In the complex landscape of tire maintenance, the choice between tire inflation using nitrogen versus air presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As businesses seek reliable solutions to enhance vehicle performance and safety, understanding the nuances of nitrogen inflation can be pivotal. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of tire inflation methods, their specific applications, and the importance of supplier vetting. Additionally, it examines the cost implications associated with both nitrogen and air inflation, enabling buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
For businesses operating across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Vietnam and Germany—this guide serves as an essential resource. By exploring the advantages and disadvantages of each inflation method, stakeholders can assess which option best suits their fleet requirements and financial constraints. Moreover, with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of tire inflation, ensuring optimal performance and value in their purchasing decisions. Whether you are managing a fleet of heavy-duty vehicles or standard passenger cars, understanding these options can significantly impact your bottom line and operational efficiency.
| Nome del tipo | Caratteristiche distintive principali | Applicazioni primarie B2B | Brevi pro e contro per gli acquirenti |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Air Inflation | Composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace gases | General consumer vehicles, light trucks | Pro: Cost-effective; widely available. Contro: Pressure loss over time; more sensitive to temperature changes. |
| Nitrogen Inflation | Pure nitrogen, larger molecules, reduced permeation | Heavy-duty vehicles, racing cars, aircraft | Pro: Maintains pressure longer; better performance; less fluctuation with temperature. Contro: Higher initial cost; limited availability. |
| Hybrid Inflation | Mix of nitrogen and air, typically around 50% nitrogen | Mixed-use vehicles, fleet operations | Pro: Cost-effective; still benefits from nitrogen properties. Contro: Reduced effectiveness compared to pure nitrogen; potential for faster pressure loss. |
| Inflation with Additives | Air or nitrogen mixed with sealants or performance additives | Commercial fleets, off-road vehicles | Pro: Enhanced puncture resistance; better performance. Contro: Increased complexity; potential compatibility issues. |
| Specialized Air Mixtures | Custom blends for specific conditions (e.g., high altitude) | Aviation, specialized automotive applications | Pro: Tailored performance; optimized for specific environments. Contro: Higher cost; requires specialized knowledge for implementation. |
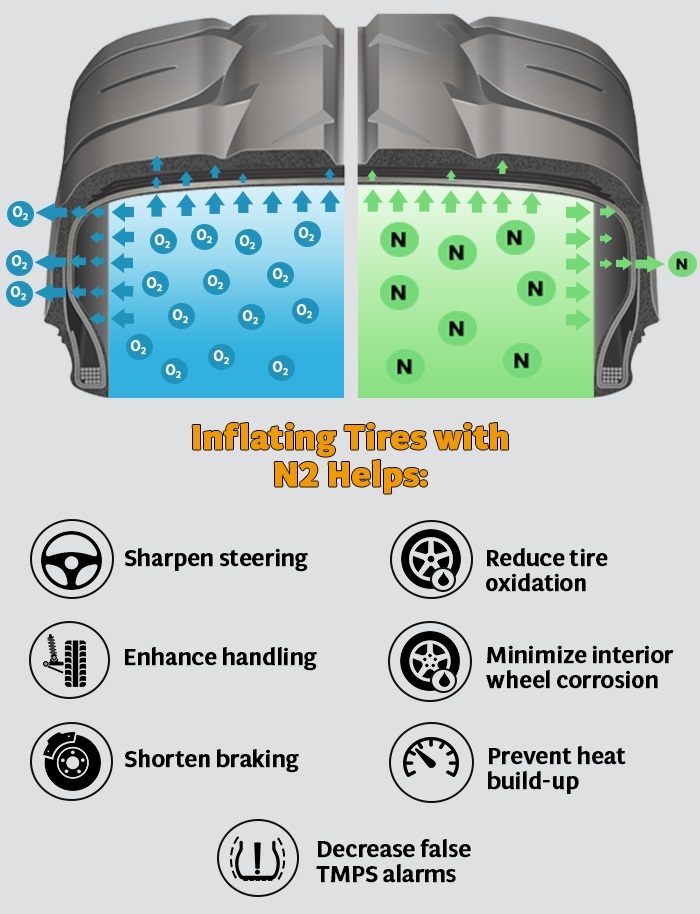
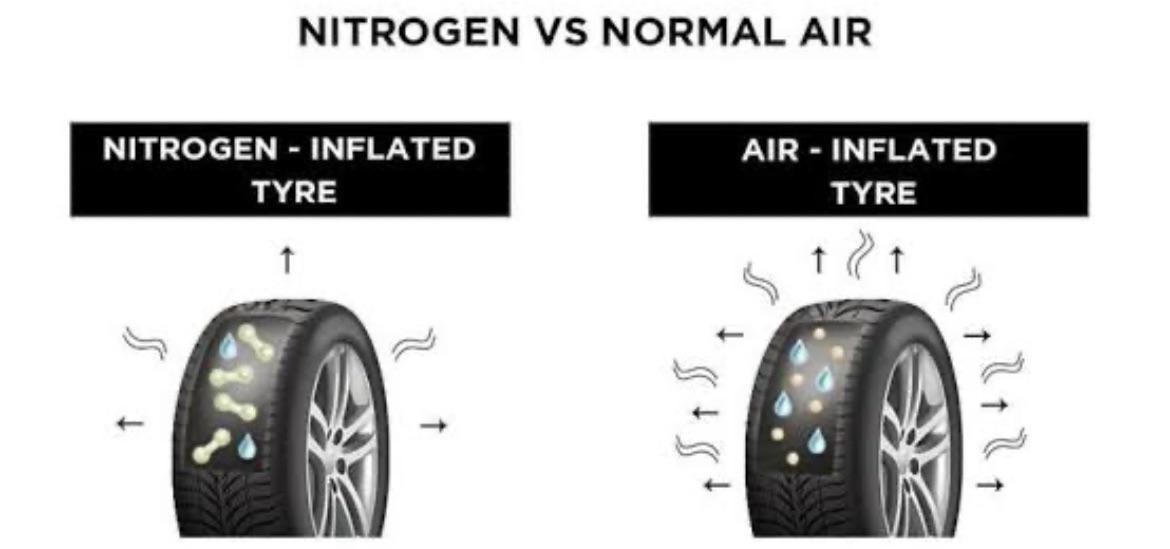
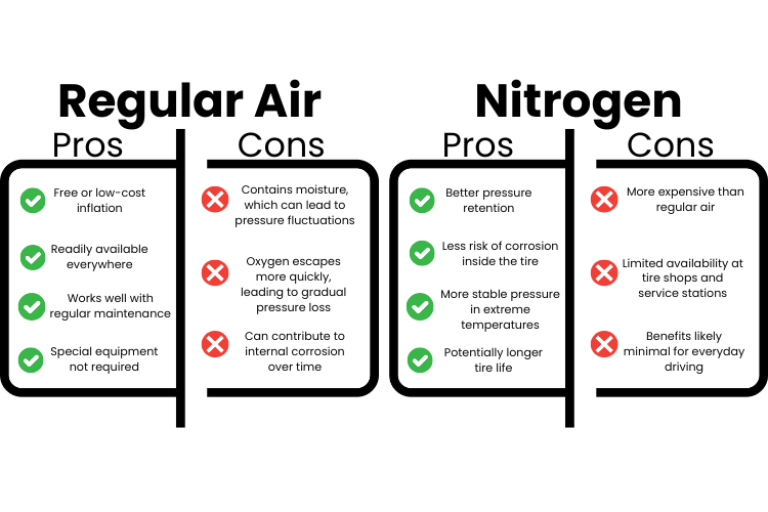
Standard air inflation utilizes a mixture of gases, predominantly nitrogen and oxygen. This option is the most commonly used for consumer vehicles and light trucks, making it readily available at most gas stations. The primary consideration for B2B buyers is cost-effectiveness, as air inflation is typically free at fuel stations. However, the downside is that tires filled with air lose pressure more quickly and are more sensitive to temperature changes, which can affect vehicle performance and safety.
Nitrogen inflation is characterized by its use of nearly pure nitrogen gas, which offers significant advantages for heavy-duty vehicles, racing cars, and aircraft. The larger nitrogen molecules reduce the rate of permeation through the tire walls, allowing for longer maintenance intervals. For B2B buyers, this means less frequent tire pressure checks and improved fuel efficiency. However, the initial investment is higher, and availability can be a challenge in certain regions, making it essential for businesses to evaluate their operational needs and local resources.
