Navigating the complexities of tire maintenance is a critical challenge for B2B buyers sourcing tire inflators across diverse global markets. Understanding how to effectively use a tire inflator not only ensures the safety and efficiency of vehicle operations but also supports cost-effective fleet management. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of tire inflators available, their specific applications, and essential features that cater to the needs of international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil.
In this guide, we will explore the distinctions between 12-volt and battery-powered inflators, highlight critical safety precautions, and provide actionable step-by-step instructions for usage. Additionally, we will cover key considerations for vetting suppliers, evaluating product quality, and understanding pricing structures to facilitate informed purchasing decisions. By equipping B2B buyers with knowledge about the functionalities and advantages of portable tire inflators, this guide empowers organizations to enhance their operational capabilities and minimize downtime. Whether for emergency roadside assistance or routine tire maintenance, mastering the use of tire inflators is essential for maintaining a reliable and efficient fleet.
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicativos B2B primários | Prós e contras resumidos para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12-Volt Tire Inflators | Connects to vehicle’s power outlet; compact and portable | Automotive service centers, fleet management | Prós: Easy to use, convenient for vehicles; Contras: Limited to vehicle battery power; may not be suitable for larger vehicles. |
| Battery-Powered Inflators | Independent power source; versatile for various inflatables | Tire repair shops, outdoor equipment rentals | Prós: No reliance on vehicle; can inflate multiple items; Contras: Limited battery life; requires recharging. |
| Digital Tire Inflators | Features digital pressure gauge; automatic shut-off | Automotive retail, service workshops | Prós: Accurate pressure readings; reduces risk of over-inflation; Contras: Higher cost; may require more maintenance. |
| Heavy-Duty Tire Inflators | Designed for larger tires; higher PSI capacity | Construction, agriculture, and off-road vehicle services | Prós: Suitable for heavy-duty applications; robust construction; Contras: Bulky; often more expensive. |
| Inflator-Sealant Kits | Combines inflator with sealant for puncture repair | Emergency roadside assistance, auto repair shops | Prós: Quick fix for flat tires; easy to use; Contras: Sealant can damage tires; limited long-term solution. |
12-Volt tire inflators are designed to connect to a vehicle’s power outlet, making them highly portable and convenient for on-the-go tire inflation. They are typically compact, allowing for easy storage in a vehicle’s trunk. These inflators are best suited for regular automotive use, particularly for service centers and fleet management, where quick tire maintenance is essential. Buyers should consider the inflator’s PSI capacity, hose length, and ease of use when making a purchasing decision.
Battery-powered tire inflators operate independently from a vehicle’s power source, making them ideal for various applications beyond just tires, such as inflating sports equipment and air mattresses. This versatility makes them valuable for tire repair shops and outdoor equipment rentals. However, buyers should evaluate battery life and recharge time, as these factors can affect usability in high-demand situations. Investing in models with longer battery life can enhance operational efficiency.
Digital tire inflators provide precise pressure readings and often come with features like automatic shut-off once the desired pressure is reached. This makes them especially useful in automotive retail and service workshops, where accurate tire pressure is critical for safety and performance. While they may come at a higher price point, the benefits of reduced risk of over-inflation and improved customer satisfaction can justify the investment.
Heavy-duty tire inflators are built to handle larger tires and higher PSI levels, making them essential for industries like construction, agriculture, and off-road vehicle services. These inflators typically feature robust construction to withstand harsh conditions. Buyers should consider the inflator’s weight and portability, as well as its compatibility with the specific types of vehicles in their fleet. While these models may be more expensive, their durability and efficiency can provide significant long-term value.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Inflator-sealant kits combine the functions of inflating a tire and sealing minor punctures, making them ideal for emergency roadside assistance and auto repair shops. They are designed for quick fixes, allowing drivers to resume their journey with minimal delay. However, buyers should be aware that sealant can damage tires and may not be a viable long-term solution. Evaluating the expiration date of sealant can also be crucial, as outdated sealants may fail to perform effectively.
| Indústria/Setor | Specific Application of how do you use a tire inflator | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Principais considerações de fornecimento para este aplicativo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Quick tire inflation for customer vehicles during service appointments | Reduces customer wait times and enhances service efficiency | Reliability, ease of use, and durability of inflators |
| Transportation & Logistics | Regular tire maintenance for fleet vehicles | Increases fleet safety and reduces downtime due to flat tires | Power source compatibility and pressure range |
| Construção | Inflation of tires on heavy machinery and equipment | Ensures operational readiness and minimizes equipment failures | Heavy-duty inflators with high pressure capacity |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control checks during tire assembly processes | Ensures product safety and compliance with industry standards | Precision gauges and automatic shut-off features |
| Recreational Vehicle Rentals | Emergency tire inflation for rental vehicles | Enhances customer satisfaction and reduces roadside assistance costs | Portability, battery life, and additional features for versatility |
Automotive repair shops often face the challenge of providing quick service to customers, especially when it comes to tire-related issues. Portable tire inflators allow technicians to efficiently inflate tires during routine maintenance or after repairs, significantly reducing customer wait times. This capability not only enhances customer satisfaction but also improves the overall efficiency of the shop. When sourcing inflators, businesses should prioritize reliability and ease of use, ensuring that the devices can withstand frequent use in a busy environment.
In the transportation and logistics sector, maintaining optimal tire pressure is crucial for fleet safety and efficiency. Regular tire maintenance using portable tire inflators helps prevent flat tires, which can lead to costly downtime. Fleet managers should consider inflators that are compatible with various power sources and capable of reaching high pressure levels to accommodate different vehicle types. Investing in reliable inflators ensures that vehicles are always road-ready, ultimately enhancing operational productivity.
