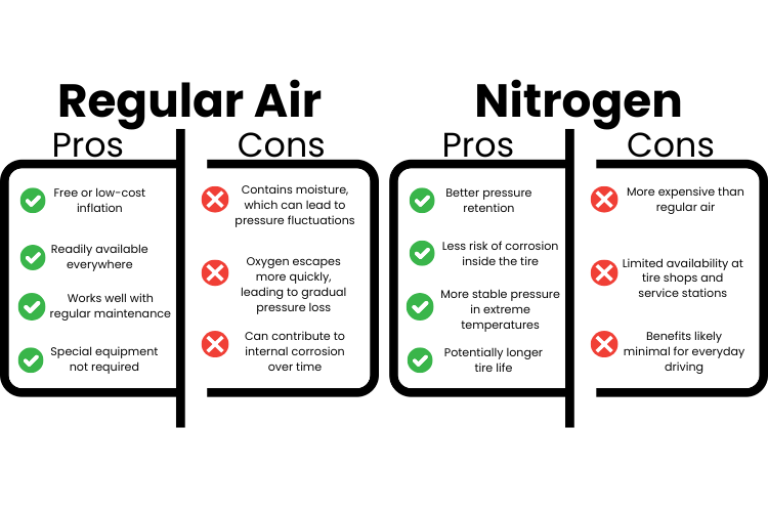
In today’s global market, one of the pressing challenges facing international B2B buyers is understanding whether they can put regular air in nitrogen-inflated tires. This question often arises in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where tire inflation practices can vary significantly. As businesses seek to optimize their fleet operations, it is crucial to have clarity on the implications of mixing air with nitrogen in tires, especially regarding safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip decision-makers with vital insights into the nuances of tire inflation options. We will explore the types of gases used in tire inflation, the specific applications of nitrogen versus regular air, and the implications for tire maintenance. Additionally, we will provide strategies for vetting suppliers, understanding the associated costs, and making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs.
By addressing these critical areas, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of tire maintenance more effectively. In doing so, it helps organizations enhance their operational efficiency and ensure the safety and performance of their vehicles, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicativos B2B primários | Prós e contras resumidos para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Nitrogen Refill | Tires are refilled exclusively with nitrogen, maintaining high purity. | Fleet management, high-performance vehicles | Pros: Optimal pressure retention; Cons: Limited availability of nitrogen refill stations. |
| Mixed Air Refill | Regular air is added to nitrogen-filled tires, lowering nitrogen purity. | General consumer vehicles, light trucks | Pros: Convenient; Cons: Reduces benefits of nitrogen. |
| Complete Air Replacement | Tires are fully deflated and filled with regular air. | Cost-sensitive businesses, budget fleets | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Loss of nitrogen benefits. |
| Hybrid Approach | Alternating between nitrogen and air refills based on availability. | Mixed-use fleets, diverse vehicle types | Pros: Flexibility; Cons: Inconsistent pressure performance. |
| Specialized Nitrogen Systems | Advanced systems for continuous nitrogen generation and monitoring. | Racing teams, specialized transport | Pros: High performance; Cons: High initial investment. |
Direct nitrogen refill involves using pure nitrogen to inflate tires, which helps maintain tire pressure longer than regular air. This method is particularly beneficial for fleet management and high-performance vehicles, where consistent tire pressure is crucial for safety and efficiency. Businesses should consider the availability of nitrogen refill stations and potential costs associated with maintaining this standard.
Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
Mixed air refill occurs when regular air is added to nitrogen-filled tires. While this method offers convenience and immediate access to air, it dilutes the nitrogen purity, thereby reducing the benefits associated with nitrogen inflation. This option is suitable for general consumer vehicles and light trucks, where cost and availability take precedence over tire performance.
Complete air replacement involves fully deflating nitrogen-filled tires and refilling them with regular air. This option is often chosen by cost-sensitive businesses and budget fleets. While it is a more economical choice, it results in the loss of the advantages provided by nitrogen, such as reduced pressure loss and improved fuel efficiency. Businesses should weigh the cost savings against potential long-term impacts on tire performance.
The hybrid approach combines the use of nitrogen and air based on availability and practicality. This method is particularly useful for mixed-use fleets and diverse vehicle types, offering flexibility in managing tire inflation. While it allows for convenience in refilling, businesses must be aware that this inconsistency can lead to variable tire pressure performance, which may affect overall safety and efficiency.

Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
Specialized nitrogen systems are designed for continuous nitrogen generation and monitoring, making them ideal for racing teams and specialized transport. These systems provide high performance and consistent tire pressure, which are critical in competitive environments. However, businesses should consider the high initial investment and maintenance costs associated with these advanced systems before implementation.
| Indústria/Setor | Specific Application of can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Principais considerações de fornecimento para este aplicativo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet Management for Trucks and Buses | Enhanced tire longevity and reduced maintenance costs | Availability of nitrogen filling stations; cost of nitrogen vs. air |
| Construção | Heavy Equipment Operations | Improved safety and performance of machinery | Access to reliable air or nitrogen sources; tire pressure monitoring |
| Automotive Service & Repair | Tire Maintenance Services | Increased customer satisfaction through effective tire management | Training for technicians on nitrogen vs. air; customer education |
| Aviation | Ground Support Equipment (GSE) | Enhanced performance and safety in aircraft operations | Compliance with aviation standards; sourcing of nitrogen filling |
| Motorsport | Racing Teams | Optimal tire performance and pressure management | Access to specialized nitrogen filling; quick service requirements |
In the transportation and logistics sector, fleet management for trucks and buses often involves the use of nitrogen-filled tires. While it is possible to top off nitrogen tires with regular air, the preferred practice is to maintain nitrogen levels for optimal performance. Businesses benefit from enhanced tire longevity and reduced maintenance costs, as nitrogen helps maintain tire pressure longer than regular air. Buyers should consider the availability of nitrogen filling stations and the cost implications of nitrogen versus regular air, particularly in regions where nitrogen services may be limited.