Hybrid inflation involves a combination of nitrogen and air, providing a middle-ground solution for mixed-use vehicles and fleet operations. This method offers some benefits of nitrogen, such as improved pressure retention, while remaining cost-effective. B2B buyers may find this option appealing due to its balance between performance and affordability. However, it’s essential to note that the effectiveness of nitrogen properties diminishes when mixed with air, which could lead to more frequent pressure loss compared to pure nitrogen.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
Inflation with additives entails using either air or nitrogen mixed with sealants or performance-enhancing additives, making it particularly advantageous for commercial fleets and off-road vehicles. This method can enhance puncture resistance and overall tire performance, addressing common challenges faced by heavy-use vehicles. However, B2B buyers should consider the increased complexity and potential compatibility issues, which may require additional training or resources to implement effectively.
Specialized air mixtures are tailored for specific conditions, such as high-altitude environments or extreme weather. These custom blends are essential for aviation and specialized automotive applications where precise performance is critical. While they offer optimized performance for unique scenarios, the higher costs and specialized knowledge required for implementation can be barriers for some businesses. B2B buyers must weigh the benefits against the investment and ensure they have the necessary expertise to manage these specialized solutions.
| Industria/Settore | Specific Application of tire inflation nitrogen vs air | Valore/Beneficio per l'azienda | Considerazioni chiave sull'approvvigionamento per questa applicazione |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Racing and Performance Vehicles | Enhanced tire pressure stability leading to improved handling and safety during high-speed maneuvers. | Access to specialized nitrogen filling equipment and trained personnel for tire maintenance. |
| Aviation | Aircraft Tires | Reduced tire pressure fluctuations, ensuring safety and performance during takeoff and landing. | Compliance with aviation regulations and availability of nitrogen filling stations at airports. |
| Heavy Machinery | Construction and Mining Equipment | Longer tire lifespan and reduced downtime due to fewer punctures and pressure loss. | Reliable supply chain for nitrogen, especially in remote job sites. |
| Transportation and Logistics | Fleet Management of Commercial Vehicles | Improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear, leading to cost savings over time. | Consideration of bulk nitrogen supply contracts and local filling stations. |
| Agricoltura | Agricultural Machinery Tires | Increased stability and traction in varying terrains, enhancing productivity in farming operations. | Availability of nitrogen filling services in rural areas and compatibility with various tire types. |
In the automotive sector, particularly in racing and performance vehicles, nitrogen is utilized for tire inflation to maintain consistent tire pressure under extreme conditions. This stability is crucial for safety and handling at high speeds, where even minor fluctuations can lead to significant performance issues. International B2B buyers in this sector must ensure they have access to specialized nitrogen filling equipment and trained personnel capable of maintaining these high-performance tires effectively.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
In aviation, nitrogen is the preferred inflation gas for aircraft tires due to its ability to minimize pressure fluctuations that can occur during flight. This consistency is vital for safe takeoffs and landings, where tire integrity is paramount. Aviation businesses must comply with stringent regulations and ensure that nitrogen filling stations are readily available at airports to maintain operational efficiency.
Heavy machinery used in construction and mining industries benefits from nitrogen-filled tires, which provide a longer lifespan and reduce the frequency of punctures and pressure loss. This durability translates to less downtime and improved productivity on job sites. B2B buyers in these sectors should consider the reliability of the nitrogen supply chain, especially when operating in remote locations where access to filling services may be limited.