Construction companies often operate heavy machinery and equipment that rely on properly inflated tires for optimal performance. Portable tire inflators provide a practical solution for quickly inflating tires on-site, ensuring that machinery remains operational and reducing the risk of equipment failures. When selecting inflators, construction firms should focus on models that offer high-pressure capacity and durability, as these features are essential for handling the demands of a rugged work environment.
In automotive manufacturing, tire inflators play a critical role in quality control during the tire assembly process. Ensuring that tires are inflated to the correct specifications is vital for product safety and compliance with industry standards. Manufacturers should look for inflators equipped with precision gauges and automatic shut-off features, as these capabilities enhance accuracy and minimize the risk of over-inflation. Investing in high-quality inflators contributes to maintaining stringent quality assurance processes.
Recreational vehicle (RV) rental companies must ensure that their vehicles are always ready for customer use, which includes maintaining proper tire pressure. Portable tire inflators allow rental staff to quickly address any tire issues before customer pickups or during emergency situations. This capability not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces the need for costly roadside assistance. When sourcing inflators, rental companies should prioritize portability, battery life, and additional features that cater to a diverse range of inflatables, ensuring they are equipped for various scenarios.
O problema: Many B2B buyers, particularly in regions where tire maintenance is not consistently taught or reinforced, often struggle to understand the correct tire pressure specifications for different vehicles. This lack of knowledge can lead to either under-inflation, which increases tire wear and affects fuel efficiency, or over-inflation, which can cause blowouts or reduced traction. For companies managing a fleet, this issue can result in increased operational costs and safety risks, especially in high-traffic areas or challenging terrains common in parts of Africa and South America.
A solução: To combat this pain point, businesses should invest in comprehensive training for their drivers and maintenance teams. This training should include clear guidance on how to locate tire pressure specifications, which are typically found on the driver’s side door jamb or in the vehicle’s manual. Additionally, sourcing portable tire inflators with digital pressure gauges that automatically shut off when the desired pressure is reached can mitigate human error. By implementing regular workshops and creating easy-to-follow reference materials, companies can ensure their teams are well-informed, reducing the risk of tire-related incidents and enhancing overall fleet safety and efficiency.
O problema: In many regions, particularly in remote areas of the Middle East and parts of South America, access to reliable power sources can be sporadic. This inconsistency poses a challenge for businesses that rely on portable tire inflators that need to be plugged into a vehicle’s power outlet. If the inflator cannot be used due to a dead car battery or a lack of available power, companies face delays in operations, which can be costly.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
A solução: To address this issue, B2B buyers should consider investing in battery-operated tire inflators that do not require a vehicle power source. These inflators offer the flexibility of being used anywhere, regardless of the vehicle’s battery condition. Additionally, companies should maintain a set of fully charged spare batteries or even consider solar-powered inflators for operations in particularly sunny regions. Training staff on how to properly charge and maintain these inflators will ensure they are always ready for use, thus minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
O problema: Many users, particularly those new to tire maintenance, may not fully understand when and how to use tire sealant in conjunction with a tire inflator. This misunderstanding can lead to improper use of sealants, causing more harm than good. For instance, using sealants in tires that can be repaired may lead to complications and increased costs in tire replacements, impacting overall fleet management budgets.
A solução: Education is key in this scenario. Businesses should provide clear guidelines on the appropriate circumstances for using tire sealant, emphasizing that it should only be used as a last resort for minor punctures. Creating a comprehensive manual that details the steps for using both the inflator and sealant, including visual aids or video tutorials, can be beneficial. Furthermore, encouraging a practice of inspecting tires regularly and identifying potential issues before they require sealant use can save money and prolong the lifespan of the tires. Establishing a culture of proactive maintenance within the organization will empower employees to take better care of their vehicles and enhance overall fleet reliability.
When selecting a tire inflator, understanding the materials used in its construction is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials: plastic, aluminum, rubber, and stainless steel. Each material has distinct properties that impact the inflator’s functionality, durability, and suitability for different markets.
Plastic is often used in the housing of tire inflators due to its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness. Key properties include good insulation against electrical components and resistance to corrosion. However, plastics can have varying temperature ratings, which may limit their performance in extreme conditions.
Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Prós: Lightweight, low cost, and good electrical insulation.
Contras: Potentially lower durability compared to metals and may degrade under UV exposure.
Impacto no aplicativo: Suitable for low-pressure applications, but may not withstand high temperatures or prolonged use.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Ensure compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials, as some regions have restrictions on certain types of plastics.
Aluminum is frequently used in tire inflators for its strength-to-weight ratio and excellent heat dissipation properties. It can handle higher pressures and temperatures than plastic, making it ideal for more robust inflators.
Prós: Durable, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant.
Contras: Higher manufacturing costs and potential for denting under impact.
Impacto no aplicativo: Excellent for high-performance inflators that require quick inflation times and can handle various environmental conditions.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Aluminum inflators should comply with standards such as ASTM for pressure vessels, especially in regions with strict safety regulations.
Rubber is primarily used in the seals and hoses of tire inflators, providing flexibility and a tight seal to prevent air leaks. Its key properties include excellent elasticity and resistance to wear and tear.
Prós: Provides a secure seal, resistant to abrasion, and can handle a range of temperatures.
Contras: May degrade over time due to exposure to ozone or UV light.
Impacto no aplicativo: Essential for maintaining pressure and ensuring the inflator operates efficiently.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Check for compliance with local standards regarding rubber materials, particularly in markets where extreme weather conditions are common.
