In the competitive landscape of global commerce, understanding the nuances of tire under inflation can significantly impact vehicle performance and safety. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing reliable tire solutions that mitigate the risks associated with under inflation is crucial. Under-inflated tires not only compromise vehicle safety but also lead to increased operational costs due to reduced fuel efficiency and greater wear on vehicle components. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring various types of tires, their applications across different industries, and the critical importance of proper inflation.
By examining supplier vetting processes, cost implications, and maintenance strategies, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It addresses common challenges faced in diverse markets, from Brazil to Vietnam, ensuring that stakeholders can effectively navigate the complexities of tire selection and management. The insights presented here are designed to equip buyers with the knowledge needed to enhance fleet safety and performance, ultimately fostering a more efficient and cost-effective operation. Whether you are looking to optimize your existing fleet or expand your procurement strategy, understanding tire under inflation is an essential component of achieving success in today’s dynamic market.
| Название типа | Ключевые отличительные особенности | Основные приложения B2B | Краткие плюсы и минусы для покупателей |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Under Inflation | Slightly below recommended PSI; minimal symptoms | Delivery fleets, logistics | Плюсы: Lower risk of blowouts. Конс: Reduced fuel efficiency over time. |
| Moderate Under Inflation | Noticeable pressure drop; increased tire wear | Construction vehicles, agriculture | Плюсы: Cost-effective for short-term use. Конс: Increased risk of handling issues. |
| Severe Under Inflation | Significantly below recommended PSI; poor handling | Mining, heavy-duty transport | Плюсы: Immediate cost savings on fuel. Конс: High risk of tire blowouts and accidents. |
| Seasonal Under Inflation | Variations due to temperature changes | Seasonal agricultural operations | Плюсы: Adaptable to changing climates. Конс: Requires regular monitoring to avoid hazards. |
| Chronic Under Inflation | Recurring low pressure issues; persistent symptoms | Long-haul trucking, fleet management | Плюсы: May indicate a need for better maintenance practices. Конс: Long-term damage to tires and vehicle components. |
Mild under inflation occurs when tire pressure is slightly below the manufacturer’s recommended PSI. This variation may not present immediate symptoms but can lead to gradual increases in rolling resistance and reduced fuel efficiency. B2B buyers in logistics or delivery fleets should consider monitoring tire pressure regularly, as maintaining optimal inflation can enhance overall vehicle performance and reduce operational costs.
Moderate under inflation is characterized by a more noticeable drop in tire pressure, leading to uneven tread wear and decreased vehicle handling. This condition is particularly relevant for construction vehicles and agricultural machinery, where performance and safety are crucial. Buyers should weigh the short-term cost benefits against the potential for increased maintenance and replacement costs due to accelerated tire wear and handling issues.
Severe under inflation poses significant risks, particularly for heavy-duty transport and mining vehicles. Tires in this condition exhibit poor handling and a high likelihood of blowouts, jeopardizing safety and operational efficiency. B2B buyers in these sectors must prioritize regular tire inspections and maintenance practices to mitigate the risks associated with severe under inflation, which can lead to costly downtime and repairs.
Seasonal under inflation refers to variations in tire pressure due to temperature fluctuations, a common issue in agricultural operations. This type of under inflation can affect tire performance during critical planting and harvesting periods. B2B buyers should ensure that tire pressure is adjusted according to seasonal changes to maintain optimal performance and safety throughout the year.
Chronic under inflation is characterized by recurring low pressure issues, often indicative of underlying maintenance problems. This condition can lead to significant long-term damage to tires and vehicle components, especially for long-haul trucking and fleet management operations. B2B buyers must implement rigorous tire maintenance protocols to prevent chronic under inflation, as it directly impacts vehicle safety, efficiency, and overall operational costs.
| Промышленность/сектор | Specific Application of Tire Under Inflation | Ценность/выгода для бизнеса | Ключевые соображения по поиску источников для данного приложения |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Управление автопарком | Enhanced safety and reduced operational costs | Supplier reliability, tire quality, and maintenance support |
| Сельское хозяйство | Agricultural Machinery | Improved efficiency and reduced fuel costs | Durability in rough terrains, local availability, and price |
| Строительство | Heavy Machinery | Lower risk of breakdowns and maintenance costs | Compliance with safety standards, tire performance ratings |
| Mining | Mining Equipment | Increased productivity and reduced downtime | Tire lifespan, resistance to punctures, and sourcing location |
| Automotive Services | Tire Retail and Service | Customer satisfaction and repeat business | Product variety, competitive pricing, and after-sales service |
In the transportation and logistics sector, tire under inflation is a critical concern for fleet management. Companies must regularly monitor tire pressure to prevent increased rolling resistance, which can lead to higher fuel consumption and safety risks. By ensuring proper tire inflation, businesses can enhance vehicle safety, improve handling, and reduce wear on suspension components. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer reliable tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and maintenance services tailored to their fleet’s operational needs.
In agriculture, tire under inflation affects the performance of machinery such as tractors and harvesters. Under-inflated tires can lead to uneven tread wear and increased fuel costs due to higher rolling resistance. By maintaining optimal tire pressure, agricultural businesses can enhance their equipment’s efficiency, prolong tire life, and reduce operational costs. Buyers in this sector should seek tires specifically designed for agricultural use, emphasizing durability on varied terrains and local sourcing options to minimize transportation costs.
In the construction industry, tire under inflation poses risks for heavy machinery, potentially leading to increased maintenance costs and operational delays. Properly inflated tires improve stability and handling, which is crucial for safety on job sites. Construction companies must ensure their tire suppliers comply with safety standards and provide tires that can withstand rough conditions. Buyers should evaluate tire performance ratings and consider suppliers who can offer comprehensive support, including installation and maintenance services.
