In the dynamic landscape of the global automotive industry, sourcing quality products like under inflated tires presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. The implications of using under inflated tires extend far beyond mere inconvenience; they can lead to increased operational costs, compromised safety, and reduced vehicle performance. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the critical aspects of under inflated tires, including their types, applications, and the nuanced factors that affect pricing and supplier selection.
International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Nigeria and Germany, will find actionable insights that empower informed purchasing decisions. The guide emphasizes the importance of vetting suppliers based on quality, reliability, and service capabilities, ensuring that your business is equipped with tires that meet both safety and performance standards.
By understanding the risks associated with under inflated tires—such as increased fuel consumption, uneven tread wear, and potential blowouts—buyers can proactively mitigate these issues, enhancing fleet efficiency and safety. This resource is designed to help you navigate the complexities of the tire market, ultimately driving better outcomes for your business operations while fostering a safer driving environment.
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicativos B2B primários | Prós e contras resumidos para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mildly Under Inflated | Slightly lower than recommended pressure, noticeable wear on outer edges | Delivery fleets, service vehicles | Prós: Cost-effective, easy to correct. Contras: Reduced fuel efficiency, potential safety risks. |
| Severely Under Inflated | Significantly below recommended pressure, pronounced deformation | Construction vehicles, heavy machinery | Prós: Often indicates immediate need for replacement. Contras: High risk of blowouts, costly repairs. |
| Unevenly Inflated | Different tire pressures across the same vehicle | Transport companies, logistics | Prós: Can highlight poor maintenance practices. Contras: Compromised handling, increased tire wear. |
| Temporarily Under Inflated | Short-term pressure drop, often due to environmental factors | Rental fleets, short-term vehicle use | Prós: Easily reversible with quick checks. Contras: Potential for severe handling issues if ignored. |
| Chronic Under Inflation | Persistent low pressure due to leaks or tire damage | Long-haul trucking, fleet management | Prós: Identifies underlying issues for maintenance. Contras: Significant safety hazards, expensive replacements. |
Mildly under inflated tires are those that are only slightly below the manufacturer’s recommended pressure. This condition often leads to uneven wear, primarily on the outer edges of the tires. For businesses operating delivery fleets or service vehicles, this type of tire can be a common issue that is relatively easy to correct. However, buyers should be aware that while the immediate costs may be low, the long-term implications include decreased fuel efficiency and potential safety risks, which could lead to higher operational costs.
Severely under inflated tires are characterized by a significant drop in pressure, resulting in noticeable deformation. This condition is prevalent in construction vehicles and heavy machinery that frequently operate under challenging conditions. While these tires might indicate an urgent need for replacement, businesses must consider the high risk of blowouts and the associated costly repairs. Proper monitoring and maintenance are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure operational efficiency.
Unevenly inflated tires occur when there are discrepancies in pressure across a vehicle’s tires. This situation is particularly relevant for transport companies and logistics operations, where tire performance directly impacts vehicle handling and safety. While identifying uneven inflation can highlight poor maintenance practices, it also poses risks such as compromised handling and increased tire wear. Buyers should prioritize regular inspections to maintain optimal tire performance and safety.
Temporarily under inflated tires usually result from short-term pressure drops due to environmental factors. This condition is common in rental fleets or vehicles used for short durations. While these tires can be easily restored to proper pressure with quick checks, ignoring them can lead to severe handling issues. For businesses, it’s crucial to establish routine tire inspections to ensure safety and reliability in their vehicle operations.
Chronic under inflation refers to tires that consistently operate below the recommended pressure, often due to leaks or damage. This condition is particularly significant for long-haul trucking and fleet management, where tire performance is critical for safety and efficiency. While these tires can reveal underlying maintenance issues, they also pose significant safety hazards and can lead to expensive replacements. Businesses must implement rigorous maintenance protocols to address chronic under inflation and ensure the longevity of their tire investments.
| Indústria/Setor | Specific Application of Under Inflated Tires | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Principais considerações de fornecimento para este aplicativo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Gerenciamento de frotas | Reduced fuel costs and improved vehicle safety | Tire pressure monitoring systems, bulk purchasing options |
| Agricultura | Agricultural Machinery | Enhanced traction and reduced soil compaction | Compatibility with various machinery, local service availability |
| Construção | Heavy Equipment Operations | Lower maintenance costs and improved stability | Durability under heavy loads, compliance with safety standards |
| Mining | Mining Vehicles | Enhanced safety and reduced risk of tire blowouts | Resilience to rough terrain, specialized tire types for specific conditions |
| Automotive Services | Tire Retail and Maintenance | Increased customer satisfaction and repeat business | Quality assurance, availability of various tire brands and types |
In the transportation and logistics sector, under inflated tires can significantly impact fleet management. While operating under inflated tires may seem like a minor issue, it leads to increased rolling resistance, causing higher fuel consumption and greater wear on vehicles. For B2B buyers, investing in advanced tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) can help mitigate these risks, ensuring that fleets operate efficiently. Buyers should consider bulk purchasing options for tires and maintenance services to enhance overall fleet performance.