In the construction industry, heavy equipment operations frequently utilize nitrogen-inflated tires for improved safety and performance. Regular air can be added to nitrogen-filled tires if necessary, but maintaining a high nitrogen concentration is ideal for minimizing pressure loss. This practice ensures that construction machinery operates efficiently, reducing the risk of tire blowouts and associated downtime. Buyers must ensure access to reliable air or nitrogen sources and consider the importance of tire pressure monitoring systems to maintain optimal performance on-site.
Automotive service and repair businesses often encounter customers with nitrogen-filled tires. Offering tire maintenance services that include the option to top off with regular air can enhance customer satisfaction by providing a convenient solution. While nitrogen offers advantages such as better pressure retention, educating customers about the implications of mixing air with nitrogen is crucial. Service providers should train technicians on the differences between nitrogen and air, ensuring they can effectively communicate the benefits and considerations to customers.
Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
In aviation, ground support equipment (GSE) often relies on nitrogen-filled tires to enhance performance and safety during aircraft operations. While it is technically feasible to mix regular air with nitrogen, aviation standards typically favor pure nitrogen for its stability and reduced risk of pressure fluctuations. Businesses in this sector must comply with strict aviation standards and ensure that their nitrogen filling sources are reliable and readily available to maintain safety and performance.
In the motorsport industry, racing teams utilize nitrogen-filled tires for optimal tire performance and pressure management during races. While teams may occasionally need to top off tires with regular air, maintaining a high nitrogen concentration is critical for achieving the best performance on the track. Quick access to specialized nitrogen filling stations is essential, as is the ability to manage tire pressure effectively under race conditions. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing reliable nitrogen services to meet the demanding needs of competitive racing.
O problema: Many B2B buyers, particularly in regions with limited access to specialized automotive services, struggle to find reliable nitrogen refill stations. This challenge is exacerbated in remote areas or countries where nitrogen tire filling is not a common practice. As a result, these buyers may face inflated operational costs and logistical hurdles, as having to travel long distances to obtain nitrogen can lead to increased downtime for their fleets.
A solução: To mitigate this issue, businesses should consider establishing partnerships with local tire service providers who can offer nitrogen refilling services. Additionally, investing in portable nitrogen generators can provide an in-house solution for tire inflation. These generators can produce nitrogen on-site, ensuring that the fleet can be serviced promptly without the need for external suppliers. Furthermore, educating staff on the importance of tire pressure maintenance and the benefits of nitrogen over air can foster a proactive approach to tire management, ultimately leading to enhanced fleet performance.
Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
O problema: B2B buyers often encounter confusion regarding the real advantages of using nitrogen-filled tires compared to regular air. Some may perceive nitrogen as merely a marketing gimmick, leading to skepticism about its necessity and effectiveness. This misunderstanding can result in companies neglecting proper tire maintenance, which may subsequently affect vehicle safety and operational efficiency.
A solução: To address this knowledge gap, businesses should invest in educational resources that clearly outline the benefits of nitrogen-filled tires, such as reduced pressure loss, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced tire longevity. Hosting workshops or training sessions for fleet managers and drivers can help reinforce the importance of maintaining the correct tire pressure and the role of nitrogen in achieving this. Furthermore, companies can consider implementing a tire management program that regularly monitors tire pressure and overall health, ensuring that the fleet operates safely and efficiently.
O problema: A common concern among B2B buyers is whether they can mix regular air with nitrogen in their tires without compromising performance. This uncertainty can lead to anxiety about maintaining optimal tire pressure and the potential risks associated with improper inflation practices. Buyers may feel pressured to choose between the convenience of regular air and the perceived benefits of nitrogen.
A solução: Educating staff on the chemical properties of air and nitrogen can alleviate concerns about mixing the two. It’s important to communicate that while it is technically possible to mix air with nitrogen, it will dilute the nitrogen concentration and may reduce the benefits associated with nitrogen inflation. B2B buyers should be encouraged to fully deflate and refill the tires with nitrogen whenever possible to maintain the intended benefits. Additionally, providing easy access to tire pressure monitoring tools can empower businesses to regularly check and adjust tire pressure, ensuring safe and efficient fleet operation regardless of the inflation method used.
When considering the use of regular air in nitrogen-inflated tires, it’s essential to analyze the materials involved in tire inflation and their implications for performance, safety, and compliance in various international markets. Below, we explore the key materials related to tire inflation and their respective properties, advantages, and limitations.
