications ensure that the products meet specific safety and environmental standards.
B2B buyers should verify whether suppliers hold these certifications, as they can significantly impact product reliability and acceptance in different markets.
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for tire inflation equipment. Key checkpoints include:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process. Suppliers should provide documentation to confirm that materials meet specified standards.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that products meet quality standards. This stage may involve monitoring machinery and operators.
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection is performed to check for defects and ensure functionality. This step is crucial for verifying that the tire inflation equipment is ready for market.
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that suppliers adhere to strict quality control measures:
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with quality standards and identify potential issues before they escalate.
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes, including the frequency of inspections and types of tests performed.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party organizations to evaluate suppliers can offer an unbiased assessment of quality control practices.
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances exist in quality control that should be considered:
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding safety and environmental impact. Understanding these regulations can help buyers ensure that products are compliant and marketable.
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly between regions. Buyers should be aware of these differences to foster effective partnerships with suppliers.
Logistics and Supply Chain Issues: International shipping can introduce risks such as damage during transit. Buyers should verify that suppliers have robust packaging and handling procedures to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in tire inflation equipment is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and adhering to international standards, businesses can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products. Verifying supplier QC through audits, reports, and third-party inspections further enhances the reliability of the supply chain, making it easier for buyers to meet their operational needs.
To ensure the optimal performance of tires and enhance safety, having a reliable tire inflation process is crucial for businesses. This guide provides a comprehensive checklist that B2B buyers can follow when procuring tire inflation solutions, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Understanding the specific requirements for tire inflation is the first step. Consider the types of vehicles in your fleet and their respective tire sizes and specifications. Additionally, assess the operational environment—whether your vehicles operate in extreme temperatures or rough terrains—as this will influence your tire inflation strategy.
Begin by evaluating potential suppliers based on their product offerings and technological capabilities. Look for suppliers that provide a range of tire inflation solutions, including portable compressors, digital gauges, and automated systems. Ensure they have experience serving businesses in your industry, as this can reflect their understanding of your unique needs.
It’s essential to confirm that your chosen suppliers have the necessary certifications and adhere to industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management can indicate a commitment to consistent product quality and service. This verification can help mitigate risks associated with product failures and ensure compliance with local regulations.
When assessing tire inflation products, focus on key specifications such as pressure range, accuracy, and ease of use. Look for features like automatic shut-off, built-in pressure gauges, and compatibility with various tire sizes. These attributes can significantly enhance operational efficiency and safety during tire maintenance.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Reliable after-sales support is vital for maintaining tire inflation equipment. Inquire about warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and technical support services. A supplier that offers robust customer service can help resolve issues quickly, minimizing downtime in your operations.
Before finalizing your procurement decision, request demonstrations or trial periods for the tire inflation products. This allows you to evaluate the equipment’s performance in real-world conditions and ensure it meets your operational expectations. Observing how products work in practice can provide valuable insights into their usability and reliability.
Finally, analyze the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase price, maintenance costs, and potential savings from improved tire longevity and fuel efficiency. A cost-effective tire inflation solution can lead to significant long-term savings and contribute positively to your bottom line.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for tire inflation solutions, ensuring they select options that enhance safety, efficiency, and overall operational performance.
When sourcing tire inflation solutions, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
Materials: The quality of raw materials significantly influences the cost. For tire inflation equipment, this encompasses rubber for hoses, metals for fittings, and electronic components for digital gauges. Sourcing high-quality materials can enhance durability and performance but may increase initial costs.
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographic location and skill level. Regions with higher wages may see increased manufacturing costs, while automated processes can reduce labor expenses. For international buyers, consider the labor cost dynamics in the supplier’s country.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, which is particularly vital for suppliers operating in competitive markets.
Tooling: Specialized tools and molds for manufacturing tire inflation products represent a significant upfront investment. Suppliers may pass these costs onto buyers, particularly for customized or specialized products.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet safety and performance standards incurs costs. Rigorous QC processes can reduce defects but may add to the overall price.
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and regional regulations. Understanding local logistics can help buyers anticipate additional costs.
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing, which can range significantly depending on market competition and product differentiation.
Several factors influence the pricing of tire inflation solutions:
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should evaluate their needs and negotiate volume discounts.