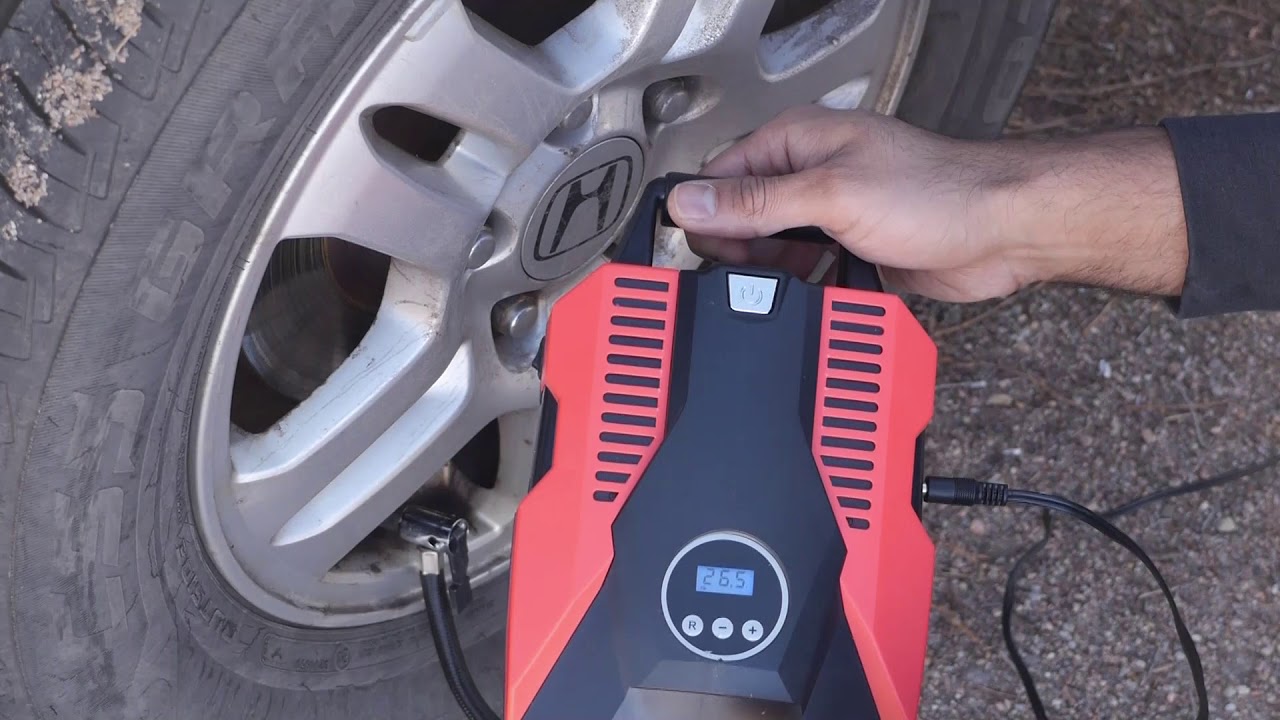

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Stainless steel is often used in the internal components of tire inflators, such as valves and fittings, due to its high strength and corrosion resistance. Its ability to withstand high pressures makes it a preferred choice for durable inflators.
Prós: Extremely durable, resistant to corrosion, and can handle high pressures.
Contras: Higher cost and weight compared to other materials.
Impacto no aplicativo: Ideal for heavy-duty inflators designed for commercial use or in harsh environments.
Considerações para compradores internacionais: Ensure that stainless steel components meet international standards such as JIS or DIN to guarantee quality and safety.
| Material | Typical Use Case for how do you use a tire inflator | Principais vantagens | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plástico | Housing and casing of portable inflators | Leve e econômico | Lower durability and UV sensitivity | Baixa |
| Alumínio | Body and structural components | Forte e resistente à corrosão | Higher manufacturing cost | Med |
| Borracha | Seals and hoses | Excellent elasticity and sealing | Degrades with ozone exposure | Baixa |
| Aço inoxidável | Internal valves and fittings | High strength and pressure resistance | Higher cost and weight | Alta |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in tire inflators, highlighting their properties, advantages, and limitations. Understanding these factors can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional compliance requirements.
The manufacturing process of tire inflators consists of several key stages that ensure the final product meets quality and performance standards. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
The first stage involves the selection and preparation of materials, which typically include plastics, metals, and electronic components. High-quality ABS or polycarbonate plastics are often used for the housing to provide durability and resistance to impact. Metal components, such as steel or aluminum, are commonly used for the internal structure and air pump mechanism due to their strength and reliability.
Before production, these materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet industry specifications. Suppliers often conduct tests to check for material integrity, chemical composition, and resistance to environmental factors.
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming and assembling the various components. This process may involve injection molding for plastic parts, stamping or machining for metal components, and PCB assembly for electronic systems.