In agriculture, under inflated tires are often used in tractors and other machinery to enhance traction while minimizing soil compaction. This is crucial for maintaining soil health and maximizing crop yield. B2B buyers in this sector need to focus on compatibility with various types of agricultural machinery and local service availability for tire maintenance. Proper tire inflation can lead to substantial savings in fuel costs and improve operational efficiency, making it a critical consideration for agricultural businesses.

Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
Heavy equipment used in construction relies on tires that can withstand significant loads. Under inflated tires can lead to lower stability and increased maintenance costs due to uneven wear. For construction companies, investing in high-quality tires that can endure harsh working conditions is essential. Buyers should prioritize durability and compliance with safety standards, ensuring that their equipment operates safely and efficiently, ultimately reducing downtime and repair costs.
In the mining industry, under inflated tires pose substantial safety risks, including an increased likelihood of blowouts on rough terrain. Mining vehicles require specialized tires that can handle extreme conditions while maintaining optimal performance. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing tires that are resilient to heavy loads and harsh environments. Ensuring proper tire inflation not only enhances safety but also minimizes the risk of costly downtime, making it a critical aspect of mining operations.
Tire retail and maintenance services can significantly benefit from addressing the issue of under inflated tires. By providing customers with solutions that enhance tire longevity and vehicle safety, businesses can improve customer satisfaction and foster repeat business. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on quality assurance and the availability of various tire brands and types to meet diverse customer needs. Offering regular tire inspections and maintenance services can help customers avoid the pitfalls of under inflation, leading to a more reliable service offering.
O problema: A logistics company in Nigeria operates a fleet of delivery trucks that frequently runs into the issue of under inflated tires. The fleet manager notices that the vehicles are consuming more fuel than usual and experiencing more frequent breakdowns. After investigating, it becomes evident that many tires are under inflated due to a lack of regular monitoring and maintenance. This not only leads to increased operational costs but also risks delivery timelines, damaging the company’s reputation and client trust.
A solução: To combat this challenge, the logistics company should implement a systematic tire pressure monitoring program. This includes investing in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) that provide real-time data on tire inflation levels. Fleet managers should establish a routine schedule for checking tire pressure—ideally before each trip or weekly for larger fleets. Additionally, training drivers on the importance of tire maintenance and how to identify signs of under inflation can further mitigate risks. By addressing tire inflation proactively, the company can improve fuel efficiency, extend tire life, and ultimately reduce overall maintenance costs.
O problema: A construction company in Brazil operates heavy machinery on rugged terrains, where under inflated tires are a common issue. The site manager has noticed that operators are struggling with equipment control, leading to safety incidents and delays in project timelines. Under inflated tires not only increase the risk of accidents but also contribute to uneven wear on the machinery, resulting in costly repairs and downtime.
A solução: The construction company should prioritize the adoption of heavy-duty tires designed specifically for uneven terrains. These tires should be regularly inspected and maintained according to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent under inflation. Incorporating a daily checklist for operators to monitor tire pressure before commencing work can enhance safety. Additionally, investing in a portable air compressor on-site can allow for quick adjustments to tire pressure as needed throughout the day, ensuring that machinery operates at peak performance and safety.
O problema: A transport company in Germany is facing significant challenges with under inflated tires across its fleet of long-haul trucks. The fleet manager observes that under inflated tires are causing slower speeds, increased fuel consumption, and longer delivery times. The company’s competitive edge is eroding as operational efficiency declines, leading to dissatisfaction among clients and higher costs.
A solução: To address these issues, the transport company should adopt a comprehensive tire management strategy that includes regular tire pressure assessments and predictive analytics. Utilizing telematics solutions can help monitor tire performance in real-time and alert the fleet manager to any irregularities. Moreover, training drivers to recognize the signs of under inflated tires and the importance of maintaining optimal tire pressure can enhance overall fleet performance. By implementing these proactive measures, the company can improve efficiency, reduce fuel costs, and ensure timely deliveries, ultimately restoring client satisfaction and enhancing profitability.
When considering the materials for tires that may be subject to under-inflation, it is essential to analyze their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for various applications. The following materials are commonly used in tire manufacturing and have specific implications for performance, durability, and safety.