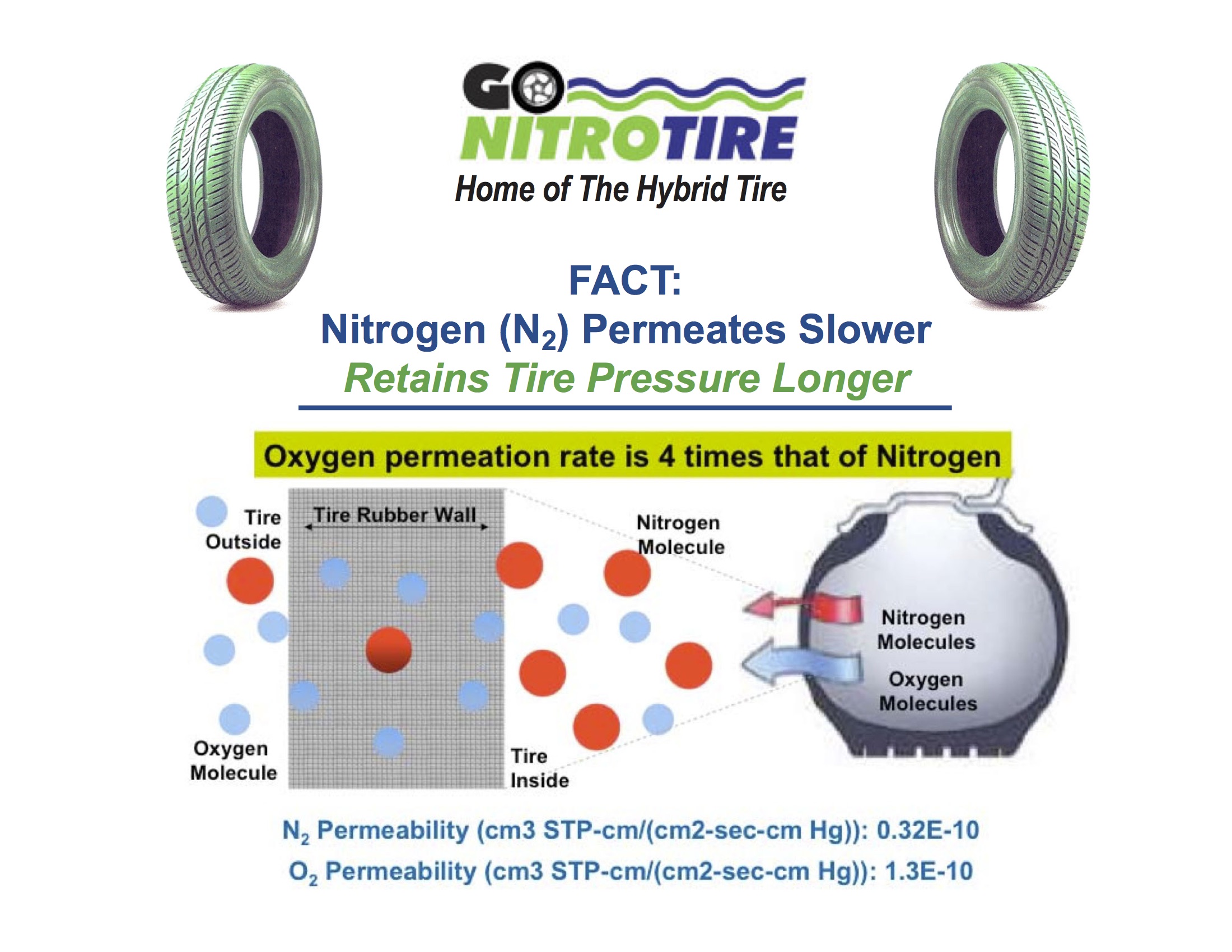
Principais propriedades: Nitrogen is an inert gas that does not support combustion and has a low permeability through rubber, which helps maintain tire pressure over time. Its molecular structure allows for better temperature stability, making it advantageous in extreme conditions.
Prós e contras: The primary advantage of using nitrogen is its ability to reduce pressure loss, extending the time between necessary refills. However, nitrogen inflation can be more expensive due to the need for specialized equipment and facilities for filling tires.
Impacto no aplicativo: Using nitrogen can lead to improved tire performance, especially in high-stress applications such as racing or heavy-duty vehicles. However, for regular street use, the benefits may be marginal.
International Considerations: Compliance with local regulations regarding gas handling and tire inflation practices is crucial. In regions like Africa and the Middle East, where nitrogen filling stations may be scarce, the practicality of maintaining nitrogen-filled tires can be limited.
Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
Principais propriedades: Compressed air is a mixture that consists of approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases. It is readily available and can be filled using standard air compressors.
Prós e contras: The major benefit of using compressed air is its accessibility and low cost, making it a practical choice for everyday vehicles. However, it has a higher moisture content than nitrogen, which can lead to pressure fluctuations and potential tire degradation over time.
Impacto no aplicativo: Regular air can be used to refill nitrogen-inflated tires without causing immediate harm; however, doing so will dilute the nitrogen concentration, negating some of the benefits associated with nitrogen inflation.
International Considerations: Different regions have varying standards for air quality. For instance, compliance with local ASTM or DIN standards may dictate the acceptable moisture levels in compressed air used for tire inflation.

Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
Principais propriedades: The rubber used in tires is designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures. It is typically reinforced with materials like steel or polyester to enhance durability.
Prós e contras: High-quality rubber provides excellent performance and longevity, but it can be sensitive to the internal gas composition. The presence of moisture from compressed air can accelerate rubber degradation.
