In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable air pressure readers poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Companies must navigate a myriad of options while ensuring that the products meet their operational standards, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Saudi Arabia and Brazil. This guide is designed to simplify the process, offering a comprehensive overview of air pressure readers, covering various types, applications, and features that cater to diverse industry needs.
Buyers will discover essential insights into the different categories of air pressure readers, from digital gauges to analog models, each with unique advantages suited for specific applications. This guide also delves into the critical factors for supplier vetting, emphasizing quality assurance and reliability—key considerations for businesses looking to maintain operational efficiency. Furthermore, we provide a detailed analysis of cost structures, helping buyers understand pricing trends and negotiate better deals.
By empowering decision-makers with actionable information, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that businesses can confidently select the right air pressure readers tailored to their requirements. With the right knowledge at hand, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, optimize performance, and ultimately achieve a competitive edge in their respective markets.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Tire Pressure Gauge | Mechanical dial display, typically robust and easy to use | Automotive service stations, fleet management | Pros: Low cost, no batteries required; Cons: Less precise than digital models. |
| Digital Tire Pressure Gauge | Electronic readout, often more accurate and easy to read | Automotive repair shops, tire retailers | Pros: High accuracy, easy to read; Cons: Requires batteries and may be more expensive. |
| Low Pressure Tire Gauge | Specifically designed for low PSI ranges (e.g., 0-15 PSI) | ATVs, off-road vehicles, lawn equipment | Pros: Precision for low-pressure applications; Cons: Limited to low-pressure measurements. |
| Inflator with Pressure Gauge | Combines inflation and pressure reading capabilities | Automotive workshops, service centers | Pros: Time-saving, multifunctional; Cons: Bulkier than standalone gauges. |
| High-Pressure Tire Gauge | Designed for high PSI ranges (e.g., 100-200 PSI) | Commercial trucking, heavy machinery | Pros: Essential for high-performance applications; Cons: May be more expensive and specialized. |
Analog tire pressure gauges feature a mechanical dial that displays pressure readings. Known for their durability, these gauges are often constructed from rugged materials, making them suitable for various environments. They are ideal for automotive service stations and fleet management due to their ease of use and low cost. However, they may lack the precision of digital counterparts, which can be a drawback for applications requiring exact measurements.
Digital tire pressure gauges are equipped with electronic displays that provide clear and precise readings. Their accuracy makes them popular in automotive repair shops and tire retailers, where reliable measurements are crucial. While they may come at a higher price point and require batteries, their ease of reading and advanced features often justify the investment for B2B buyers seeking quality tools.
Low pressure tire gauges are specifically designed for measuring pressures in the range of 0-15 PSI, making them essential for ATVs, off-road vehicles, and lawn care equipment. Their precision in low-pressure applications ensures optimal performance and safety. Buyers should consider their specific needs when purchasing, as these gauges are limited to low-pressure measurements, which may not suit all vehicles.
Inflators with built-in pressure gauges combine the functions of inflating tires and measuring pressure, making them efficient tools for automotive workshops and service centers. Their multifunctionality saves time and enhances productivity. However, they tend to be bulkier than standalone gauges, which may be a consideration for businesses with limited storage space.