Mining operations rely heavily on the performance of specialized equipment, making tire under inflation a significant concern. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased wear and the risk of blowouts, resulting in costly downtime. Maintaining optimal tire pressure enhances productivity and safety in challenging environments. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing tires with high puncture resistance and long lifespan capabilities, ensuring that suppliers can deliver products suited for the harsh mining conditions prevalent in various regions, including Africa and South America.
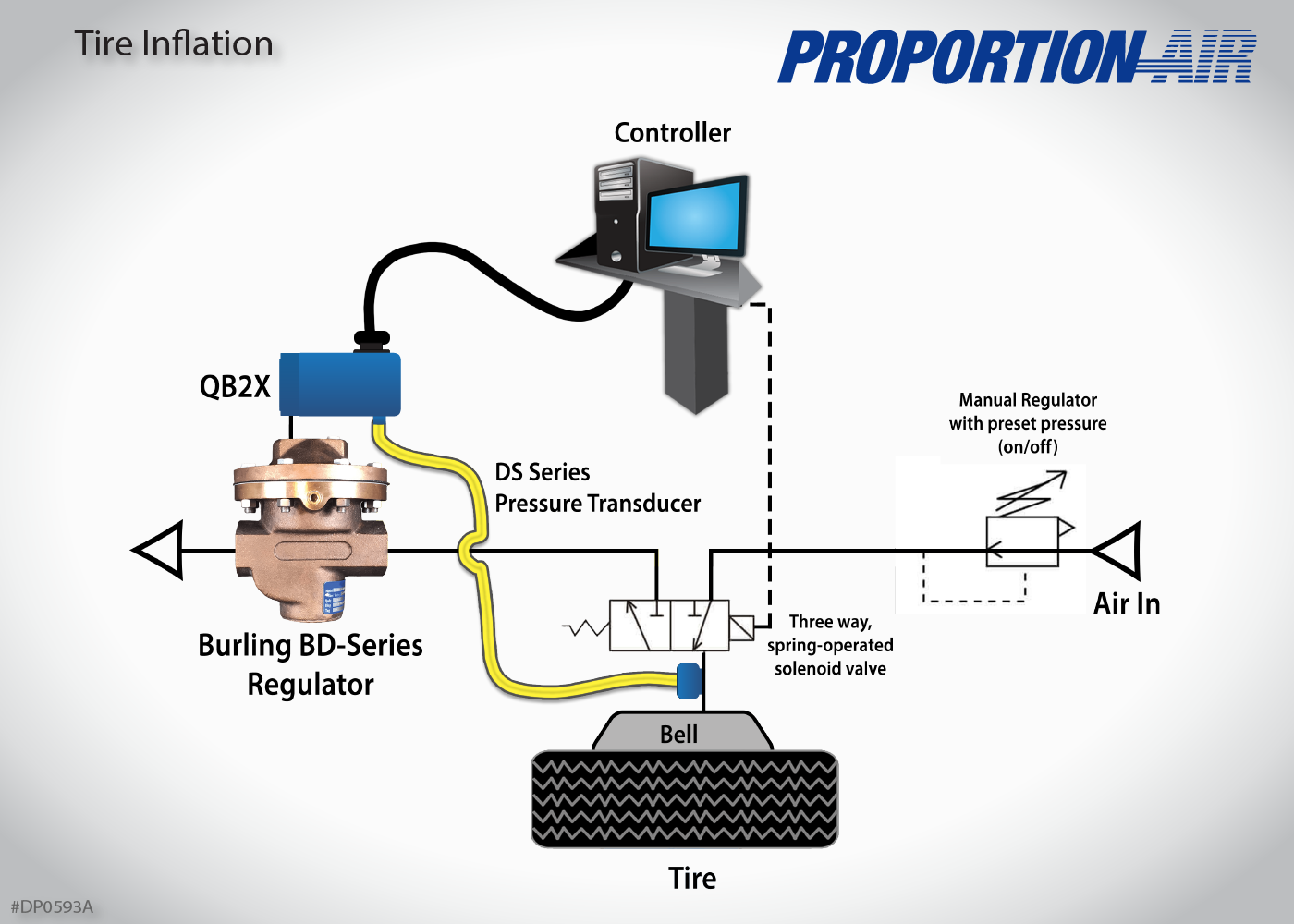
Illustrative image related to tire under inflation
For automotive service providers, understanding the implications of tire under inflation is vital for customer satisfaction. Offering services that address tire pressure issues can enhance vehicle safety and fuel efficiency for clients. Service centers should invest in training and equipment to effectively diagnose and remedy tire inflation problems. B2B buyers in this sector should consider suppliers that provide a wide range of tire options and competitive pricing to cater to diverse customer needs, ensuring they can maintain a loyal customer base.
Проблема: Many B2B buyers, especially those managing fleets in logistics or transportation, face significant challenges with under-inflated tires leading to increased fuel costs. When tire pressure is low, rolling resistance rises, forcing vehicles to consume more fuel to maintain speed. This not only impacts the bottom line but can also lead to budget overruns, particularly for businesses operating in regions where fuel prices are volatile. Additionally, the added strain on the engine can lead to more frequent maintenance needs, further compounding operational expenses.