Natural rubber is a primary material used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent elasticity and resilience. Its temperature rating typically ranges from -40°C to 70°C, making it suitable for various climates. The corrosion resistance of natural rubber is moderate, but it can degrade with prolonged exposure to ozone and UV light.
Prós: Natural rubber offers superior grip and flexibility, which enhances traction, especially in wet conditions. It is also relatively low-cost compared to synthetic alternatives.

Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
Contras: Its susceptibility to environmental degradation can lead to reduced lifespan. Additionally, natural rubber may not perform well under extreme temperatures or in highly abrasive environments.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it’s crucial to consider local climate conditions and potential exposure to UV light, which can affect the longevity of natural rubber tires.
Synthetic rubber, particularly styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and butyl rubber, is widely used in tire production for its enhanced durability and resistance to wear and tear. These materials can withstand higher temperatures and pressures than natural rubber, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Prós: Synthetic rubber offers better resistance to aging, ozone, and UV light, ensuring a longer lifespan. It also provides excellent fuel efficiency due to lower rolling resistance.

Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
Contras: The manufacturing process for synthetic rubber is more complex and costly, which can drive up the overall price of the tires.
For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential when selecting synthetic rubber tires, as these regions often have stringent regulations regarding material performance and safety.
Reinforcing materials, such as steel belts and nylon fabric, are critical in enhancing the structural integrity of tires. Steel belts provide strength and stability, while nylon fabric improves flexibility and resistance to punctures.
Prós: The use of steel belts significantly increases durability and resistance to deformation under load, which is vital for maintaining performance in under-inflated conditions. Nylon fabric adds an extra layer of protection against punctures.
Contras: The addition of reinforcing materials can increase the weight of the tire, potentially affecting fuel efficiency. Furthermore, the manufacturing complexity increases, which may lead to higher costs.
International buyers should consider the specific road conditions in their regions, such as the prevalence of potholes or rough terrains, which may necessitate the use of reinforced tires for enhanced durability.
Specialty compounds, such as silica-infused rubber, are designed to improve performance in specific conditions. These compounds enhance wet traction and reduce rolling resistance, making them suitable for fuel-efficient tires.
Prós: Specialty compounds can significantly improve fuel efficiency and provide better grip in wet conditions, which is particularly beneficial in regions with heavy rainfall.
Contras: The cost of specialty compounds is generally higher due to advanced manufacturing processes. Additionally, their performance may vary based on temperature and road conditions.
For buyers in regions like Nigeria and Germany, understanding local weather patterns and road conditions can help in selecting the appropriate specialty compounds that align with their operational needs.
| Material | Typical Use Case for Under Inflated Tires | Principais vantagens | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | General passenger tires | Excellent grip and flexibility | Susceptible to environmental degradation | Baixa |
| Synthetic Rubber | Heavy-duty and performance tires | Superior durability and wear resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | Médio |
| Reinforcing Materials | All tire types for added strength | Increased durability and puncture resistance | Can increase tire weight and cost | Médio |
| Specialty Compounds | Fuel-efficient and performance tires | Improved fuel efficiency and wet traction | Higher cost and variable performance | Alta |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in tires, focusing on their performance under conditions of under-inflation. Understanding these materials will assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and regional conditions.
Understanding the manufacturing process of tires is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and performance in their fleet operations. The manufacturing of tires, especially those that may be under-inflated, involves several critical stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Preparação de materiais
The tire manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. This includes various types of rubber compounds, textile fabrics, and steel cords. The rubber compounds are formulated to provide specific properties, such as elasticity, strength, and heat resistance. The preparation of these materials involves mixing raw rubber with chemicals, carbon black, and other additives to create a compound that meets performance requirements.
Formação
In the forming stage, the prepared rubber compounds are shaped into tire components. This includes creating the inner liners, treads, and sidewalls. Techniques like extrusion are used to form rubber into sheets or specific shapes, while calendering is employed to create fabric-reinforced rubber. The precise dimensions and characteristics of these components are crucial, as they directly impact the tire’s performance, including its resistance to under-inflation.
Montagem
Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into a tire structure. This involves layering the components, including the bead (which secures the tire to the wheel), sidewalls, and tread. The assembly process requires careful handling and precise alignment to ensure that the tire maintains its integrity under various conditions. Advanced techniques such as automated tire-building machines are often used to enhance accuracy and efficiency in this phase.
Acabamento
The finishing stage includes curing the assembled tire in a mold under heat and pressure. This vulcanization process causes chemical reactions that enhance the tire’s durability and elasticity. After curing, tires are inspected for any defects, and additional processes like trimming and painting may be performed. The final quality of the tire depends heavily on the precision of the manufacturing processes conducted in the earlier stages.
