In the fast-paced global market, understanding whether to inflate tires to maximum PSI is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize vehicle performance and safety. Misconceptions surrounding tire pressure can lead to costly mistakes, impacting both operational efficiency and safety standards. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of tire inflation, addressing key challenges faced by international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Saudi Arabia.
Throughout this guide, we will explore various tire types, their applications, and the implications of inflating to maximum pressure versus the manufacturer’s recommended levels. Additionally, we will provide insights on vetting suppliers, understanding cost structures, and the long-term benefits of proper tire maintenance. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable knowledge, this resource empowers informed purchasing decisions that prioritize safety, reduce costs, and enhance vehicle longevity.
Navigating the complexities of tire inflation is not just a technical issue; it’s a strategic business decision that can influence a company’s bottom line. With the right information at hand, businesses can avoid common pitfalls and ensure their fleets operate at peak performance, ultimately fostering a more sustainable and profitable operation.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended Tire Pressure | Manufacturer-specified optimal PSI for safety and performance | Fleet management, automotive servicing | Pros: Enhances safety, reduces fuel costs; Cons: Requires regular monitoring. |
| Maximum Tire Pressure | Upper limit of tire pressure indicated on tire sidewall | Heavy-duty transport, construction vehicles | Pros: Can handle heavy loads; Cons: Risk of blowouts and uneven wear. |
| Under-Inflation | Pressure below recommended levels | Cost-sensitive operations, older vehicle fleets | Pros: Lower initial costs; Cons: Increased tire wear, reduced safety. |
| Seasonal Adjustments | Adjusting pressure for temperature changes | Agricultural vehicles, logistics | Pros: Improved handling in varying conditions; Cons: Requires knowledge of optimal adjustments. |
| Temporary Pressure Increase | Briefly inflating above recommended levels for towing | Transportation of heavy goods | Pros: Enhanced load capacity; Cons: Increased risk of blowouts if prolonged. |
Recommended tire pressure is the optimal PSI specified by vehicle manufacturers, ensuring safety, performance, and fuel efficiency. For B2B buyers in fleet management or automotive servicing, adhering to these specifications is crucial. Regular monitoring helps prevent accidents and reduces operational costs related to fuel consumption and tire replacements. Companies must establish protocols for checking and adjusting tire pressure to maintain compliance and safety standards.
Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
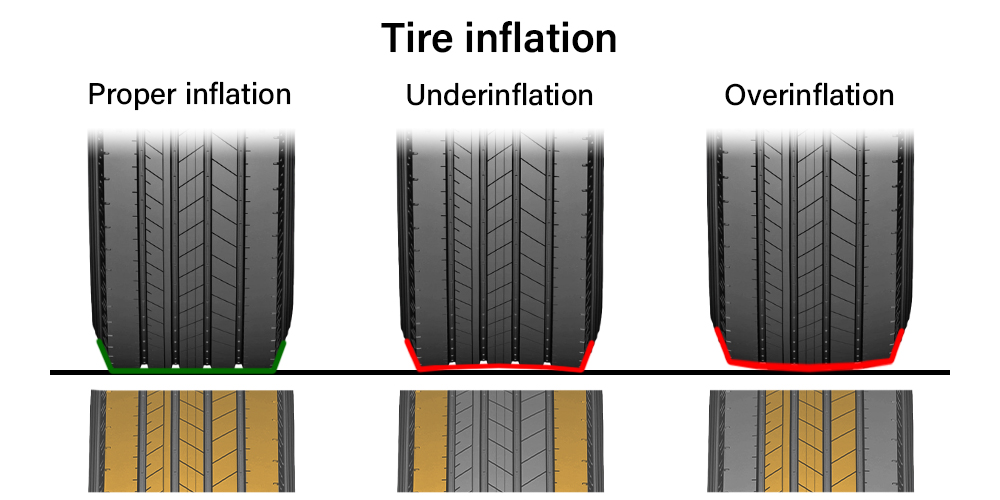
Maximum tire pressure refers to the highest PSI a tire can withstand, as indicated on the sidewall. This is particularly relevant for heavy-duty applications, such as construction vehicles and freight transport. While this pressure allows for carrying heavy loads, it poses risks such as blowouts and uneven tire wear, which can lead to costly downtime. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of load capacity against the potential safety hazards associated with over-inflation.
Under-inflation occurs when tire pressure falls below the recommended levels, often seen in cost-sensitive operations where maintenance is deprioritized. While it may reduce immediate costs, under-inflated tires lead to increased wear and tear, higher fuel consumption, and compromised safety. B2B buyers should prioritize regular tire pressure checks to mitigate these risks and ensure the longevity of their vehicle fleets.