Specifications and Customization: Customized products can incur higher costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. Clearly defined specifications can help manage costs.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials impacts pricing. High-quality, certified components may cost more upfront but offer better longevity and performance, ultimately reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service level can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices, but the assurance of performance can justify the cost.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the final price and logistics responsibilities.
To achieve favorable pricing, B2B buyers can adopt several strategies:
Research and Benchmarking: Gather market data to understand standard pricing and negotiate effectively. Knowing the average market rates can provide leverage during discussions.
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing, especially for repeat orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for loyal customers.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating pricing, factor in long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and efficiency. A higher initial investment in quality products may yield savings over time.
Be Flexible with Payment Terms: Offering upfront payment or flexible payment options may encourage suppliers to provide better pricing or discounts.
Leverage Competition: Engage multiple suppliers to foster competition. This can help negotiate better terms and prices.
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances can affect pricing:
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact the final cost. Buyers should monitor currency trends and negotiate terms that mitigate risks.
Import Duties and Taxes: Understanding local regulations regarding import duties and taxes is essential for accurate cost assessments.
Local Market Conditions: Prices may vary based on local demand and supply dynamics. Buyers should assess regional markets to identify competitive pricing.
Prices for tire inflation products can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough due diligence and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate and up-to-date pricing tailored to their specific needs.
When considering tire inflation solutions, it’s essential to evaluate alternatives that can deliver similar benefits while addressing specific business needs. Various technologies and methods can optimize tire performance and safety, each with distinct characteristics. This analysis provides a comparative overview of traditional tire inflation against two notable alternatives: nitrogen tire inflation and automatic tire inflation systems.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
| Comparison Aspect | Tire Inflation | Nitrogen Tire Inflation | Automatic Tire Inflation Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Standard performance; effective for maintaining PSI | Improved performance; maintains pressure longer, reduces oxidation | Consistent pressure management; automatically adjusts PSI |