Impacto no aplicativo: The compatibility of tire rubber with both nitrogen and air is generally high. However, the introduction of moisture from air can lead to premature wear and reduced performance.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure that the rubber materials comply with international standards such as ISO or JIS, particularly in regions with extreme climates, where temperature fluctuations can affect tire performance.
Principais propriedades: Tire valves are often made from brass or plastic, designed to withstand the internal pressures of the tire and provide a seal against leakage.
Prós e contras: Brass valves are durable and resistant to corrosion, while plastic valves are lightweight and cost-effective. However, plastic may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as brass.
Impacto no aplicativo: The choice of valve material can affect the longevity and safety of both nitrogen and air-filled tires. A compromised valve can lead to air loss, regardless of the gas used.
International Considerations: Compliance with local manufacturing standards is essential, particularly in regions like Europe where stringent regulations may apply to automotive components.
| Material | Typical Use Case for can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires | Principais vantagens | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Gas | High-performance and racing applications | Maintains tire pressure longer | Higher filling cost and limited availability | Alta |
| Compressed Air | Everyday vehicle maintenance | Readily available and cost-effective | Higher moisture content can degrade tires | Baixa |
| Tire Rubber Material | All types of tires for various vehicles | Excellent durability and performance | Sensitive to moisture from compressed air | Médio |
| Tire Valve Materials | Used in all tire types for inflation | Durable and effective sealing | Plastic valves may not withstand high temperatures | Médio |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in the process of filling nitrogen-inflated tires with regular air, highlighting key properties, advantages, and considerations that international B2B buyers should keep in mind. Understanding these factors can aid in making informed decisions that align with operational needs and regional compliance standards.
Manufacturing tires filled with nitrogen involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets both performance and safety standards. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
The production of nitrogen-inflated tires starts with the careful selection of raw materials. Rubber compounds, fabric, and steel belts are the primary materials utilized. The rubber must be formulated to withstand the rigors of driving while maintaining elasticity and durability.
In this phase, suppliers often leverage advanced materials technology to enhance performance characteristics. For instance, incorporating silica into the rubber can improve fuel efficiency and grip. B2B buyers should inquire about the sourcing of materials and whether they comply with international safety standards.
Once materials are prepared, the next phase is tire forming. This involves several techniques, including:
B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that utilize automated systems for consistency and precision during the assembly process. Automation can reduce human error and improve production efficiency.

Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
Quality assurance (QA) in tire manufacturing is crucial to ensure safety and performance. Various international and industry-specific standards govern these practices.
Manufacturers often adhere to ISO 9001, a standard that outlines quality management principles. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that a company maintains effective processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, CE marking may be relevant for products sold in European markets, indicating compliance with safety and environmental standards.
For B2B buyers, understanding a supplier’s adherence to these standards can provide confidence in the quality of the products. Requesting certificates of compliance can help verify this.
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process to identify defects and ensure product quality. Key checkpoints include:
B2B buyers should inquire about the frequency and methodology of these inspections. Regular audits and reports can provide insights into a manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
Testing methods vary but typically include:
Inquire about the specific testing protocols used by suppliers to ensure that their products meet both local and international safety standards.
Verification of a supplier’s quality control practices is vital for B2B buyers. Here are several actionable steps:
When sourcing from international suppliers, B2B buyers should be aware of potential nuances in quality control:
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for nitrogen-inflated tires is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, assembly techniques, and stringent quality control measures, buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products that meet their needs.
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers considering the implications of using regular air to refill nitrogen-inflated tires. Understanding the technical and operational aspects of tire inflation is crucial for ensuring safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness in your vehicle fleet or operations. This checklist will help you make informed decisions about tire maintenance and supplier selection.
Familiarize yourself with the composition of both nitrogen and regular air. Regular air is approximately 78% nitrogen, while nitrogen inflation typically increases nitrogen content to about 85-90%. Understanding this will help you gauge the impact of mixing air with nitrogen, particularly regarding tire pressure maintenance and performance.
Determine the specific performance requirements of your vehicles and how tire inflation impacts these needs. For high-performance or specialized vehicles, maintaining higher nitrogen purity may be more beneficial compared to regular vehicles.
Inspect the current condition of your nitrogen-inflated tires. If they are losing pressure, it may be necessary to refill them. Consider the rate of pressure loss, which can indicate the need for a more thorough evaluation.
Research local facilities that provide nitrogen refilling services. If nitrogen refill stations are scarce, consider the feasibility of using regular air. This is particularly relevant in regions with limited access to specialized services.

Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
Evaluate the cost differences between nitrogen and regular air refilling. While nitrogen typically comes at a premium, it may offer savings in tire maintenance over time due to improved pressure retention.
Engage with tire professionals or consultants who can provide tailored advice based on your specific fleet needs. They can help clarify misconceptions about nitrogen and air mixing and suggest optimal practices.
Establish a clear policy regarding tire inflation practices within your organization. This should include guidelines on when to refill with nitrogen versus regular air, based on the insights gathered in previous steps.
Illustrative image related to can you put regular air in nitrogen inflated tires
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions about tire inflation practices that align with their operational needs and enhance overall vehicle safety and performance.