Seasonal adjustments involve modifying tire pressure based on temperature fluctuations, which is vital for vehicles in agriculture and logistics. Properly inflated tires during different seasons enhance vehicle handling and safety. B2B buyers should implement training for their drivers to understand how temperature affects tire pressure, ensuring optimal performance and safety throughout the year.
Temporary pressure increases are sometimes necessary when towing heavy loads. While this can improve load capacity, it also raises the risk of blowouts if maintained for extended periods. B2B buyers should establish guidelines for when and how to implement temporary pressure increases, ensuring that safety is not compromised in pursuit of operational efficiency.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of should i inflate tires to max psi | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation and Logistics | Fleet vehicle maintenance and tire management | Enhanced safety, reduced operational costs, and extended tire life | Availability of tire pressure monitoring systems, local regulations on tire maintenance, and training for staff |
| Construction | Heavy machinery and equipment tire inflation | Improved equipment reliability, reduced downtime, and safety compliance | Access to rugged tires suitable for construction sites, inflation equipment, and maintenance training |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery tire inflation | Maximized efficiency in field operations and reduced fuel consumption | Compatibility of tires with specific machinery, availability of inflation equipment, and local agricultural practices |
| Mining | Tire pressure management for mining vehicles | Increased safety in hazardous environments and reduced tire wear | Heavy-duty tire specifications, local terrain considerations, and emergency response protocols |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Quality control in tire production | Consistent product quality and reduced warranty claims | Supplier reliability, compliance with international safety standards, and material sourcing for tire production |
In the transportation and logistics industry, maintaining optimal tire pressure is crucial for fleet management. Companies often utilize tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) to ensure that vehicles are not over-inflated or under-inflated. Proper inflation leads to enhanced safety, improved fuel efficiency, and a reduction in tire wear, which directly translates to lower operational costs. International buyers should consider local regulations regarding tire maintenance and ensure they have access to reliable TPMS technology.

Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
In construction, heavy machinery relies on correctly inflated tires to operate efficiently. Over-inflation can lead to reduced traction and increased risk of accidents, while under-inflation can cause excessive wear. By regularly monitoring and maintaining the recommended tire pressure, construction firms can reduce downtime and enhance safety compliance on job sites. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing rugged tires that can withstand harsh conditions and ensure their teams are trained in proper tire maintenance practices.
For agricultural machinery, proper tire inflation is essential for maximizing efficiency and minimizing fuel consumption during field operations. Under-inflated tires can lead to soil compaction, reducing crop yields, while over-inflation can cause uneven wear and potential blowouts. Agricultural businesses must ensure compatibility between tires and machinery, and they should have access to inflation equipment that can withstand outdoor conditions. Buyers should also consider local agricultural practices when sourcing tires and equipment.
In the mining industry, tire pressure management is vital for the safety of personnel and the longevity of mining vehicles. Properly inflated tires can handle the rough terrain, reducing the risk of blowouts and enhancing vehicle stability. This is particularly important in hazardous environments where safety is paramount. Buyers should focus on sourcing heavy-duty tires designed for extreme conditions and ensure they have protocols in place for regular tire pressure checks.
In automotive manufacturing, maintaining the correct tire pressure during production is critical for quality control. Inflated to the correct specifications, tires ensure consistent product quality and reduce the likelihood of warranty claims due to tire failure. Manufacturers must ensure that their suppliers comply with international safety standards and provide high-quality materials for tire production. Furthermore, establishing reliable sourcing channels for tire components can enhance operational efficiency and product reliability.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those managing fleets or vehicle maintenance, face confusion regarding the difference between maximum tire pressure (PSI) and the recommended tire pressure for specific vehicles. This misunderstanding can lead to over-inflation, which poses safety risks and can result in premature tire wear. In markets with varying climate conditions, such as Africa or the Middle East, the implications of this confusion can lead to even greater operational challenges, including increased fuel consumption and vehicle instability.
The Solution: To address this issue, it is essential to educate your team on the importance of adhering to the recommended tire pressure specified by the vehicle manufacturer. This information can typically be found in the owner’s manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. Implementing regular training sessions can ensure that all employees understand how to check and maintain the correct tire pressure. Additionally, investing in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) can provide real-time data, helping to alert your team when tire pressure deviates from the recommended range. By fostering a culture of safety and proactive maintenance, businesses can improve their fleet’s performance and reduce overall costs.
The Problem: A common challenge for B2B buyers is the tendency to inflate tires to the maximum PSI to enhance fuel efficiency and load capacity. However, this practice often backfires, leading to decreased handling, increased stopping distances, and a higher likelihood of tire blowouts. In regions like South America, where road conditions can be unpredictable, over-inflated tires can lead to accidents that not only jeopardize safety but also result in costly downtime and repairs for businesses.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with over-inflation, businesses should establish clear guidelines on tire pressure management. Begin by conducting an audit of all vehicles to ensure that tires are inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended levels. Implementing a routine tire inspection schedule can help maintain optimal tire health. Additionally, consider using tire inflators equipped with built-in pressure gauges that automatically shut off when the desired pressure is reached. This technology can help prevent human error and ensure that all team members consistently follow best practices, leading to safer operations and reduced maintenance costs.