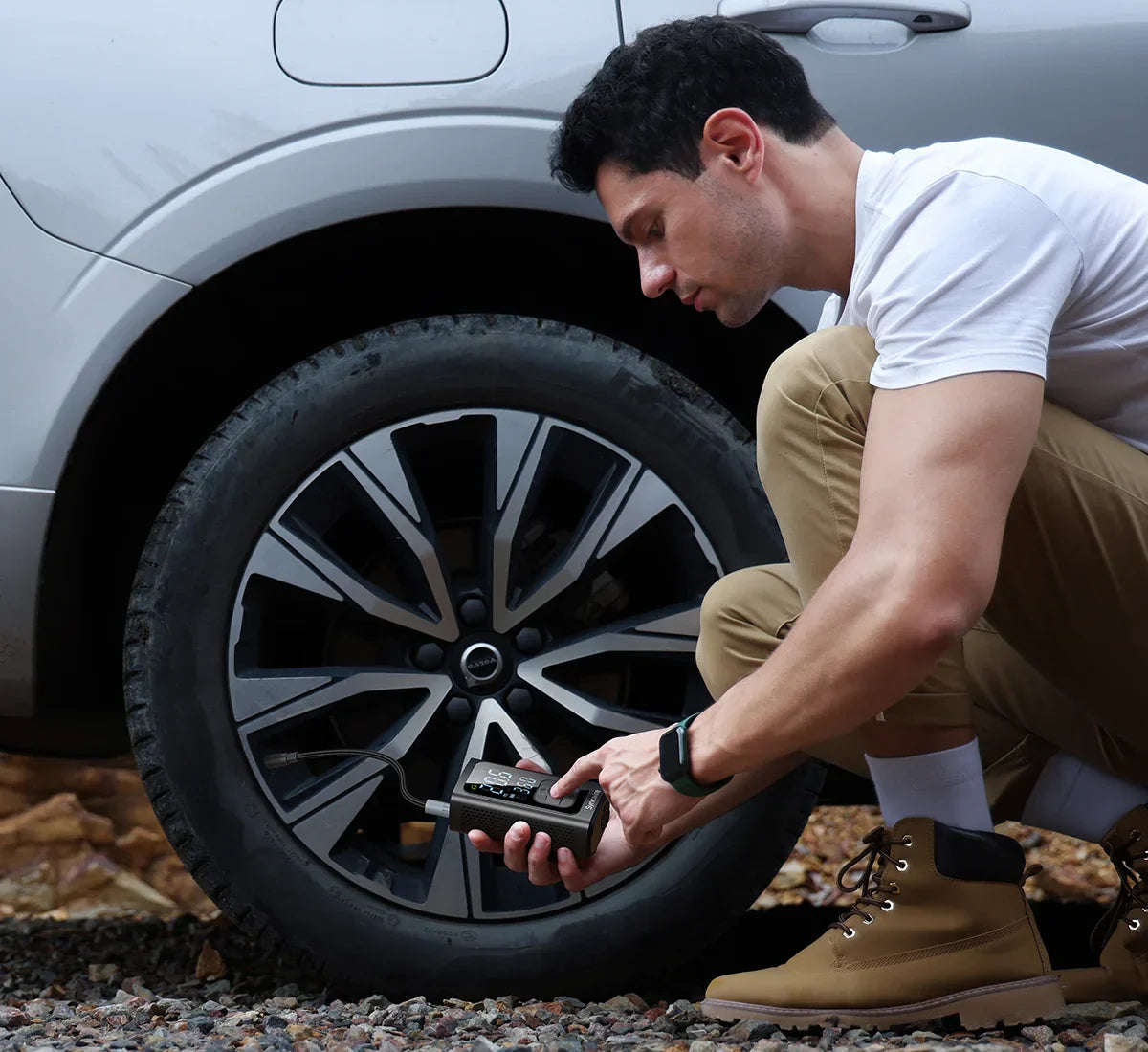

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Automated assembly lines are commonly used to increase efficiency and reduce human error. During this stage, components such as the air pump, power supply, and control interface are assembled into the housing. Quality checks are implemented at various points in this stage to ensure that each component fits correctly and functions as intended.
After assembly, the tire inflators undergo finishing processes, which may include surface treatment, painting, and final inspections. Surface treatments enhance durability and resistance to wear, while painting or coating provides aesthetic appeal and additional protection.
Final inspections are critical at this stage, where the inflators are tested for functionality, pressure output, and safety features. Any defects identified during this phase can lead to rework or scrapping of the product, ensuring that only high-quality units proceed to the market.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of tire inflators is guided by various international standards. Understanding these standards helps B2B buyers ensure they are sourcing products from compliant manufacturers.
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards applicable to tire inflator manufacturing. It focuses on meeting customer expectations and delivering consistent products. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have established processes for quality control, continuous improvement, and risk management.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industry certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for certain components may be relevant. CE certification indicates that the product meets European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, while API certification ensures the product meets the necessary performance criteria for pressure and safety.
Quality control (QC) is essential throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that tire inflators meet specified standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with the common QC checkpoints.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Incoming Quality Control (IQC) involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line. This step ensures that only materials meeting quality standards are used, preventing defects from arising in the final product.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) occurs at various stages of the manufacturing process. This may include checks for dimensional accuracy, assembly integrity, and functional testing of individual components. Regular audits during production help identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
Final Quality Control (FQC) is the last checkpoint before the product is shipped. It involves a comprehensive review of the finished tire inflators, including performance tests, safety checks, and aesthetic evaluations. This stage is vital for ensuring that the product is ready for market and meets all regulatory requirements.
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance.
One effective method is conducting supplier audits, where buyers assess the manufacturing facility’s adherence to quality standards and processes. This includes reviewing documentation, observing manufacturing practices, and evaluating the efficacy of the quality management system in place.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Requesting quality reports and certifications from suppliers can provide additional assurance regarding their compliance with international standards. Third-party inspections by accredited organizations can further validate the supplier’s quality control processes, offering an unbiased assessment of their practices.
B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances that can affect quality assurance.
Cultural differences may influence manufacturing practices, communication styles, and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should consider these factors when evaluating suppliers from different regions. Additionally, understanding local regulatory requirements is crucial, as compliance varies by country and region.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Market demand can affect the quality control processes employed by manufacturers. In regions with high demand for tire inflators, suppliers may prioritize speed over quality, which could lead to potential issues. B2B buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to maintain quality standards, even during peak production times.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for tire inflators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source reliable and high-quality products for their markets.