| Cost | Low initial cost; ongoing maintenance required | Higher initial cost; longer-term savings on tire life and fuel | High upfront investment; potential savings on labor and tire wear |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple process; requires manual checks | Requires specialized equipment for filling | Complex setup; requires installation and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed; prone to air loss | Less frequent checks; nitrogen remains stable | Minimal; relies on sensors and automated systems |
| Best Use Case | General use; effective for most vehicles | Fleets and high-performance vehicles | Commercial fleets needing constant pressure monitoring |
Nitrogen tire inflation involves filling tires with nitrogen gas instead of regular air. This method offers several advantages, such as reduced oxidation and moisture, which can lead to longer tire life and improved fuel efficiency. Nitrogen molecules are larger than oxygen, which reduces the rate of pressure loss. However, the initial cost of nitrogen filling equipment can be higher, and it may require specialized service providers, making it less accessible for some businesses.
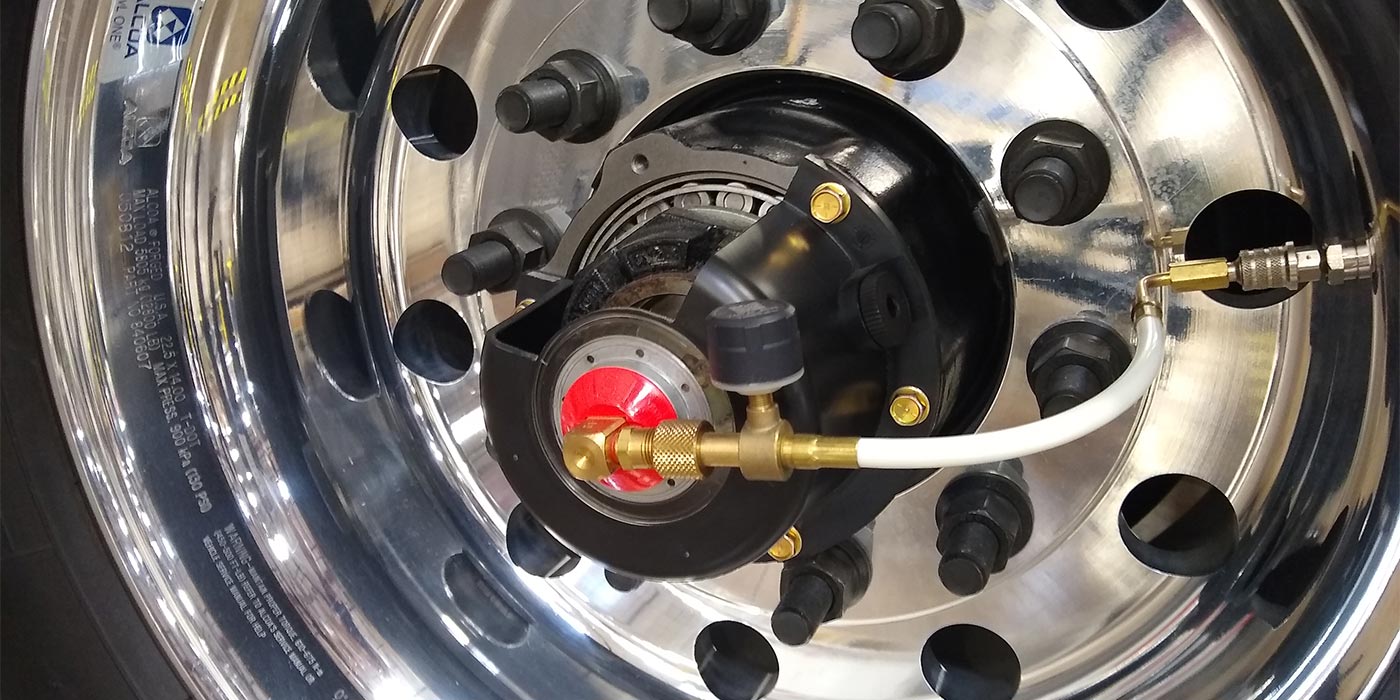
Automatic tire inflation systems (ATIS) utilize sensors to monitor and adjust tire pressure continuously. This technology ensures that tires remain within the optimal PSI range, enhancing safety and performance. ATIS can significantly reduce the risk of under-inflation and associated hazards, providing a proactive approach to tire management. However, the complexity and high initial investment can be a barrier for smaller operations. Ongoing maintenance and potential repairs may also be necessary, adding to the overall cost.
Selecting the appropriate tire inflation method depends on your specific needs, operational scale, and budget constraints. For businesses with diverse vehicle types and limited resources, traditional tire inflation may suffice. However, for those managing large fleets or prioritizing performance and safety, nitrogen inflation or automatic systems could provide significant long-term benefits. Assessing the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and potential savings in tire wear and fuel efficiency, will guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
When discussing tire inflation, several technical properties are critical for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Understanding these specifications can significantly benefit B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
PSI measures the air pressure inside the tire, which is crucial for vehicle performance. Proper PSI ensures optimal tire wear, fuel efficiency, and safety. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased fuel consumption and tire wear, while over-inflated tires can compromise traction and handling. For B2B buyers, knowing the correct PSI specifications for different tire types and vehicles is essential to avoid costly replacements and enhance vehicle safety.
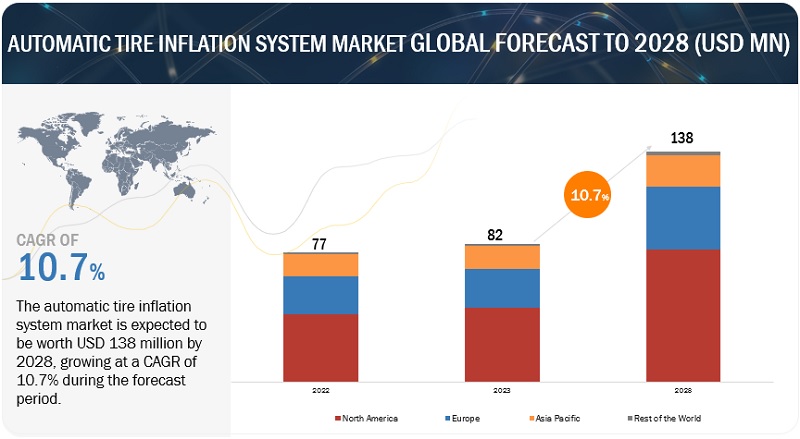
Illustrative image related to tire inflation
The load index indicates the maximum weight a tire can safely support at a specified PSI. It is vital for ensuring that the tires are suitable for the vehicle’s intended use, especially for commercial vehicles carrying heavy loads. B2B buyers must match the load index to their operational needs to maintain safety standards and prevent tire failures.