High-pressure tire gauges are designed to handle PSI ranges of 100-200, making them crucial for commercial trucking and heavy machinery applications. Their specialized design ensures accurate readings for high-performance tires. While they may carry a higher price tag, the investment is often justified for businesses that require reliable performance in demanding conditions.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of air pressure reader | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) | Enhances vehicle safety and fuel efficiency | Accuracy, durability, and compatibility with various vehicle models |
| Manufacturing | Pneumatic Tool Operation | Optimizes production efficiency and equipment lifespan | Calibration standards, pressure range, and industrial-grade robustness |
| Agriculture | Irrigation Systems | Ensures optimal water usage and crop yield | Resistance to environmental factors and ease of integration |
| Construction | Heavy Machinery Maintenance | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs | Precision, ruggedness, and compliance with safety standards |
| Aerospace | Aircraft Tire Pressure Monitoring | Critical for safety and operational efficiency | High accuracy, lightweight design, and adherence to aviation standards |
In the automotive sector, air pressure readers are integral to Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS). These devices continuously monitor tire pressure, alerting drivers when levels fall below safe thresholds. This application is vital for enhancing vehicle safety, improving fuel efficiency, and extending tire life. For B2B buyers, sourcing reliable air pressure readers requires attention to accuracy and durability, especially in regions with varying climate conditions, such as Africa and the Middle East, where extreme temperatures can affect tire performance.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
In manufacturing, air pressure readers are crucial for the operation of pneumatic tools. By ensuring that tools operate within optimal pressure ranges, businesses can enhance production efficiency and prolong equipment lifespan. Accurate pressure readings help prevent tool malfunction and reduce maintenance costs. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing products that meet industrial calibration standards and demonstrate robust performance under continuous use, which is particularly important in high-demand environments across South America and Europe.
In agriculture, air pressure readers are essential for managing irrigation systems. By monitoring air pressure in irrigation lines, farmers can optimize water usage, ensuring crops receive adequate hydration without wastage. This application not only enhances crop yield but also contributes to sustainable farming practices. Buyers must consider the device’s resistance to environmental factors such as dust and moisture, which are prevalent in agricultural settings, especially in arid regions of Africa and the Middle East.
In the construction industry, air pressure readers are vital for the maintenance of heavy machinery. Regular monitoring of tire pressure on construction vehicles reduces downtime and maintenance costs, ensuring that projects remain on schedule. For B2B buyers, sourcing robust and precise air pressure readers that comply with safety standards is crucial, particularly in high-stakes environments where equipment reliability is paramount.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
In the aerospace sector, air pressure readers are critical for monitoring aircraft tire pressure. Maintaining proper tire pressure is essential for safe takeoffs and landings, directly impacting operational efficiency. Aerospace buyers need to focus on high-accuracy, lightweight designs that adhere to strict aviation standards, as any failure in pressure monitoring can lead to serious safety risks. This application highlights the necessity for precision and reliability in sourcing air pressure readers for international aviation markets.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of inconsistent readings from air pressure readers, which can lead to operational inefficiencies. For instance, a logistics company relying on accurate tire pressure measurements for its fleet may find that some gauges provide different readings for the same tire. This inconsistency can lead to under-inflated tires, causing premature wear and tear, increased fuel consumption, and even accidents, which ultimately affect the bottom line.
The Solution: To tackle this issue, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality, reliable air pressure readers known for their accuracy. When selecting a gauge, look for models that have been independently tested and certified for precision, such as those that have received awards for accuracy. Implementing a regular calibration schedule can also ensure that all gauges provide consistent readings. Consider investing in digital gauges that feature automatic calibration, which can simplify maintenance and enhance reliability over time. Additionally, training staff on proper usage techniques can prevent user errors that may lead to misleading readings.
The Problem: Many businesses operate in environments that expose tools, including air pressure readers, to challenging conditions such as moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures. For example, a construction company may find that its air pressure gauges frequently fail due to exposure to water and dirt, leading to increased costs for replacements and lost time due to inaccurate readings during critical equipment checks.
The Solution: When purchasing air pressure readers, it’s essential to choose models designed specifically for rugged conditions. Look for gauges that are water-resistant, dustproof, and built with robust materials that can withstand shocks and impacts. Additionally, consider investing in gauges that come with protective casings or are equipped with features like reinforced connections. It may also be beneficial to implement a rotation system, ensuring that tools are regularly serviced or replaced before they fail. Educating teams on how to properly clean and maintain these tools can further extend their lifespan.
