In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding how to inflate a car tire properly is essential for international B2B buyers across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge many businesses face is not just sourcing the right equipment, but ensuring their teams are well-informed on the critical aspects of tire maintenance to maximize safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide demystifies the process of tire inflation, covering everything from the types of inflation methods available to the specifications needed for various vehicle applications.
By exploring crucial topics such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the environmental impact of tire maintenance, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of tire inflation can lead to longer tire lifespans, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced vehicle safety—key factors that resonate across global markets. Whether you’re operating in Nigeria or Vietnam, this resource serves as a foundational tool, empowering businesses to optimize their tire management practices and ultimately drive better operational outcomes. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your procurement strategies and ensure your fleet remains road-ready, no matter where you operate.
| Nome do tipo | Principais características distintivas | Aplicativos B2B primários | Prós e contras resumidos para compradores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Inflation | Utilizes a standard tire pump or compressor; requires manual effort. | Automotive repair shops, fleet maintenance | Prós: Cost-effective, no electricity needed. Contras: Labor-intensive, time-consuming. |
| Automatic Inflation Systems | Integrated systems that inflate tires automatically based on sensors. | Commercial fleets, luxury vehicle markets | Prós: Saves time, ensures optimal pressure. Contras: Higher initial investment, maintenance required. |
| Portable Tire Inflators | Compact devices powered by car battery or AC outlet for on-the-go inflation. | Emergency roadside assistance, personal vehicles | Prós: Convenient, easy to use. Contras: Limited air capacity, may require frequent recharging. |
| Nitrogen Inflation | Tires filled with nitrogen instead of air to reduce pressure loss. | High-performance vehicles, racing teams | Prós: Less frequent inflation, improved tire lifespan. Contras: Limited availability, higher cost. |
| Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) | Sensors that monitor tire pressure and alert drivers of changes. | New vehicle manufacturers, fleet management | Prós: Enhances safety, reduces tire wear. Contras: Can be expensive to install and maintain. |
Manual inflation involves using a standard tire pump or compressor to inflate tires. This method is commonly employed in automotive repair shops and fleet maintenance environments due to its simplicity and low cost. B2B buyers should consider the labor intensity and time required for this method, as it necessitates manual effort. While it is cost-effective, it may not be the most efficient solution for businesses with a high volume of vehicles requiring regular maintenance.
Automatic inflation systems are integrated with vehicles and utilize sensors to maintain optimal tire pressure without manual intervention. These systems are particularly beneficial for commercial fleets and luxury vehicles, where time efficiency and performance are paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment against the long-term savings in fuel consumption and tire longevity. Although they require maintenance, the convenience they offer can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
Portable tire inflators are compact devices that can be powered by a car battery or an AC outlet, making them ideal for emergency roadside assistance or personal vehicle use. They are particularly useful for businesses that require quick solutions for tire issues on the go. Buyers should consider the convenience and ease of use, but they should also be aware of the limited air capacity and the need for frequent recharging, which may not suit all business models.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
Nitrogen inflation is a method where tires are filled with nitrogen instead of regular air, helping to minimize pressure loss over time. This method is particularly popular in high-performance vehicles and racing teams, where maintaining optimal tire pressure is crucial for safety and performance. B2B buyers should evaluate the availability of nitrogen inflation services and the associated costs, as this method can lead to longer tire lifespan and reduced maintenance frequency.
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) utilize sensors to continuously monitor tire pressure and alert drivers when there are significant changes. This technology is increasingly being adopted by new vehicle manufacturers and fleet management services, providing a proactive approach to tire maintenance. B2B buyers should consider the safety benefits and potential reduction in tire wear, although they must also account for the installation and maintenance costs associated with these systems.
| Indústria/Setor | Specific Application of how to inflate a car tire | Valor/benefício para a empresa | Principais considerações de fornecimento para este aplicativo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet Vehicle Maintenance | Enhanced safety and reduced operational costs | Reliability of inflation equipment; availability of trained personnel; compliance with local regulations. |