Решение: To combat this issue, businesses should implement a proactive tire maintenance program that includes regular tire pressure checks. Using tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) can provide real-time data on tire inflation levels, allowing fleet managers to address any under-inflation before it becomes a larger issue. Furthermore, establishing a routine schedule for tire inspections—ideally every two weeks—can ensure that tires remain within the optimal pressure range. For fleets operating in regions with extreme temperatures, consider investing in tires designed to maintain pressure stability under varying conditions. By prioritizing tire maintenance, companies can significantly reduce fuel costs and improve overall fleet efficiency.
Проблема: For B2B buyers responsible for employee transportation or delivery services, under-inflated tires pose serious safety risks. Reduced tire pressure can lead to decreased vehicle control, longer stopping distances, and an increased likelihood of tire blowouts. These safety hazards not only jeopardize the well-being of employees and goods but can also lead to costly legal liabilities if an accident occurs. The ramifications of such incidents can severely impact a company’s reputation and financial stability.

Illustrative image related to tire under inflation
Решение: To mitigate these risks, it is essential to establish a comprehensive safety training program that emphasizes the importance of tire maintenance. This training should include instruction on recognizing signs of under-inflation and understanding the critical role tire pressure plays in vehicle safety. Additionally, businesses should consider integrating advanced telematics systems that monitor tire pressure and vehicle performance, alerting drivers and managers to issues before they escalate. Investing in high-quality tires with built-in safety features, such as reinforced sidewalls, can also enhance durability and reduce the likelihood of blowouts. By fostering a culture of safety and investing in technology, companies can protect their employees and mitigate liability risks associated with under-inflated tires.
Проблема: B2B buyers managing vehicle fleets often encounter unexpected repair costs due to the damage caused by under-inflated tires. When tires are not properly inflated, they can wear unevenly, leading to premature tire replacements and potential damage to suspension components. This not only disrupts operational efficiency but also results in financial strain from unplanned repair expenses and lost productivity during vehicle downtime.
Решение: To address this challenge, businesses should conduct regular tire audits and implement a tire rotation schedule that aligns with the manufacturer’s recommendations. This practice can help to evenly distribute tire wear, extending the lifespan of the tires and reducing replacement costs. Additionally, companies should consider training their maintenance staff on the importance of proper tire inflation and the long-term benefits of preventive maintenance. Utilizing tire management software can streamline this process, providing insights into tire health and helping to forecast replacement needs. By taking a proactive approach to tire maintenance and repair, businesses can minimize costs and enhance the longevity of their fleet assets.
When selecting materials for tire under inflation applications, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and disadvantages. This analysis focuses on four common materials: rubber, steel, nylon, and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). Each material has unique characteristics that can influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Rubber is the primary material used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent elasticity and grip. It has a high temperature and pressure rating, making it suitable for various environmental conditions. Rubber’s inherent flexibility allows it to absorb shocks and maintain contact with the road surface, which is critical for tire performance.
Плюсы: Rubber provides durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-term use. It is also relatively cost-effective, which is advantageous for large-scale manufacturing.
Cons: However, rubber can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and ozone, leading to cracking and loss of performance. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specific formulations to achieve desired properties.
Влияние на применение: Rubber is compatible with various media, including air and moisture, but may require additives to enhance its resistance to environmental factors.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and JIS. Understanding the local climate’s impact on rubber durability is also vital.
Steel is often used in tire belts and beads, providing structural integrity and strength. It has a high tensile strength and excellent resistance to deformation under pressure, making it suitable for high-load applications.
Плюсы: The primary advantage of steel is its durability and ability to withstand significant stress without failure. This enhances the tire’s overall performance and safety.
Cons: On the downside, steel can be susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid environments. Its weight can also contribute to increased rolling resistance, which may affect fuel efficiency.
Влияние на применение: Steel’s compatibility with air and moisture is generally good, but it requires protective coatings to prevent rusting, particularly in regions with high humidity.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers should consider local corrosion standards and ensure that the steel components meet specific requirements for durability in their geographic area.
Nylon is commonly used in tire carcasses due to its high tensile strength and flexibility. It offers excellent resistance to punctures and tears, making it a popular choice for high-performance tires.
Плюсы: Nylon’s lightweight nature contributes to better fuel efficiency and handling. It also provides good thermal stability, which is essential for maintaining tire performance under varying conditions.
Cons: However, nylon can be more expensive than rubber and may require additional treatments to enhance its resistance to environmental degradation.
Влияние на применение: Nylon is compatible with air and moisture, but its performance can be affected by extreme temperatures.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers should verify that nylon materials comply with local manufacturing standards and consider the cost implications of using nylon in tire production.
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine the properties of rubber and plastic, offering flexibility and durability. TPEs have good temperature and pressure ratings, making them suitable for tire applications.
Плюсы: The main advantage of TPEs is their ease of processing, which can reduce manufacturing complexity and costs. They also provide excellent resistance to weathering and UV exposure.
Cons: However, TPEs may not offer the same level of durability as traditional rubber, especially under high-stress conditions.
Влияние на применение: TPEs are compatible with air and moisture and can be formulated to enhance specific performance characteristics.
Соображения для международных покупателей: Buyers should assess TPEs based on local standards and preferences, particularly in regions where traditional materials may be favored.