When considering the sourcing of tires that may require a mix of nitrogen and regular air, understanding the cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include:
Materiais: The cost of the tires themselves, which can vary based on the manufacturer, tire specifications, and performance characteristics. Additionally, there are costs associated with nitrogen filling equipment if a business opts to provide this service.
Trabalho: Labor costs encompass the expenses related to tire installation, maintenance, and refilling. Skilled technicians may be required for nitrogen filling, which could elevate costs.
Custos indiretos de fabricação: This includes costs related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses, which are factored into the final pricing of tires.
Ferramentas: Specialized tools for tire maintenance and nitrogen filling may incur additional costs. Businesses must evaluate whether to invest in these tools or outsource services.
Controle de qualidade (QC): Ensuring that tires meet safety and performance standards is crucial. QC costs may include inspections and testing, which can affect overall pricing.
Logística: Transportation costs for delivering tires and nitrogen filling equipment can vary significantly, especially for international buyers. Understanding these logistics is key to cost management.
Margem: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand and competition.
Several factors can influence pricing strategies in the tire market, especially for international B2B buyers:
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) significantly affects pricing. Higher volumes often lead to discounts, making it crucial for businesses to assess their purchasing needs.
Especificações e personalização: Custom tires tailored to specific vehicle types or performance needs can incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate whether standard options suffice to save on expenses.
Materiais: The quality of materials used in tire manufacturing can impact pricing. Premium materials may offer better performance but at a higher cost.
Certificações de qualidade: Tires that meet specific quality and safety certifications may come at a premium. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in certified products.
Fatores do fornecedor: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service offerings can influence pricing. Developing relationships with reputable suppliers may lead to better pricing and terms.
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and responsibilities (Incoterms) is vital for cost prediction. Different terms can significantly affect landed costs.
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
Negociação: Leverage relationships with suppliers to negotiate better pricing, especially for bulk orders. Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to more favorable terms.
Custo total de propriedade (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential savings from longer-lasting nitrogen-filled tires. This holistic view can justify initial higher costs.
Nuances de preços para mercados internacionais: Buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local market conditions, tariffs, and import duties that can affect pricing. Understanding these nuances can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Regular Maintenance: Ensuring that tires are properly maintained can extend their lifespan and optimize performance, ultimately reducing costs over time.
Educating Staff: Training employees on the benefits and maintenance of nitrogen-filled tires can enhance operational efficiency and reduce errors that may lead to unnecessary costs.
Prices for nitrogen and air tire solutions can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
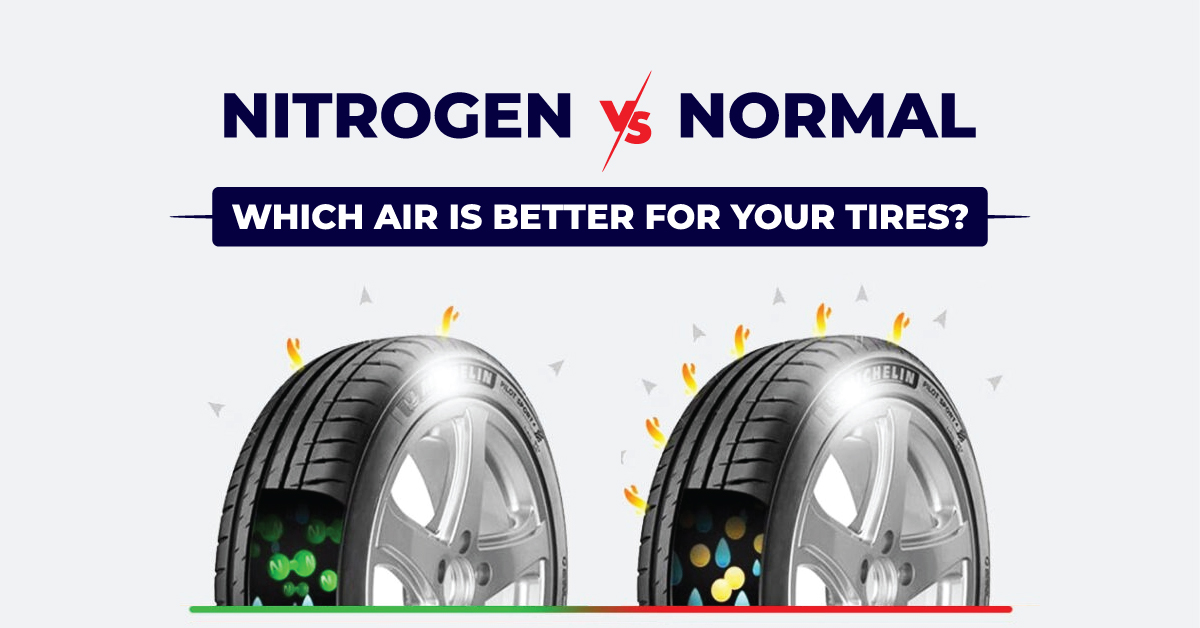
When considering tire inflation options, businesses often evaluate the practicality and efficiency of using regular air versus nitrogen in tires. While nitrogen inflation is frequently marketed for its benefits, many tire users wonder about the feasibility and implications of mixing regular air with nitrogen. This section explores this comparison against alternative methods, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding tire maintenance strategies.