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of tire manufacturing, particularly for those intended for high-performance applications. International standards such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications like CE and API guide manufacturers in establishing robust quality management systems.
Relevant International Standards
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system. It emphasizes customer satisfaction, process approach, and continuous improvement. Compliance with ISO 9001 can enhance a manufacturer’s credibility and assure B2B buyers of consistent product quality. In addition, certifications like CE mark compliance ensure that products meet European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Pontos de verificação de controle de qualidade
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that every aspect meets the required standards:
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is vital for ensuring reliable tire performance.
Realização de auditorias de fornecedores
Regular audits of suppliers provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. These audits can assess compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of their QC systems. Buyers should inquire about the frequency and scope of these audits to ensure thorough evaluations.
Solicitação de relatórios de qualidade
Manufacturers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC practices, testing results, and compliance with standards. Buyers can review these reports to gauge the manufacturer’s commitment to quality and identify any potential issues.
Inspeções de terceiros
Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. These inspections can validate the manufacturer’s claims and provide additional assurance regarding product quality.
When sourcing tires from international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances that can impact procurement decisions.
Understanding Local Regulations
Different regions may have unique regulations regarding tire manufacturing and safety standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure that the tires meet local compliance needs.
Considerações culturais
Cultural differences can influence manufacturing practices and quality assurance. Building strong relationships with suppliers and understanding their operational ethos can lead to improved communication and collaboration.
Logistical Challenges
Importing tires from different regions may present logistical challenges, including shipping delays and customs regulations. Buyers should account for these factors in their procurement strategies to minimize disruptions.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices surrounding tires, particularly those susceptible to under-inflation, are critical for ensuring safety and performance. By understanding the key manufacturing stages, quality control checkpoints, and how to verify supplier practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and mitigate risks associated with under-inflated tires.
To assist B2B buyers in procuring tires that maintain optimal pressure and avoid the pitfalls associated with under-inflated tires, this guide outlines a practical, step-by-step checklist. Ensuring the proper selection and maintenance of tires is crucial for safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in transportation operations.
Understanding the specific requirements of your fleet is the first step in sourcing the right tires. Consider factors such as the types of vehicles in your fleet, typical load weights, and driving conditions. This assessment will guide you in selecting tires that are not only appropriate but also enhance performance and safety.
Once you have a clear understanding of your fleet’s needs, define the technical specifications for the tires you require. This includes tire size, load capacity, and tread design. Ensure that your specifications align with the manufacturer’s recommendations for each vehicle to optimize safety and performance.
Before making a purchase, conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in tires suitable for your operational needs. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation, particularly in your region, and those who understand local road conditions and climate impacts on tire performance.
It’s essential to verify that potential suppliers meet industry certifications and standards. Certifications like ISO 9001 or those specific to tire safety (e.g., DOT compliance) indicate that the supplier adheres to quality management principles. This step is crucial for ensuring that the tires you procure meet safety and performance benchmarks.
Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
Before finalizing your order, request samples or conduct performance tests of the tires. This step allows you to assess the tire’s handling, durability, and fuel efficiency under conditions that mimic your operational environment. It’s a practical way to ensure that the tires meet your specifications and perform as expected.
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier and confirmed the tire specifications, it’s time to negotiate pricing and terms. Discuss bulk purchase discounts, warranty conditions, and after-sales support. Ensure that the terms align with your budget while also considering the long-term value and potential cost savings from reduced fuel consumption and improved vehicle performance.
Finally, once the tires are procured, establish a regular maintenance schedule to monitor tire pressure and condition. Regular inspections help in identifying under-inflated tires before they lead to safety issues or increased operating costs. Ensure that all personnel involved in vehicle maintenance are trained on the importance of tire health and the procedures for checking and maintaining proper tire pressure.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing tires, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing tires, particularly those affected by under-inflation, several components must be taken into account.
Materiais: The primary cost driver in tire manufacturing is the raw materials, which typically include rubber, fabric, and steel. The quality of these materials significantly impacts durability and performance. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers that offer high-quality, certified materials, even if they come at a premium, to minimize the risk of under-inflation issues.
Trabalho: Labor costs can vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, manufacturers may offer more competitive pricing. However, buyers should ensure that quality standards are not compromised, as poor labor practices can lead to defects and safety issues.
Custos indiretos de fabricação: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, which can be beneficial for pricing negotiations.