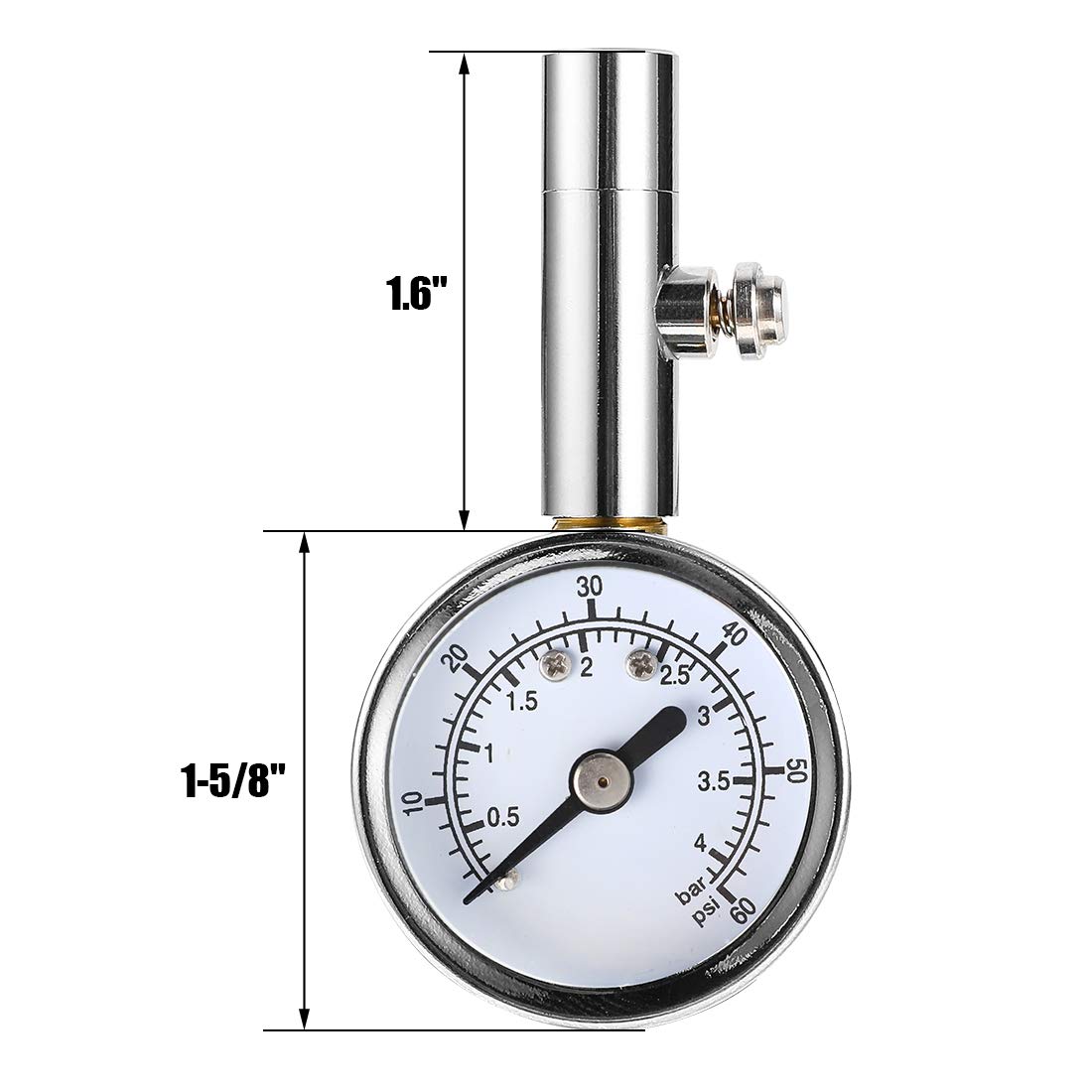
Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
The Problem: Another common pain point is the complexity involved in training staff to use air pressure readers correctly. In many organizations, especially those with high turnover rates or diverse employee backgrounds, inadequate training can result in improper use of gauges. This can lead to safety risks and operational inefficiencies, as untrained staff may misread the gauges or fail to use them altogether.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, B2B buyers should look for air pressure readers that are user-friendly and come with clear instructions or visual guides. When selecting a gauge, consider models that have been designed with intuitive interfaces, such as digital displays that provide clear, easy-to-read measurements. Implementing a structured training program that includes hands-on demonstrations can significantly enhance staff proficiency. Regular refresher courses can also help maintain knowledge levels among existing employees and ensure that new hires quickly become competent in using the equipment. Additionally, creating easy-access reference materials, such as quick-start guides or instructional videos, can support ongoing learning and promote best practices in using air pressure readers.