| Aspecto de comparação | Can You Put Regular Air In Nitrogen Inflated Tires | Alternative 1: Pure Nitrogen Inflation | Alternative 2: Regular Air Inflation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Maintains pressure but reduces nitrogen purity | Excellent pressure retention | Moderate pressure retention |
| Custo | Low (minimal additional costs for air) | Moderate (cost of nitrogen refills) | Very low (air is generally free) |
| Facilidade de implementação | Easy (air is widely available) | Moderate (requires nitrogen access) | Very easy (accessible everywhere) |
| Manutenção | Requires frequent checks (every 2-4 weeks) | Less frequent checks (every 4-6 weeks) | Regular checks (every 2 weeks) |
| Melhor caso de uso | General use, budget-conscious applications | Performance vehicles, racing | Everyday driving, low-cost solutions |
Pure nitrogen inflation involves filling tires exclusively with nitrogen gas. The main advantage of this method is enhanced pressure retention due to nitrogen’s larger molecular size, which reduces the rate of permeation through the tire walls. Consequently, businesses that prioritize performance and safety—such as those in the transportation or racing sectors—may benefit from this method. However, the downside is the cost and availability of nitrogen filling stations, which can be a barrier for some businesses, particularly in regions with limited access to specialized services.
Regular air inflation is the most straightforward and cost-effective method for maintaining tire pressure. Comprising approximately 78% nitrogen, using regular air effectively dilutes the nitrogen in the tire but does not pose significant risks. This approach is ideal for everyday vehicles and fleets where cost minimization is crucial. However, users may need to check tire pressures more frequently, which can be a disadvantage for businesses focused on reducing maintenance time.
For B2B buyers evaluating tire inflation options, the decision hinges on specific operational needs and budget constraints. While mixing regular air with nitrogen is permissible and cost-effective, businesses needing high-performance solutions may lean toward pure nitrogen inflation despite its higher costs. Ultimately, understanding the trade-offs among these alternatives allows companies to select the best tire inflation method that aligns with their operational goals, ensuring safety, performance, and cost-efficiency in their vehicle maintenance strategies.
When considering whether to add regular air to nitrogen-inflated tires, it’s essential to understand the technical properties and industry terminology associated with this practice. This knowledge is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where tire maintenance practices may vary significantly.
Gas Composition:
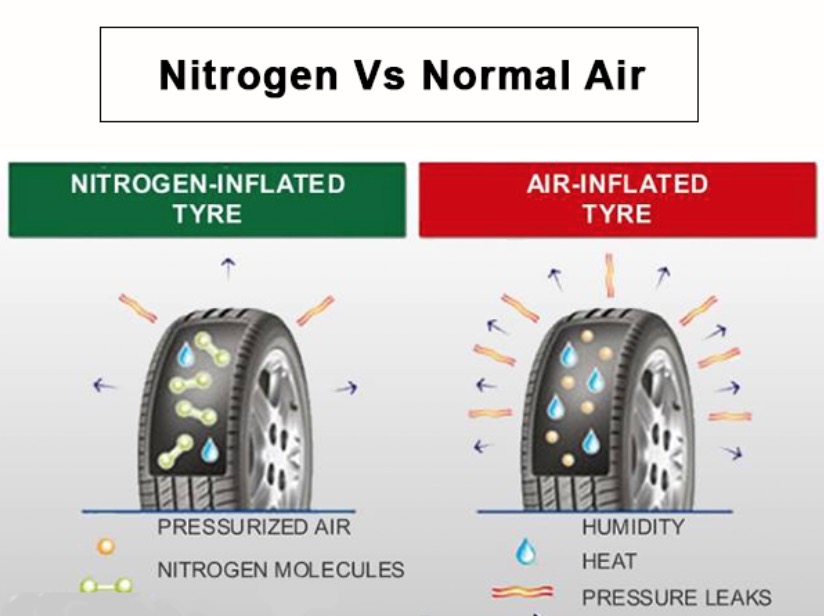
– Definição: Nitrogen gas (N2) makes up about 78% of regular air, with the remaining 21% primarily being oxygen (O2) and trace gases.
– Importância: Understanding gas composition is vital for tire inflation. While nitrogen is a more stable gas under temperature fluctuations, mixing it with air dilutes its benefits. This knowledge helps businesses maintain optimal tire performance and safety.
Pressure Retention:
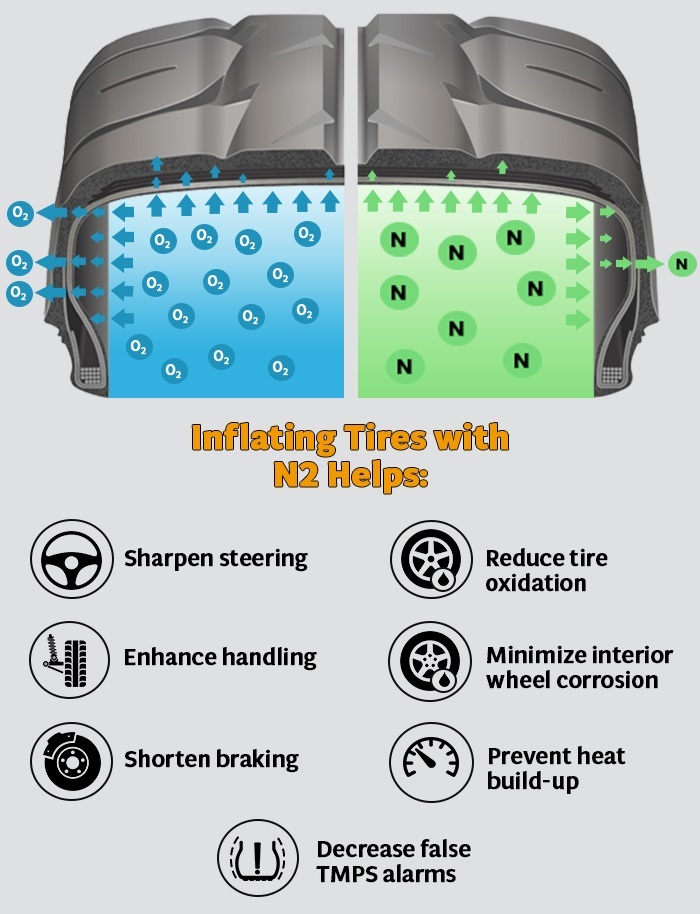
– Definição: Nitrogen-filled tires typically retain pressure longer than those filled with regular air due to nitrogen’s larger molecular size, which reduces permeation through tire walls.