Ferramentas: The initial investment in tooling for tire production can be substantial, particularly for custom designs or specifications. Buyers interested in unique tire features may face higher initial costs, but long-term savings can be achieved through bulk orders.
Controle de qualidade (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes is essential to ensure that tires meet safety and performance standards. While this adds to the cost, it significantly reduces the risk of costly recalls and repairs associated with under-inflation.
Logística: Transportation and shipping costs can greatly influence the final pricing, particularly for international buyers. Understanding the Incoterms and selecting the most cost-effective shipping methods can lead to substantial savings.
Margem: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the tires.
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost structure:
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often yields discounts. International buyers should consider consolidating orders to meet minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can significantly reduce unit costs.
Especificações e personalização: Customized tires tailored to specific vehicle types or conditions may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
Qualidade do material e certificações: Tires with higher quality materials or specific certifications (e.g., eco-friendly or performance ratings) tend to command higher prices. Investing in certified products can lead to long-term savings by reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Fatores do fornecedor: Supplier reputation, reliability, and after-sales support can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may justify higher prices compared to lesser-known manufacturers.
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial. Buyers should clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, as these can impact the overall cost.
To achieve the best pricing and value for tires, particularly when considering the implications of under-inflation, buyers should employ several strategies:
Negociação: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing flexibility, especially if you can commit to larger volumes. Establishing a long-term relationship can also help secure better terms over time.
Eficiência de custo: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. Investing in higher-quality tires may result in lower long-term expenses due to reduced risk of under-inflation and associated damages.
Nuances de preços para compradores internacionais: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local taxes that can impact pricing. Establishing contracts in a stable currency can mitigate some of these risks.
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on regional suppliers and market trends. Understanding the competitive landscape can empower you during negotiations and help you identify the best value propositions.
Prices for tires can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct their own market research and reach out to multiple suppliers for quotes to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
In the realm of vehicle maintenance and safety, under inflated tires present significant challenges, including decreased performance, increased fuel consumption, and heightened risk of accidents. However, there are alternative solutions and technologies that can help mitigate these risks while enhancing overall vehicle performance. Understanding these alternatives can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
| Aspecto de comparação | Under Inflated Tires | Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) | Automatic Tire Inflation Systems (ATIS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Reduced handling and increased wear | Maintains optimal tire pressure, enhancing safety and efficiency | Automatically adjusts tire pressure, ensuring consistent performance |
| Custo | Low upfront cost but high long-term repair costs | Moderate initial investment, potential savings on fuel and tire replacement | Higher initial cost but reduced long-term maintenance expenses |
| Facilidade de implementação | Simple to overlook; requires regular manual checks | Requires installation and periodic maintenance | Installation complexity varies; may require professional setup |
| Manutenção | High maintenance; frequent checks needed | Minimal; alerts for low pressure | Low; self-regulating system reduces manual checks |
| Melhor caso de uso | Short-term, low-cost solutions | Fleets needing real-time monitoring for safety | High-utilization vehicles requiring consistent performance under varying conditions |
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) provide an effective alternative to under inflated tires by continuously monitoring tire pressure. When tire pressure drops below a specified threshold, the system alerts the driver, enabling timely intervention. The primary advantage of TPMS is its ability to enhance safety and fuel efficiency by ensuring that tires are always inflated to the optimal level. However, the initial investment can be moderate, and regular maintenance is needed to ensure the system functions correctly. This technology is particularly beneficial for fleets that prioritize safety and operational efficiency.
Automatic Tire Inflation Systems (ATIS) represent a more advanced solution for maintaining tire pressure. These systems automatically adjust tire pressure, keeping it within the optimal range regardless of driving conditions. The key benefits include enhanced vehicle performance, reduced tire wear, and increased fuel efficiency. Although the initial setup cost may be higher compared to other options, the long-term savings on tire replacements and maintenance can be significant. ATIS is ideal for high-utilization vehicles, such as those used in logistics and transportation, where consistent tire performance is critical for operational success.
When evaluating alternatives to under inflated tires, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their operations, including vehicle types, usage patterns, and maintenance capabilities. While under inflated tires may appear cost-effective initially, the long-term implications on safety and maintenance can be detrimental. Technologies like TPMS and ATIS offer proactive solutions that can lead to greater efficiency, safety, and cost savings over time. By assessing the benefits and potential drawbacks of each alternative, businesses can make strategic decisions that enhance their fleet performance and reduce operational risks.