| Automotive Repair Services | Tire Service Centers | Improved service offerings and customer satisfaction | Quality of tire inflation tools; availability of spare parts; training for staff on inflation techniques. |
| Agricultura | Farm Vehicle Maintenance | Increased productivity and reduced downtime | Access to portable inflation solutions; durability of equipment in rural settings; local supplier support. |
| Construção | Heavy Equipment Maintenance | Enhanced safety and machinery longevity | Robustness of inflation equipment; compatibility with diverse machinery; supplier reliability. |
| Car Rental Services | Vehicle Readiness Checks | Improved customer experience and safety standards | Calibration of inflation gauges; availability of quick service solutions; adherence to manufacturer guidelines. |
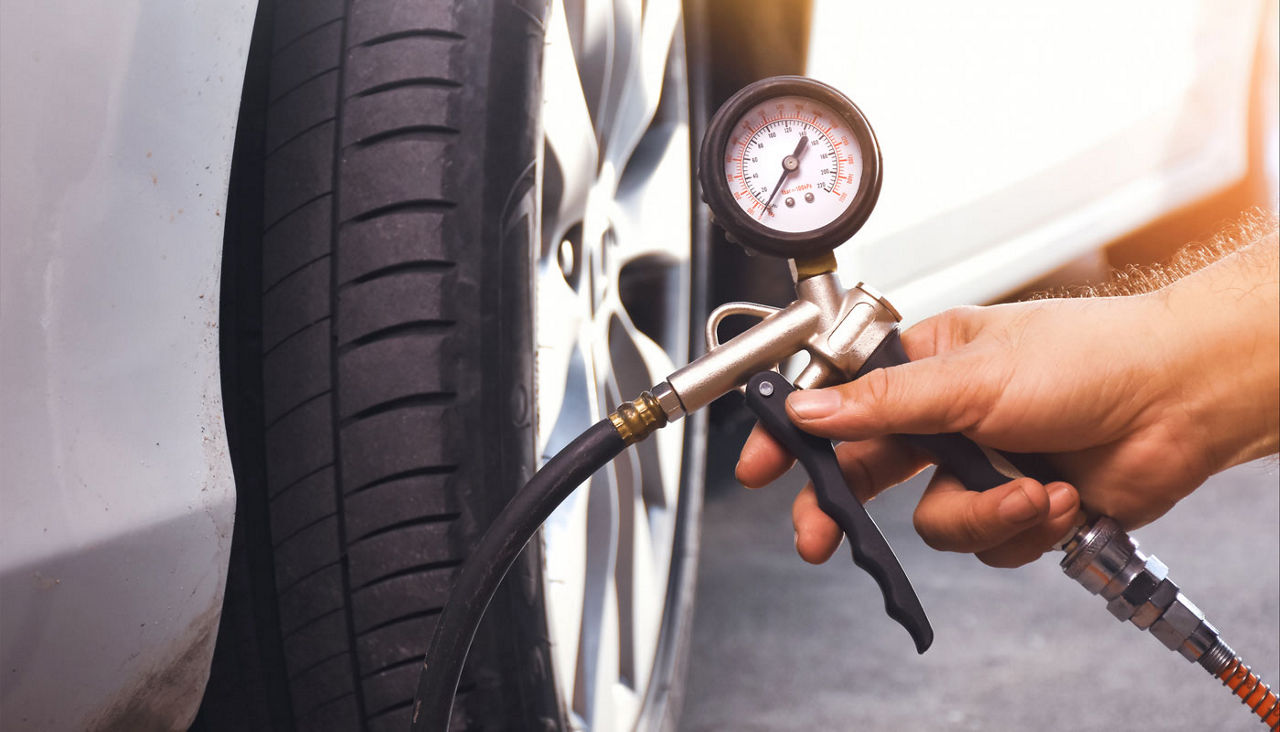
In the transportation and logistics sector, maintaining tire pressure is vital for fleet vehicle safety and efficiency. Properly inflated tires enhance fuel economy and reduce wear, thus minimizing operational costs. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable tire inflation equipment and ensuring staff are trained in proper inflation techniques can mitigate risks associated with under-inflation, such as blowouts and accidents. Fleet managers must consider the local climate’s impact on tire pressure and invest in equipment that can withstand various environmental conditions.
Automotive repair services that provide tire maintenance can significantly boost customer satisfaction and retention. By offering tire inflation as part of their service portfolio, these centers can address common issues like uneven tire wear and fuel inefficiency. Buyers in the automotive sector should prioritize sourcing high-quality tire inflation tools and ensuring that technicians are well-trained in inflation methods. Additionally, establishing relationships with reliable suppliers for spare parts can enhance service efficiency and minimize downtime, particularly in competitive markets across Europe and the Middle East.
In agriculture, maintaining the right tire pressure for farm vehicles is crucial for productivity and operational efficiency. Proper inflation reduces the risk of tire failure, which can lead to costly downtime during critical planting or harvesting periods. B2B buyers in agricultural sectors must consider portable tire inflation solutions that can be easily transported to remote locations. Additionally, durability and ease of use are key factors, especially in rural areas where access to service centers may be limited. Ensuring that inflation equipment is suitable for various types of agricultural machinery can enhance overall productivity.
Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
For the construction industry, maintaining the correct tire pressure on heavy machinery is essential for safety and equipment longevity. Properly inflated tires improve handling and reduce the risk of accidents on job sites, which can be critical in environments with heavy machinery. Buyers should focus on sourcing robust inflation equipment that can handle the demands of construction work. Compatibility with different types of machinery and the reliability of suppliers in providing timely support are also significant considerations for businesses operating in this sector.
For car rental services, ensuring vehicles are properly inflated before rental can significantly enhance customer experience and safety. Regular tire pressure checks can prevent accidents and reduce maintenance costs. B2B buyers in this sector should invest in calibrated inflation gauges and portable inflation solutions for quick service. Additionally, adherence to manufacturer guidelines for tire pressure is essential to maintain the fleet’s integrity and ensure customer satisfaction, particularly in regions with diverse climates, such as Europe and the Middle East.
O problema: For businesses operating vehicle fleets—whether for delivery, transportation, or logistics—maintaining optimal tire pressure is a critical but often overlooked task. Fleet managers may face issues such as fluctuating tire pressures due to temperature changes, leading to inconsistent handling, increased fuel consumption, and accelerated tire wear. In regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can vary significantly, underinflated or overinflated tires can drastically affect safety and operational costs. This inconsistency can result in unexpected breakdowns, impacting service delivery and customer satisfaction.
A solução: Implementing a systematic tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) can be an effective solution for fleet operators. These systems alert managers when tire pressure falls below recommended levels, enabling timely adjustments. Additionally, businesses should conduct regular training for drivers on the importance of tire maintenance and the correct methods to check tire pressure. Investing in portable tire inflation compressors can also empower drivers to address pressure issues on the go, reducing downtime. Establishing a routine check schedule—ideally every month and before long trips—will ensure that all vehicles maintain proper tire pressure, enhancing safety and efficiency.