The Problem: Another critical pain point for B2B buyers is the impact of temperature fluctuations on tire pressure. In regions like Europe, where seasonal temperature changes are significant, tires can lose or gain pressure based on weather conditions. This variability can lead to either under-inflation, which increases rolling resistance and fuel consumption, or over-inflation, which affects tire performance and safety.
The Solution: To counteract the effects of temperature changes, businesses should develop a seasonal tire pressure adjustment strategy. This can include regular pressure checks during significant temperature shifts, ensuring that tires are inflated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations for different conditions. Additionally, consider providing employees with portable tire pressure gauges for on-the-go checks. Educating staff about the importance of adjusting tire pressure with temperature changes will foster a proactive maintenance culture. Moreover, utilizing high-quality, temperature-resistant tires can help minimize fluctuations and enhance overall vehicle performance, ensuring that fleets operate efficiently regardless of environmental conditions.
When considering the appropriate materials for tire inflation systems, particularly regarding the question of whether to inflate tires to maximum PSI, several key materials come into play. Each material has distinct properties and implications for performance, safety, and cost, which are critical for B2B buyers in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties: Rubber is the primary material used in tire manufacturing due to its flexibility and ability to withstand varying pressures and temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of -40°C to 100°C and can handle pressures exceeding 40 PSI.
Pros & Cons: Rubber is durable and offers excellent traction and flexibility, making it suitable for various terrains. However, its susceptibility to degradation from UV exposure and ozone can limit its lifespan, especially in harsh climates. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as rubber requires specific formulations for different tire types.
Impact on Application: Rubber tires perform well under standard conditions but may not be ideal in extreme temperatures or environments with high chemical exposure.

Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with regional standards such as ASTM and ISO. In regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia, where climate conditions vary significantly, selecting the right rubber formulation is crucial for performance and safety.
Key Properties: Steel belts are often used in tire construction to enhance strength and durability. Steel can withstand high pressures and has excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and ability to maintain tire shape under high loads. However, steel can add weight to the tire, potentially affecting fuel efficiency. The manufacturing process is more complex and costly compared to rubber.
Impact on Application: Steel-reinforced tires are ideal for commercial vehicles that carry heavy loads, but they may not perform as well in lighter applications due to increased weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards for steel quality is essential, especially in regions with rigorous safety regulations. Buyers in Europe, for instance, may prioritize tires with specific steel compositions for enhanced safety and performance.
Key Properties: Nylon is often used in tire construction for its lightweight and flexible properties. It can handle pressures up to 40 PSI and operates effectively in a temperature range of -30°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of nylon is its lightweight nature, which can improve fuel efficiency. However, it may not provide the same level of durability as rubber or steel, leading to potential wear issues over time. Manufacturing complexity is lower compared to steel.
Impact on Application: Nylon tires are suitable for passenger vehicles and light trucks but may not be ideal for heavy-duty applications where durability is paramount.
Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the local climate and terrain when selecting nylon tires. In regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can be challenging, the durability of nylon may be a concern.
Key Properties: Polyurethane is gaining traction as an alternative material in tire manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance and ability to maintain performance under varying temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of polyurethane is its superior durability and resistance to wear, which can lead to longer tire life. However, it can be more expensive to produce, and its performance in extreme temperatures is still being evaluated.
Impact on Application: Polyurethane tires are suitable for specialized applications, such as in industrial settings, where durability and low maintenance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: As a newer material in tire production, buyers should ensure that polyurethane tires meet local safety and performance standards. This is especially important in regions with stringent regulations, such as Europe.
| Material | Typical Use Case for should i inflate tires to max psi | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Standard passenger and commercial tires | Excellent flexibility and traction | Susceptible to UV and ozone damage | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty and commercial vehicle tires | High strength and durability | Increased weight affects efficiency | High |
| Nylon | Passenger vehicles and light trucks | Lightweight, improves fuel efficiency | Less durable than rubber or steel | Medium |
| Polyurethane | Specialized industrial applications | Superior durability and wear resistance | Higher production cost | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials involved in tire inflation considerations, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs and regional conditions.
Tire manufacturing is a complex process that involves several critical stages, each vital for ensuring the safety and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers who need to ensure the tires they purchase meet specific performance criteria, including inflation recommendations.