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to understand and utilize a tire inflator effectively. Whether you’re procuring inflators for a fleet, workshop, or retail outlet, following these steps ensures that you choose the right equipment and know how to operate it safely and efficiently.
Assess the types of vehicles and tires you will be inflating. Different vehicles, from passenger cars to heavy-duty trucks, may require inflators with varying pressure capacities and hose lengths. Understanding your specific needs will guide you in selecting an inflator that meets your operational requirements.
Familiarize yourself with the different types of tire inflators available in the market. The main categories include 12-volt inflators, which connect to a vehicle’s power source, and battery-powered models that offer more portability.
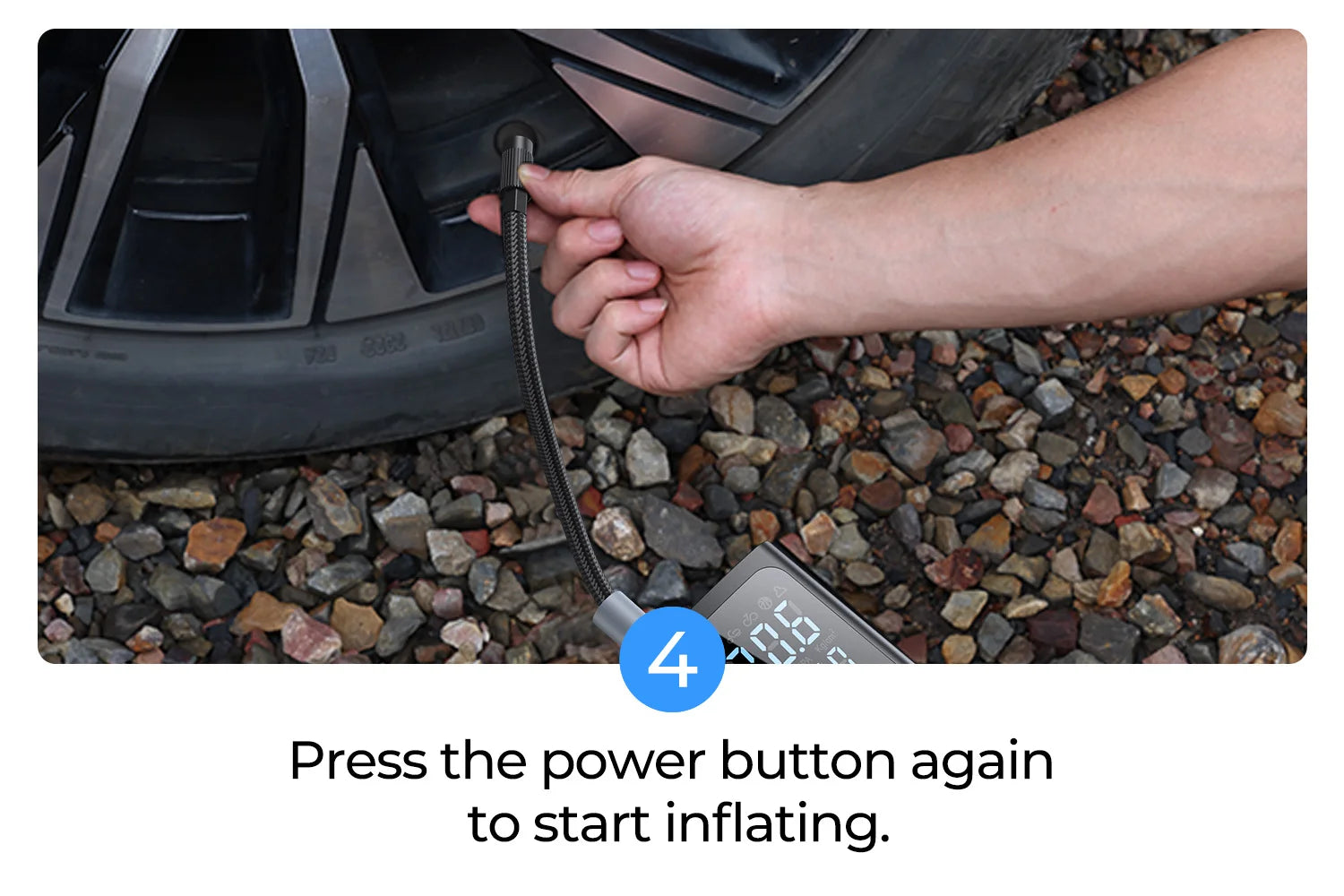
Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Before making a procurement decision, verify that the suppliers adhere to relevant safety and quality standards. This is critical to ensure the reliability and safety of the inflators you will be using.
Analyze the performance specifications of different inflators, focusing on maximum pressure, inflation speed, and duty cycle. These factors will determine how quickly and efficiently the inflator can perform under your specific conditions.
A robust warranty and responsive support services are essential when investing in equipment. This will protect your investment and ensure you have access to assistance if issues arise.
Once you’ve procured your tire inflator, conduct a dry run to familiarize yourself and your team with its operation. This step will help prevent operational mistakes and ensure everyone knows how to use the equipment effectively.
Implement a regular maintenance schedule to ensure the longevity and accuracy of your tire inflators. Regular checks will help identify potential issues before they become significant problems.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively utilize tire inflators, ensuring operational efficiency and safety in their vehicle maintenance practices.
