In the realm of tire maintenance and safety, the question of whether tires should be inflated to max PSI is a critical concern for international B2B buyers. Understanding the implications of tire pressure is essential for companies involved in transportation, logistics, and automotive sectors, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Brazil. This comprehensive guide will delve into the nuances of tire inflation, highlighting the difference between recommended and maximum pressures, and how these affect vehicle performance, safety, and operational costs.
As businesses increasingly prioritize safety and efficiency, the correct tire pressure becomes a pivotal factor in enhancing vehicle longevity and reducing fuel expenses. This guide will equip B2B buyers with essential insights on tire types, their applications, and best practices for supplier vetting. Moreover, we will explore cost implications associated with improper tire inflation, emphasizing how informed purchasing decisions can lead to significant savings and improved safety standards.
By navigating the complexities of tire inflation, this resource empowers international buyers to make educated choices that align with their operational needs and safety requirements. The insights provided will not only enhance fleet management but also contribute to a safer driving experience across diverse global markets.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Recommended Pressure | Pressure defined by the vehicle manufacturer, typically between 28-36 PSI. | General automotive maintenance and fleet services. | Pros: Ensures safety and optimal performance. Cons: May not account for load variations. |
| Maximum Tire Pressure | The highest pressure a tire can safely hold, usually found on the tire sidewall. | Heavy-duty transportation and logistics. | Pros: Useful for specific heavy-load scenarios. Cons: Increases risk of blowouts and handling issues. |
| Cold Tire Pressure | Pressure measurement taken when tires are cold, reflecting accurate inflation status. | Tire service and repair shops. | Pros: Provides accurate readings for safety. Cons: Requires careful timing for checks. |
| Seasonal Adjusted Pressure | Pressure adjustments made based on seasonal changes (higher in winter, lower in summer). | Automotive service providers in varying climates. | Pros: Enhances tire performance in different weather. Cons: Requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. |
| Load-Specific Pressure | Tailored pressure settings based on the vehicle’s load capacity and weight distribution. | Commercial transport and logistics companies. | Pros: Maximizes safety and tire longevity under heavy loads. Cons: Complexity in determining correct settings. |
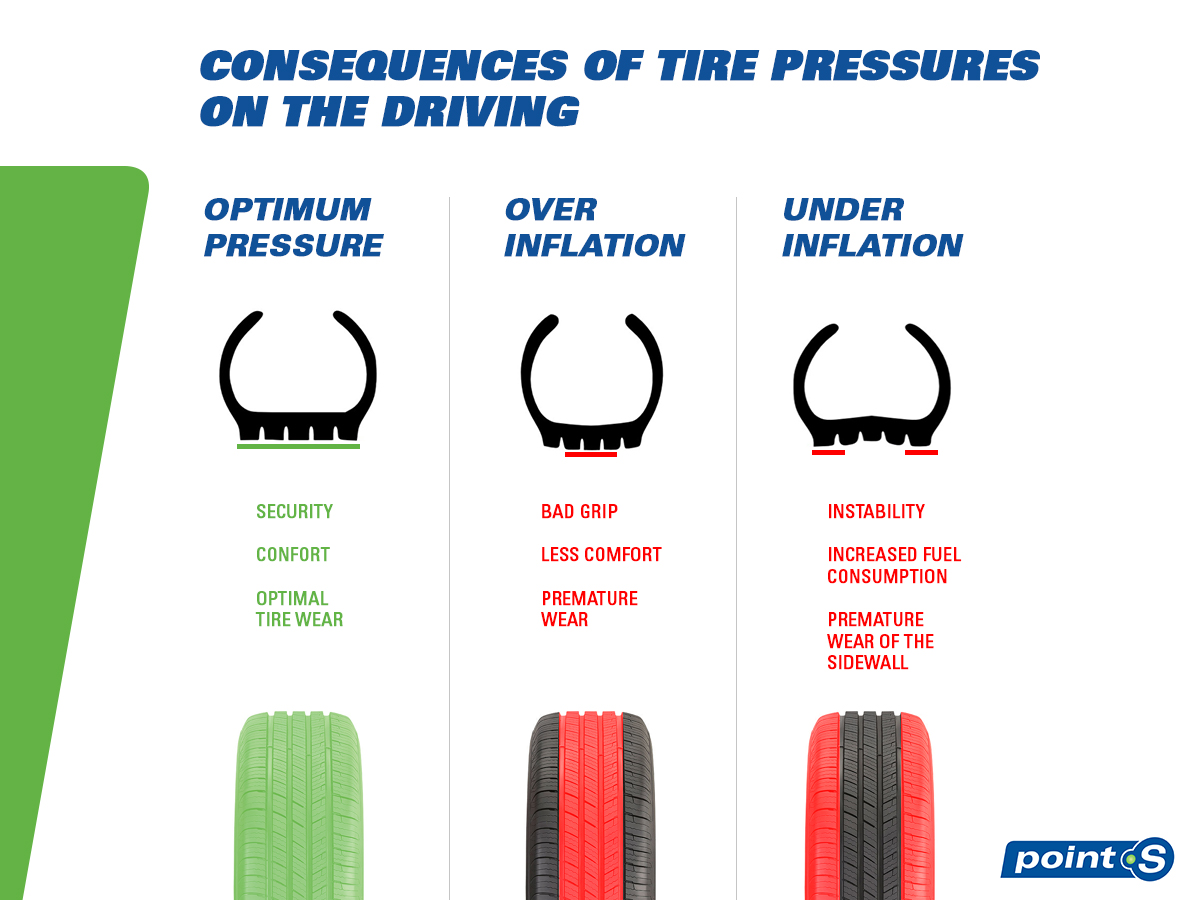
Standard recommended pressure is the tire inflation level specified by the vehicle manufacturer, generally ranging from 28 to 36 PSI. This pressure is crucial for ensuring vehicle safety, optimal handling, and fuel efficiency. For B2B buyers managing fleets, adhering to these specifications helps minimize operational costs by prolonging tire life and improving vehicle performance. Regular checks and maintenance at this pressure can lead to fewer breakdowns, thereby enhancing overall productivity.