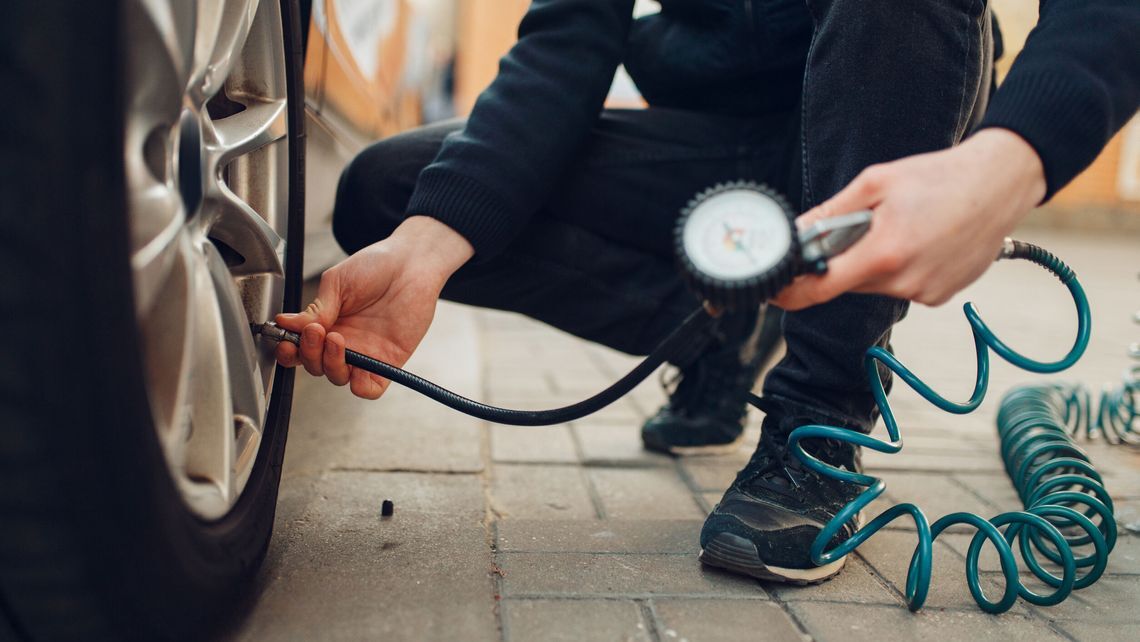
O problema: Many B2B buyers, particularly those new to vehicle maintenance, may lack the knowledge and confidence to properly inflate car tires. This gap in understanding can lead to mistakes, such as overinflation or underinflation, which not only jeopardizes vehicle safety but also increases operational costs through poor fuel economy and accelerated tire wear. In emerging markets where automotive education is less accessible, the consequences of improper tire inflation can be particularly severe, affecting the reliability of transportation services.
A solução: To address this knowledge gap, businesses can invest in comprehensive training programs that cover the essentials of tire maintenance. Workshops led by automotive experts can provide hands-on experience in using tire pressure gauges and inflators. Additionally, creating easily accessible instructional materials—such as video guides and infographics—can support ongoing education. Encouraging a culture of safety and maintenance within the organization will empower employees to take charge of tire health proactively, thereby reducing the risk of costly errors.
O problema: In many regions, particularly in developing markets, access to reliable tire inflation equipment can be a significant hurdle for businesses. Service stations may be scarce, and the quality of inflation equipment can vary widely, leading to inaccurate pressure readings. This lack of reliable access can force businesses to operate with improperly inflated tires, increasing the likelihood of accidents, reduced fuel efficiency, and overall higher operational costs.
A solução: To mitigate this issue, companies should consider investing in high-quality portable tire inflators and calibrated pressure gauges. These tools can be stored in vehicles and used for on-the-spot inflation, ensuring that tires are always at the correct pressure regardless of location. Establishing partnerships with local tire service providers can also create a network of reliable resources for regular tire checks and maintenance. Additionally, businesses can explore group purchasing options to acquire bulk tire maintenance tools at a reduced cost, improving accessibility for all vehicles in the fleet. By ensuring that proper equipment is readily available, businesses can significantly enhance their tire management processes and reduce the risks associated with improper inflation.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
When it comes to inflating car tires, the choice of materials used in the equipment can significantly impact performance, durability, and overall user experience. Here, we analyze four common materials used in tire inflation systems: rubber, metal, plastic, and composite materials.
Rubber is a primary material used in various components of tire inflation systems, such as hoses and seals. Its key properties include excellent flexibility, good temperature resistance, and the ability to withstand high pressures, making it suitable for tire inflation applications.
Prós: Rubber is durable and can handle the stress of repeated use, ensuring longevity in tire inflation equipment. It is also relatively inexpensive, which is a significant advantage for manufacturers looking to keep costs down.
Contras: However, rubber can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and ozone, which may lead to cracks and reduced effectiveness. Additionally, it may not perform well in extremely high-temperature environments.
Impacto no aplicativo: Rubber’s flexibility allows it to fit snugly around tire valves, ensuring a good seal during inflation. However, international buyers should consider the varying quality of rubber products available in different regions, as this can affect performance.
Metal, particularly aluminum and steel, is commonly used in tire inflators and compressors. Metals offer high strength, durability, and resistance to deformation under pressure.
Prós: Metal components can withstand high pressures without failing, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. They are also resistant to corrosion when properly treated, which is essential for equipment exposed to various environmental conditions.
Contras: The primary disadvantage is the higher cost associated with metal components compared to rubber or plastic. Additionally, metal parts can be heavier, which may affect the portability of tire inflation equipment.
Impacto no aplicativo: Metal is especially suitable for high-performance tire inflators that require consistent pressure outputs. Buyers in regions with high humidity or saline environments, such as coastal areas in Africa or South America, should prioritize corrosion-resistant metals.
Plastic is often used in the construction of lighter components, such as gauges and connectors. Its key properties include lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of manufacturing.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
Prós: The lightweight nature of plastic makes it easy to handle and transport, which is beneficial for portable tire inflation devices. Additionally, plastics can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Contras: However, plastic components may not withstand high pressures as effectively as metal, and they can become brittle over time, especially under UV exposure.
Impacto no aplicativo: Plastics are suitable for low-pressure applications, but international buyers should be cautious about the quality and specifications of plastic materials, as substandard products can lead to failures.