For transportation and logistics companies managing large fleets, nitrogen inflation can lead to improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear. These benefits result in significant cost savings over time, making nitrogen a valuable investment for fleet operators. When sourcing nitrogen for tire inflation, businesses should look into bulk supply contracts and the availability of local filling stations to streamline operations.
In agriculture, nitrogen is increasingly used for inflating tires on farming equipment, as it provides better stability and traction across diverse terrains. This enhanced performance can lead to increased productivity during planting and harvesting seasons. Buyers in the agricultural sector should ensure that nitrogen filling services are accessible in rural areas and that the tires are compatible with various types of agricultural machinery.
Il problema: Many B2B buyers operating fleets face the challenge of maintaining consistent tire pressure across multiple vehicles. Fluctuations in tire pressure can lead to increased fuel consumption, reduced tire lifespan, and safety concerns. This problem is exacerbated in regions with extreme temperature variations, where air-filled tires can lose pressure more rapidly due to the expansion and contraction of air with temperature changes. As a result, fleet managers may find themselves constantly monitoring and adjusting tire pressure, leading to increased operational costs and downtime.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
La soluzione: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should consider switching to nitrogen for tire inflation. Nitrogen molecules are larger than those of oxygen, which means they permeate through tire walls more slowly, leading to better pressure retention. By investing in a nitrogen inflation system, fleet operators can enjoy longer intervals between tire pressure checks and reductions in fuel costs due to improved fuel efficiency. Establish partnerships with local tire service providers that offer nitrogen inflation services or consider setting up an in-house nitrogen generation system for larger fleets to ensure easy access. Regular training for maintenance staff on the benefits and handling of nitrogen inflation can further optimize tire performance and operational efficiency.
Il problema: For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in remote or underserved regions, access to nitrogen inflation services can be limited. Many gas stations and tire service centers may not offer nitrogen filling due to the higher costs and equipment requirements. This presents a significant challenge for businesses that have invested in nitrogen-filled tires, as they may find themselves unable to maintain proper tire pressure during long trips or in areas lacking service infrastructure.
La soluzione: B2B buyers should proactively evaluate their operational routes and establish strategic partnerships with reliable tire service providers that offer nitrogen inflation. Consider negotiating service agreements that include mobile nitrogen filling services for fleets on the road. Additionally, companies can invest in portable nitrogen inflation equipment that allows for on-site inflation, ensuring that tire maintenance can be conducted regardless of location. By creating a comprehensive plan that includes both local partnerships and portable solutions, businesses can alleviate the risk of being stranded with improperly inflated tires.
Il problema: Cost is a significant factor for many B2B buyers when deciding between nitrogen and air for tire inflation. While nitrogen offers advantages such as better pressure retention and improved tire longevity, the initial investment for nitrogen systems and the ongoing costs can deter businesses from making the switch. Fleet managers may struggle to justify the higher upfront costs when they have been using air without issues for years.
La soluzione: To address cost concerns, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that includes long-term savings from using nitrogen. This analysis should factor in the potential for improved fuel efficiency, reduced tire wear, and fewer maintenance interventions. Additionally, businesses can consider implementing a phased approach where a portion of their fleet transitions to nitrogen inflation initially. Monitoring the performance and cost savings of these vehicles can provide tangible data to support broader adoption. Collaborating with tire suppliers to explore bulk purchasing agreements or financing options for nitrogen systems can also help mitigate upfront costs and make the transition more feasible.
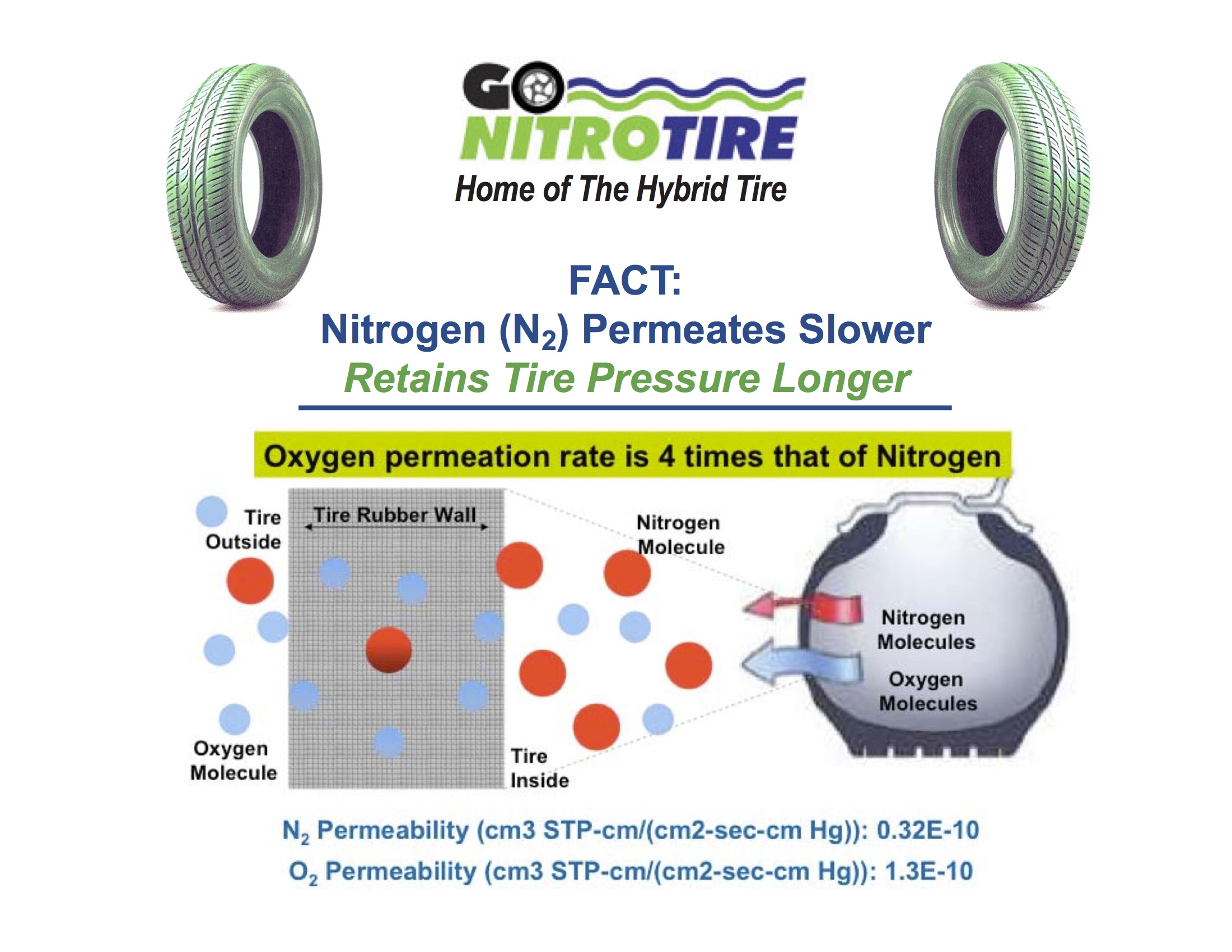
Nitrogen is a noble gas that is increasingly used for tire inflation, particularly in high-performance and heavy-duty applications. One of its key properties is its molecular structure; nitrogen molecules are larger than those of oxygen, which allows them to permeate through tire walls at a slower rate. This results in better tire pressure retention, especially in varying temperatures. Nitrogen is also non-corrosive, reducing the risk of oxidation within the tire, which can lead to premature wear.