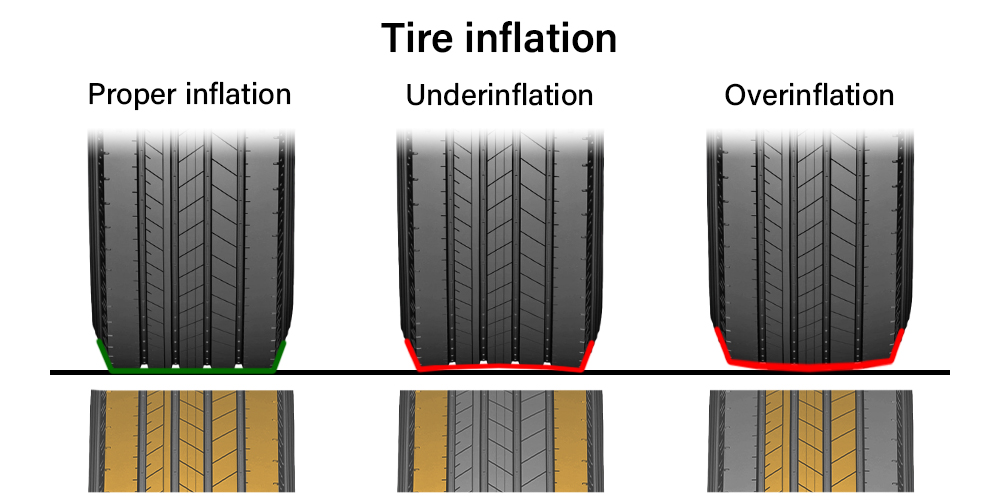
Maximum tire pressure indicates the upper limit a tire can withstand, often printed on the tire’s sidewall. While this pressure may be tempting to use for everyday driving, it is primarily relevant for specific scenarios, such as towing heavy loads. B2B buyers in logistics and transportation should be cautious when considering this pressure. Over-inflation can lead to safety risks, including blowouts and reduced traction, which can result in costly accidents and liability issues.
Cold tire pressure refers to the pressure reading taken when the tires are cold, providing a true reflection of the tire’s inflation status. For B2B buyers, particularly those in tire service and repair, understanding the importance of cold pressure readings is essential. Accurate measurements help in maintaining safety standards and optimizing tire performance. Regular monitoring can prevent under-inflation, which leads to increased rolling resistance, higher fuel consumption, and premature tire wear.
Seasonal adjusted pressure involves modifying tire inflation based on environmental factors, with higher pressures often recommended in winter and lower in summer. This practice is especially relevant for automotive service providers operating in diverse climates. By adjusting tire pressure seasonally, B2B buyers can enhance traction and handling, ultimately improving safety. However, this requires diligent monitoring and adjustments, which may increase operational complexity.
Load-specific pressure settings are tailored to accommodate the weight and distribution of cargo in commercial vehicles. For logistics companies, maintaining the correct tire pressure relative to load is vital for maximizing safety and tire longevity. This approach can prevent uneven wear and blowouts, which are critical concerns in the transport industry. However, determining the right pressure can be complex, necessitating training and resources to ensure compliance with safety standards.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of should tires be inflated to max psi | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet management for delivery vehicles | Enhanced safety and reduced maintenance costs | Reliability of tire suppliers, regional availability |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery tire maintenance | Improved efficiency and reduced downtime | Compatibility with various machinery types, local support |
| Construction | Heavy equipment tire pressure management | Increased safety and operational efficiency | Supplier reputation, availability of specialized tires |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control in tire production | Consistent performance and safety standards | Compliance with international regulations, sourcing quality materials |
| Mining | Tire management for mining vehicles | Enhanced safety in harsh environments and cost savings | Durability of tires, local sourcing, and service options |
In the transportation and logistics sector, maintaining the correct tire pressure is crucial for fleet management. Delivery vehicles operating at the max PSI face increased risks, such as reduced traction and longer braking distances, leading to potential accidents. Proper tire inflation ensures safety, enhances fuel efficiency, and minimizes maintenance costs. For B2B buyers, sourcing reliable tires that meet recommended pressure specifications is essential, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can vary significantly.