The first stage of tire manufacturing involves the selection and preparation of raw materials. Tires are primarily made from rubber, along with various additives such as carbon black, sulfur, and chemical accelerators. These materials are chosen for their specific properties—rubber provides flexibility and grip, while carbon black enhances durability and resistance to wear.

Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
Additionally, manufacturers often source synthetic rubber and fabric components for reinforcement. The quality and origin of these materials can significantly impact tire performance, including how they respond to inflation pressures. B2B buyers should inquire about material sourcing and specifications to ensure they meet international safety standards.
In the forming stage, the prepared materials are combined and shaped into the tire’s components. This process typically involves the following:
B2B buyers should evaluate the technology used in the forming process, as advanced machinery can yield higher precision and quality.
The assembly stage is where the various tire components are brought together. This process requires meticulous attention to detail, as any misalignment can lead to performance issues. Manufacturers typically implement several quality control measures during assembly, including:
These quality control steps are critical to ensuring that the tire can safely accommodate recommended inflation pressures.
The finishing stage involves several steps aimed at preparing the tire for sale. This includes final inspections, branding, and certification. Tires are often subjected to rigorous testing to assess their performance under various conditions, including pressure tests.
B2B buyers should verify that the manufacturer follows rigorous finishing protocols to ensure the product meets all necessary safety standards. Proper finishing ensures that the tire can handle the pressures associated with both recommended and maximum inflation levels.
Quality assurance is crucial in tire manufacturing, particularly concerning inflation pressures. B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international and industry-specific standards that guarantee tire safety and performance.
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international quality management standards. It ensures that manufacturers have established systems to maintain quality throughout the production process. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer prioritizes quality, which is essential for tires that must withstand specific inflation pressures.
In addition to ISO 9001, other certifications, such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in specific markets, indicate compliance with regional safety and performance requirements. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers possess these certifications.
Quality control in tire manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
Buyers should ask potential suppliers about their quality control processes and the frequency of inspections at each stage.
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that tires can safely handle specified pressures. Common methods include:
B2B buyers should request documentation of these tests from suppliers, as they provide critical insights into the quality and reliability of the tires being purchased.
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are several effective strategies:
This due diligence is particularly crucial for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where standards and practices may vary.

Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
When sourcing tires internationally, B2B buyers must consider several nuances:
By being vigilant and informed, B2B buyers can make better purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and safety standards.
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to understand the implications of tire inflation, particularly regarding whether to inflate tires to maximum PSI. Proper tire pressure is crucial for vehicle safety, performance, and cost efficiency. This checklist will equip you with actionable steps to ensure informed decisions about tire pressure management in your fleet or operations.