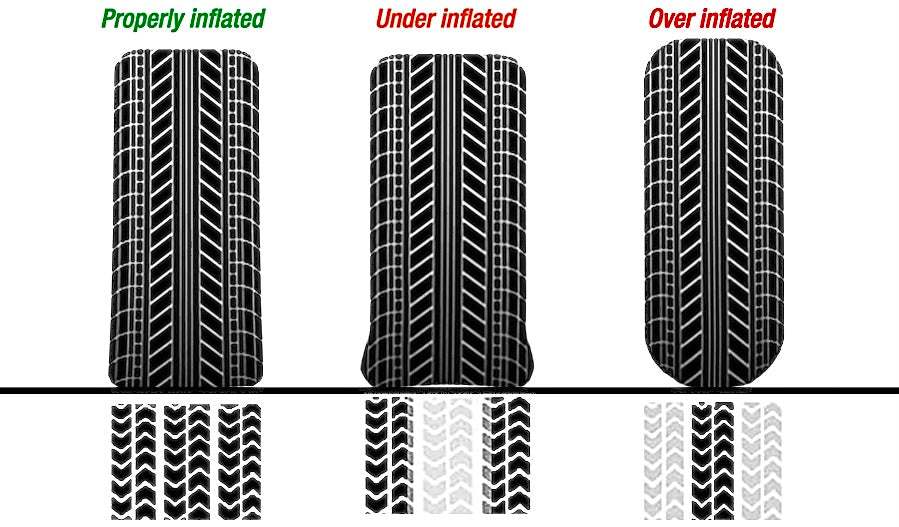
Understanding the technical specifications of under inflated tires is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when considering safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some essential technical properties to consider:
Tire pressure is measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) and indicates the amount of air within the tire. Maintaining the correct PSI is vital for optimal tire performance. Under inflated tires can cause excessive friction, leading to overheating and potential blowouts. For international buyers, understanding the manufacturer’s recommended PSI is essential for compliance with local safety regulations.
Tread depth refers to the vertical measurement between the top of the tire’s tread and the bottom of the tire’s grooves. Adequate tread depth is necessary for effective water drainage and traction. Under inflated tires can lead to uneven tread wear, which compromises safety and increases the frequency of tire replacements. B2B buyers should prioritize tires with a consistent tread depth to ensure longevity and performance.
The load index indicates the maximum weight a tire can support when properly inflated. Under inflated tires may not bear the intended load effectively, leading to premature wear or failure. For businesses relying on transport, understanding load indices is crucial to avoid operational disruptions and costly repairs.
Tires are typically made from a combination of rubber, steel, and other materials that affect durability and performance. The material grade influences the tire’s resistance to wear and tear. For B2B buyers, selecting tires made from high-quality materials can minimize operational costs over time, especially in demanding environments.
Sidewall flexibility refers to how much a tire can flex when it encounters different road conditions. Under inflated tires tend to flex excessively, which can lead to reduced control and increased risk of blowouts. For buyers in regions with varied terrain, understanding sidewall flexibility is essential for ensuring safety and vehicle performance.
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some key trade terms relevant to under inflated tires:
OEM refers to the company that manufactures the original tires for a vehicle. Understanding OEM specifications is important for B2B buyers looking to maintain brand consistency in fleet operations. Using OEM tires ensures compatibility and performance standards.
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and costs. Understanding the MOQ helps in budget planning and negotiating better deals with suppliers.

Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
An RFQ is a document that solicits price proposals from suppliers. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs when sourcing tires to ensure they receive competitive pricing and terms. An effective RFQ process can lead to cost savings and better supplier relationships.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Knowledge of Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This understanding can prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
A warranty is a guarantee from the manufacturer regarding the tire’s performance and durability over a specified period. For B2B buyers, understanding warranty terms can provide assurance of product quality and serve as a risk management tool. Buyers should carefully review warranty conditions to ensure they align with their operational needs.
In summary, being well-versed in the technical properties and trade terminology associated with under inflated tires can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
The market for under inflated tires is driven by a combination of safety concerns, regulatory standards, and advancements in tire technology. Globally, rising awareness regarding road safety has led to increased scrutiny of tire maintenance practices, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can be challenging. The European Union and other regulatory bodies are also tightening regulations on vehicle safety, which includes mandates for regular tire pressure checks.
Emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping how businesses monitor tire conditions. Smart tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are becoming more prevalent, providing real-time data that helps fleet operators manage tire health proactively. These technologies not only enhance safety but also improve operational efficiency, making them attractive for international buyers.
Additionally, the market is seeing an increase in demand for sustainable tire solutions. With growing concerns over environmental impact, B2B buyers are increasingly interested in sourcing tires made from eco-friendly materials or those that minimize rolling resistance, thereby improving fuel efficiency. This trend is particularly strong in Europe, where consumers are willing to pay a premium for green alternatives.