Tread depth affects traction, handling, and safety. A minimum tread depth is required for effective water evacuation and to reduce the risk of hydroplaning. B2B buyers should be aware of the legal requirements for tread depth in their region, as well as the implications for tire performance and replacement cycles.
Temperature ratings indicate a tire’s ability to dissipate heat. Tires that operate at high temperatures are prone to accelerated wear and potential blowouts. Understanding temperature ratings helps B2B buyers select tires that are appropriate for their environmental conditions, ensuring longevity and safety.
The materials used in tire construction, including rubber compounds and reinforcing materials, influence durability, performance, and cost. Different applications may require specific material grades to achieve desired performance characteristics. B2B buyers should consider these factors to optimize their tire selection based on specific operational needs.
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in tire procurement. Here are key trade terms relevant to tire inflation.
OEM refers to tires produced by the original manufacturer of the vehicle or component. Purchasing OEM tires ensures compatibility and performance as intended by the vehicle manufacturer. B2B buyers often prefer OEM tires for fleet vehicles to maintain warranty coverage and vehicle integrity.
MOQ is the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and costs effectively. Suppliers may set MOQs based on production capabilities, which can influence purchasing decisions.
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products. This process allows B2B buyers to compare options and negotiate terms, ensuring they receive the best value for tire purchases.
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations, which are vital for effective supply chain management.
The aftermarket refers to tires sold after the initial purchase of a vehicle. This sector is significant for B2B buyers, particularly in fleet management, as it involves the replacement and maintenance of tires. Understanding aftermarket dynamics can aid in strategic sourcing and cost control.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure tire performance and safety.
The tire inflation sector is currently experiencing a transformative phase driven by multiple global factors. One of the foremost trends is the increasing focus on vehicle safety and performance. With growing awareness around road safety, both consumers and fleet operators are recognizing that proper tire inflation not only extends tire life but also enhances fuel efficiency and safety. This is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can be challenging.
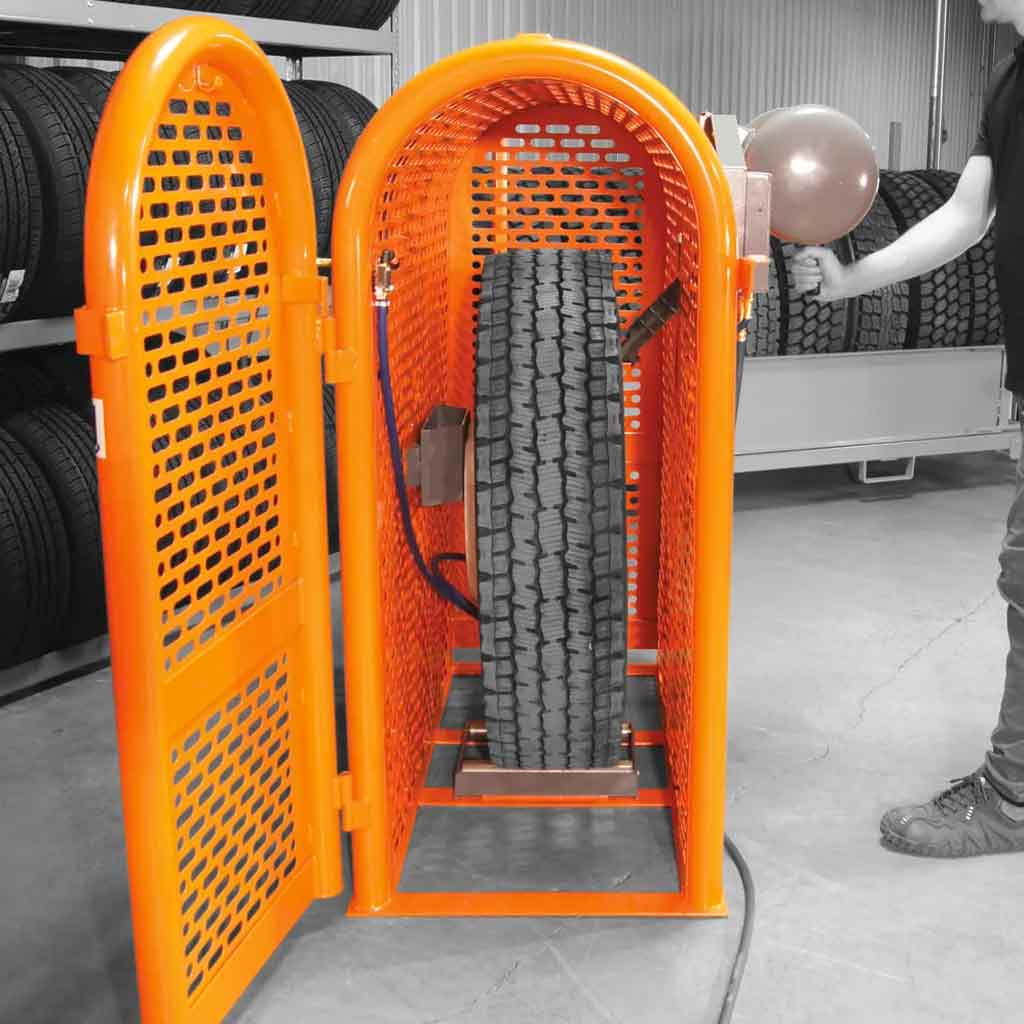