Understanding the specific tire pressure requirements for your vehicles is the first step. Each vehicle model has a recommended tire pressure, typically found in the owner’s manual or on a label inside the driver’s door. Familiarize yourself with these specifications to avoid the common mistake of inflating to maximum PSI, which can lead to safety hazards and increased costs.

Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
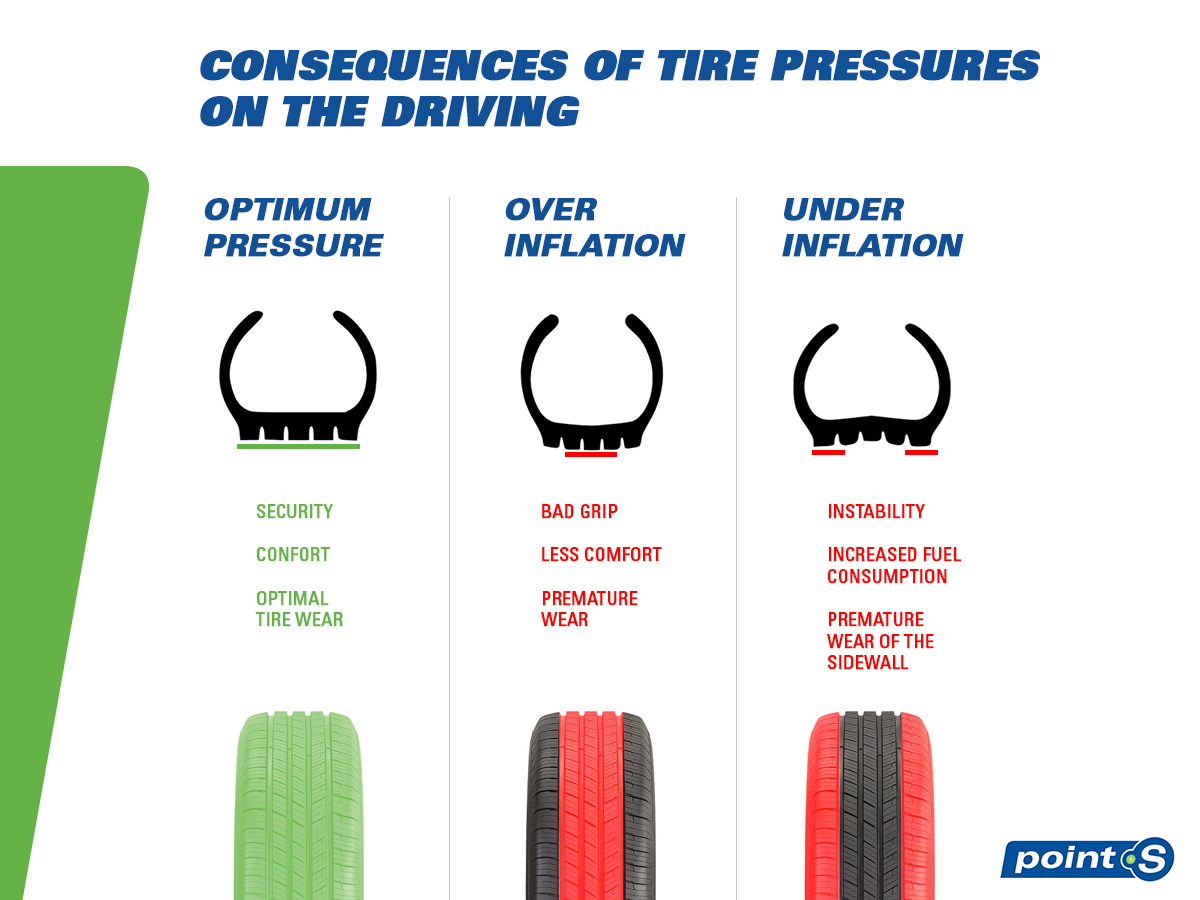
It is essential to distinguish between the recommended tire pressure and the maximum tire pressure indicated on the tire’s sidewall. The recommended pressure ensures optimal performance and safety, while the maximum pressure indicates the upper limit that the tire can safely withstand. Inflating tires to maximum PSI can compromise vehicle handling and increase the risk of blowouts.
For fleets, consider equipping vehicles with Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS). These systems alert drivers when tire pressure falls below a safe threshold, promoting timely maintenance. Regularly monitoring tire pressure can prevent issues related to under-inflation, such as uneven tire wear and increased fuel consumption.
Implement a routine for checking tire pressure and overall tire condition. Use a reliable tire pressure gauge to ensure accuracy, and always check tire pressure when tires are cold. Establishing a regular inspection schedule will help identify potential problems before they escalate, ensuring the longevity of your tires and the safety of your vehicles.
Educate your team on the importance of maintaining the correct tire pressure and the risks associated with over-inflation. Provide training sessions that cover how to read tire specifications, use pressure gauges, and recognize the signs of tire wear. An informed workforce is critical to maintaining vehicle safety and performance.
When procuring tires, choose suppliers who provide high-quality products that meet industry standards. Look for suppliers that offer detailed specifications and warranties, ensuring that the tires you purchase will perform well under the recommended pressure. Verify their certifications and customer reviews to ensure reliability and service excellence.
Keep track of fuel consumption and tire wear patterns as part of your tire management strategy. Over-inflation can lead to reduced fuel efficiency and increased costs due to premature tire replacements. Regular assessments will help you identify trends and make necessary adjustments to your tire maintenance practices.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions regarding tire pressure management, optimizing safety and efficiency within your fleet or operations.
When considering the sourcing of equipment related to tire inflation, particularly in the context of inflating tires to their maximum PSI, various cost components come into play. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The primary materials involved in tire inflation systems include durable rubber for hoses, metal for connectors, and electronic components for pressure gauges. The quality of these materials directly impacts both performance and durability, influencing overall costs.
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in the manufacturing process, as well as any specialized technicians needed for assembly or quality assurance. In regions with varying labor costs, such as Africa and South America, these expenses can significantly affect the final price.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and other indirect costs associated with the production facility. Efficient manufacturing processes can help lower overhead costs, making it essential for manufacturers to optimize their operations.
Tooling: Investment in the right tooling is crucial for producing high-quality tire inflation equipment. Custom tooling can lead to higher initial costs but may improve efficiency and output quality in the long run.
Quality Control: Rigorous QC procedures are necessary to ensure that tire inflation equipment meets safety and performance standards. This may include testing for maximum pressure capabilities, which can add to the overall cost.
Logistics: The costs associated with transporting equipment from manufacturers to buyers can vary widely based on distance, shipping methods, and the complexity of international shipping regulations, particularly for buyers in diverse regions like the Middle East and Europe.
Margin: Lastly, manufacturers and suppliers need to include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the overall economic environment.