The primary advantage of nitrogen-filled tires is their ability to maintain consistent pressure over time, which can enhance fuel efficiency, improve handling, and extend tire life. This is particularly beneficial for businesses operating fleets or heavy machinery, where tire performance directly impacts operational costs. However, nitrogen inflation comes with a higher upfront cost—typically $20 per tire—compared to air, which is often free at gas stations. Additionally, the availability of nitrogen filling stations can be limited, particularly in remote areas.
Air, composed of approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases, is the traditional medium for tire inflation. Its key properties include widespread availability and cost-effectiveness. Air is suitable for everyday driving and can be easily topped off at virtually any gas station, making it a practical choice for consumers and businesses alike.
The main disadvantage of air is its tendency to lose pressure more quickly than nitrogen, especially in extreme temperature conditions. This can lead to increased maintenance efforts and costs for businesses that rely on optimal tire performance. However, for many applications, the cost savings associated with air make it an attractive option.
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local regulations and standards is crucial. In Europe, for example, adherence to DIN standards is essential, while in Japan, JIS standards may apply. Buyers should also consider the availability of nitrogen filling stations in their region, as well as the cost implications of using nitrogen versus air.
In areas where tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are common, the benefits of nitrogen can be more pronounced, as these systems can help maintain optimal tire pressure and improve safety. Additionally, understanding the local market preferences and operational conditions can guide the decision-making process regarding tire inflation methods.
| Materiale | Typical Use Case for tire inflation nitrogen vs air | Vantaggio chiave | Svantaggi/limitazioni principali | Costo relativo (Basso/Medio/Alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Heavy-duty vehicles, racing, aircraft | Maintains pressure longer, reduces oxidation | Higher initial cost, limited availability | Alto |
| Air | Everyday vehicles, light-duty applications | Widespread availability, low cost | Loses pressure faster, less effective in extreme temperatures | Basso |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the strategic selection of materials for tire inflation, highlighting the advantages and limitations of nitrogen and air while considering regional compliance and operational needs.
The manufacturing process for tire inflation systems, whether utilizing nitrogen or air, involves several key stages that ensure the end product meets industry standards and customer expectations.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
The first stage of production includes sourcing high-quality materials. For nitrogen inflation systems, this often involves specialized equipment to extract and compress nitrogen gas. Air systems rely on standard air compressors. The materials used in tire manufacturing—such as rubber compounds, steel belts, and synthetic fibers—must meet specific quality standards. Suppliers should provide certifications verifying material compliance with international standards like ISO 9001, ensuring that the materials used are durable and reliable.
In this phase, the prepared materials are shaped into tire components. This involves processes such as molding rubber compounds into the desired tire shape. For nitrogen systems, additional attention is given to the integration of the nitrogen inflation valve, which must be designed to prevent gas leakage. Advanced forming techniques, such as precision molding and computer-aided design (CAD), help ensure that components fit perfectly, which is crucial for maintaining tire integrity and performance.
Once the components are formed, they are assembled into complete tire units. This includes fitting the inner liner, which is particularly important for nitrogen systems to minimize gas permeability. Automated assembly lines are commonly used to enhance efficiency and consistency. Quality assurance checkpoints during assembly ensure that each tire meets specifications, especially for those intended for high-performance applications.
The final stage involves curing and finishing the tires. Curing is a heat process that solidifies the rubber, enhancing its strength and durability. For nitrogen-filled tires, additional tests may be conducted to verify the integrity of the nitrogen retention systems. Finishing touches include inspection for surface defects and final testing of pressure retention capabilities.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
B2B buyers must be aware of the international standards and certifications that govern tire manufacturing and quality assurance.
ISO 9001 is a crucial quality management standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers with this certification demonstrate their commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification as it reflects a structured approach to quality management.
For manufacturers in Europe, CE marking is essential as it indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area. This certification can be particularly important for tires that are part of larger vehicle systems.
In specific industries, such as aviation or heavy machinery, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply. These standards help ensure that the tires can withstand extreme conditions and operational demands.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that tires perform safely and efficiently.
The first QC checkpoint occurs at the material preparation stage. Incoming materials, including rubber compounds and gas for inflation, are inspected for quality. Testing methods may include visual inspections, tensile strength tests, and chemical composition analyses to ensure compliance with specifications.