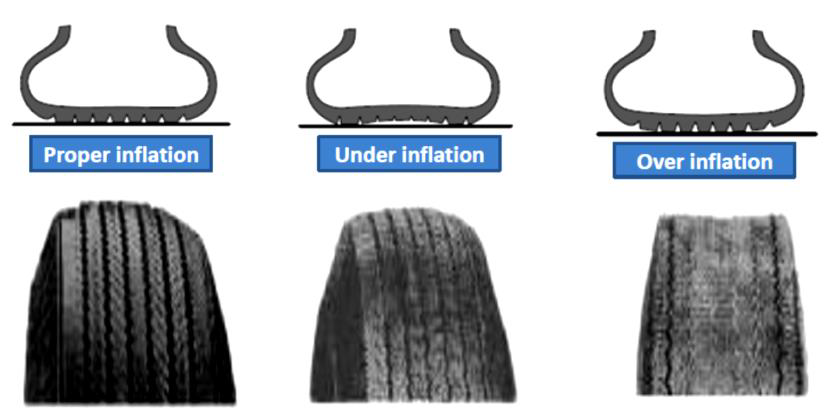
Illustrative image related to tire under inflation
| Материал | Typical Use Case for tire under inflation | Ключевое преимущество | Основные недостатки/ограничения | Относительная стоимость (низкая/средняя/высокая) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Резина | Tire tread and sidewalls | Excellent elasticity and grip | Degrades over time due to environmental factors | Низкий |
| Сталь | Tire belts and beads | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Средний |
| Нейлон | Tire carcasses | Puncture resistance | More expensive than rubber | Высокий |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Flexible components in tires | Easy processing and weather resistance | May lack durability under high stress | Средний |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of the materials relevant to tire under inflation, facilitating informed decision-making tailored to their regional needs and standards.
Manufacturing tires that effectively resist under inflation begins with a series of meticulously planned stages. These stages ensure that the final product meets safety, performance, and durability standards.
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials, which include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, carbon black, and various chemical additives. The quality of these materials is crucial as they directly influence the tire’s performance and resistance to wear. Manufacturers often establish strict criteria for material selection, including elasticity, durability, and heat resistance.
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming the tire structure. This involves mixing the rubber compounds in large blenders to ensure uniformity. After mixing, the rubber is shaped into different components such as the tread, sidewalls, and inner linings using specialized machinery.
Key techniques used in this stage include:
– Extrusion: This is used to create the tire’s tread and sidewalls, where rubber is forced through a mold to achieve the desired shape.
– Calendering: A process that forms rubber sheets which can be layered to create the tire’s inner components.
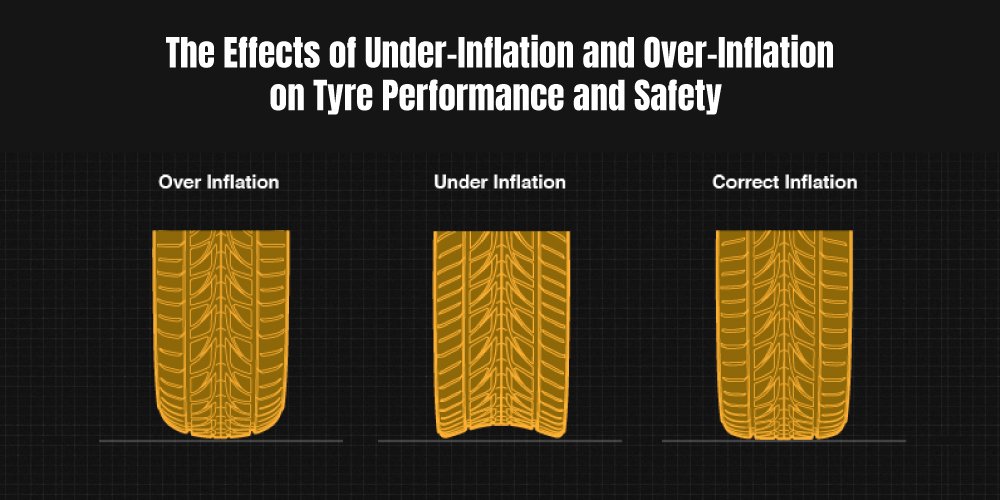
Illustrative image related to tire under inflation
The assembly stage brings together the various components created in the previous steps. The tire’s inner liner, which helps maintain air pressure, is placed inside the structure. Layers of fabric and steel belts are added for strength and stability. This stage is critical for ensuring that the tire can withstand the stresses of under inflation without compromising safety.
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing, which includes curing and quality inspections. The tires are placed in molds and heated to cure the rubber, allowing it to achieve its final shape and properties. This process also involves applying the tread pattern, which is essential for traction and performance.
Quality control (QC) is vital in tire manufacturing, particularly concerning under inflation risks. Manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems.
In addition to ISO 9001, there are industry-specific certifications like CE (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) that ensure compliance with safety and performance standards. These certifications are especially important for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory requirements may vary.
Quality checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. These include:
Common testing methods employed in tire manufacturing include:
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers meet quality standards. This can be achieved through:
B2B buyers from diverse regions, such as Brazil and Vietnam, need to be aware of the local regulatory landscape concerning tire manufacturing. Different countries may have specific requirements for tire safety and performance, which can influence the certification process.