Sustainability is emerging as a critical factor in the tire supply chain, particularly for B2B buyers concerned about environmental impact. The production and disposal of tires contribute significantly to landfill waste and pollution, making ethical sourcing a priority for many businesses. Buyers are now seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or developing biodegradable tires.
Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Global Recycling Standard (GRS) are becoming benchmarks for companies in this sector. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also fulfill the growing consumer demand for transparency in sourcing.
Moreover, the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is creating new opportunities for manufacturers specializing in low-resistance tires that can enhance EV performance while reducing environmental impact. As B2B buyers from regions like the Middle East and Africa begin to recognize the long-term cost savings associated with sustainable tire options, the importance of ethical supply chains will continue to grow.
Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
The under inflated tires market has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, tire technology focused primarily on durability and performance. However, as road safety became a pressing global concern, the focus shifted towards tire pressure management and the implications of under inflation on vehicle safety.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of mandatory tire pressure monitoring systems in various countries marked a pivotal moment in tire safety regulations. This led to a greater emphasis on maintenance and awareness among consumers and fleet operators alike. Today, the integration of advanced technologies, such as IoT and AI, is revolutionizing tire monitoring, allowing for real-time data and predictive maintenance.
As the market continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make educated sourcing decisions that not only enhance operational efficiency but also align with sustainability goals.
How can I identify under inflated tires before purchasing?
To identify under inflated tires, look for visual signs such as uneven wear patterns, where the edges may be worn more than the center. Additionally, check for any alerts from the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) if applicable. Request detailed inspection reports from suppliers that include tire pressure measurements and tread depth evaluations. Conducting a thorough inspection can prevent costly issues down the line and ensure you are sourcing quality tires.
What are the risks associated with using under inflated tires in business operations?
Using under inflated tires can lead to increased risks such as tire blowouts, reduced vehicle control, and decreased fuel efficiency, all of which can impact operational efficiency and safety. The increased rolling resistance can lead to higher fuel costs, while uneven tire wear may necessitate more frequent replacements, impacting your bottom line. Prioritizing proper tire maintenance is crucial for maintaining fleet safety and minimizing operational disruptions.
What should I look for in a supplier of under inflated tires?
When vetting suppliers, consider their reputation, certifications, and industry experience. Look for suppliers that provide detailed product specifications, including compliance with international safety standards. It’s also essential to assess their customer service and responsiveness, as well as their ability to provide timely delivery and support. Request references from other businesses to gauge reliability and quality before finalizing any agreements.
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for under inflated tires?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, larger manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for bulk orders, while smaller suppliers might have higher MOQs due to limited inventory. Always clarify MOQs during negotiations, and consider your storage capacity and demand forecasts to ensure you are making a cost-effective decision.
What payment terms are typically offered for purchasing under inflated tires?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and your business relationship. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or even payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer discounts for upfront payments or bulk orders. Discuss payment options during negotiations to find terms that align with your cash flow and financial strategy while ensuring security for both parties.
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing under inflated tires?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications that confirm compliance with international safety and performance standards. Implement a quality control process that includes receiving inspection, testing for durability, and verifying tread depth and pressure ratings. Additionally, consider establishing a partnership with suppliers who offer warranty programs, as this can provide further assurance of their product quality.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing under inflated tires?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to handle logistics, including documentation and compliance with international shipping laws. It’s also crucial to account for lead times and potential delays in customs to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. Partner with a logistics provider experienced in tire imports to streamline the process.
How can I customize under inflated tires for my specific needs?
Customization options may include specific tread patterns, rubber compounds, or sizes tailored to your operational requirements. Engage with your supplier to discuss your needs and explore any available customization options. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications to ensure the final product meets your performance criteria. Additionally, inquire about lead times and costs associated with customization to effectively plan your procurement strategy.