In agriculture, the performance of machinery is directly tied to tire pressure. Over-inflated tires can lead to uneven soil compaction and reduced traction, negatively impacting productivity. Ensuring tires are inflated to recommended levels enhances the efficiency of farm operations, reduces downtime, and improves safety. Buyers in this sector must consider compatibility with various machinery types and the availability of local support for tire maintenance, especially in rural areas of Europe and the Middle East.

Illustrative image related to should tires be inflated to max psi
In the construction industry, managing tire pressure is vital for heavy equipment safety and operational efficiency. Over-inflation can lead to tire blowouts and increased wear, which can halt projects and incur significant costs. Ensuring tires are inflated to the correct PSI maximizes performance and minimizes risks on job sites. When sourcing tires, businesses should prioritize suppliers with a strong reputation for durability and availability of specialized tires suitable for construction environments.
For automotive manufacturers, maintaining quality control in tire production is essential. Tires that are inflated to max PSI during testing can yield misleading performance data, impacting safety standards. Adhering to recommended pressure levels ensures consistent performance across vehicles. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers who comply with international regulations and provide high-quality materials, ensuring the end product meets safety and performance benchmarks.
In the mining sector, tire management is critical due to the harsh operating conditions. Proper inflation prevents tire failures, which can lead to unsafe situations and costly downtime. Ensuring that tires are inflated to the recommended PSI enhances safety and extends tire lifespan, leading to significant cost savings. Buyers should prioritize sourcing durable tires suited for rugged environments, along with local sourcing options for timely service and support.
Illustrative image related to should tires be inflated to max psi
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those in logistics and transportation, often face challenges adhering to regional tire pressure regulations. For instance, in certain European countries, there are stringent laws regarding vehicle safety, including tire maintenance. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines, increased liability, and even suspension of operations. Buyers may struggle to interpret the legal requirements and often inflate tires to maximum PSI, thinking it would enhance safety and performance, only to realize it poses a significant risk.
The Solution: To ensure compliance and safety, B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with the manufacturer’s recommended tire pressure for their specific vehicle models. This information is typically found in the vehicle’s manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. Establishing a routine for monitoring tire pressure using high-quality tire gauges can also help maintain the recommended PSI. Implementing a digital tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) can automate this process, providing alerts when pressures deviate from the optimal range. By prioritizing the recommended pressure, buyers can enhance vehicle safety, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce legal risks.
The Problem: For B2B buyers managing a fleet, there is often confusion regarding the implications of inflating tires to maximum PSI. Many mistakenly believe that higher tire pressure enhances fuel efficiency and prolongs tire life. However, this misconception can lead to overinflation, which reduces the tire’s contact with the road, resulting in compromised handling, longer stopping distances, and uneven tire wear. Such issues can significantly affect fleet performance and safety, leading to increased operational costs and potential accidents.
The Solution: Buyers should educate their teams on the differences between maximum and recommended PSI. Conducting training sessions that focus on tire maintenance and the importance of adhering to the manufacturer’s specifications can be beneficial. Additionally, establishing a regular tire maintenance schedule that includes pressure checks can help ensure that tires are inflated correctly. Investing in tire management software that tracks tire pressure and provides reminders for regular checks can also streamline this process. By maintaining the correct PSI, fleets can enhance safety, optimize performance, and reduce maintenance costs.
The Problem: B2B buyers operating in regions with extreme seasonal variations often encounter difficulties in managing tire pressure effectively. Temperature fluctuations can significantly affect tire pressure, leading to under-inflation in colder months and potential over-inflation during warmer weather. This can create unsafe driving conditions, especially in industries reliant on timely deliveries, such as logistics and transportation. The challenges of adjusting tire pressure in response to seasonal changes can lead to costly accidents and operational delays.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with seasonal tire pressure changes, B2B buyers should implement a proactive tire management strategy. This includes educating drivers about the effects of temperature on tire pressure and encouraging them to check tire pressure regularly, especially during seasonal transitions. Utilizing tire pressure monitoring systems that provide real-time data can help fleet managers respond quickly to pressure fluctuations. Additionally, providing guidelines for adjusting tire pressure based on seasonal temperature changes can empower drivers to make informed decisions, ensuring safety and reliability throughout the year. By taking these steps, businesses can maintain optimal tire performance, enhance safety, and reduce the risk of operational disruptions.