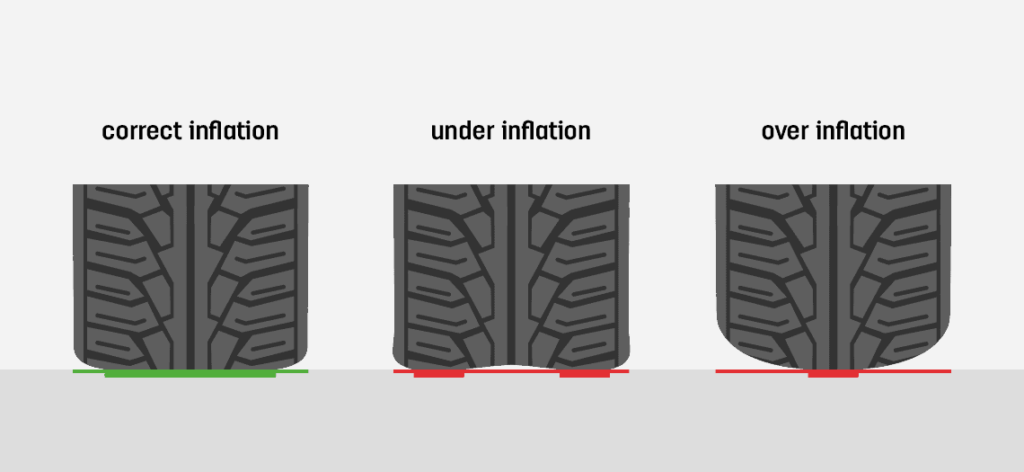
Illustrative image related to tire under inflation
It is essential for buyers to engage with suppliers who have a comprehensive understanding of both local and international standards. This ensures that products not only comply with international certifications but are also suitable for the specific market conditions in which they will be used.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in tire production is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier quality control, adhering to international standards, and utilizing proper testing methods, buyers can significantly mitigate the risks associated with tire under inflation. This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also contributes to the overall efficiency and longevity of their fleet operations.
This guide provides a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to address tire under-inflation issues effectively. Ensuring proper tire inflation is crucial not only for vehicle safety and performance but also for reducing operational costs associated with fuel consumption and maintenance. By following these steps, you can source the right solutions and suppliers to mitigate risks related to under-inflated tires.
Begin by evaluating your existing tire management protocols. Identify if there are regular checks for tire pressure, maintenance schedules, and training for staff on recognizing signs of under-inflation. This assessment will help you understand gaps in your current practices and inform your sourcing decisions.
Clearly outline the specifications you require for tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and related equipment. Consider the types of vehicles in your fleet and the specific environments they operate in. This step is crucial to ensure that the solutions you procure are compatible and effective for your operational needs.
Research and create a list of suppliers specializing in tire management solutions, including TPMS and tire inflation systems. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation in the industry and those who understand the unique challenges faced by businesses in your region. Consider reaching out to industry peers for recommendations to ensure you find reliable partners.
Ensure that your shortlisted suppliers hold relevant certifications and adhere to industry standards. Certifications can include ISO standards, safety compliance, and environmental regulations. This verification not only assures product quality but also reflects the supplier’s commitment to best practices.
Before finalizing your decision, request product demonstrations or trials from potential suppliers. This allows you to assess the functionality and ease of use of their systems. Pay attention to how the products integrate with your existing fleet management software, as seamless integration can enhance efficiency.
Evaluate the total cost of ownership for the products being considered. Analyze initial investment costs alongside potential savings in fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance, and increased tire lifespan. This financial assessment is vital for justifying your procurement choices to stakeholders.
Once you select a supplier, negotiate a maintenance and support agreement that includes regular check-ups, training for your team, and emergency support. This step is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and reliability of the tire management systems you implement.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance safety, reduce costs, and improve overall fleet efficiency related to tire under-inflation management.
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing tires that address under inflation issues, several components come into play. The primary cost components include:
Материалы: The type of rubber, additives, and other materials used significantly impact pricing. Higher quality materials often lead to better durability and performance but also increase costs.
Труд: Labor costs can vary based on location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. In regions with higher labor costs, overall pricing will likely reflect this.
Производственные накладные расходы: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs.
Инструментальная оснастка: The initial setup for tire production can require significant investment in molds and machinery. These costs are typically amortized over the production volume, impacting the per-unit cost.
Контроль качества (QC): Ensuring that tires meet safety and performance standards incurs costs. Effective QC processes can reduce the likelihood of defects, which is crucial for maintaining reputation and compliance.
Логистика: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and volume. Effective logistics planning can help mitigate these expenses.
Маржа: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profit. This can vary based on market conditions and competition.
Several factors can influence the pricing of tires designed to combat under inflation:
Объем/MOQ (минимальное количество заказа): Larger orders often lead to discounted pricing. Buyers should consider their inventory needs to negotiate better rates.
Технические характеристики/настройка: Custom tires tailored for specific vehicle types or conditions may incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
Материалы: The choice of materials directly impacts price. High-performance tires may utilize advanced compounds, which can be more expensive but offer better performance and longevity.
Качество/сертификация: Tires that meet international safety and performance standards may command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate the importance of certifications in their market.
Факторы поставщика: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Well-established suppliers may charge more due to their proven quality and service.
Инкотермс: The terms of shipping and delivery can also influence costs. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers manage logistics expenses effectively.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
Обсудите условия: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a strong relationship can lead to favorable terms.
Оцените общую стоимость владения (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs, but also long-term implications such as maintenance, fuel efficiency, and lifespan. Investing in higher-quality tires may reduce overall costs over time.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional market variations that may affect pricing. For instance, tariffs, taxes, and local regulations can lead to price fluctuations.
Использование технологий: Utilize data analytics to assess tire performance and optimize purchasing decisions. This can help in identifying the best value options in the market.
Plan for Long-Term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more consistent quality.
It is important to note that the pricing discussed in this analysis is indicative and can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to ensure competitive pricing and quality in tire sourcing.