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Another significant trend is the integration of technology into tire management systems. Smart tire inflation systems equipped with sensors are emerging, allowing real-time monitoring of tire pressure and temperature. This technology reduces the likelihood of under-inflation or over-inflation, leading to better fuel efficiency and lower emissions. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe, where regulatory frameworks increasingly mandate sustainability, will find value in these innovations.
Additionally, the market is seeing a shift toward more sustainable practices, with manufacturers adopting eco-friendly materials and production methods. This trend is not only driven by consumer demand but also by regulations aimed at reducing carbon footprints. As a result, international B2B buyers are encouraged to evaluate suppliers based on their sustainability credentials and innovations in tire inflation technologies.
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the tire inflation market. The environmental impact of tire manufacturing and disposal is prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate ethical practices. This includes the use of sustainable materials, such as recycled rubber and bio-based additives, which contribute to reducing the overall carbon footprint of the tires.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are gaining traction. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the origins of raw materials and the conditions under which they are sourced. Certifications such as ISO 14001 and the Global Recycled Standard are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract B2B clients focused on sustainability. In regions like Europe, where regulatory pressure is strong, ensuring compliance with environmental standards can be a decisive factor in supplier selection.
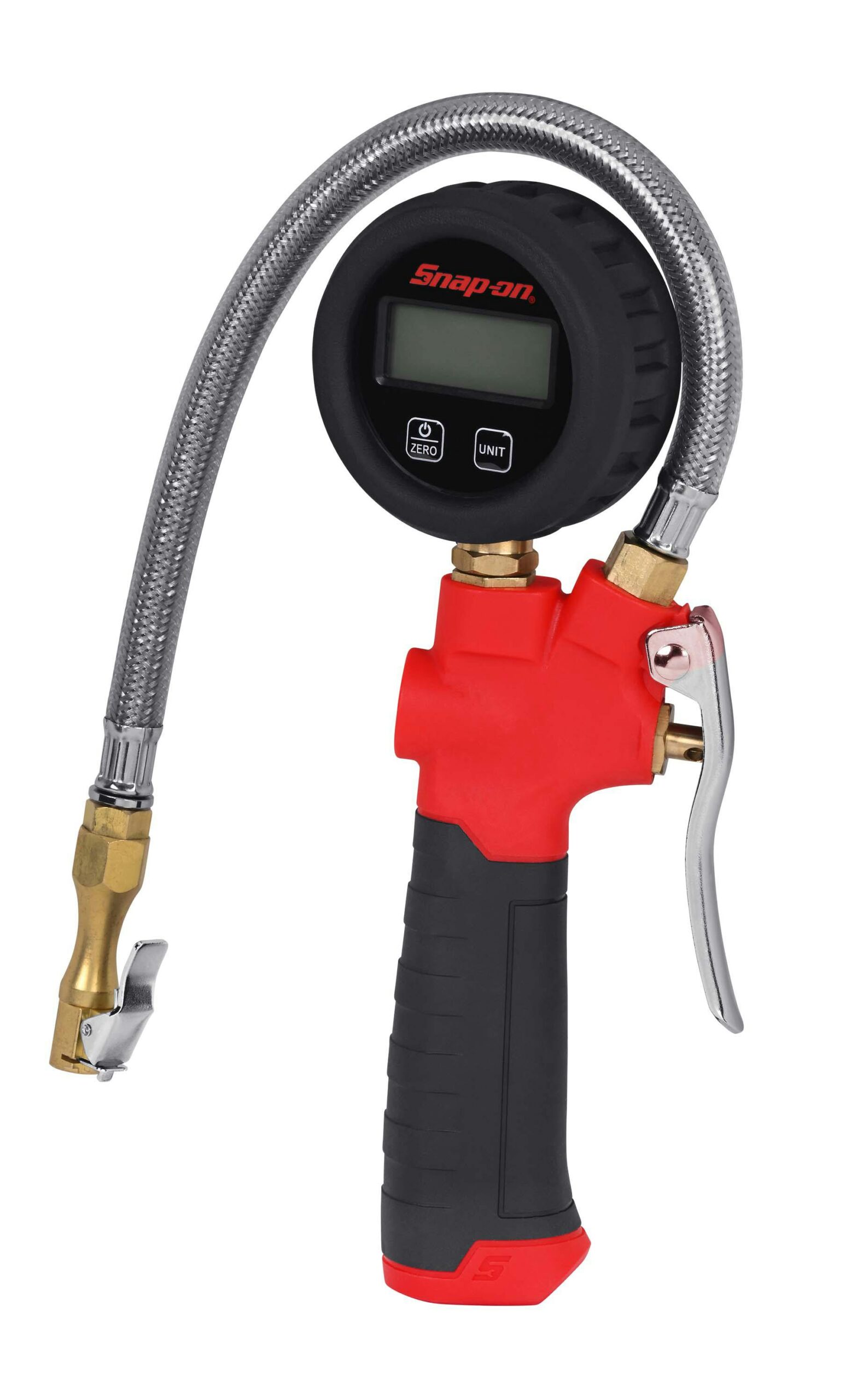

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
Investing in suppliers that prioritize sustainability not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. Buyers should assess their suppliers’ sustainability initiatives and look for partnerships that support a circular economy, which includes recycling and proper tire disposal practices.
The tire inflation sector has undergone significant evolution over the decades, primarily driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer expectations. Initially, tire inflation was a manual process, relying heavily on basic gauges and pumps. As automotive technology advanced, the introduction of air compressors and automated systems revolutionized the way tires were inflated.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies has further transformed the landscape. Smart tire systems that monitor pressure in real-time have emerged, providing drivers with essential data to maintain optimal tire conditions. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who are looking for reliable and efficient tire management solutions.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability has led to innovations in tire design and materials, including the development of low-rolling-resistance tires that enhance fuel efficiency. As the industry continues to adapt to environmental demands, B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest trends and technologies to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with both their operational goals and sustainability commitments.
1. How do I solve tire underinflation issues for my fleet?
To address tire underinflation, implement a routine tire pressure monitoring system across your fleet. Regularly check tire pressure at least once a month and before long trips, as tires lose approximately 1 PSI per month. Invest in high-quality tire pressure gauges and consider using digital monitoring systems that alert you to low pressure in real time. Ensure that all drivers are trained to recognize the signs of underinflation, such as increased fuel consumption and uneven tire wear, which can lead to costly repairs and safety hazards.
2. What is the best tire inflation method for commercial vehicles?
The best method for inflating tires on commercial vehicles involves using a calibrated tire inflator or a portable air compressor. This ensures accuracy in achieving the manufacturer-recommended pressure, which can be found on the driver’s side door jamb or in the vehicle’s manual. For larger fleets, investing in a central tire inflation system can automate the process and ensure consistent pressure across all vehicles, enhancing safety and extending tire life.
3. How can I ensure compliance with international tire inflation standards?
To comply with international tire inflation standards, familiarize yourself with the regulations specific to your target markets, such as the EU, Middle East, or South America. Ensure that your suppliers adhere to these standards by requesting certifications and compliance documentation. Regular audits of your suppliers’ facilities can also help maintain quality control. Additionally, staying updated on changes in regulations is crucial for ongoing compliance.
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for tire inflation equipment?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for tire inflation equipment can vary significantly by supplier. Generally, MOQs may range from 50 to 500 units, depending on the type of equipment and the manufacturer’s policies. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about flexible MOQs for first-time orders or bulk purchases, as many manufacturers are willing to accommodate smaller orders to build long-term relationships.