During the forming and assembly stages, in-process quality control is vital. This involves continuous monitoring and testing of production processes. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) help identify variations in manufacturing that could affect product quality. Regular checks ensure that each tire meets dimensional and performance specifications.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
Final quality control occurs after the curing and finishing stages. Tires undergo rigorous testing for pressure retention, durability, and performance under various conditions. Common testing methods include road simulations and pressure tests to verify that nitrogen-filled tires maintain optimal inflation levels.
For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control processes is essential for maintaining product integrity.
Buyers should conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and QC systems. These audits can reveal whether suppliers adhere to international standards and internal quality protocols.
Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline testing methods, results, and any deviations from expected standards. These documents serve as a record of the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can verify compliance with industry standards and assess the reliability of the manufacturer’s processes.
International buyers face unique challenges when evaluating suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations governing tire manufacturing. Buyers must familiarize themselves with local compliance requirements, which can differ significantly from international norms.
Language differences can complicate the understanding of quality documentation. Buyers should ensure that all quality-related documentation is available in a language they understand or seek translation services to clarify any uncertainties.
Cultural attitudes toward quality and compliance can differ from one region to another. Buyers should consider these cultural nuances when engaging with suppliers, particularly in negotiations regarding quality expectations and adherence to standards.
By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance for tire inflation systems, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain reliability and product performance.
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers considering whether to procure nitrogen or air for tire inflation. Understanding the differences between these two gases, along with their respective benefits and drawbacks, is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and cost considerations.
Begin by assessing the specific requirements of your fleet or operations. Consider factors such as vehicle types, average load weights, and the typical driving conditions. Understanding your operational context will help determine whether nitrogen or air is more suitable.
Evaluate the costs associated with both nitrogen and air filling options. While air is generally less expensive and widely available, nitrogen offers potential long-term savings through improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear.
Research potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specific needs. Look for companies that specialize in tire inflation solutions and have experience with your type of vehicles or equipment.
Quality assurance is crucial when selecting a supplier. Ensure that the nitrogen or air they provide meets industry standards and certifications.
Consider the equipment necessary for tire inflation and the maintenance needed for both nitrogen and air systems.
Access to nitrogen filling stations can be limited in certain regions, especially in remote areas. Consider the availability of nitrogen services relative to your operational locations.
After making your decision, monitor the performance of your tires and overall fleet efficiency. Collect data on tire pressure maintenance, fuel consumption, and maintenance costs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions regarding tire inflation options, ultimately enhancing vehicle performance and operational efficiency.
When evaluating the cost structure for tire inflation using nitrogen versus air, several cost components must be considered.
I materiali: The primary difference in materials lies in the gases themselves. Nitrogen is typically produced through fractional distillation or membrane separation, which incurs higher production costs compared to the readily available air. The costs associated with compressing, purifying, and storing nitrogen can be significant, influencing the overall pricing model.
Lavoro: Labor costs are associated with the handling and inflation process. While inflating tires with air is straightforward and can be done quickly at various service points, nitrogen inflation often requires specialized training and equipment, resulting in higher labor costs.
Spese generali di produzione: Companies providing nitrogen inflation services might have higher overhead due to the need for specialized equipment and maintenance. This includes nitrogen generators or storage tanks, which require regular upkeep and monitoring.
Utensili: The equipment needed for nitrogen inflation is generally more expensive than standard air pumps. This includes high-pressure nitrogen tanks and inflation systems designed to ensure precise control over tire pressure.
Controllo qualità (CQ): Ensuring the purity and pressure of nitrogen-filled tires requires rigorous quality control measures, which can add to operational costs. In contrast, air does not require the same level of scrutiny.
Logistica: The distribution of nitrogen involves additional logistics costs, especially if the service provider needs to transport nitrogen tanks or generators to various locations. This is less of a concern with air, which is widely available.
Margine: Given the higher costs associated with nitrogen inflation, suppliers often mark up prices to maintain a profit margin. This margin can vary significantly based on the local market dynamics and competition.
Several factors influence pricing for nitrogen and air tire inflation:
Volume/MOQ (quantità minima d'ordine): Bulk purchasing of nitrogen services can lead to discounts. Larger fleets or businesses with high-volume needs may negotiate better pricing due to their buying power.
Specifiche/Personalizzazione: Customization requests, such as specific tire pressure requirements or specialized services for different vehicle types, can lead to increased costs. Businesses should assess whether these additional services are necessary.
Materiali e certificazioni di qualità: The quality of nitrogen (e.g., purity levels) and certifications can influence pricing. Suppliers who provide certified nitrogen may charge a premium due to the assurance of quality and performance.
Fattori di fornitura: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service quality can also impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. The terms determine who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect the overall cost of procurement.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
Negoziazione: Leverage purchasing power and competitive offers to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may be willing to lower costs for long-term contracts or bulk orders.
Costo totale di proprietà (TCO): Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Factors such as tire longevity, fuel efficiency, and maintenance costs should be included in the decision-making process.
Le sfumature dei prezzi per gli acquirenti internazionali: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Engaging with local suppliers may mitigate some of these costs.
Evaluate Local Suppliers: In regions with limited access to nitrogen inflation services, local suppliers may offer competitive pricing for air inflation, which could be more cost-effective in the short term.
Rimanete informati sulle tendenze del mercato: Keeping abreast of market trends and pricing models can provide leverage during negotiations and help buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
Prices for nitrogen and air tire inflation services can vary widely based on local market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and service offerings. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing.