When considering the question of whether tires should be inflated to max PSI, it is essential to analyze the materials used in tire construction. The choice of materials directly impacts performance, safety, and durability. Below are analyses of four common materials used in tire manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and relevant considerations for international B2B buyers.
Key Properties: Natural rubber possesses excellent elasticity and resilience, allowing tires to maintain their shape under various conditions. It also offers good temperature resistance, which is crucial for performance during high-speed driving.

Illustrative image related to should tires be inflated to max psi
Pros & Cons: Natural rubber is known for its durability and ability to provide a comfortable ride due to its shock-absorbing properties. However, it can be more expensive than synthetic alternatives and may require more complex manufacturing processes. In terms of end-product suitability, while it excels in performance, it may not be as resistant to aging and ozone damage.
Impact on Application: Natural rubber is particularly effective in applications requiring flexibility and comfort. However, it may not be ideal for extreme environments where ozone resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the local climate, as natural rubber can degrade faster in high UV exposure areas. Compliance with ASTM standards is crucial for ensuring quality and safety.
Key Properties: Synthetic rubber, often made from petrochemicals, offers superior resistance to abrasion, aging, and weathering compared to natural rubber. It can also be engineered to provide specific performance characteristics, such as increased traction or reduced rolling resistance.

Illustrative image related to should tires be inflated to max psi
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of synthetic rubber is its versatility and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for mass production. However, it may not provide the same level of comfort as natural rubber and can be less environmentally friendly.
Impact on Application: Synthetic rubber is ideal for high-performance tires and those designed for specific conditions, such as all-weather or off-road tires. Its durability makes it a preferred choice for commercial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with various international standards, such as DIN or JIS, is essential for synthetic rubber products. Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, may prefer synthetic options for their performance attributes.
Key Properties: Steel belts are commonly used in tire construction to enhance structural integrity. They provide excellent tensile strength and resistance to punctures, which is critical for maintaining tire shape under load.
Pros & Cons: The inclusion of steel reinforcement significantly improves tire durability and safety, especially under heavy loads. However, it can increase the overall weight of the tire, which may affect fuel efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel-reinforced tires are particularly beneficial for commercial vehicles and heavy-duty applications where safety and load-bearing capacity are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with rough terrain, such as parts of Africa and South America, may prioritize steel-reinforced tires for their robustness. Compliance with safety standards is also crucial.
Key Properties: Composite materials combine various elements, such as synthetic rubber and reinforcing fibers, to create a lightweight yet strong tire structure. They can be engineered for specific performance metrics, including fuel efficiency and traction.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their ability to reduce weight while maintaining performance, which can enhance fuel efficiency. However, they may be more expensive to produce and require advanced manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composite materials are increasingly used in high-performance and specialty tires, where weight reduction is critical for performance and efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe may be more inclined to invest in composite materials due to their focus on sustainability and fuel efficiency. Compliance with environmental regulations is also a consideration.
| Material | Typical Use Case for should tires be inflated to max psi | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Passenger and comfort tires | Excellent elasticity and comfort | Higher cost, less ozone resistance | High |
| Synthetic Rubber | High-performance and all-weather tires | Cost-effective, durable | Less comfort, environmental concerns | Medium |
| Steel Reinforcement | Commercial and heavy-duty tires | Enhanced durability and safety | Increased weight | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Specialty and high-performance tires | Lightweight, engineered performance | Higher production costs | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for tire manufacturing, particularly in the context of tire inflation practices. Understanding the properties and implications of each material can help in making informed purchasing decisions that align with safety, performance, and regulatory compliance.
The manufacturing of tires is a complex process that involves several critical stages to ensure the final product meets safety and performance standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
The first step in tire manufacturing involves sourcing high-quality raw materials. Key materials include natural and synthetic rubber, carbon black, and various chemical additives. Each component plays a crucial role in the tire’s performance. For instance, carbon black enhances durability and wear resistance, while specific additives can improve heat resistance and traction.
Once the materials are sourced, they undergo a thorough quality check to ensure they meet the required specifications. This initial inspection is crucial as any subpar materials can compromise the tire’s overall integrity and performance.
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. This process involves mixing the rubber compounds to achieve the desired properties. Advanced machinery blends the components, ensuring uniform consistency.
Following mixing, the rubber is shaped into various components of the tire, such as the tread, sidewalls, and inner linings. This is typically done using extrusion and calendering techniques. Extrusion shapes the rubber into long strips, while calendering forms sheets of rubber that will be cut to size for the tire’s construction.
The assembly stage is where the tire components come together. Each tire is built layer by layer, starting with the inner liner, followed by the body plies, belts, and tread. The assembly process is highly automated, but skilled workers monitor the operations to ensure precision.