When sourcing tire inflators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
Materiais: The quality of components, such as the motor, hose, and casing, significantly affects the price. High-quality materials can enhance durability and performance but will increase the initial cost.
Trabalho: Labor costs encompass the wages for workers involved in manufacturing and assembly. Regions with lower labor costs can provide a price advantage, but this may affect quality.
Custos indiretos de fabricação: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs.
Ferramentas: Specialized tools for production can be a significant upfront investment. Custom designs may require unique tooling, impacting the cost structure.
Controle de qualidade (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing can add to costs. However, investing in QC can reduce returns and enhance customer satisfaction.
Logística: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, can vary based on distance and the mode of transport. Import duties and tariffs are also important considerations for international transactions.
Margem: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary widely based on brand reputation, market demand, and competition.
Several factors influence the pricing of tire inflators, particularly for international buyers:
Volume/MOQ (quantidade mínima de pedido): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating for higher volumes can be beneficial.
Especificações e personalização: Custom inflators with specific features or branding may incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against potential cost increases.
Materiais e certificações de qualidade: Inflators made with premium materials or those that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) will typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess the value of these certifications for their target markets.
Fatores do fornecedor: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for determining who bears the cost and risk during shipping. This can impact the total landed cost of the product.
B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to optimize sourcing and achieve cost-efficiency:
Negociação: Always negotiate terms, prices, and delivery schedules with suppliers. Building long-term relationships can lead to better pricing and service.
Custo total de propriedade (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential resale value. Lower initial costs may not always translate to long-term savings.
Nuances de preços para compradores internacionais: Be aware of currency fluctuations, local taxes, and import duties when sourcing from international suppliers. These factors can significantly affect the final cost.
Local Market Insights: Understanding local market dynamics in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can provide leverage in negotiations. Buyers should research regional preferences and competitor offerings.
Diversificação de fornecedores: Relying on multiple suppliers can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and provide leverage in pricing discussions.
Prices for tire inflators can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes before making purchasing decisions. Always factor in additional costs, such as shipping and customs duties, to achieve a comprehensive understanding of the total expenditure involved in sourcing tire inflators.
In the realm of tire maintenance, the tire inflator is a popular solution for quickly addressing low tire pressure or flat tires. However, various alternatives exist that can also meet the needs of B2B buyers, depending on specific circumstances and requirements. Below, we compare the use of a tire inflator with two viable alternatives: a traditional air compressor and tire sealant kits.
| Aspecto de comparação | How Do You Use A Tire Inflator | Traditional Air Compressor | Tire Sealant Kits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Quickly inflates tires; portable | High inflation capacity; versatile | Seals punctures and inflates tires |
| Custo | $30 – $200 | $50 – $300 | $10 – $40 |
| Facilidade de implementação | Simple operation; minimal setup | Requires electrical outlet; heavier | Straightforward; can be messy |
| Manutenção | Low; periodic checks recommended | Moderate; requires upkeep and storage | Disposable; replace sealant canister |
| Melhor caso de uso | Emergency roadside assistance | Commercial use; heavy-duty vehicles | Temporary fix for small punctures |
Traditional air compressors are robust machines capable of inflating tires quickly and efficiently. They can be used in various settings, including garages and workshops, making them ideal for businesses with a fleet of vehicles. However, they require a power source and are typically bulkier, which may hinder portability. Additionally, they often come at a higher initial cost and require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
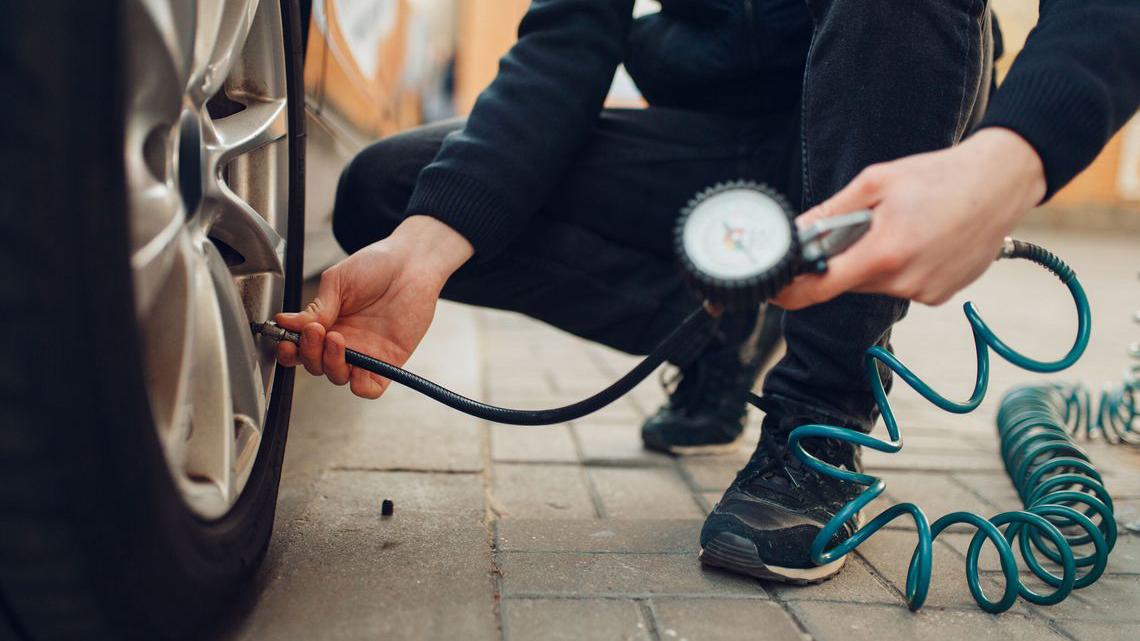

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
Tire sealant kits provide a convenient solution for minor punctures by sealing the hole while simultaneously inflating the tire. They are generally less expensive and easy to use, making them an attractive option for quick fixes. However, they are not suitable for large punctures and can make future tire repairs more complicated due to the sealant’s residue. Moreover, these kits often have a limited shelf life, necessitating periodic replacement.