Several key influencers can affect pricing in the tire inflation equipment market:
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Buying in bulk often leads to lower per-unit costs. For B2B buyers, negotiating higher MOQs can result in significant cost savings.
Specifications and Customization: Customized tire inflation systems tailored to specific vehicle types or operational needs can increase costs. However, they can provide greater efficiency and safety, justifying the investment.
Materials: The choice of materials plays a crucial role in pricing. High-quality materials may incur higher upfront costs but can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
Quality and Certifications: Equipment that meets international safety and quality standards often comes at a premium. However, ensuring compliance can reduce liability and enhance brand reputation.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge more but can offer better service and support.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. These terms dictate shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, impacting the total price and delivery timelines.
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating costs, consider the TCO, which includes purchase price, operational costs, and maintenance. This holistic view can lead to more informed sourcing decisions.
Negotiate for Better Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate on volume discounts, payment terms, and warranties. Suppliers often have flexibility in pricing, especially for larger orders.
Focus on Quality: Investing in higher-quality equipment may result in lower long-term costs through reduced maintenance and fewer replacements. Prioritize quality over the lowest price.
Research Supplier Backgrounds: Conduct due diligence on potential suppliers to ensure they have a proven track record. This can help mitigate risks associated with poor-quality products.
Be Aware of Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing can vary significantly based on geographic region. Understanding local market conditions can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Please note that the prices and cost components mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers for accurate pricing information tailored to your needs.

Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
When it comes to tire maintenance, the decision to inflate tires to maximum PSI often raises questions among B2B buyers. While it may seem like a straightforward solution for optimal performance, there are alternative approaches that can provide better safety, efficiency, and longevity for tire usage. Below, we compare the practice of inflating tires to maximum PSI against two viable alternatives: maintaining recommended tire pressure and utilizing tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS).
| Comparison Aspect | Should I Inflate Tires To Max PSI | Maintaining Recommended Tire Pressure | Utilizing Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Poor handling, increased wear | Optimal handling and wear | Continuous monitoring, alerts for low pressure |
| Cost | Higher long-term replacement costs | Lower replacement costs | Initial investment but reduces long-term costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, but risky | Requires knowledge of specs | Installation needed, but user-friendly alerts |
| Maintenance | High due to wear and blowouts | Moderate, periodic checks needed | Low, automated checks and alerts |
| Best Use Case | Temporary heavy loads | Everyday driving | Fleet management and regular vehicle use |
Maintaining the recommended tire pressure is widely regarded as the best practice for tire health. By adhering to the manufacturer’s specifications, businesses can ensure optimal vehicle handling, safety, and fuel efficiency. The primary advantage is that it minimizes tire wear and prevents blowouts, which can lead to costly accidents or downtime. However, it requires regular monitoring and a good understanding of the vehicle’s specifications, which can be a challenge for some organizations.
TPMS technology provides a proactive approach to tire management. These systems continuously monitor tire pressure and alert drivers when levels fall below the recommended threshold. The key benefits include reduced maintenance efforts and the prevention of under-inflation or over-inflation, which can lead to safety hazards and increased costs. While the initial investment in TPMS might be higher, the long-term savings through improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire replacements can make it a financially sound choice for businesses managing a fleet of vehicles.
When deciding between inflating tires to maximum PSI and alternative methods, B2B buyers should consider the specific needs of their operations. Maintaining recommended tire pressure is typically the safest and most effective choice for everyday vehicle use, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. For businesses looking to enhance their tire management further, investing in TPMS can offer significant benefits, particularly in fleet operations where monitoring multiple vehicles is crucial. Ultimately, the best approach will depend on individual business objectives, vehicle types, and operational demands. Prioritizing safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness will guide B2B buyers in selecting the most appropriate tire maintenance solution.
Understanding the technical specifications of tire inflation is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making purchasing decisions for vehicles or tire products. Here are some essential properties to consider:
Recommended Tire Pressure (RTP)
RTP is the optimal air pressure specified by the vehicle manufacturer, usually found in the owner’s manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. Maintaining tires at this pressure is vital for safety, fuel efficiency, and longevity. For businesses, adhering to RTP can reduce operational costs associated with tire replacements and fuel consumption.
Maximum Inflation Pressure (MIP)
MIP indicates the highest pressure a tire can withstand without risking damage or failure. This specification is critical for understanding the limits of tire performance. For B2B buyers, knowing the MIP helps in making informed decisions regarding tire safety, especially in environments where load and stress conditions vary significantly.
Cold Tire Pressure (CTP)
CTP refers to the tire pressure when the tires are cold, meaning they haven’t been driven for at least three hours. This measurement is essential as tire pressure can increase with temperature from driving. For fleet operators, checking CTP ensures accurate monitoring of tire health, thereby enhancing safety and reducing maintenance costs.