Composite materials, which combine two or more materials to enhance performance, are increasingly being used in tire inflation systems. Their properties can vary widely based on the constituents used.
Prós: Composites can offer a balance of strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors, making them versatile for various applications. They can be engineered to meet specific performance criteria, such as weight reduction and enhanced durability.
Contras: The main downside is the cost, as composite materials can be more expensive to produce than traditional materials. Additionally, manufacturing processes for composites can be complex, which may lead to longer lead times.
Impacto no aplicativo: Composites can be particularly useful in high-performance tire inflation systems that require lightweight yet durable components. Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards, as composite materials can vary significantly in quality.
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to inflate a car tire | Principais vantagens | Principal desvantagem/limitação | Custo relativo (baixo/médio/alto) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borracha | Hoses and seals in tire inflators | Excellent flexibility and durability | Degrades over time in UV exposure | Baixa |
| Metal | Heavy-duty tire inflators and compressors | High strength and pressure resistance | Higher cost and weight | Alta |
| Plástico | Gauges and connectors in portable inflators | Leve e resistente à corrosão | Brittle under pressure | Med |
| Composto | High-performance tire inflation components | Balanced strength and flexibility | Custo mais alto e fabricação complexa | Alta |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in tire inflation systems, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
The manufacturing process for tire inflation equipment, such as air compressors and tire inflators, involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. These stages include:
Preparação de materiais: The first step involves selecting high-quality materials, such as metals for compressor housings and durable plastics for nozzle attachments. Suppliers often undergo rigorous vetting processes to ensure material quality aligns with international standards. Material testing for durability and heat resistance is essential, particularly for components exposed to high pressures.
Formação: This stage includes processes such as machining, molding, and welding. For instance, metal components are often machined to precise specifications to ensure proper fitting and function. Injection molding is commonly used for plastic parts, requiring temperature and pressure control to maintain consistency. Attention to detail during this phase is crucial to prevent defects that could lead to failure during operation.
Montagem: After forming, the components are assembled. This can involve manual labor and automated systems, depending on the scale of production. Each unit undergoes a series of assembly checks to ensure that parts fit correctly and function as intended. For instance, seals must be fitted correctly to prevent air leaks, which can compromise inflation efficiency.
Acabamento: The final stage includes surface treatment, painting, and packaging. Surface treatments may involve coatings that enhance corrosion resistance, particularly for products intended for markets with varying climates, such as humid environments in parts of Africa and South America. Quality checks during this phase ensure that the product not only looks good but is also functional and durable.
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the manufacturing process of tire inflation equipment. Implementing robust QC measures helps ensure that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. Here are the essential QC components:

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
International Standards Compliance: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which focus on quality management systems. Compliance with these standards can enhance a supplier’s credibility and marketability, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where quality assurance is a critical factor in supplier selection.
Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the market, additional certifications may be necessary. For example, CE marking is crucial for products sold in the European market, while API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply to equipment used in conjunction with petroleum products. Buyers should inquire about these certifications to ensure compliance.
Quality Checkpoints: Effective QC involves several checkpoints:
– Controle de qualidade de entrada (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
– Controle de qualidade durante o processo (IPQC): Regular checks during production help identify defects early, minimizing waste and rework.
– Controle de qualidade final (FQC): Completed products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they function correctly under expected conditions. This may include pressure testing for compressors and inflators.
Several testing methods are employed during the QC process to guarantee that tire inflation equipment meets safety and performance standards:
Pressure Testing: This method verifies the integrity of air compressors and inflators. Units are subjected to pressure levels that exceed normal operating conditions to ensure they can handle real-world usage without failure.
Leak Testing: Manufacturers often use methods like soap bubble tests or electronic leak detectors to identify any potential air leaks in the system. This is crucial as even minor leaks can lead to significant performance issues.
Teste de durabilidade: Products are subjected to various stress tests to simulate extended use. This may include cycling the unit on and off repeatedly to assess wear on components.
Performance Testing: This involves measuring the speed and efficiency of the inflation process under controlled conditions. The results help ensure that products meet the performance expectations set by the manufacturer.
B2B buyers must conduct thorough due diligence to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are actionable steps to ensure suppliers maintain high standards:
Auditorias de fornecedores: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and QC measures. Buyers should request audits focusing on compliance with international and industry-specific standards.
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their QC processes, including results from testing methods. These reports should indicate how often tests are conducted and the standards used.
Inspeções de terceiros: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide unbiased verification of a supplier’s quality claims. These services can conduct on-site inspections, review quality documentation, and perform product testing.
Certifications Verification: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold the necessary certifications. This can often be done through online databases or by directly contacting certifying bodies.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider in the QC process:
Cultural and Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding product quality and compliance. Understanding local regulations and quality standards is crucial for successful procurement.
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can impact product quality. Buyers should ensure that suppliers use appropriate packaging and handling procedures to protect products during transit, especially those sensitive to pressure changes.
Post-Sale Support and Warranty: B2B buyers should inquire about warranty terms and post-sale support. A robust support system can mitigate risks associated with product defects and ensure that any issues are addressed promptly.
Building Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and improvements. Long-term partnerships often lead to enhanced product quality and reliability.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for tire inflation equipment, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and ensure customer satisfaction.
This practical guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring the necessary resources and equipment for inflating car tires. Proper tire inflation is crucial not only for vehicle safety and efficiency but also for extending tire lifespan and reducing operational costs. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they are making informed decisions when sourcing tire inflation solutions.