In the tire inflation market, the debate between nitrogen and air is well-known. However, several alternative solutions exist that can also enhance tire performance and efficiency. This section compares tire inflation with nitrogen versus air against other viable methods, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their operational needs.
| Aspetto di confronto | Tire Inflation Nitrogen Vs Air | Alternative 1: Helium Inflation | Alternative 2: Tire Sealant Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prestazioni | Maintains pressure longer, reduces oxidation | Lower density can improve fuel efficiency, but less stable | Provides puncture protection, maintains pressure |
| Costo | Higher initial cost (up to $20/tire), but potential long-term savings | Generally expensive; availability can be limited | Moderate cost; varies by product, but generally affordable |
| Facilità di implementazione | Requires specialized equipment, not universally available | Requires specialized handling and storage | Easy to implement; can be added during routine maintenance |
| Manutenzione | Low maintenance, but nitrogen refills can be costly | Limited maintenance; helium is less common and can leak faster | Regular checks needed for effectiveness; may need replacement |
| Il miglior caso d'uso | Ideal for high-performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications | Best for specialized applications requiring weight reduction | Suitable for everyday vehicles needing puncture protection |
Helium inflation is an alternative that utilizes the lighter-than-air properties of helium. Theoretically, helium can reduce rolling resistance and improve fuel efficiency due to its lower density compared to air. However, helium is not as stable within tires as nitrogen, leading to potential pressure loss over time. Additionally, helium inflation can be significantly more expensive and requires specialized handling. This option is best suited for specialized applications, such as racing or high-performance vehicles where every ounce of weight matters.
Tire sealant systems provide an innovative solution by incorporating a sealant liquid that fills punctures and maintains tire pressure. This method is particularly advantageous for everyday vehicles, as it mitigates the need for frequent inflation. Sealants can effectively seal punctures up to a certain size, ensuring safety and performance. However, regular checks are necessary to ensure the sealant remains effective, and in some cases, the sealant may require replacement after a certain mileage. While the initial investment is moderate, the long-term benefits may outweigh the costs for many fleet operators.
When evaluating tire inflation options, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, including vehicle type, usage patterns, and budget constraints. For high-performance or heavy-duty applications, nitrogen may provide the best long-term benefits despite its higher initial cost. Conversely, businesses focused on cost-effective solutions for everyday vehicles might find tire sealant systems to be more practical. Ultimately, understanding the pros and cons of each option will empower buyers to choose the best solution that aligns with their operational goals and enhances their overall efficiency.
When considering tire inflation options, understanding the technical properties of nitrogen and air is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications and their B2B significance:
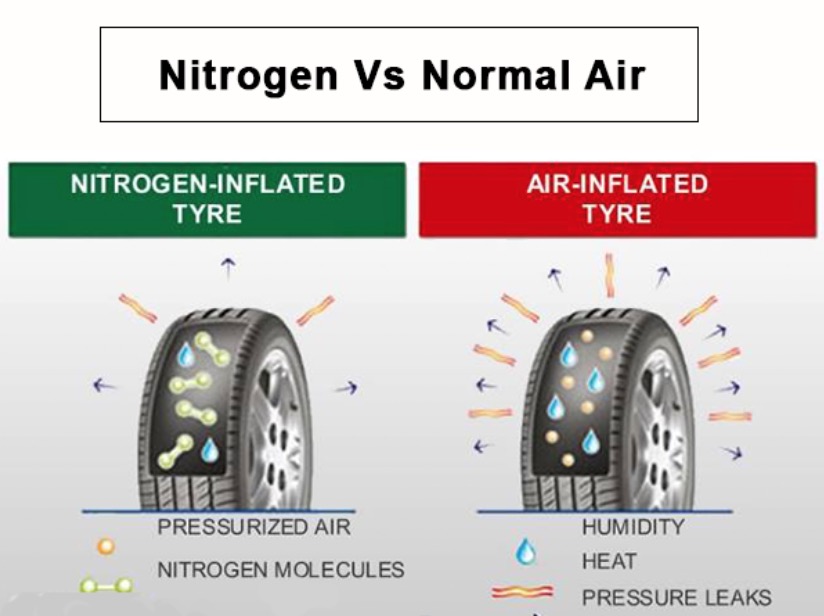
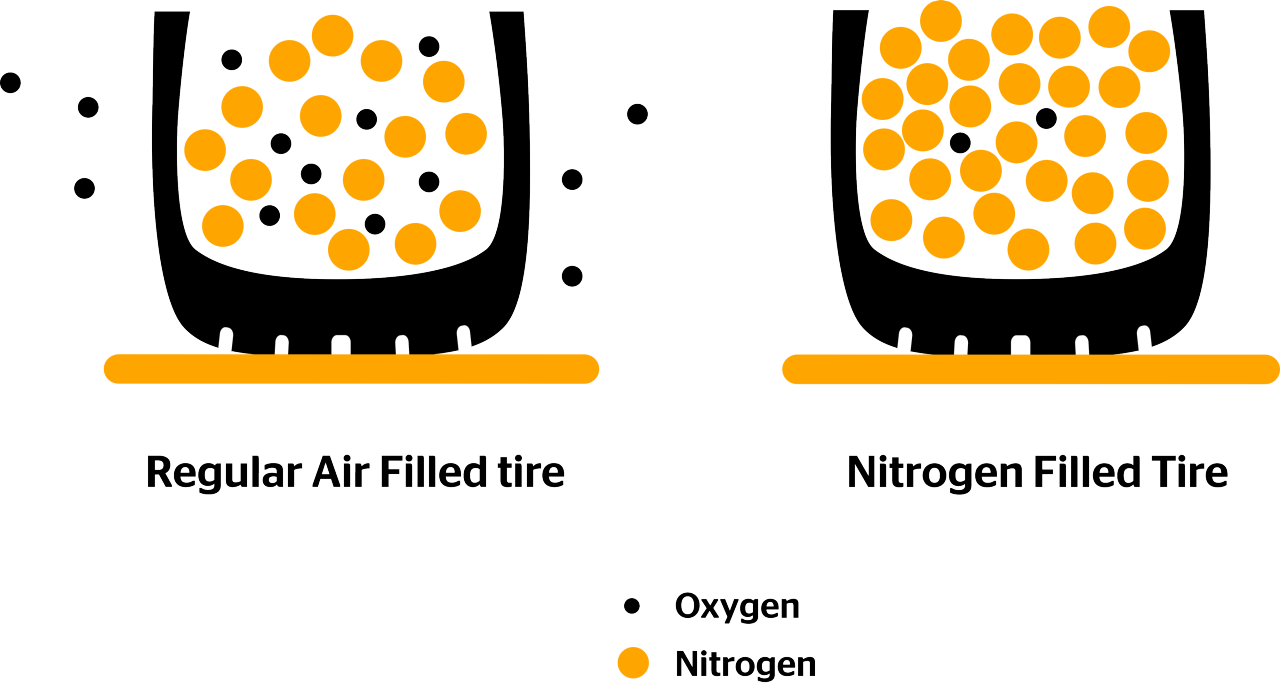
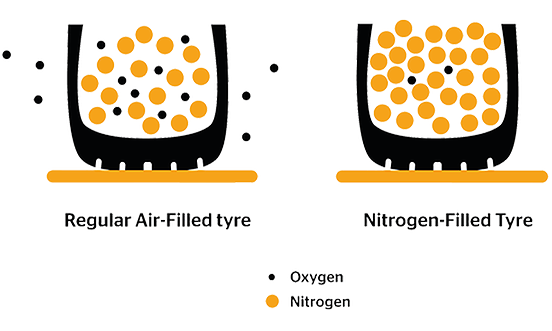
Nitrogen molecules are larger than oxygen molecules, which means they are less likely to permeate through the rubber of the tire. This property is essential for maintaining tire pressure over time, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. For B2B buyers, this translates into reduced maintenance costs and increased safety through better tire management.