When selecting the appropriate tire maintenance solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, such as the type of vehicles in use, the frequency of tire issues, and budget constraints. A tire inflator is ideal for quick, emergency situations, while a traditional air compressor is better suited for businesses with high-volume tire maintenance needs. Tire sealant kits serve as a temporary fix but may not replace the need for regular tire checks and maintenance. Ultimately, understanding the advantages and limitations of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements.
When evaluating tire inflators for commercial use, several technical properties are critical to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and safety. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should prioritize:
Fonte de energia
Tire inflators can be powered by either a 12-volt outlet from a vehicle or a built-in rechargeable battery. Understanding the power source is essential for operational flexibility, particularly in regions where vehicle power outlets may not be readily accessible. Battery-powered options provide greater mobility but require periodic recharging.
Maximum Pressure Capacity (PSI)
The maximum pressure capacity, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the highest pressure the inflator can achieve. For most passenger vehicles, a range of 30-35 PSI is standard. Commercial buyers should consider inflators capable of higher pressures for heavy-duty applications, such as trucks or larger vehicles, to ensure versatility across various fleet needs.
Inflation Speed (CFM)
The inflation speed, often measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), indicates how quickly the inflator can pump air into a tire. A higher CFM rating means faster inflation, which is crucial for businesses that rely on quick turnaround times, such as roadside assistance services or fleet management companies.
Durability and Material Grade
The construction materials used in tire inflators, such as high-grade plastic or metal components, impact durability and longevity. Inflators designed for commercial use should withstand harsh environmental conditions and frequent handling, minimizing the risk of equipment failure during critical operations.
Hose Length and Fittings
The length of the air hose and the type of fittings can significantly affect usability. A longer hose allows for easier access to tires in various positions, while compatible fittings ensure a secure connection to different tire valve types. This is particularly important for businesses managing diverse vehicle fleets.
Automatic Shut-off Feature
An automatic shut-off feature helps prevent over-inflation by stopping the inflator once the set pressure is reached. This not only enhances safety but also reduces the risk of tire damage, making it a vital feature for B2B buyers who prioritize operational safety and efficiency.
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms related to tire inflators:
OEM (fabricante original do equipamento)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for buyers looking for compatible replacement parts or accessories for their tire inflators.
MOQ (Quantidade mínima de pedido)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they meet supplier requirements without overcommitting resources.
RFQ (Request for Quotation, solicitação de cotação)
An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products. This is particularly useful for businesses looking to procure tire inflators in bulk, allowing them to compare pricing and features across different suppliers.
Incoterms (Termos Comerciais Internacionais)
These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in international procurement of tire inflators to avoid misunderstandings related to shipping, insurance, and risk management.
Prazo de entrega
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For businesses relying on tire inflators for daily operations, understanding lead times is essential for planning and ensuring that equipment is available when needed.
Período de garantia
The warranty period indicates the duration that a product is guaranteed against defects and failures. A longer warranty period can provide peace of mind and reduce long-term costs, making it an important consideration for B2B buyers evaluating tire inflator options.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting tire inflators that best meet their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
The tire inflator market is experiencing significant growth globally, driven by several key factors. Increasing vehicle ownership in emerging economies, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, is one of the primary catalysts. As more consumers and businesses rely on personal and commercial vehicles, the demand for portable tire inflators has surged. Additionally, rising awareness about vehicle maintenance and safety is encouraging both individual consumers and fleet operators to invest in tire inflators as a proactive measure against flat tires.
Technological advancements are also shaping the market dynamics. The introduction of smart tire inflators equipped with digital displays, automatic shut-off features, and compatibility with various tire types is enhancing user convenience. Moreover, the growing trend towards electric vehicles (EVs) has led to the development of specialized inflators that cater to EV tire specifications, further expanding the market.
Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms is transforming the sourcing landscape, allowing international B2B buyers to access a wider range of products at competitive prices. This trend is particularly relevant for businesses in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where quick access to high-quality tools is essential.
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the sourcing of tire inflators. As environmental concerns continue to rise, international B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing products that have a lower environmental impact. This includes tire inflators made from recyclable materials and those that consume less energy during operation.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction. Buyers are now looking for suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and adhere to ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can enhance a supplier’s reputation and appeal to eco-conscious businesses.
Moreover, manufacturers are exploring innovative materials and technologies that reduce waste and enhance product lifespan. For instance, some companies are developing inflators with modular components that can be easily replaced, extending the product’s life cycle and minimizing waste. B2B buyers who prioritize sustainability can not only meet regulatory requirements but also strengthen their brand image and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally-conscious consumers.
The evolution of tire inflators can be traced back to the early 20th century when manual pumps were the primary tools for inflating tires. These pumps required significant physical effort and were not particularly user-friendly. The introduction of electric tire inflators in the late 20th century marked a significant technological advancement, offering convenience and efficiency that manual pumps could not provide.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
As vehicles became more advanced, so did tire inflators. Today’s portable tire inflators incorporate digital technology, allowing users to set desired pressure levels and receive real-time feedback. This evolution reflects broader trends in consumer electronics, where ease of use and automation are becoming standard expectations. The focus on compact, portable designs has also made tire inflators an essential item for drivers, ensuring that they are well-equipped to handle emergencies on the road.