This stage also involves integrating additional components such as steel belts for strength and fabric layers for flexibility. Each layer is carefully aligned and bonded using heat and pressure, ensuring a robust final product.
The finishing stage of tire manufacturing includes curing or vulcanization, where the assembled tire is heated in a mold. This process transforms the rubber into a durable and elastic material. The curing time and temperature are meticulously controlled to ensure optimal tire performance.
Once curing is complete, the tires undergo a series of inspections to check for defects, uniformity, and balance. This ensures that each tire meets the stringent safety and performance standards set by regulatory bodies.
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of tire manufacturing, ensuring that each tire is produced to the highest standards. Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system.
Quality control (QC) in tire manufacturing involves several checkpoints:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first line of defense, where raw materials are inspected upon arrival. Ensuring that only quality materials enter the production process is critical for maintaining overall tire quality.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring takes place. This includes checking the mixing ratios, temperature controls during curing, and ensuring that each layer of the tire is properly aligned.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After tires are cured, they undergo a final inspection. This involves checking for visual defects, measuring dimensions, and conducting performance tests to ensure that the tire meets all specifications.
Several testing methods are employed to verify tire quality, including:
For B2B buyers, especially those in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are effective strategies:
Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facilities allows buyers to see the QC processes in action. This is crucial for assessing compliance with international standards.
Requesting Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, inspection results, and compliance with relevant standards.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide unbiased assessments of a supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly valuable in regions where regulatory oversight may vary.
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific certification requirements that can vary by region. For instance, European buyers may look for CE marking, indicating compliance with EU safety standards, while buyers in the Middle East might require adherence to local regulations.
Understanding these nuances is critical for ensuring that tires not only meet safety standards but also align with local market requirements. Buyers should engage with suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with both international and local regulations.
For B2B buyers, understanding the complexities of tire manufacturing and the importance of quality assurance is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on reputable suppliers who adhere to stringent QC processes and international standards, businesses can ensure they receive high-quality tires that meet their operational needs. This commitment to quality not only enhances safety but also contributes to improved performance and cost savings in the long run.
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers evaluating the optimal tire inflation levels for their fleets or vehicles. Understanding the implications of tire pressure not only ensures safety and performance but also helps in maximizing tire lifespan and fuel efficiency. Properly inflated tires can significantly impact operational costs, especially for businesses relying on transportation.
Before purchasing or inflating tires, confirm the recommended tire pressure for your specific vehicle models. This information is typically found in the vehicle’s owner manual or on a sticker located inside the driver’s door. Knowing the correct PSI is crucial to maintain safety, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity.
Familiarize yourself with the maximum PSI listed on the tire sidewall. This figure indicates the highest pressure the tire can safely hold under maximum load conditions. It is essential to differentiate between this maximum and the recommended pressure to avoid over-inflation risks, which can lead to decreased traction and increased blowout potential.

Illustrative image related to should tires be inflated to max psi
Consider the operating environment and load conditions when determining tire pressure. Factors such as temperature, road conditions, and load weight can affect tire performance. For example, higher temperatures can increase tire pressure, and heavy loads may require adjustments to maintain safety and efficiency.
Invest in a reliable TPMS to ensure consistent monitoring of tire pressure across your fleet. A TPMS will alert you when pressure falls below the recommended levels, preventing under-inflation and potential safety hazards. Regular checks can also help in optimizing fuel efficiency and extending tire life.
Establish a routine for checking tire pressure, ideally before long trips or at regular intervals. Regular maintenance not only ensures compliance with safety standards but also allows for early detection of issues such as leaks or uneven wear. Set reminders for these checks to enhance fleet reliability.
Educate your drivers and maintenance personnel about the importance of proper tire inflation and its impact on vehicle performance. Provide training on how to read tire pressure gauges correctly and the implications of inflating to max PSI versus recommended levels. Knowledgeable staff can significantly reduce risks and enhance operational efficiency.
Engage with tire suppliers or manufacturers for insights into best practices for tire inflation specific to your industry. They can provide valuable information on tire types, recommended pressures, and adjustments based on unique operational demands. Building a relationship with your suppliers can lead to tailored solutions and better pricing for bulk purchases.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they make informed decisions regarding tire inflation, ultimately enhancing safety, performance, and cost-efficiency across their operations.
When sourcing tires with the appropriate inflation guidelines, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The quality of rubber, steel belts, and other components significantly affects the cost. Higher-grade materials that ensure better performance and durability typically incur higher expenses.
Labor: Skilled labor is required for tire production. Regions with varying labor costs can impact the overall pricing. For instance, manufacturing in countries with lower labor costs can provide a cost advantage.
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can reduce these overheads, allowing for more competitive pricing.