When selecting materials for air pressure readers, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and compatibility with specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: brass, stainless steel, plastic, and aluminum.
Brass is a popular choice for air pressure readers due to its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for various applications. Brass components typically have a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can handle pressures exceeding 300 PSI.
Pros: Brass is durable, offers good machinability, and is cost-effective compared to other metals. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in humid or corrosive environments.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
Cons: While brass is robust, it can tarnish over time, which may affect readability. Additionally, its higher density can lead to increased weight in portable applications.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with most gases and liquids, making it versatile for different pressure reading scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM B453 for brass materials, to avoid issues with quality and safety.
Stainless steel is another widely used material for air pressure readers, known for its exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion and oxidation. It can operate effectively in extreme temperatures, often rated between -200°C and 600°C, and can handle high-pressure applications.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
Pros: Stainless steel is incredibly durable and resistant to rust, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial environments. Its aesthetic appeal also makes it suitable for consumer-facing products.
Cons: The primary drawback of stainless steel is its higher cost compared to brass and plastic. Additionally, it can be more challenging to machine, leading to increased manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive gases, which makes it a preferred choice in chemical and petrochemical industries.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A276 is crucial for ensuring product quality and performance in various markets, including Europe and South America.
Plastic materials, particularly high-grade polymers, are increasingly used in air pressure readers due to their lightweight and cost-effective nature. They typically have a lower temperature rating, often around 60°C, and can handle pressures up to 100 PSI.
Pros: The main advantages of plastic include low cost, lightweight, and resistance to corrosion. Plastic is also easier to mold into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Cons: The limitations of plastic include lower durability compared to metals and susceptibility to degradation from UV exposure and extreme temperatures.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for low-pressure applications and is often used in consumer-grade products where weight and cost are significant factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific type of plastic used, ensuring compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile strength, especially in regions with varying climate conditions.
Aluminum is a lightweight metal that strikes a balance between strength and weight, making it a viable option for air pressure readers. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and can handle pressures around 200 PSI.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offers good thermal conductivity. Its lower cost compared to stainless steel makes it an attractive option for many manufacturers.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it is softer than brass and stainless steel, making it more prone to dents and scratches. This can affect the long-term usability of the product.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in portable devices or automotive uses.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is necessary to ensure quality and performance across different markets.
| Material | Typical Use Case for air pressure reader | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | General-purpose gauges | Good corrosion resistance | Can tarnish over time | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial and outdoor applications | Exceptional durability | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic | Consumer-grade products | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower durability | Low |
| Aluminum | Portable devices and automotive uses | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Prone to dents and scratches | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions about air pressure readers, considering performance, cost, and regional compliance.
The manufacturing process of air pressure readers, such as tire pressure gauges, involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards for accuracy and reliability.
The first step involves selecting high-quality materials, typically metals like brass or stainless steel, and durable plastics for the casing. These materials are chosen for their strength, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand the pressures they will measure. After material selection, the raw materials are subjected to various treatments, such as annealing for metals, to enhance their properties.
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. This may include machining, where components are cut to precise dimensions using CNC machines. For plastic parts, injection molding is often employed to create complex shapes with high precision. The choice of forming technique directly affects the accuracy and durability of the final product.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
The assembly stage is critical and involves the integration of various components, including the pressure sensor, display (analog or digital), and housing. This process may be automated or manual, depending on the complexity of the design. Each component must be carefully fitted to ensure that the gauge functions correctly and provides accurate readings.