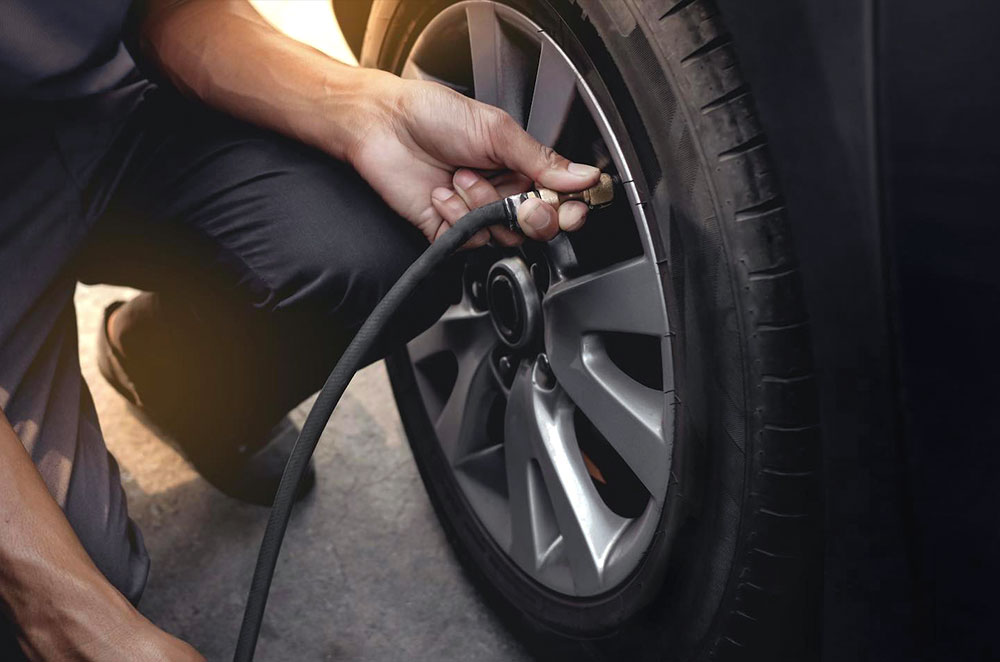
Understanding your specific tire inflation requirements is the first step in the procurement process. This includes assessing the types of vehicles in your fleet, the average tire sizes, and the typical tire pressure recommendations. Knowing these details will help you choose the right equipment and supplies that meet your operational demands.
Investing in the right equipment is vital for effective tire inflation. Look for high-quality tire inflators, pressure gauges, and accessories such as valve caps and portable compressors. Ensure the equipment can handle the pressure ranges required by your fleet’s vehicles and consider features like durability and ease of use.
Before finalizing a supplier, check their certifications and industry standards compliance. Reliable suppliers should have relevant certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety, such as ISO certifications. This ensures that the products you source are trustworthy and meet global standards.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
Whenever possible, request samples of tire inflators and gauges from potential suppliers. Testing these products firsthand allows you to assess their performance and reliability in real-world conditions. Pay attention to how user-friendly the equipment is, as ease of use can significantly impact efficiency in tire maintenance.
An effective procurement strategy includes evaluating after-sales support offered by suppliers. Inquire about warranty terms, maintenance services, and availability of spare parts. A supplier that provides robust after-sales support can help you minimize downtime and ensure continuous operations.
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare their pricing structures and payment terms. Look beyond just the initial cost; consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and potential savings from improved tire longevity and fuel efficiency. Ensure that the pricing aligns with your budget while still meeting quality standards.
Building a long-term relationship with your chosen suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to the latest products. Maintain open communication to discuss your evolving needs and any potential issues. A strong partnership can enhance your operational efficiency and overall satisfaction with the procurement process.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement of tire inflation solutions, ensuring that their vehicles remain safe, efficient, and cost-effective on the road.
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing tire inflation solutions, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materiais: The primary materials involved in tire inflation include the inflation equipment (manual pumps, electric compressors) and any additives such as nitrogen for inflation. The quality and type of materials used can significantly influence the overall cost. For instance, heavy-duty compressors designed for commercial use will typically incur higher material costs than basic consumer-grade pumps.
Trabalho: Labor costs encompass the wages for workers involved in the manufacturing and assembly of tire inflation equipment. This can vary significantly by region, with labor costs being generally lower in developing markets such as parts of Africa and South America compared to Europe.
Custos indiretos de fabricação: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and other operational expenses necessary for running manufacturing facilities. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overhead costs.
Ferramentas: The cost of specialized tools required for production can be substantial, especially if custom tooling is needed for specific inflation products. This cost is generally amortized over the volume of products produced.
Controle de qualidade (QC): Ensuring the reliability and safety of tire inflation products requires investment in quality control processes. This can involve both material testing and final product inspections, which are essential for maintaining certifications and meeting industry standards.
Logística: Shipping and handling costs must also be factored into the overall pricing structure. This includes transportation costs from the manufacturing facility to distribution centers and ultimately to the buyer. International shipping can be particularly costly, influenced by factors such as fuel prices and customs duties.
Margem: Finally, suppliers will build a profit margin into their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the uniqueness of the product offering.
Several factors can influence the pricing of tire inflation solutions, particularly in international B2B contexts:
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Bulk purchases often come with discounts, making it economically advantageous for buyers to source larger quantities.
Especificações e personalização: Customized solutions, such as branded compressors or specific pressure gauges, typically incur additional costs. Buyers should assess whether these custom features are essential for their operations.
Materiais e certificações de qualidade: The choice of materials impacts durability and safety, which can influence pricing. Products that meet international quality certifications may command higher prices due to the assurance of reliability.
Fatores do fornecedor: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge premium prices compared to lesser-known competitors.
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is crucial for international buyers, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly impact the total cost of acquisition.
To optimize costs while sourcing tire inflation solutions, buyers should consider the following strategies:
Negociação: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure the best possible prices, especially for bulk orders. Building long-term relationships can also lead to better terms and discounts.
Custo total de propriedade (TCO): Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the purchase price. This includes maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs associated with equipment failures.