Nitrogen-filled tires tend to retain pressure longer compared to those filled with air. This is particularly important for industries reliant on heavy machinery or transportation, where consistent tire pressure can significantly impact operational efficiency. Businesses can benefit from fewer tire-related issues, leading to lower downtime and maintenance expenses.
Nitrogen is less affected by temperature fluctuations than air. This characteristic ensures that tire pressure remains stable in varying environmental conditions, which is critical for operations in regions with extreme temperatures. For B2B buyers, this stability can enhance the reliability of their fleet, contributing to better performance and safety.
Air contains water vapor, which can lead to tire degradation and pressure changes. In contrast, nitrogen is dry, reducing the risk of corrosion and maintaining tire integrity. For businesses, this means extended tire life and reduced replacement costs, making nitrogen a more cost-effective option in the long run.
While nitrogen inflation is generally more expensive than air inflation, the benefits of improved tire performance can justify the initial investment. For B2B buyers, understanding the cost-benefit ratio is crucial for budgeting and operational planning.
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and decision-making in B2B contexts. Here are some essential terms related to tire inflation:
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For tire suppliers, knowing the OEM specifications ensures that the tires purchased meet the original vehicle standards, crucial for maintaining warranty and performance.
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of tire inflation, understanding the MOQ can help B2B buyers negotiate better pricing and manage inventory levels effectively, ensuring they meet operational demands without overstocking.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
An RFQ is a formal document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers. For tire procurement, submitting an RFQ can streamline the sourcing process, allowing businesses to compare options and secure the best deals based on their specific needs.
These are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers involved in cross-border tire purchases, as they determine who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall cost and logistics.
PSI is a unit of pressure commonly used to measure tire inflation levels. For businesses, maintaining the correct PSI is crucial for vehicle safety and performance, making it essential to understand how nitrogen and air affect pressure retention.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding tire inflation options, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
The tire inflation market is witnessing a transformative phase, driven by the increasing awareness of safety, efficiency, and environmental impact. The adoption of nitrogen over conventional air for tire inflation is gaining traction, particularly among fleet operators and high-performance vehicle users. Key drivers include the growing emphasis on fuel efficiency, as nitrogen-filled tires maintain pressure longer, leading to better mileage. Additionally, the automotive industry is increasingly focusing on performance metrics, with nitrogen providing enhanced handling and stability under varying temperature conditions.
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are also influencing sourcing trends. These systems can alert users about tire pressure changes in real-time, facilitating the use of nitrogen for its superior pressure retention capabilities. International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should note that nitrogen inflation stations are becoming more prevalent, although availability remains a concern in remote areas.
Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
The market is also witnessing a shift towards more integrated supply chains, where manufacturers are exploring partnerships with local service providers to offer nitrogen inflation services. This trend enhances accessibility for B2B buyers and supports the growing demand for specialized tire maintenance solutions.
Sustainability is a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the tire inflation sector. The environmental impact of tire performance, particularly regarding fuel consumption and emissions, has led to increased scrutiny of sourcing practices. Nitrogen has a lower carbon footprint compared to air due to its efficiency in maintaining tire pressure, which translates to better fuel economy and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly important, with buyers looking for suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. This includes using ‘green’ certifications and materials in the production and supply chain processes. Companies that adopt eco-friendly practices can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Additionally, the rise of circular economy principles is influencing sourcing strategies. Buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers who recycle used tires or offer tire retreading services, reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency. By prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing decisions, B2B buyers can contribute to a more responsible industry while also potentially reducing costs associated with waste management.
The evolution of tire inflation practices has been significant, particularly with the introduction of pneumatic tires in the late 19th century. Initially, tires were filled with air, which became the standard for automotive applications due to its accessibility and cost-effectiveness. However, as vehicle technology advanced, the limitations of air became apparent, particularly in high-performance and heavy-duty applications.
The use of nitrogen for tire inflation began to gain popularity in the late 20th century, initially in aviation and motorsports, where pressure stability and performance were paramount. This trend gradually expanded into the consumer automotive market, driven by the need for better fuel efficiency and safety.
Today, nitrogen inflation is being recognized not only for its performance benefits but also for its contribution to sustainability. As B2B buyers navigate the market, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into current practices and future trends in tire inflation.
How do I choose between nitrogen and air for tire inflation in my fleet?
Choosing between nitrogen and air for tire inflation depends on your fleet’s operational needs. Nitrogen maintains tire pressure longer due to its larger molecule size, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear. If your vehicles operate in extreme conditions or require maximum performance, nitrogen may be beneficial. However, for everyday use, particularly in regions with limited access to nitrogen filling stations, air may be more practical and cost-effective. Assess your specific usage, maintenance capabilities, and cost implications before making a decision.