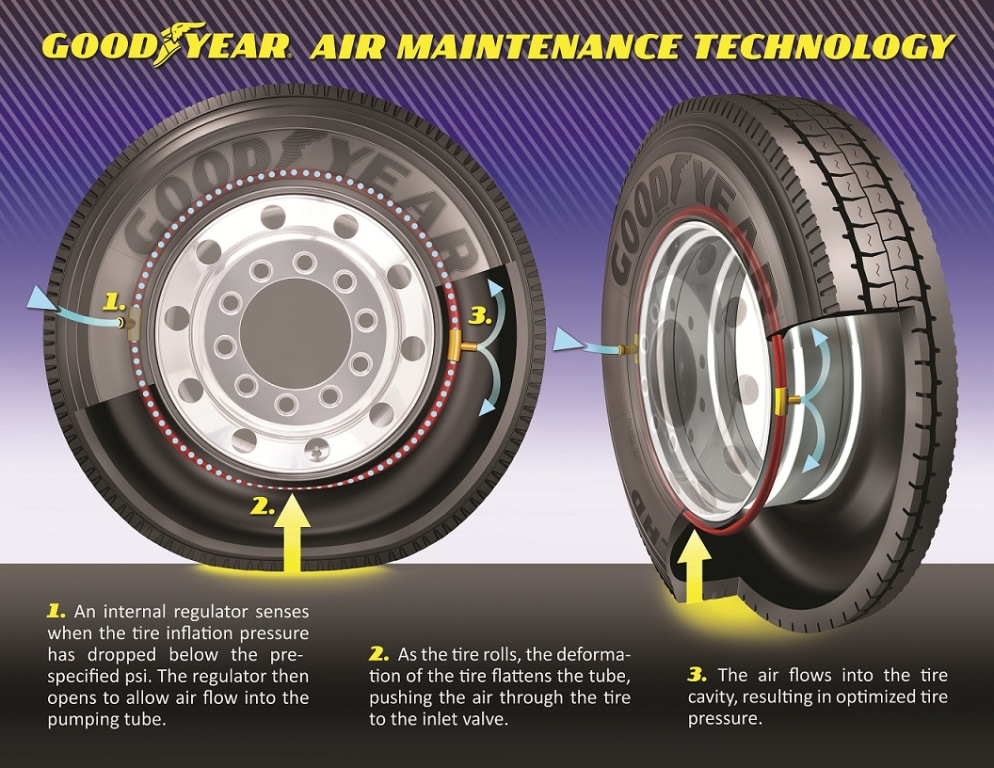
In the realm of tire management, the issue of tire under inflation is critical. However, various alternatives exist to address the challenges associated with maintaining optimal tire pressure. This section compares tire under inflation with two viable alternatives: Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) и Automatic Tire Inflation Systems (ATIS). Understanding these options can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
| Сравнительный аспект | Tire Under Inflation | Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) | Automatic Tire Inflation Systems (ATIS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Производительность | Decreased traction, increased wear, and risk of blowouts | Continuous monitoring, alerts for low pressure | Maintains optimal pressure automatically |
| Стоимость | Potentially high due to repairs and replacements | Moderate upfront cost; savings on fuel and tire wear | Higher initial investment; long-term savings on maintenance |
| Простота реализации | Minimal effort; relies on manual checks | Requires installation; user training needed | Complex installation; ongoing maintenance required |
| Техническое обслуживание | Regular manual checks needed | Low maintenance; battery changes may be needed | Requires periodic system checks and maintenance |
| Лучший пример использования | Typical passenger vehicles; occasional checks | Fleets and commercial vehicles for efficiency | Heavy-duty and commercial vehicles needing constant pressure control |
TPMS offers a technology-driven approach to tire management by providing real-time monitoring of tire pressure. This system alerts drivers when pressure drops below a certain threshold, thereby preventing the risks associated with under inflation. The key advantage of TPMS is its ability to enhance safety and extend tire lifespan through proactive alerts. However, while TPMS can reduce the frequency of under inflation, it does require an initial investment for installation and may involve some training for effective utilization.
ATIS takes tire management a step further by automatically maintaining optimal tire pressure while the vehicle is in operation. This system uses a network of sensors and compressors to adjust tire pressure in real-time, ensuring that tires remain inflated according to manufacturer specifications. The primary benefits include enhanced safety, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced tire wear. However, the complexity and cost of installation can be significant, making ATIS best suited for heavy-duty and commercial vehicles where the return on investment is more pronounced.
When selecting the appropriate solution to address tire under inflation, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the nature of their fleet. For businesses managing light-duty vehicles, implementing a TPMS may suffice to mitigate the risks of under inflation, providing a balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. Conversely, companies operating heavy-duty fleets may find that investing in an ATIS yields significant long-term savings through improved efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
Ultimately, understanding the comparative advantages and limitations of tire under inflation, TPMS, and ATIS will guide businesses toward the best tire management strategy, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Understanding the essential technical properties of tires, especially concerning under inflation, is crucial for B2B buyers who prioritize safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some critical specifications:
Tire Pressure Rating (PSI)
The tire pressure rating, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the optimal inflation level for a tire. Maintaining this pressure is essential for ensuring the tire’s performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. Under inflated tires can lead to increased rolling resistance, reduced fuel economy, and higher risks of blowouts. For B2B buyers, adhering to recommended PSI levels can translate into significant cost savings and improved vehicle longevity.
Load Index
The load index represents the maximum weight a tire can safely support when properly inflated. Each tire has a designated load index that correlates with its size and type. Understanding this index is vital for businesses that rely on transportation, as under inflated tires can easily exceed their load capacity, leading to catastrophic failures and increased operational costs.