Nuances de preços para compradores internacionais: Be mindful of currency fluctuations and local economic conditions that can affect pricing. Additionally, consider local regulations and tariffs that may impact the overall cost.
Research Local Suppliers: Particularly in regions like Africa and South America, local suppliers may offer competitive pricing and reduced logistics costs. Conducting thorough market research can uncover valuable sourcing opportunities.
Quality vs. Cost: While it may be tempting to choose the cheapest option, consider the long-term implications of quality. Investing in reliable, high-quality tire inflation solutions can lead to cost savings over time through reduced maintenance and improved efficiency.
The prices and cost structures outlined in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their own research and consult with suppliers for accurate pricing and terms tailored to their needs.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
When it comes to maintaining optimal tire pressure, several methods exist beyond the traditional approach of inflating a car tire at a service station. These alternatives can offer unique advantages depending on the specific needs of businesses operating in diverse environments. Below, we will compare the conventional tire inflation method with two viable alternatives: using a portable tire inflator and nitrogen tire inflation.
| Aspecto de comparação | How To Inflate A Car Tire | Inflador de pneus portátil | Nitrogen Tire Inflation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desempenho | Reliable for regular use; pressure can be easily adjusted. | Effective for quick inflation; often portable and user-friendly. | Reduces air loss over time; maintains pressure better than air. |
| Custo | Typically free or low-cost at gas stations. | Initial purchase cost; generally affordable ($20-$100). | Higher service cost; may require specialized facilities. |
| Facilidade de implementação | Requires access to a service station; can be inconvenient. | Very convenient; can be used anywhere with power source. | Limited to specialized shops; less accessible in remote areas. |
| Manutenção | Minimal; requires periodic checks of pressure. | Requires occasional battery or power source maintenance. | Minimal; but requires periodic checks for leaks. |
| Melhor caso de uso | Ideal for regular vehicle maintenance and long trips. | Perfect for emergency situations or remote locations. | Beneficial for fleet vehicles or high-performance applications. |
Inflador de pneus portátil
A portable tire inflator is an invaluable tool for businesses that require immediate tire inflation solutions. These devices are compact, easy to store, and can often be plugged into a vehicle’s power outlet. The convenience of having a portable inflator means that companies can quickly address tire pressure issues on-site, reducing downtime. However, they do require an upfront investment and may vary in quality. Additionally, they are dependent on power sources, which could be a limitation in some scenarios.
Nitrogen Tire Inflation
Using nitrogen to inflate tires has gained popularity due to its ability to maintain tire pressure over longer periods. Nitrogen molecules are larger than those in regular air, which reduces the rate of air loss. This method can lead to improved fuel efficiency, longer tire life, and enhanced handling, making it particularly advantageous for businesses with fleet vehicles. On the downside, nitrogen inflation typically incurs higher costs and requires access to specialized facilities, which might not be practical for all businesses, especially those in remote areas.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
When selecting a tire inflation method, B2B buyers should consider factors such as operational needs, budget constraints, and accessibility to services. For businesses that require immediate, on-the-go solutions, a portable tire inflator is an excellent choice. Conversely, for companies that prioritize long-term tire health and performance, particularly those managing fleets, nitrogen inflation may be the best option. Ultimately, understanding the specific operational context will enable businesses to make informed decisions that enhance safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their vehicle maintenance strategies.
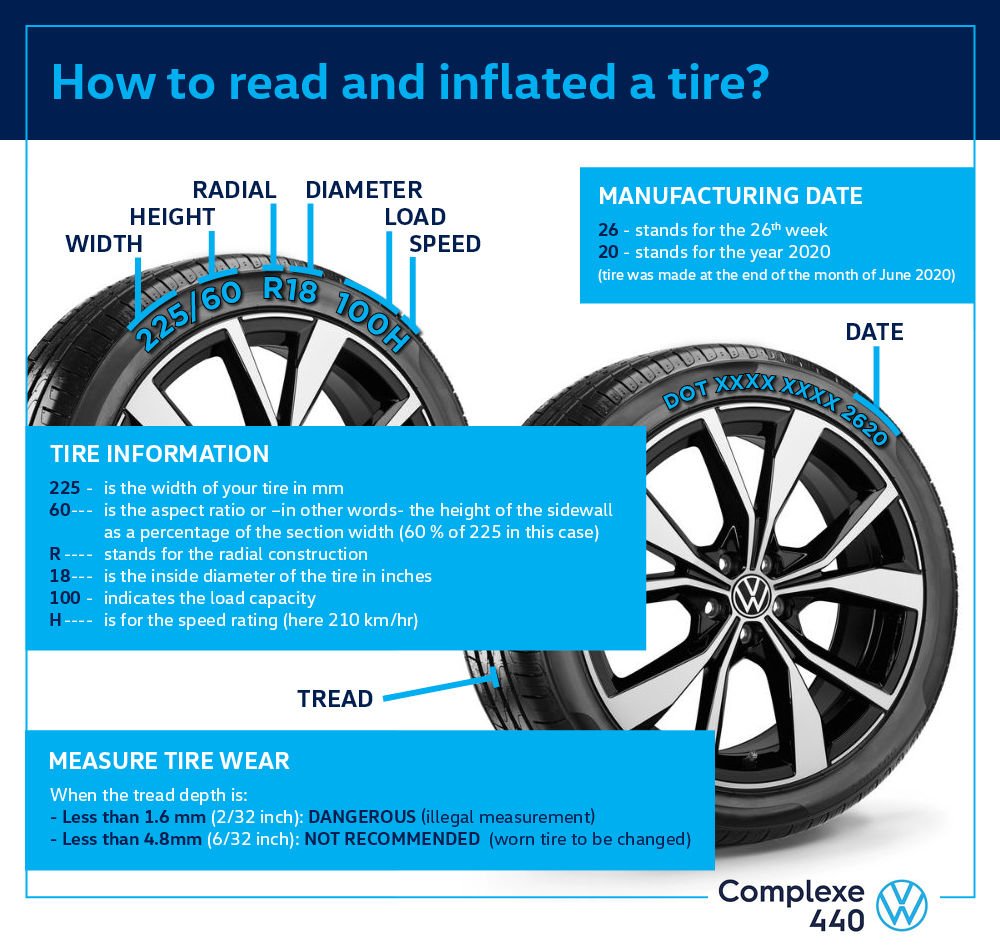
1. Tire Pressure (PSI):
Pounds per square inch (PSI) is the standard unit for measuring tire pressure. Maintaining the correct PSI is crucial for optimal tire performance, safety, and fuel efficiency. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased fuel consumption and reduced tire lifespan, while over-inflated tires may cause uneven wear and compromised handling. For B2B buyers, understanding and maintaining proper PSI can significantly impact operational costs and vehicle safety.