What are the key benefits of using nitrogen over air for tire inflation?
The primary benefits of nitrogen include better pressure retention, reduced oxidation of tire materials, and improved safety due to more stable tire pressure under varying temperatures. Nitrogen-filled tires can also enhance fuel efficiency, comfort, and handling, making them advantageous for performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications. However, the cost of nitrogen inflation and availability should be considered, particularly in regions where air is readily accessible and free at gas stations.
Can I mix nitrogen and air in my tires, and what are the implications?
Yes, you can mix nitrogen and air in your tires, but it’s not recommended if you want to maximize the benefits of nitrogen inflation. Mixing will dilute the nitrogen concentration, leading to less effective pressure retention and potentially negating the advantages of using nitrogen. If you need to inflate a nitrogen-filled tire, try to top it off with nitrogen to maintain its benefits. Regular checks and maintenance are crucial to ensure optimal tire performance regardless of the inflation method used.
What should I consider when sourcing nitrogen inflation systems for my business?
When sourcing nitrogen inflation systems, consider factors such as system efficiency, cost, maintenance requirements, and supplier reputation. Evaluate the technology’s compatibility with your existing tire maintenance operations. Look for systems that offer reliable performance and support, including installation services and training. Additionally, assess whether the supplier can provide ongoing service and parts availability, especially if you’re operating in regions with limited technical support.
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for nitrogen inflation equipment?
Minimum order quantities for nitrogen inflation equipment can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may offer flexible MOQ options to accommodate smaller businesses, while others may require bulk orders to provide competitive pricing. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify the MOQ and explore options for scaling your order as your business grows. Additionally, inquire about the possibility of trial units or rental agreements to test the equipment before committing to larger purchases.
How can I ensure the quality of nitrogen inflation systems from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet international suppliers by checking their certifications, customer reviews, and industry experience. Request samples or demonstrations of their nitrogen inflation systems to evaluate performance. Additionally, inquire about quality assurance processes, warranties, and after-sales support. Establishing a good communication channel with the supplier can also help clarify any concerns regarding product quality and compliance with local regulations.
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing tire inflation equipment internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation leverage. Common terms include upfront payments, net 30 or net 60 days, and letters of credit for larger orders. Ensure to discuss and agree on payment terms that protect your business interests, especially considering currency fluctuations and international transaction fees. Establishing a solid relationship with your supplier can also facilitate more favorable terms over time.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for importing nitrogen inflation systems?
When importing nitrogen inflation systems, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply. Choose a logistics partner experienced in international trade to navigate the complexities of importing equipment. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Additionally, factor in lead times for shipping and delivery to align with your operational needs and minimize downtime.
Dominio: principlevolvocarssanantonio.com
Registrato: 2017 (8 anni)
Introduzione: Nitrogen-filled tires can hold their pressure longer, potentially improving comfort and fuel economy. Filling tires with air is less expensive and more commonly available at gas stations. Both nitrogen and air can effectively fill tires, each having unique advantages and disadvantages. Nitrogen is preferred in heavy-duty applications and race cars due to its larger molecular size, which helps main…
Dominio: continentaltire.com
Registrato: 1996 (29 anni)
Introduzione: Nitrogen is offered as an alternative to air for tire inflation. It is an inert gas that does not support moisture or combustion, primarily used in specialized applications like aircraft, mining, and professional auto racing. Nitrogen may marginally reduce tire inflation loss by permeation but does not prevent loss from punctures or leaks. Continental Tire recommends checking tire inflation pressu…
Dominio: generaltire.com
Registrato: 1996 (29 anni)
Introduzione: Nitrogen is used as an alternative to air for tire inflation due to its inert properties, which do not support moisture or combustion. It is primarily beneficial in specialized applications such as aircraft, mining, commercial/heavy use, and professional auto racing, where precise tire pressure is critical. For everyday consumer use, nitrogen inflation is not required or overly beneficial, but it …
In evaluating the strategic sourcing of tire inflation options, the choice between nitrogen and air reveals significant implications for operational efficiency and cost management. Nitrogen-filled tires offer enhanced pressure retention, improved fuel efficiency, and better performance under varying temperatures, making them particularly advantageous for heavy-duty vehicles and fleets. Conversely, air remains a more accessible and cost-effective option for everyday consumers and businesses with less specialized needs.

Illustrative image related to tire inflation nitrogen vs air
International B2B buyers should prioritize understanding their unique operational requirements when selecting a tire inflation method. The strategic sourcing of nitrogen could yield long-term benefits for organizations seeking to optimize tire performance and reduce maintenance costs. However, the availability and pricing of nitrogen services in specific regions, especially in Africa and South America, must be factored into decision-making processes.
As the market continues to evolve, businesses should stay informed about advancements in tire technology and inflation options. By aligning their sourcing strategies with the specific needs of their operations, companies can leverage these insights to enhance fleet performance and drive competitive advantage. Embrace the opportunity to evaluate your tire inflation strategies and make informed decisions that propel your business forward.
Le informazioni fornite in questa guida, compresi i contenuti relativi ai produttori, alle specifiche tecniche e all'analisi di mercato, hanno uno scopo puramente informativo ed educativo. Non costituiscono una consulenza professionale in materia di acquisti, né una consulenza finanziaria o legale.
Pur avendo compiuto ogni sforzo per garantire l'accuratezza e la tempestività delle informazioni, non siamo responsabili di eventuali errori, omissioni o informazioni non aggiornate. Le condizioni di mercato, i dettagli aziendali e gli standard tecnici sono soggetti a modifiche.
Gli acquirenti B2B devono condurre una due diligence indipendente e approfondita. prima di prendere qualsiasi decisione di acquisto. È necessario contattare direttamente i fornitori, verificare le certificazioni, richiedere campioni e chiedere una consulenza professionale. Il rischio di affidarsi alle informazioni contenute in questa guida è esclusivamente a carico del lettore.