In summary, the tire inflator market is shaped by global demand for convenience, sustainability, and technological innovation. B2B buyers should consider these dynamics when sourcing products to meet the needs of their customers effectively.
How do I solve a flat tire using a tire inflator?
To solve a flat tire, first inspect it for any visible damage such as cuts or bulges. If the tire appears safe, connect the tire inflator to a power source (12V outlet or rechargeable battery), and attach the hose to the tire valve. Set the desired pressure according to the vehicle’s specifications, turn on the inflator, and monitor the pressure gauge to avoid over-inflation. Once the desired pressure is reached, turn off the inflator and disconnect the hose. Always check the tire pressure with a separate gauge to ensure accuracy.
What is the best tire inflator for commercial use?
For commercial applications, consider a tire inflator that offers high PSI capabilities, durability, and a fast inflation rate. Look for models with a robust motor, multiple power options (like 12V and AC), and features such as automatic shut-off and digital pressure gauges. Brands that provide good warranties and customer support can also be beneficial. Depending on your specific needs (e.g., for trucks or buses), you may want an inflator with additional adapters and longer hoses for ease of use.
What safety precautions should I take when using a tire inflator?
Before using a tire inflator, ensure the tire is in good condition, checking for damage. Use the inflator in a safe location away from traffic, and avoid over-inflating by adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended tire pressure. Keep the inflator running under supervision and allow it to cool down after use to prevent overheating. Additionally, keep flammable materials away from the working area and ensure all connections are secure to prevent air leaks.
How can I ensure quality when sourcing tire inflators from suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing tire inflators, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request samples to evaluate the product’s durability and performance. Look for suppliers with certifications such as ISO or CE, indicating adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, check customer reviews and case studies, and consider visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facilities if possible. Implement quality assurance checks in your procurement process to maintain consistent standards.
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for tire inflators?
Minimum order quantities for tire inflators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of inflator. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to several hundred units for standard models. For customized or branded inflators, MOQs may be higher. It’s advisable to discuss your specific requirements with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you’re looking to test a new product line or enter a new market.
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing tire inflators internationally?
When purchasing tire inflators from international suppliers, payment terms can vary. Common options include a 30% deposit with the balance due before shipment, or full payment upfront for smaller orders. Consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment. Always clarify payment terms in advance and ensure they are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings.
How can I customize tire inflators for my brand?
To customize tire inflators for your brand, start by discussing your requirements with potential suppliers. Many manufacturers offer branding options such as private labeling, where your logo can be printed on the product. Additionally, you may explore features like color, packaging, or included accessories to align with your brand identity. Be clear about your specifications and timelines, and request prototypes to ensure the final product meets your expectations.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing tire inflators?
When sourcing tire inflators, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose suppliers that can provide reliable shipping options and trackability. Understand the import duties and taxes applicable in your region to accurately calculate total costs. Collaborate with freight forwarders experienced in handling automotive products to streamline the shipping process and mitigate any potential delays.
Domínio: reddit.com
Registrado: 2005 (20 anos)
Introdução: Automatic air station for vehicle tires, typically found at locations like Wawa or Sheets. Features include: setting tire pressure using up and down arrows (default pressure is usually 32 PSI), a nozzle for attaching to the tire valve, and a lever to pump air. The machine performs pressure checks before and during the inflation process, stopping to check pressure multiple times, and signals comple…
Domínio: wikihow.com
Registrado: 2004 (21 anos)
Introdução: This company, WikiHow – Tire Inflation Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Domínio: macheforum.com
Registrado: 2018 (7 anos)
Introdução: Tire inflator and sealant kit; instructions located on pages 329-330 of the vehicle manual; recommended to perform a dry run before use; ensure dial is set to ‘air only’; sealant should only be used in critical situations as it can gum up the tire and make repairs impossible; sealant canisters expire in 5-6 years; replace with the correct sealant canister after use.
Domínio: lincoln.com
Registrado: 1997 (28 anos)
Introdução: The Tire Inflator and Sealant Kit is designed to temporarily fix flat tires, allowing drivers to reach a Lincoln Retailer for service. It is an alternative to a spare tire and provides a temporary repair. The kit contains enough sealant for one tire repair only. Users should refer to their Owner’s Manual for specific instructions, speed and distance limitations after use, and the kit’s location in…
In conclusion, understanding how to effectively use a tire inflator is essential for enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring vehicle safety across various industries. By incorporating portable tire inflators into your fleet management strategy, businesses can minimize downtime due to flat tires, reduce dependency on roadside assistance, and empower drivers with the tools needed for quick repairs.

Illustrative image related to how do you use a tire inflator
When sourcing tire inflators, consider factors such as power source, pressure capacity, and additional features that cater to your specific needs. Investing in high-quality inflators can lead to long-term savings and increased productivity, particularly in regions where access to repair services may be limited.
Looking ahead, the demand for reliable tire maintenance solutions will continue to grow as global transportation networks expand. We encourage international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to explore innovative tire inflator options that meet their operational requirements. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you can enhance fleet reliability and ensure that your vehicles are always road-ready. Engage with reputable suppliers to secure the best products for your business needs and drive your operations forward.
As informações fornecidas neste guia, inclusive o conteúdo referente a fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análise de mercado, são apenas para fins informativos e educacionais. Elas não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre compras, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos feito todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e a atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem realizar sua própria due diligence independente e completa antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contato diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar as certificações, solicitar amostras e buscar consultoria profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é de responsabilidade exclusiva do leitor.