Tooling: Specialized machinery for tire production requires significant investment. The cost of tooling can vary based on the technology used and the production volume.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures tire safety and performance, which is critical for compliance with international standards. While this adds to costs, it ultimately protects against liabilities and enhances brand reputation.
Logistics: Transportation costs depend on the distance from the manufacturing facility to the buyer, as well as the mode of transport. International buyers must consider customs duties and tariffs, which can significantly affect total costs.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and competition levels.
Several factors influence pricing when sourcing tires:
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate for favorable terms based on projected usage.
Specifications and Customization: Customized tires for specific vehicles or conditions (e.g., off-road, winter) can command higher prices. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary costs.
Materials and Quality Certifications: Tires made from premium materials with necessary certifications (e.g., ISO, DOT) may be more expensive but offer better performance and safety, reducing long-term ownership costs.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better service and product quality.
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs. Different Incoterms can affect who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and duties, thus impacting the overall price.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing is essential:
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a good relationship can lead to better deals over time.
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the purchase price but also the longevity, fuel efficiency, and safety performance of the tires. Investing in quality tires may reduce overall costs by minimizing replacements and accidents.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of how regional market conditions, currency fluctuations, and local regulations can affect prices. For example, tariffs on imported tires can significantly impact costs in South America compared to Europe.
Plan for Seasonal Variations: Prices may fluctuate based on demand cycles, particularly in regions with distinct seasons. Timing purchases to align with off-peak times can result in cost savings.
Pricing for tires and related components can vary widely based on numerous factors outlined above. The figures discussed in this analysis serve as a guideline and may not reflect current market prices. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing for their specific needs.
When it comes to tire inflation, the debate between inflating tires to their maximum PSI and adhering to the manufacturer-recommended pressure is essential for ensuring safety and performance. However, various alternatives exist that can also enhance vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. This analysis will compare the conventional method of inflating tires to maximum PSI against two viable alternatives: using tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and adopting automatic tire inflation systems (ATIS).
Illustrative image related to should tires be inflated to max psi
| Comparison Aspect | Should Tires Be Inflated To Max PSI | Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) | Automatic Tire Inflation System (ATIS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Can reduce traction and comfort | Maintains optimal pressure automatically | Ensures consistent pressure, improving safety |
| Cost | Low initial cost, but potential high maintenance | Moderate initial cost, low maintenance | Higher initial investment, but low ongoing costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, requires manual checking | Easy to install, requires minimal user input | Complex installation, may require professional setup |
| Maintenance | Requires regular manual checks | Low maintenance, alerts for pressure drops | Minimal maintenance, self-adjusting system |
| Best Use Case | General driving, short-term use | Ideal for fleet vehicles and long-distance driving | Best for commercial fleets with high usage |
Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
TPMS provides an efficient way to maintain tire pressure by alerting drivers when tire pressure deviates from the recommended levels. This system can significantly improve safety by preventing under-inflation, which is a common issue that leads to increased rolling resistance and fuel consumption. The initial costs for a TPMS can be moderate, but the long-term maintenance is low, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses operating fleets. However, while TPMS helps maintain recommended pressures, it does not actively inflate the tires, meaning manual intervention is still required for adjustments.
Automatic Tire Inflation System (ATIS)
ATIS takes tire maintenance a step further by actively managing tire pressure. This system automatically adjusts tire pressure based on real-time data, ensuring that tires are always operating at optimal levels. While the initial investment for ATIS can be higher than other solutions, its long-term benefits include enhanced safety, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced tire wear. It is particularly advantageous for commercial fleets that require consistent performance under varying loads. However, the complexity of installation may necessitate professional services, which could be a consideration for businesses with limited technical resources.
For B2B buyers, selecting the right tire inflation solution hinges on specific operational needs and budget considerations. If your focus is on cost-effectiveness and simplicity, adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended PSI with regular checks may suffice. However, for businesses managing fleets or operating in high-demand environments, investing in a TPMS or ATIS can offer significant long-term advantages in safety and efficiency. Ultimately, evaluating the trade-offs between initial costs, maintenance requirements, and performance outcomes will guide buyers to the best choice for their unique circumstances.
Understanding the technical properties of tire inflation is crucial for B2B buyers involved in automotive manufacturing, maintenance, and sales. Here are some essential specifications that influence tire performance and safety:

Illustrative image related to should tires be inflated to max psi
Recommended Pressure (Cold PSI)
This is the pressure specified by the vehicle manufacturer for optimal tire performance under normal driving conditions. Typically ranging from 28 to 36 PSI, this value ensures safe handling, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity. B2B buyers should prioritize vehicles with clear manufacturer guidelines to avoid safety risks and enhance customer satisfaction.