2. Tire Temperature:
Tire temperature affects pressure; tires heat up during operation, leading to increased PSI. Monitoring tire temperature is important for fleet operators, as excessive heat can indicate under-inflation or overloading. Regular checks can prevent blowouts and extend tire life, thus minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
3. Valve Type and Quality:
Tire valves are critical components that maintain pressure and prevent air leaks. The quality of the valve affects reliability; a defective valve can lead to rapid air loss. For B2B transactions, sourcing high-quality valves ensures durability and reduces the risk of tire-related issues, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
4. Tire Composition:
The material used in tire construction (e.g., rubber compounds, reinforcement layers) impacts performance characteristics such as grip, durability, and resistance to punctures. Understanding the properties of different tire materials helps buyers choose the right tires for specific applications, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
5. Tread Depth and Pattern:
Tread depth influences traction, handling, and water displacement. Legal regulations often mandate minimum tread depths, which vary by region. B2B buyers must consider these specifications to ensure compliance and safety in different markets, especially in regions with diverse weather conditions.
6. Load Index:
The load index indicates the maximum weight a tire can safely carry. This specification is vital for fleet managers to match tires with vehicle capacities, ensuring safety and efficiency. Misjudging the load index can lead to tire failure, risking both safety and financial implications for businesses.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in the manufacturing of vehicles. For tire suppliers, understanding OEM specifications ensures that the tires they provide meet the original performance standards required by vehicle manufacturers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In tire distribution, knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and optimize purchasing strategies, especially for large fleets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation):
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For tire procurement, submitting an RFQ allows businesses to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and suitable terms.
4. Incoterms:
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions involving tire imports and exports, as they clarify who bears the risk and cost of transportation, insurance, and duties.
5. TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System):
TPMS is a technology that monitors tire pressure in real-time and alerts drivers to under-inflation. For businesses operating fleets, TPMS can enhance safety and efficiency by reducing the chances of tire blowouts and improving fuel economy.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
6. Tire Rotation:
Tire rotation refers to the practice of changing the position of tires on a vehicle to promote even wear. For fleet managers, implementing a tire rotation schedule can extend tire life and reduce replacement costs, making it a critical aspect of tire maintenance strategy.
By comprehending these technical properties and terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their tire management processes, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
The global tire inflation market is experiencing significant transformations driven by various factors including technological advancements, rising safety concerns, and environmental sustainability. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for efficient tire management solutions is on the rise due to increasing vehicle ownership and the subsequent need for maintenance. B2B buyers in these markets are particularly focused on solutions that enhance safety and reduce operational costs.
Emerging technologies such as smart tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are gaining traction, offering real-time data on tire conditions. These systems not only alert drivers to under-inflation but also contribute to overall vehicle performance by optimizing fuel efficiency and extending tire lifespan. Additionally, the availability of portable tire inflation compressors is becoming more common, catering to the growing preference for convenience among consumers and businesses alike.
Market dynamics indicate a shift towards integrated solutions, where tire manufacturers and service providers collaborate to offer comprehensive tire management services. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to streamline operations and ensure compliance with safety regulations. By investing in innovative tire inflation technologies, B2B buyers can enhance their service offerings and gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
The environmental impact of tire inflation practices is becoming a focal point for B2B buyers, particularly in light of increasing regulations and consumer demand for sustainable practices. Proper tire inflation not only reduces fuel consumption and CO2 emissions but also extends the life of tires, thereby minimizing waste. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers that prioritize sustainable manufacturing processes and materials, which contribute to a more ethical supply chain.
Adopting ‘green’ certifications and materials in tire production is crucial. Suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials or processes, such as those reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs), are increasingly preferred. Additionally, implementing effective recycling programs for used tires can further enhance a company’s sustainability profile. By prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainability, businesses can not only meet regulatory standards but also attract environmentally conscious consumers, thereby enhancing their brand reputation and market share.
The evolution of tire inflation technology has been marked by significant milestones that have improved safety and efficiency. Initially, tire inflation was a manual process reliant on basic tools and gauges. The introduction of air compressors and inflation stations in the mid-20th century revolutionized this practice, making it more accessible to consumers.
In recent years, advancements in technology have ushered in smart tire inflation systems that integrate digital monitoring and automated inflation capabilities. These innovations not only enhance user experience but also align with the growing demand for safety and efficiency in vehicle maintenance. As a result, the tire inflation sector is transitioning towards more sophisticated solutions that cater to the needs of modern drivers and businesses alike, ensuring optimal performance and safety on the roads.
How do I ensure proper tire inflation for safety and efficiency?
To ensure proper tire inflation, first, locate the manufacturer’s recommended pressure, which can usually be found on a sticker inside the driver’s door or in the vehicle’s user manual. Regularly check tire pressure at least once a month and before long trips. Use a calibrated pressure gauge to measure the current PSI and adjust accordingly—adding air if below the recommended level or releasing air if overinflated. This practice enhances vehicle safety, improves fuel efficiency, and prolongs tire life.