Tread Depth
Tread depth is a crucial factor in tire performance, affecting traction, handling, and safety. A minimum tread depth ensures adequate water displacement to prevent hydroplaning. For B2B buyers, monitoring tread depth can help in planning tire replacements and maintaining fleet safety, thereby reducing liability and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Temperature Resistance
Tires are engineered to withstand specific temperature ranges. Under inflation can cause tires to overheat, increasing the risk of blowouts and reducing the lifespan of the tire. For businesses operating in extreme climates, understanding the temperature resistance of tires can inform better purchasing decisions and reduce the likelihood of costly downtime due to tire failures.
Состав материала
The materials used in tire construction, such as rubber compounds and reinforcing fibers, impact performance, durability, and resistance to wear. High-quality materials can provide better performance under various conditions, reducing the frequency of replacements. B2B buyers should consider tires with superior material properties to enhance their operational efficiency and safety.
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some common trade terms relevant to tire under inflation:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the tire industry, OEM tires are those that are specifically designed to meet the performance specifications of vehicle manufacturers. B2B buyers should consider OEM tires for reliability and compatibility with their fleet vehicles.
MOQ (минимальное количество заказа)
MOQ defines the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for bulk tire purchases, as it affects pricing and inventory management. Understanding MOQ can help businesses optimize their purchasing strategies and avoid overstocking or stockouts.
RFQ (запрос котировок)
An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of tire purchases, an RFQ can help businesses compare pricing, quality, and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they secure the best deal possible.
Инкотермс (международные коммерческие термины)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify how costs, risks, and responsibilities are divided during shipping. For B2B buyers in different regions, understanding Incoterms is essential for managing logistics and ensuring that all parties meet their obligations.
TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System)
This electronic system monitors tire pressure in real-time and alerts drivers when pressure drops below a certain threshold. TPMS is crucial for preventing issues associated with under inflation, as it helps maintain optimal tire performance. Businesses should consider vehicles equipped with TPMS for enhanced safety and efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance safety, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency in their tire management strategies.
The tire under inflation sector is influenced by several global drivers, including the increasing focus on vehicle safety and performance, rising fuel prices, and the growing emphasis on sustainability. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for tires that maintain optimal inflation levels is driven by the need to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce vehicle maintenance costs. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that offer innovative tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and smart tires equipped with sensors that provide real-time data on tire performance.
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and IoT, are becoming integral in the tire industry. These technologies enable predictive maintenance and proactive monitoring, allowing businesses to reduce operational costs and enhance safety. B2B buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who are adopting these technologies, as they can provide a competitive edge in reducing the risks associated with under-inflated tires, such as blowouts and uneven wear.
Additionally, the market is witnessing a shift toward digital platforms for procurement, enabling easier access to a wider range of products and suppliers. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing regions, where buyers are leveraging online marketplaces to find cost-effective solutions and negotiate better terms.
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the tire industry as environmental concerns gain prominence. The production and disposal of tires contribute significantly to pollution and waste. Therefore, international buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who utilize sustainable materials, such as recycled rubber and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies that prioritize transparency and fair labor practices in their sourcing strategies are likely to resonate more with B2B buyers, especially in markets that value corporate social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for sustainable materials can serve as key differentiators for suppliers in the tire under inflation sector.
Moreover, the integration of green technologies in tire production—such as the use of bio-based materials—can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with tire manufacturing. B2B buyers should assess potential suppliers based on their commitment to sustainability and the certifications they hold, ensuring that their procurement choices align with their corporate values.
The tire under inflation sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, tire inflation was a manual process, with drivers relying on analog gauges to check tire pressure. However, the introduction of TPMS in the early 2000s marked a turning point, enabling automatic monitoring of tire pressure and enhancing safety.
As technology advanced, smart tires equipped with sensors emerged, providing real-time data on not just tire pressure but also temperature and tread depth. This evolution has transformed the approach to tire maintenance, shifting from reactive to proactive strategies. Today, the focus is not only on maintaining tire pressure but also on utilizing data analytics to predict tire performance and lifespan, helping businesses optimize their fleet operations and reduce costs.
Illustrative image related to tire under inflation
In summary, understanding the market dynamics, embracing sustainability, and recognizing the evolution of tire technology are crucial for B2B buyers in the tire under inflation sector. By aligning with suppliers that prioritize innovation and ethical practices, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and contribute positively to the environment.
How do I solve tire under-inflation issues in my fleet?
To address tire under-inflation in your fleet, implement a regular tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS). This technology provides real-time data on tire pressures, enabling prompt action when levels drop. Schedule routine maintenance checks, ideally bi-weekly or monthly, to ensure tires are inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended pressure. Additionally, consider training your drivers to recognize signs of under-inflation, such as decreased fuel efficiency or unusual noises, and encourage them to perform pre-trip inspections.
What is the best tire maintenance strategy for preventing under-inflation?
The best strategy involves a combination of proactive monitoring and education. Invest in a reliable TPMS that alerts you to low tire pressure. Regularly scheduled maintenance should include checking tire pressure during routine vehicle servicing. Educating your drivers on the importance of tire maintenance, including recognizing signs of wear and tear, can also help prevent under-inflation. Implementing a tire rotation schedule can promote even wear, enhancing tire longevity and performance.
What factors should I consider when sourcing tires to avoid under-inflation?
When sourcing tires, consider quality, compatibility with your vehicles, and manufacturer specifications. Look for suppliers that provide detailed product information, including recommended pressure ranges. Assess the tire’s construction materials; high-quality tires often have better durability and resistance to punctures, which can contribute to maintaining proper inflation. Additionally, inquire about warranty and service options to ensure you receive ongoing support in case of performance issues.