Domínio: hendrickatlanta.com
Registrado: 2007 (18 anos)
Introdução: Rick Hendrick Chevrolet Duluth offers tire services including inspections, replacements, and rotations. They emphasize the importance of maintaining properly inflated tires to avoid dangers such as total tire failure, costly vehicle damage, difficulty handling the vehicle, and increased fuel consumption. Symptoms of under inflated tires include alerts from the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS…
Domínio: eastcoasttoyota.com
Registrado: 2000 (25 anos)
Introdução: The article discusses the hidden dangers of overinflated and underinflated tires, emphasizing the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure for vehicle performance and safety. Key risks include uneven tread wear, reduced vehicle control, increased risk of blowouts, decreased fuel efficiency, adverse impact on the car’s suspension, compromised safety in wet conditions, and potential damage to …
Domínio: rnrtires.com
Registrado: 2006 (19 anos)
Introdução: RNR Tire Express offers a range of tire and car-care services, including tire checks and replacements. They emphasize the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure to avoid dangers such as blowouts, compromised handling, extended braking distances, poor fuel efficiency, and uneven tire wear. Customers can visit their locations in Lubbock, TX, for expert assistance and to browse their tire inv…
In conclusion, addressing the challenges posed by under-inflated tires is paramount for enhancing vehicle safety, performance, and overall operational efficiency. The risks associated with under-inflation—including increased fuel consumption, uneven tire wear, and reduced vehicle control—underscore the necessity for businesses to implement strategic sourcing practices. By prioritizing high-quality tires and establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers, companies can mitigate these risks while also ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
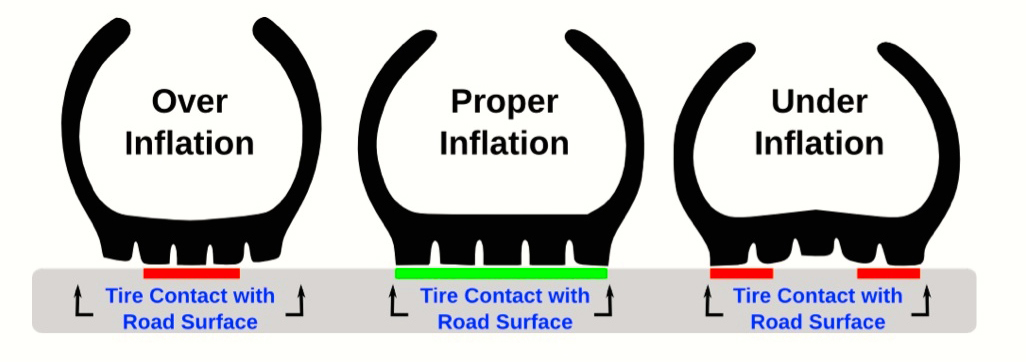
Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in premium tire solutions is not merely a cost—it’s a strategic decision that enhances fleet reliability and reduces maintenance expenses. As the global marketplace continues to evolve, staying ahead requires a commitment to quality and sustainability in tire sourcing.
To move forward, consider conducting a thorough review of your current tire suppliers and exploring innovative options that prioritize safety and efficiency. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your fleet’s performance today, ensuring your operations are not only safe but also economically viable for the future.
As informações fornecidas neste guia, inclusive o conteúdo referente a fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análise de mercado, são apenas para fins informativos e educacionais. Elas não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre compras, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
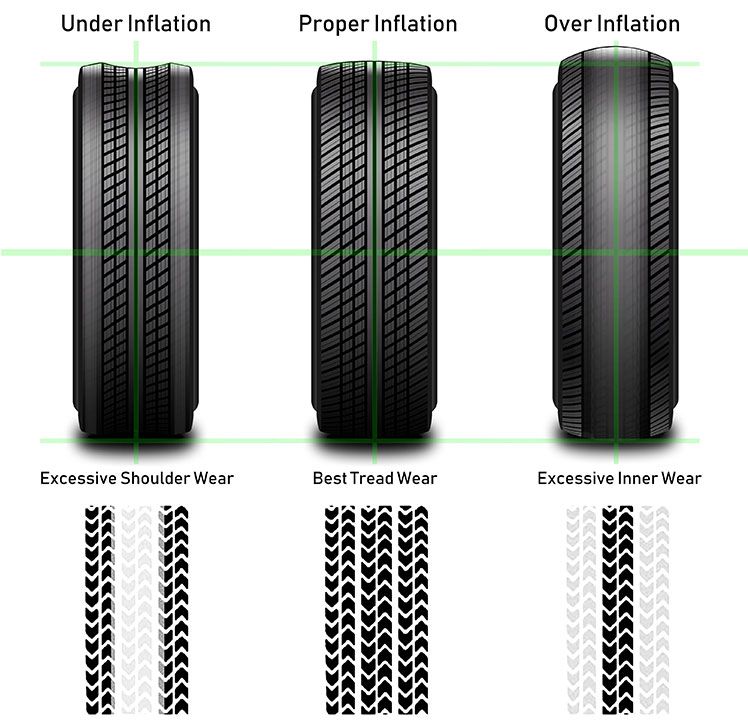
Illustrative image related to under inflated tires
Embora tenhamos feito todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e a atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem realizar sua própria due diligence independente e completa antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contato diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar as certificações, solicitar amostras e buscar consultoria profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é de responsabilidade exclusiva do leitor.