Maximum Pressure (Max PSI)
Indicated on the tire sidewall, Max PSI represents the highest pressure a tire can safely endure when carrying its maximum load. While it may seem desirable to inflate tires to this level, doing so can lead to diminished traction and increased risk of blowouts. Understanding the distinction between recommended and maximum pressure helps buyers avoid costly damages and liability issues.
Tire Load Index
This numerical value indicates the maximum load a tire can support at its maximum pressure. It is essential for ensuring that tires are suitable for specific vehicles, especially in commercial applications. Buyers must ensure that the tire load index meets or exceeds the requirements of the vehicles in their fleet to maintain safety and performance.
Tread Depth
The depth of the tread is critical for maintaining traction, especially in adverse weather conditions. Tread depth can vary significantly among tire types and is often measured in millimeters. B2B buyers should consider tires with adequate tread depth to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations.
Temperature Resistance
Tires must withstand various temperature extremes during operation. Understanding a tire’s temperature resistance can help buyers select tires that perform reliably in their specific regional climates. This knowledge is vital for reducing the risk of tire failure and ensuring consistent vehicle performance.
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for B2B buyers to navigate procurement effectively. Here are several key terms that are commonly encountered:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of tires, OEM tires are those that are specifically designed and manufactured for a particular vehicle model. Buyers should consider OEM options for guaranteed compatibility and performance.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers in managing inventory costs and ensuring they meet their operational needs without overcommitting financially.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document requesting price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. An RFQ allows B2B buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms, ensuring they receive competitive pricing for tire procurement.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
A set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for buyers to navigate shipping, insurance, and risk management effectively.
TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System)
A safety feature that monitors tire pressure and alerts the driver when it falls below a certain threshold. Buyers should consider vehicles equipped with TPMS to enhance safety and reduce the risk of tire-related incidents.
Rolling Resistance
This term describes the energy lost as a tire rolls over a surface. Lower rolling resistance can lead to better fuel efficiency. B2B buyers should evaluate tires based on their rolling resistance characteristics to optimize operational costs for their fleet.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness in their tire procurement strategies.
The global tire market is witnessing a shift driven by advancements in technology, evolving consumer preferences, and increasing regulatory pressures. One of the key trends is the growing emphasis on tire pressure management systems (TPMS), which enhance safety and fuel efficiency. With the increasing number of vehicles equipped with TPMS, international B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing tires that are compatible with these systems to meet customer expectations. In regions such as Africa and South America, where road conditions can be challenging, the importance of adhering to recommended tire pressures becomes even more critical to ensure safety and performance.
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce in tire sales is reshaping sourcing strategies for B2B buyers. Companies are leveraging digital platforms to streamline procurement, enabling them to access a broader range of suppliers and competitive pricing. In Europe, particularly Germany, there is a notable trend towards high-performance tires that offer better handling and comfort, often emphasizing the need for correct inflation to maximize their benefits. This shift influences sourcing decisions, as buyers seek suppliers who can provide detailed specifications regarding optimal tire pressures.
Additionally, as sustainability becomes a focal point in the automotive industry, buyers are increasingly considering the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. This includes selecting tires that not only perform well under recommended pressures but also minimize rolling resistance to enhance fuel efficiency.
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the tire industry, particularly in the context of tire inflation practices. As concerns about climate change and resource depletion grow, B2B buyers are under pressure to source products that adhere to sustainable practices. The environmental impact of tires is significant, as they contribute to pollution during production and disposal. Companies that prioritize sourcing tires made from eco-friendly materials or those that have received ‘green’ certifications can enhance their market position while demonstrating corporate social responsibility.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are increasingly relevant in the sourcing of tires. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to labor and environmental standards, particularly in regions where such regulations may be lax. This focus on ethical sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also appeals to consumers who are increasingly aware of the brands they support. Furthermore, tires designed with sustainability in mind often perform better when inflated to their recommended PSI, as they are engineered to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce wear over time.
The practice of tire inflation has evolved significantly over the decades, influenced by technological advancements and changing safety standards. Historically, tire pressure was often a secondary consideration for vehicle manufacturers. However, as the automotive industry recognized the critical role that proper tire inflation plays in safety, performance, and fuel economy, manufacturers began to standardize recommended tire pressures.
The introduction of tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) in the early 2000s marked a turning point, making it easier for drivers to maintain optimal tire pressure. This shift has led to increased awareness among consumers and businesses alike about the implications of overinflation and underinflation. As a result, sourcing practices have become more sophisticated, with a focus on obtaining tires that not only meet safety regulations but also align with modern performance standards. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers as they navigate current market dynamics and consider the long-term implications of their sourcing decisions.
How do I determine the correct tire pressure for my vehicle?
To find the correct tire pressure, refer to the vehicle’s owner manual or locate the sticker on the driver’s side door jamb. This pressure is specified by the car manufacturer and is crucial for optimal performance, safety, and fuel efficiency. Ensure to check the pressure when the tires are cold for the most accurate reading. Under-inflation can lead to increased tire wear and higher fuel costs, while over-inflation can compromise handling and safety.