– Importância: For fleet operators, maintaining consistent tire pressure is critical for safety, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity. Recognizing the difference in pressure retention can guide purchasing decisions related to tire maintenance services.
Temperature Stability:
– Definição: Nitrogen is less affected by temperature changes compared to air, which can expand and contract more dramatically.
– Importância: In regions with extreme temperatures, this property can enhance tire performance and safety. B2B buyers should consider this when selecting tire solutions for vehicles operating in varying climates.
Moisture Content:
– Definição: Regular air contains moisture, which can lead to increased pressure fluctuations as tires heat up during use.
– Importância: Understanding moisture levels is crucial for industries reliant on vehicle performance. Using dry nitrogen can minimize pressure changes, providing more predictable handling and performance.
Purity Levels:
– Definição: Nitrogen inflation often targets a purity level of 85-90%, meaning that the remaining percentage may consist of other gases, including oxygen.
– Importância: For businesses, maintaining high purity levels in nitrogen can enhance tire longevity and performance. B2B buyers should evaluate supplier capabilities in providing high-purity nitrogen.
OEM (fabricante original do equipamento):
– Definição: Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevância: Understanding OEM standards is crucial for businesses purchasing tires or related equipment to ensure compatibility and quality.
MOQ (Quantidade mínima de pedido):
– Definição: A menor quantidade de um produto que um fornecedor está disposto a vender.
– Relevância: B2B buyers must consider MOQs when placing orders for tires or nitrogen inflation services to ensure they meet supply chain needs efficiently.
RFQ (Request for Quotation, solicitação de cotação):
– Definição: A document issued when a company wants to buy a product or service and is soliciting quotes from suppliers.
– Relevância: Understanding the RFQ process helps businesses effectively communicate their needs and negotiate better pricing for tire services.
Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais):
– Definição: A series of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– Relevância: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in international procurement, as they define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
Treadwear Indicator:
– Definição: A feature built into tires to indicate when they need replacement due to tread wear.
– Relevância: Recognizing the importance of treadwear indicators helps businesses maintain safety standards and avoid liability issues.
By understanding these technical properties and terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding nitrogen inflation practices, ensuring optimal performance and safety for their vehicle fleets.
The global tire market is witnessing a notable shift towards nitrogen-filled tires, primarily driven by the growing emphasis on performance, safety, and fuel efficiency. B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America, are increasingly aware of the benefits of nitrogen over regular air, including reduced tire pressure fluctuations and improved fuel economy. In regions such as the Middle East and Europe, where vehicle performance is paramount, nitrogen inflation is becoming a standard practice among fleet operators and automotive manufacturers.
Emerging technologies are also influencing sourcing trends. Innovations in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and nitrogen generation systems are enabling businesses to optimize their tire maintenance processes. For instance, on-site nitrogen generation technology is becoming more accessible, allowing businesses to produce nitrogen on demand, thus reducing dependency on external suppliers. This trend is particularly relevant in regions with limited access to nitrogen refilling stations, such as remote areas in Africa or South America.
Furthermore, as sustainability becomes a core business strategy, international B2B buyers are increasingly evaluating the environmental impact of their tire choices. The shift toward nitrogen-filled tires aligns with broader sustainability goals by extending tire life and reducing fuel consumption, making it an attractive option for companies looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles.
The environmental impact of tire production and maintenance is gaining attention from B2B buyers worldwide. The use of nitrogen in tires can contribute to a more sustainable business model by reducing the frequency of tire replacements and improving fuel efficiency, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This is particularly relevant for companies operating large fleets, as even small improvements in fuel efficiency can lead to significant cost savings and reduced environmental footprints.
Ethical sourcing is also becoming paramount in the tire industry. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as responsible sourcing of raw materials and minimizing waste during production. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the Global Recycling Standard (GRS) are becoming essential in supplier evaluations. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also provide a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Moreover, the integration of ‘green’ materials in tire manufacturing is gaining traction. For instance, manufacturers are exploring bio-based materials and sustainable rubber sources, which can enhance the overall sustainability profile of nitrogen-filled tires. B2B buyers should consider these factors when selecting suppliers to ensure they align with their sustainability goals.