After assembly, the air pressure readers undergo finishing processes, which may include surface treatments, painting, or coating to enhance durability and aesthetics. Final inspection is crucial, where each unit is tested for functionality, accuracy, and overall quality.
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of manufacturing air pressure readers, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards.
Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in the oil and gas sector, may also apply.
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage checks the quality of raw materials before they enter production. Materials are verified against specifications to prevent defects in the final product.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that components meet quality standards.
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the product is assembled, it undergoes final testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This may include pressure testing, calibration checks, and functionality assessments.
Testing methods for air pressure readers include:
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure product reliability.
Conducting audits is one of the most effective ways to verify a supplier’s QC processes. Buyers should consider:
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies often conduct pre-shipment inspections, ensuring that products meet specified standards before they are dispatched.
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification:
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Understanding these can help buyers ensure compliance and avoid potential issues.
Language Barriers: Documentation and communication may be in different languages, so having bilingual staff or translators can facilitate smoother interactions.
Local Certifications: Some regions may require additional certifications beyond international standards, so it’s crucial to research local requirements.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for air pressure readers is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, and rigorous quality control, buyers can ensure they procure reliable and high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
When sourcing an air pressure reader, also known as a tire pressure gauge, it’s essential to follow a structured approach to ensure you make informed decisions. This checklist will guide B2B buyers through the necessary steps to procure high-quality air pressure readers that meet their specific needs.
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is vital. Consider the range of pressure measurements you need, whether in PSI or bar, and the gauge type (analog or digital) that best suits your applications. Additionally, take into account the durability and accuracy required for your operational environment, which will affect the long-term reliability of the equipment.
Stay informed about the latest advancements in air pressure readers. Look for features such as Bluetooth connectivity for digital gauges, which can enhance usability, or ergonomic designs that improve handling. Understanding current market trends can also help you identify leading brands and products that are favored in your industry.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
Before finalizing any agreements, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and certifications. Seek references from other businesses in your sector to ensure that the supplier has a proven track record of reliability and customer satisfaction.
Never underestimate the importance of testing before bulk procurement. Request samples of the air pressure readers you are considering to evaluate their performance firsthand. This will help you assess accuracy, ease of use, and overall quality.
Carefully compare pricing structures from different suppliers while considering the total cost of ownership. Look beyond the initial purchase price; assess factors like shipping costs, warranties, and potential after-sales support. Negotiate payment terms that align with your budget and cash flow requirements.
Strong after-sales support is crucial for maintaining equipment longevity and functionality. Verify what kind of warranty is offered and the terms surrounding it. A reliable supplier should provide comprehensive customer support, including technical assistance and repair services.
Once you have completed all previous steps, it’s time to finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms discussed are documented, including delivery timelines, payment schedules, and quality assurance protocols. Establish clear communication channels for any future correspondence or issues that may arise post-purchase.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for air pressure readers, ensuring they select high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Understanding the cost structure of air pressure readers is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials for air pressure readers include brass, plastic, and electronic components for digital gauges. Premium materials can enhance durability and accuracy, but they also increase costs.
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the final pricing. In regions with higher wage rates, such as Europe, labor costs will be a more significant factor compared to regions like Africa or South America.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient factories often have lower overhead, which can lead to more competitive pricing.
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial, especially for custom designs. This cost is typically amortized over the production volume, so higher volume orders can reduce the per-unit tooling cost.
Quality Control: Ensuring product accuracy and reliability is essential in air pressure gauges, leading to additional QC costs. Certifications (like ISO) can also add to these expenses but may be necessary to meet international standards.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly depending on the shipping terms (Incoterms) and the distance between supplier and buyer. For international buyers, it’s essential to consider customs duties and taxes as part of the total logistics cost.
Margin: Suppliers will typically apply a profit margin on top of their cost structure, which can vary based on market competition and demand.
Several factors can influence the pricing of air pressure readers, especially for B2B buyers:
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Ordering in bulk often leads to lower prices per unit due to economies of scale. Suppliers are more likely to negotiate better terms for larger orders.