What are the risks of inflating tires to max PSI?
Inflating tires to the maximum PSI indicated on the tire sidewall is not advisable for regular driving. This practice reduces the tire’s contact patch with the road, leading to decreased traction, longer stopping distances, and a higher risk of blowouts. Additionally, over-inflated tires result in a harsher ride, transferring road imperfections directly to the vehicle, which can be uncomfortable for drivers and passengers.
What should I consider when sourcing tires internationally?
When sourcing tires internationally, consider factors such as compliance with local regulations, quality certifications, and the reputation of the manufacturer. Evaluate the supplier’s production capacity, lead times, and ability to meet your specific requirements. Additionally, assess logistics, including shipping costs and delivery times, to ensure timely availability of tires in your market.
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for tires?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for tires can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors like the type of tire and the manufacturer’s policies. Generally, MOQs can range from a few dozen to several hundred units. It’s essential to negotiate with suppliers to find an MOQ that aligns with your business needs while ensuring cost-effectiveness and supply chain efficiency.
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing tires internationally?
Payment terms for international tire purchases typically include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or open account terms. The specific terms will depend on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Always clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process, particularly when dealing with currency fluctuations and international banking regulations.
How can I ensure the quality of tires from international suppliers?
To ensure tire quality, request certifications such as ISO or other relevant industry standards from your suppliers. Implement a quality assurance (QA) process that includes pre-shipment inspections and testing. Building a strong relationship with your supplier and maintaining open communication can also help address quality concerns promptly and effectively.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for tire shipments?
Logistics for tire shipments involve careful planning regarding transportation methods, customs clearance, and warehousing. Evaluate shipping options (air, sea, or land) based on cost, speed, and reliability. Additionally, ensure compliance with import regulations and consider partnering with logistics providers experienced in handling tires to streamline the process and mitigate risks.
Can I customize tire specifications for my business needs?
Yes, many tire manufacturers offer customization options, such as tread patterns, sizes, and compounds, to meet specific business requirements. Engage with suppliers early in the negotiation process to discuss your needs and explore available options. Customization can enhance performance and cater to unique market demands, providing a competitive edge in your region.
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Max Tire Pressure: 44 psi; Recommended Tire Pressure: 32 psi (front), 33 psi (front full load), 44 psi (rear full load); Vehicle: Mazda 3 2007; Tire Size: Same as stock; Load Index: Same as stock; Speed Rating: Same as stock.
Domain: pirelli.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Recommended tire pressure is the optimal air pressure for tires established by the vehicle manufacturer, typically between 28 and 36 PSI. This pressure can be found in the car’s operator manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. It is important to check tire pressure when tires are cold for accuracy. Maximum tire pressure is indicated on the tire’s sidewall and should not be used for everyd…
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: 2003-2007 Honda Accord 7th Gen, Tire sidewall says 51 psi max
Domain: mastercrafttires.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Recommended inflation pressures for tires are specified in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascals (kPa) as indicated on the vehicle’s tire placard, certification label, or owner’s manual. Never set tire inflation pressures below the recommended levels. Underinflation causes excessive heat buildup and internal structural damage, potentially leading to tire failure. Overinflated tires are more …
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Tire with a maximum inflation pressure of 44 psi. Recommended tire pressure for optimal performance is typically 10-15% below the maximum rating. Vehicle-specific tire pressure can be found on a placard inside the driver’s side door. Common pressures mentioned include 31 psi, 33-34 psi, and 36 psi for various vehicles. Importance of checking tire pressure regularly, especially before long trips or…
Understanding the nuances of tire inflation is crucial for B2B buyers involved in vehicle fleets or automotive industries. The recommended tire pressure, as specified by manufacturers, typically ranges between 28 to 36 PSI, tailored for optimal safety, performance, and fuel efficiency. Inflating tires to their maximum PSI, often indicated on the tire’s sidewall, can lead to decreased traction, longer braking distances, and increased risk of blowouts. This practice not only jeopardizes safety but also affects overall vehicle handling and comfort, potentially leading to higher operational costs.
Strategic sourcing enables businesses to procure high-quality tires that meet specific performance needs while ensuring compliance with safety regulations. By aligning tire selection with the correct inflation practices, international buyers can enhance fleet reliability and reduce maintenance costs. This strategic approach is particularly vital in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where driving conditions may vary significantly.
As you navigate the complexities of tire procurement and management, prioritize ongoing education about tire maintenance and inflation standards. Engaging with trusted suppliers and leveraging advanced tire monitoring technologies will empower your business to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to enhanced safety and cost efficiency. Embrace these insights to drive your operations forward, ensuring that your fleet performs optimally in any market environment.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.