The use of nitrogen in tires dates back to the aviation industry, where it was adopted for its benefits in maintaining consistent tire pressure under varying temperatures and conditions. Over time, these advantages have been recognized in automotive applications, particularly in performance and racing contexts. The transition to nitrogen-filled tires for everyday vehicles began to gain momentum in the late 1990s and early 2000s, coinciding with increasing consumer interest in tire performance and safety.
Today, nitrogen inflation is widely adopted in both passenger and commercial vehicles, driven by advancements in tire technology and the growing focus on performance and fuel efficiency. As international B2B buyers seek to optimize their tire maintenance practices, understanding the evolution of nitrogen use can provide valuable insights into its potential benefits and applications in modern fleet management.
How do I solve the issue of low tire pressure in nitrogen-filled tires?
To address low tire pressure in nitrogen-filled tires, you can add regular air if nitrogen refill stations are unavailable. Since regular air is composed of approximately 78% nitrogen, mixing it with nitrogen will only slightly reduce the nitrogen purity. However, it’s advisable to monitor tire pressure regularly, as both nitrogen and air can leak over time. If possible, seek a nitrogen refill when convenient to maintain optimal tire performance.
What are the benefits of nitrogen over regular air in tires?
Nitrogen-filled tires can maintain pressure longer than those filled with regular air, reducing the frequency of pressure checks. Nitrogen is less susceptible to temperature fluctuations, which can help prevent pressure changes during driving. For heavy-duty or performance vehicles, the stability offered by nitrogen can enhance tire longevity and performance. However, for everyday driving, the benefits may be marginal compared to regular air.
Can I completely deflate my nitrogen-filled tires and refill them with regular air?
Yes, you can fully deflate nitrogen-filled tires and refill them with regular air, but it’s unnecessary. If you choose to mix the two, understand that the nitrogen content will decrease with each air addition. For most drivers, maintaining proper tire pressure is more critical than the gas composition, so regular air can suffice for day-to-day use without significant risk.
What should I consider when sourcing nitrogen tire filling services?
When sourcing nitrogen tire filling services, consider the provider’s reputation, service availability, and pricing. Ensure they use high-quality nitrogen that meets industry standards. Additionally, check if they offer bulk services for commercial fleets, as this can lead to cost savings. Establish a reliable partnership to ensure timely service, especially in regions where nitrogen filling stations are limited.
How do I vet suppliers for tire inflation equipment and services?
To vet suppliers for tire inflation equipment and services, evaluate their certifications, customer reviews, and industry experience. Request case studies or references from other businesses they have served. Assess their response time and customer support capabilities, as these factors are crucial for maintaining tire performance. A thorough background check on their financial stability can also provide assurance for long-term partnerships.
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for nitrogen tire filling equipment?
The minimum order quantity for nitrogen tire filling equipment varies by supplier and the type of equipment required. Some suppliers may have flexible MOQs for smaller businesses, while others may require bulk orders for cost efficiency. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to find a mutually beneficial agreement, particularly if you are part of a larger fleet operation or automotive service center.
What payment terms are common for international tire supply contracts?
Common payment terms for international tire supply contracts include letters of credit, advance payments, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30, net 60). It’s essential to negotiate terms that suit both parties’ cash flow needs while ensuring security in transactions. Consider using escrow services for large orders to mitigate risks associated with international trade. Always confirm the currency of payment to avoid exchange rate fluctuations.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing tires?
When importing tires, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure compliance with local regulations and standards for tire safety and performance. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling automotive products to streamline the import process. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs clearance, especially in regions with stringent import regulations, and plan your inventory management accordingly.
Domínio: m3post.com
Registrado: 2005 (20 anos)
Introdução: The discussion revolves around the use of nitrogen in tires for BMW models, specifically addressing whether it’s acceptable to refill tires filled with nitrogen using regular air. Key points include: 1. Nitrogen is used in tires to reduce moisture and improve pressure stability. 2. Air is composed of 78% nitrogen, so mixing it with nitrogen will lower the purity but should not cause adverse effect…
In summary, the decision to mix regular air with nitrogen in tires hinges on a few critical factors that international B2B buyers should consider. While nitrogen inflation offers advantages such as maintaining tire pressure longer and reducing moisture buildup, it is essential to note that adding regular air—composed of 78% nitrogen—will dilute the nitrogen purity but will not result in significant adverse effects. For businesses operating fleets or managing vehicle maintenance, the practical approach may be to prioritize regular tire pressure checks and consider nitrogen refills when feasible, particularly in high-performance scenarios.
Strategic sourcing in tire management can lead to cost savings and efficiency improvements. By partnering with suppliers who understand regional needs—whether in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—companies can ensure they are making informed decisions about tire maintenance practices. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, staying ahead of trends in tire technology and inflation methods will be key to optimizing fleet performance and safety.
We encourage B2B buyers to explore partnerships with reliable tire suppliers and service providers to enhance their operational effectiveness. Embracing a proactive approach to tire management can yield long-term benefits, driving both safety and cost efficiency in your fleet operations.
As informações fornecidas neste guia, inclusive o conteúdo referente a fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análise de mercado, são apenas para fins informativos e educacionais. Elas não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre compras, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos feito todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e a atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem realizar sua própria due diligence independente e completa antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contato diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar as certificações, solicitar amostras e buscar consultoria profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é de responsabilidade exclusiva do leitor.