How can I vet suppliers for tire quality and reliability?
To vet suppliers, review their certifications and industry reputation. Look for ISO certifications or compliance with international safety standards. Request samples or detailed product specifications to assess quality firsthand. Check customer reviews and testimonials from other businesses in your region. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can also help gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your concerns, which is crucial for long-term partnerships.
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for tires in international trade?
MOQs for tires can vary significantly based on the supplier, region, and type of tire. Typically, for commercial tires, MOQs may range from 50 to 200 units. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate acceptable MOQs that align with your inventory and budget strategies. Additionally, some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for first-time buyers or for larger contracts, so it’s worthwhile to explore these options.
What payment terms are commonly offered for tire purchases in international trade?
Payment terms for tire purchases can vary but typically include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or net terms (e.g., net 30, net 60). Many suppliers prefer letters of credit for large orders to mitigate risk. Always discuss payment terms upfront to ensure they align with your cash flow requirements. Additionally, consider the implications of exchange rates and transaction fees in international trade, as these can affect overall costs.
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my tire orders?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier before placing orders. Request product certifications and quality control processes to verify that tires meet international safety standards. Conduct periodic inspections of shipments upon arrival, checking for defects or inconsistencies. Building a relationship with suppliers that prioritize quality assurance can also help facilitate smoother resolutions should issues arise.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing tires?
When importing tires, consider the logistics of shipping routes, customs regulations, and tariffs that may apply. Engage a reliable freight forwarder familiar with tire logistics to navigate the complexities of international shipping. Additionally, factor in storage and handling requirements, as tires can be bulky and require specific conditions to prevent damage. Timely communication with suppliers and logistics partners is crucial to ensure smooth delivery and minimize delays.
Домен: hendrickatlanta.com
Зарегистрирован: 2007 (18 лет)
Введение: Rick Hendrick Chevrolet Duluth offers tire services including inspections, replacements, and rotations. They emphasize the dangers of driving on under inflated tires, which can lead to total tire failure, costly vehicle damage, difficulty handling, and increased fuel consumption. Symptoms of under inflated tires include TPMS alerts, poor fuel economy, unusual noises, decreased steering abilities, …
Домен: eastcoasttoyota.com
Зарегистрирован: 2000 (25 лет)
Введение: The article discusses the hidden dangers of overinflated and underinflated tires, emphasizing the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure for vehicle performance and safety. Key risks include uneven tread wear, reduced vehicle control, increased risk of blowouts, decreased fuel efficiency, adverse impact on the car’s suspension, compromised safety in wet conditions, and potential damage to …
Домен: rnrtires.com
Зарегистрирован: 2006 (19 лет)
Введение: RNR Tire Express offers a range of tire and car-care services, including tire inspections and replacements. They emphasize the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure to avoid dangers such as blowouts, compromised handling, extended braking distances, poor fuel efficiency, and uneven tire wear. Customers can visit their locations in Lubbock, TX, for expert assistance in ensuring their tires…
Домен: mylegalneeds.com
Зарегистрирован: 2000 (25 лет)
Введение: Signs of underinflated tires include poor handling, vibrations in the steering wheel, and sidewall cracks. Underinflated tires can lead to tire failure, blowouts, and rollovers. While vehicles have tire monitoring systems, they may not prevent all tire malfunctions. Drivers should be aware that underinflated tires can cause serious accidents, and negligence may be attributed to drivers with such t…
Домен: haralsontire.com
Зарегистрирован: 2006 (19 лет)
Введение: Haralson Tire Pros & Auto Service offers a large selection of tires from top quality brands including Continental, General, Michelin®, BFGoodrich®, Uniroyal®, Hercules, and Mastercraft. They provide tire care tips and emphasize the importance of proper tire inflation for fuel economy, handling, and preventing premature tire wear.
As the global market continues to evolve, the importance of addressing tire under inflation cannot be overstated. B2B buyers must recognize that strategic sourcing of high-quality tires and monitoring solutions is essential to mitigate the risks associated with under inflated tires, including safety hazards, increased operational costs, and compromised vehicle performance. Regular tire maintenance, including pressure checks and timely replacements, not only extends the lifespan of tires but also enhances fuel efficiency and vehicle handling.
Investing in advanced tire management systems can further empower businesses by providing real-time monitoring and alerts, allowing for proactive measures that reduce downtime and enhance safety. As companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe look to optimize their fleets, prioritizing tire health will yield significant long-term benefits.
Looking ahead, the integration of innovative technologies in tire sourcing and management will be pivotal in driving operational excellence. We encourage international B2B buyers to explore partnerships that emphasize quality, sustainability, and efficiency in tire procurement. By taking a proactive approach to tire under inflation, businesses can not only safeguard their assets but also position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Информация, представленная в данном руководстве, включая сведения о производителях, технические характеристики и анализ рынка, предназначена исключительно для информационных и образовательных целей. Она не является профессиональной консультацией по закупкам, финансовой или юридической консультацией.
Illustrative image related to tire under inflation
Несмотря на то, что мы приложили все усилия для обеспечения точности и своевременности информации, мы не несем ответственности за любые ошибки, упущения или устаревшую информацию. Условия рынка, сведения о компании и технические стандарты могут быть изменены.
Покупатели B2B должны проводить независимую и тщательную юридическую экспертизу перед принятием решения о покупке. Это включает в себя прямые контакты с поставщиками, проверку сертификатов, запрос образцов и обращение за профессиональной консультацией. Риск, связанный с использованием любой информации, содержащейся в данном руководстве, несет исключительно читатель.