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected price hikes.
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (such as CE marking or ANSI standards) can enhance product value but will also raise costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits against the price increase.
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and geographic location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher rates due to their track record and quality assurance.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. The chosen terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can impact shipping costs and responsibilities, affecting the total price.
To maximize cost efficiency, B2B buyers should consider several strategies:
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially regarding bulk orders or long-term contracts. Be prepared to leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers.
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
Understanding Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of regional market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and potential tariffs. This knowledge can provide leverage in negotiations and help avoid unforeseen costs.
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority service. Regular communication and feedback can foster trust and collaboration.
In conclusion, understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers of air pressure readers is essential for international B2B buyers. By leveraging this knowledge and employing effective negotiation strategies, buyers can achieve more favorable pricing and supplier relationships. Always remember that prices may vary, so it’s advisable to request quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure the best value.
In the realm of measuring and monitoring air pressure, particularly in tires and other pneumatic systems, the air pressure reader stands out as a widely used tool. However, various alternatives exist that may cater to specific needs and contexts for B2B buyers. Understanding these alternatives can lead to more informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that businesses choose the best solution for their operational requirements.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
| Comparison Aspect | Air Pressure Reader | Digital Tire Pressure Gauge | Tire Inflator with Pressure Gauge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy; manual reading | Very high accuracy; instant digital readout | High accuracy; integrated inflating capability |
| Cost | Moderate (typically $20-$30) | Moderate to high ($25-$40) | Higher ($35-$90) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple; requires manual operation | Very simple; requires minimal setup | Simple; requires connection to air compressor |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional calibration | Low; battery replacement needed | Low; requires periodic checks on inflator functionality |
| Best Use Case | Personal vehicles, small fleets | Professional garages, high-volume tire shops | Automotive service centers, workshops needing quick inflation |
Digital tire pressure gauges are advanced alternatives that provide instantaneous readings with high accuracy. They often feature large, easy-to-read displays, making them user-friendly. Their primary advantages lie in their precision and speed, which are essential in high-traffic environments like automotive service centers. However, they typically require battery replacements, which can be a minor inconvenience. The cost is slightly higher than manual gauges, but many businesses find the investment worthwhile for the enhanced functionality.
Tire inflators with integrated pressure gauges combine two functionalities: measuring air pressure and inflating tires. This dual capability makes them particularly valuable in automotive workshops where efficiency is paramount. They often feature digital displays that offer precise readings and can inflate tires quickly, saving time during service. The main downside is the higher initial cost, and they require a connection to an air compressor, which may not be suitable for all environments. Nevertheless, they are ideal for businesses that prioritize speed and efficiency in tire servicing.
When selecting the best air pressure measurement solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including the volume of usage, the level of precision needed, and the operational context. While air pressure readers are excellent for basic applications, digital gauges and tire inflators with integrated gauges provide advanced features that may enhance productivity in professional settings. Ultimately, the choice should align with the business’s operational goals, budget constraints, and the necessity for accuracy and efficiency in tire maintenance. By carefully evaluating these factors, buyers can select the most appropriate solution for their needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
When selecting an air pressure reader, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for ensuring reliability and performance. Here are some essential properties to consider:
Measurement Range
The measurement range indicates the minimum and maximum pressure levels the gauge can accurately measure, typically expressed in PSI (pounds per square inch). For example, a gauge with a range of 0-100 PSI is suitable for most automotive applications. Choosing the right range is important for ensuring that the gauge can handle the specific requirements of your operations without risk of damage or inaccurate readings.
Accuracy
Accuracy is a critical property that reflects how closely a gauge’s reading matches the true pressure. It is often specified as a percentage of the reading, such as ±1%. High accuracy is essential in industries where precise pressure readings are necessary for safety and efficiency, such as in automotive and aerospace sectors. A gauge with higher accuracy can reduce the likelihood of errors that could lead to equipment failure or safety hazards.