Load Index (LI)
The Load Index indicates the maximum load a tire can carry at its specified pressure. Each tire has a corresponding LI that helps buyers match tires to their vehicle’s load requirements. Understanding LI is crucial for companies involved in logistics and transportation, as improper load handling can lead to increased tire wear and accidents.
Treadwear Indicators (TWI)
TWI are small raised bars within the tire grooves that indicate when the tread has worn down to a level where the tire should be replaced. Monitoring tread wear is vital for maintaining safety and efficiency. Businesses that rely on vehicle performance need to prioritize TWI to avoid costly breakdowns and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms relevant to tire inflation:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to the company that manufactures parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For tire buyers, understanding OEM specifications ensures compatibility and quality, especially when replacing tires on vehicles.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical in B2B transactions as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to avoid excess inventory and optimize purchasing budgets.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. In the context of tire purchasing, an RFQ allows businesses to compare prices and terms from various manufacturers, ensuring they receive the best deal.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border tire purchases, as it clarifies shipping, insurance, and delivery obligations.
TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System)
TPMS is a safety feature in vehicles that monitors tire pressure and alerts drivers when it falls below a certain threshold. For fleet operators, investing in vehicles equipped with TPMS can significantly enhance safety and reduce the risk of tire-related incidents.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions about tire purchases, leading to improved safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
The tire pressure sector is experiencing significant evolution, driven by a combination of safety regulations, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the emphasis on vehicle safety and fuel efficiency is leading to increased awareness about tire maintenance. Regulatory bodies are introducing stricter guidelines around tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS), making it essential for B2B buyers to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Emerging technologies, including smart tire pressure monitoring solutions, are gaining traction. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring of tire pressure, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. Additionally, the growing trend of electric vehicles (EVs) is influencing tire design and specifications, as manufacturers adapt to the unique requirements of these vehicles. International buyers must stay informed about these technological shifts to make informed sourcing decisions.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a surge in demand for high-performance tires that maintain optimal pressure under various driving conditions. This trend underscores the importance of sourcing tires that not only meet safety standards but also contribute to overall vehicle performance and longevity.
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern sourcing strategies within the tire industry. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize ethical sourcing and environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of tire production, including carbon emissions and resource consumption, necessitates a shift towards greener alternatives.
Buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who utilize sustainable materials, such as recycled rubber and bio-based compounds. Certifications like the Global Recycling Standard (GRS) and the Sustainable Rubber Initiative (SRI) are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By prioritizing these certifications, businesses can ensure that their procurement strategies align with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, adopting sustainable practices can enhance a company’s reputation, as consumers and stakeholders are increasingly favoring brands that demonstrate environmental responsibility. This not only fosters customer loyalty but can also lead to cost savings through improved operational efficiencies and reduced waste.

Illustrative image related to should i inflate tires to max psi
The evolution of tire pressure standards can be traced back to the early 20th century when automobiles became more widespread. Initially, there was little regulation regarding tire pressure, leading to safety issues and increased maintenance costs. As automobile technology advanced, the need for standardized tire pressure guidelines became apparent.
In the 1970s, the introduction of tire pressure monitoring systems began to reshape how drivers and manufacturers approached tire maintenance. Regulatory bodies started mandating the inclusion of recommended tire pressures in vehicle manuals and on doorjamb stickers, promoting awareness about the importance of maintaining optimal tire pressure for safety and efficiency.
Today, the dialogue around tire pressure is not just about compliance; it encompasses technological advancements and sustainability, reflecting the ongoing evolution of industry standards. International B2B buyers must navigate this historical context to better understand the current market dynamics and sourcing trends.
1. How do I determine the correct tire pressure for my vehicles?
To find the correct tire pressure for your vehicles, refer to the manufacturer’s specifications, which are typically located in the owner’s manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. This recommended pressure is crucial for optimal vehicle performance and safety. Always check the pressure when the tires are cold, as heat from driving can artificially inflate the reading. For businesses managing fleets, maintaining correct tire pressure can lead to improved fuel efficiency and reduced tire wear, ultimately lowering operational costs.
2. What are the risks of inflating tires to maximum pressure?
Inflating tires to their maximum pressure, as indicated on the tire sidewall, can pose serious safety risks. Over-inflation reduces the tire’s contact with the road, leading to poorer handling and longer stopping distances. Additionally, it increases the likelihood of blowouts, especially when encountering road hazards. For B2B buyers, understanding these risks is essential to ensure the safety of your fleet and to avoid costly liabilities associated with tire failures.
3. How can I ensure quality when sourcing tires for my fleet?
To ensure quality when sourcing tires, it’s essential to vet suppliers thoroughly. Look for manufacturers with certifications and a proven track record in tire production. Request samples and conduct quality assurance tests before placing bulk orders. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties or guarantees on their products, as this can provide added security for your investment. Engaging in discussions about tire specifications and compliance with international standards can also help ensure the quality of the tires you purchase.