What is the best equipment for inflating car tires?
The best equipment for inflating car tires includes a reliable portable air compressor and a quality tire pressure gauge. A portable air compressor allows for on-the-go inflation, especially useful in remote areas or during emergency situations. Ensure the compressor has an integrated pressure gauge for easy monitoring. For larger fleets, investing in commercial-grade tire inflation systems may be beneficial, offering faster and more efficient service.
How do I choose a reliable supplier for tire inflation equipment?
When selecting a supplier for tire inflation equipment, evaluate their reputation, customer reviews, and industry experience. Consider suppliers with established networks in your region and those who offer after-sales support, such as maintenance and repairs. Request samples or demonstrations of their products to assess quality and functionality. Additionally, inquire about certifications that guarantee compliance with international safety and quality standards.
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect for tire inflation products?
Minimum order quantities for tire inflation products can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of equipment. Typically, for commercial-grade equipment, MOQs can range from 10 to 50 units. For smaller, portable compressors, some suppliers may allow lower MOQs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your purchasing strategy.
What payment terms are common for international B2B tire equipment purchases?
Common payment terms for international B2B purchases of tire equipment include letters of credit, advance payments, and net payment terms (30, 60, or 90 days). The choice of payment terms often depends on the buyer’s relationship with the supplier and the order size. Establishing a secure payment method is crucial to mitigate risks associated with international transactions, especially in regions with fluctuating currencies.
How can I verify the quality of tire inflation equipment before purchase?
To verify the quality of tire inflation equipment, request certifications and compliance documentation from the supplier. Look for ISO certifications or other industry standards that validate the quality of their products. Additionally, consider asking for references from other customers who have purchased similar equipment. Testing samples before bulk ordering can also provide insights into the equipment’s durability and performance.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing tire inflation equipment?
When importing tire inflation equipment, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping fees and taxes, to ensure budget compliance. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in international shipping can streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. Additionally, keep in mind local regulations regarding equipment safety and compliance standards.
How do I manage after-sales service and support for tire inflation equipment?
Managing after-sales service and support for tire inflation equipment involves establishing clear communication channels with your supplier. Ensure they offer warranties and a service level agreement (SLA) outlining response times for support requests. Regular maintenance and training on equipment use can enhance longevity and performance. Building a relationship with the supplier can facilitate better service and quicker access to replacement parts when needed.
Domínio: reddit.com
Registrado: 2005 (20 anos)
Introdução: This company, Reddit – Tire Pressure Compressor, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Domínio: michelinman.com
Registrado: 2001 (24 anos)
Introdução: Michelin offers a complete range of tires for various mobility needs, including passenger cars, SUVs, light commercial vehicles, and electric/hybrid vehicles. Their tire families include CrossClimate, Defender, Pilot Sport, Primacy, LTX, X Ice, Energy™, Latitude Sport, Pilot Alpin, and Premier. Michelin also provides tires for motorcycles and bicycles, with specific categories for different riding…
Domínio: wikihow.com
Registrado: 2004 (21 anos)
Introdução: 1. Tire Pressure Gauge: Available at auto parts stores and big-box retailers; types include pencil, dial, and digital gauges. 2. Recommended Tire Pressure: Typically ranges from 28 to 36 psi or 195 to 250 kPa; check owner’s manual or vehicle stickers for specifics. 3. Air Sources: Gas stations often have air compressors; portable tire inflators are also available. 4. Valve Cap: The screw-on cap on…
Domínio: acg.aaa.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introdução: AAA Auto Club Group provides services in Colorado, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, Nebraska, North Carolina, North Dakota, Puerto Rico, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Wisconsin. The guide emphasizes the importance of maintaining correct tire pressure for vehicle safety, fuel efficiency, and performance. It outlines the necessary tools for inflating tires, including …
In the realm of strategic sourcing for tire maintenance, understanding the nuances of tire inflation is paramount. Ensuring that tires are inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended pressure not only enhances vehicle performance but also reduces operational costs associated with fuel consumption and tire replacement. International buyers should prioritize sourcing quality tire inflation equipment and services, as these can significantly impact both safety and efficiency on the road.

Illustrative image related to how to inflate a car tire
Moreover, with the increasing emphasis on sustainability, maintaining proper tire pressure can help reduce carbon emissions, aligning with global environmental goals. This aspect is particularly relevant for businesses operating in regions such as Africa and South America, where environmental considerations are becoming increasingly crucial.
As you look to enhance your fleet operations, consider investing in portable tire inflation compressors and regular tire pressure monitoring systems. These solutions will not only streamline maintenance processes but also foster a culture of safety and responsibility within your organization.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality tire maintenance solutions is set to grow. Engage with reliable suppliers and stay informed about the latest innovations in tire technology to ensure that your operations remain competitive and environmentally conscious.
As informações fornecidas neste guia, inclusive o conteúdo referente a fabricantes, especificações técnicas e análise de mercado, são apenas para fins informativos e educacionais. Elas não constituem aconselhamento profissional sobre compras, aconselhamento financeiro ou aconselhamento jurídico.
Embora tenhamos feito todos os esforços para garantir a precisão e a atualidade das informações, não nos responsabilizamos por quaisquer erros, omissões ou informações desatualizadas. As condições de mercado, os detalhes da empresa e os padrões técnicos estão sujeitos a alterações.
Os compradores B2B devem realizar sua própria due diligence independente e completa antes de tomar qualquer decisão de compra. Isso inclui entrar em contato diretamente com os fornecedores, verificar as certificações, solicitar amostras e buscar consultoria profissional. O risco de confiar em qualquer informação contida neste guia é de responsabilidade exclusiva do leitor.