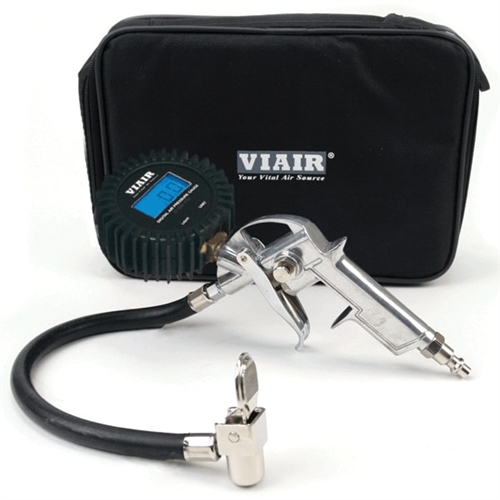

Illustrative image related to tire inflation
5. How do I vet suppliers for tire inflation products?
Vetting suppliers for tire inflation products involves several steps. Begin by researching their reputation and customer reviews online. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Request samples to evaluate product quality and performance. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, to assess their production capabilities and quality control processes. Engaging in direct conversations with their sales representatives can also provide insights into their reliability and responsiveness.
6. What payment terms should I negotiate with tire inflation suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms with tire inflation suppliers, aim for terms that balance cash flow with supplier confidence. Common terms include a 30% upfront deposit with the remaining balance due upon delivery. For larger orders, consider negotiating extended payment terms, such as net 60 or net 90 days, which can help manage cash flow better. Always ensure that payment methods are secure, and consider using letters of credit for international transactions to mitigate risk.
7. What quality assurance practices should I expect from tire inflation suppliers?
Quality assurance practices from tire inflation suppliers should include regular testing of their products, adherence to international quality standards (like ISO 9001), and documented quality control processes. Ask about their testing procedures for tire inflators and gauges, including calibration methods. Additionally, inquire if they offer warranties or guarantees on their products, as this can be an indicator of their confidence in product quality and reliability.
8. How can logistics impact my tire inflation procurement process?
Logistics plays a critical role in the procurement process for tire inflation products. Factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs clearance can significantly affect your overall budget and timelines. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to manage logistics efficiently, including their shipping partners and warehousing capabilities. Additionally, consider the geographical location of your suppliers, as proximity can reduce shipping times and costs, particularly for international orders.
Domain: bridgestoneamericas.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Proper tire inflation is crucial for maximizing tire performance and mileage. Tires should be checked at least once a month, as they lose approximately 1 PSI of pressure monthly. Tire pressure changes with temperature, losing about 1 PSI for every 10 degrees F change. The correct tire pressure can be found on the driver’s side door jamb or in the vehicle owner’s manual, not on the tire’s sidewall,…
Domain: pirelli.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Recommended tire pressure is the optimal air pressure for tires established by the vehicle manufacturer, typically between 28 and 36 PSI. It can be found in the car’s operator manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. The pressure should be checked when the tire is cold. Maximum pressure is indicated on the tire sidewall and should not be used for everyday driving. Under-inflation can lead …
Domain: toyotires.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Load and Inflation Tables provide assistance for replacing tires with optional sizes, including plus sizes not listed on the vehicle’s tire information placard (T.I.P) or in the owner’s manual. For original equipment (OE) size inflation pressure, refer to the T.I.P. found on the vehicle door jam, glove compartment, or near the gas cap. Important: Consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific s…
In the evolving landscape of tire inflation, strategic sourcing stands as a pivotal factor in enhancing operational efficiency and safety for businesses across diverse markets. Proper tire inflation not only extends the lifespan of tires but also significantly impacts fuel economy and reduces environmental footprints, making it a critical aspect for companies aiming to optimize their fleet management and logistics operations.
As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of tire maintenance and inflation can lead to substantial cost savings and improved safety standards. By establishing reliable partnerships with manufacturers and service providers who prioritize quality and innovation, businesses can ensure access to the best tire technologies and maintenance solutions.
Looking ahead, organizations should prioritize regular tire pressure monitoring and adopt advanced inflation technologies to stay competitive in their respective markets. Embracing these practices not only enhances vehicle performance but also contributes to sustainability efforts. Take proactive steps today—evaluate your sourcing strategies, invest in tire maintenance training, and explore partnerships that will elevate your operational efficiency and safety standards in tire management.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.