4. What should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQ) when purchasing tires?
When purchasing tires, MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers. It’s crucial to discuss and negotiate these terms upfront to avoid overcommitting your resources. Consider your fleet’s size and projected needs to determine an appropriate MOQ. Additionally, inquire about flexibility in order sizes for future purchases, as this can help manage inventory levels and ensure you are not left with excess stock that could tie up capital.
5. What payment terms are common in international tire transactions?
Common payment terms for international tire transactions often include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and financial strategy. Additionally, consider the reliability of the supplier and the risks associated with international transactions, such as currency fluctuations and shipping delays, when agreeing on payment terms.
6. How do logistics impact my tire procurement strategy?
Logistics plays a critical role in tire procurement, especially for international buyers. Evaluate the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including lead times, transportation methods, and costs. Efficient logistics can minimize delays and reduce overall costs. Establish clear communication channels with suppliers regarding shipping schedules and any customs requirements. For businesses operating in regions with challenging logistics, building a strong partnership with a reliable logistics provider can enhance the procurement process.
7. What are the customization options available for tires?
Many tire manufacturers offer customization options, including tread patterns, rubber compounds, and sizes to suit specific operational needs. When sourcing tires, inquire about these options to ensure they align with your fleet’s requirements. Customization can enhance vehicle performance and safety, particularly in diverse driving conditions encountered in regions like Africa or South America. Understanding the implications of these customizations on tire performance and longevity is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
8. How can I monitor tire pressure effectively across a fleet?
Implementing a tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) across your fleet can help maintain optimal tire pressure, enhancing safety and efficiency. A TPMS provides real-time data on tire pressure, alerting you to any deviations from the recommended levels. Regular training for drivers on the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure and conducting routine checks can further support this effort. By prioritizing tire maintenance, you can extend tire lifespan, improve fuel economy, and reduce the risk of tire-related incidents.
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Max Tire Pressure: 44 psi; Recommended Tire Pressure: 32 psi (front and rear for up to 3 persons), 33 psi (front) and 44 psi (rear) for full load; Vehicle: Mazda 3 2007; Tire Size: Same as stock; Load Index and Speed: Same as stock.
Domain: pirelli.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Recommended tire pressure is established by the vehicle manufacturer and typically falls between 28 and 36 PSI. The correct pressure can be found in the car’s operator manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. It is important to check tire pressure when the tires are cold. Maximum tire pressure is indicated on the tire’s sidewall and should not be used for everyday driving as it can impair …
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Tire Inflation Tips, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Domain: airforums.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The “MAX” psi on tires refers to the maximum pressure required to support the maximum load stated on the tire sidewall. It is not the highest pressure a tire can tolerate, and undamaged tires do not explode if this psi number is exceeded. Tire pressure increases by about 2% for each 10°F increase in ambient temperature. It is recommended to inflate tires according to industry tables based on the l…
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Tire maximum pressure: 44 psi; Recommended pressure range: 10-15% below maximum for optimal performance; Vehicle-specific pressure indicated on door placard; Common pressures mentioned: 31 psi (vehicle spec), 33-34 psi (user experience), 36 psi (user plan), 38 psi (user experience), 40 psi (user experience), 35 psi (Toyota Prius 2012 spec).
Domain: grassrootsmotorsports.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 2020 GMC Express Van; Tire pressure light indicates rear tires at 60 psi; All four tires initially inflated to 80 psi; Manufacturer max tire pressure is 80 psi; Recommended cold tire pressure for rear is 80 psi, front is 50 psi; Light truck tires designed for higher pressures (50-80 psi); Importance of checking door jamb sticker for recommended pressures; Potential for tire pressure to increase wh…
In summary, the importance of adhering to the recommended tire pressure cannot be overstated, particularly for B2B buyers managing fleets across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Proper tire inflation directly impacts safety, operational efficiency, and cost management. Over-inflating tires not only increases the risk of blowouts and accidents but also leads to uneven wear and higher fuel consumption. This can result in significant financial implications for businesses reliant on transportation.
Strategic sourcing of tire maintenance supplies, including pressure gauges and monitoring systems, is essential for optimizing vehicle performance and enhancing safety protocols. By investing in reliable tire management solutions, businesses can ensure their fleets operate efficiently and safely, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
As the global market continues to evolve, staying informed on best practices for tire maintenance will be crucial. We encourage international B2B buyers to prioritize tire pressure management in their procurement strategies and leverage partnerships with trusted suppliers. This proactive approach will not only safeguard assets but also contribute to a more sustainable and efficient operation moving forward.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.