Material Grade
The material composition of the pressure gauge affects its durability and resistance to environmental factors. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. For B2B buyers, selecting a gauge made from high-grade materials ensures longevity and reliability in demanding conditions, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance costs.
Response Time
This refers to how quickly the gauge can provide a reading after being exposed to a pressure change. Fast response times are critical in dynamic environments where pressure fluctuations occur rapidly. Understanding the response time helps businesses choose gauges that can keep up with their operational demands, especially in industries like manufacturing and automotive service.
Calibration
Calibration indicates how the gauge is adjusted to ensure accurate readings. Many gauges come pre-calibrated, but regular recalibration is necessary to maintain accuracy over time. B2B buyers should look for gauges that can be easily calibrated or those that come with calibration certifications, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some commonly used terms:

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of air pressure readers, OEM gauges are often preferred for their compatibility and reliability, as they are specifically designed for use with particular equipment.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to assess inventory needs and budget constraints. It can affect purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies that may not require large quantities of gauges.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products or services. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ helps ensure that the quotes received align with the buyer’s requirements, allowing for more informed decision-making.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs, making them essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border procurement of air pressure readers.
Calibration Certificate
This document verifies that a gauge has been calibrated according to industry standards. It is crucial for buyers to request calibration certificates to ensure that the gauges they purchase meet accuracy requirements, particularly in regulated industries.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting air pressure readers, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards.
The air pressure reader sector is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing demand for accurate and reliable measurement tools across various industries, including automotive, aviation, and manufacturing. The global push towards safety and efficiency in vehicle maintenance has heightened the need for high-quality tire pressure gauges, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers are increasingly favoring digital gauges over analog options due to their precision, ease of use, and additional features such as backlit displays and automatic shut-off functions.
Emerging technologies are also shaping the market dynamics. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities into air pressure readers is a key trend, enabling real-time monitoring and data analysis. This technology allows fleet managers and automotive service providers to track tire pressure remotely, thus optimizing maintenance schedules and enhancing safety. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce has transformed sourcing practices, allowing international buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers, facilitating competitive pricing and improved inventory management.
Additionally, regulatory standards regarding safety and environmental impact are influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly seeking products that comply with international quality certifications, which not only ensures reliability but also enhances brand reputation in the marketplace.
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing strategies of B2B buyers in the air pressure reader sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in the extraction and use of materials, has led to a heightened awareness of ethical sourcing. International buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient production methods.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise. Buyers are looking for products that carry certifications such as ISO 14001, which indicates adherence to environmental management standards. This not only helps in reducing the carbon footprint but also enhances the credibility of the buyer in the eyes of environmentally conscious consumers.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly viewed as a competitive advantage. Buyers who source from companies that prioritize fair labor practices and transparency are likely to foster stronger relationships with end customers who value social responsibility. By aligning with suppliers committed to sustainability, businesses can not only reduce their environmental impact but also appeal to a growing demographic of eco-conscious consumers, thus driving sales and brand loyalty.
The evolution of the air pressure reader market reflects broader technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Initially dominated by basic analog gauges, the market has transitioned significantly toward digital solutions, driven by the demand for accuracy and user-friendly features. Early models were limited in functionality, primarily providing basic pressure readings. However, advancements in sensor technology and microelectronics have led to the development of sophisticated devices capable of offering real-time data, connectivity features, and enhanced durability.
The introduction of smart technology has further revolutionized the sector. Modern air pressure readers are now equipped with Bluetooth connectivity, enabling users to sync data with mobile applications for better monitoring and analysis. This evolution not only enhances user experience but also aligns with the growing trend of digitization across industries.
As the market continues to evolve, it is essential for international B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements and sourcing trends to make strategic purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
1. How do I choose the right air pressure reader for my business needs?
When selecting an air pressure reader, consider factors such as the measurement range, accuracy, and display type. For commercial applications, digital gauges often provide higher precision and easier readability. Assess the compatibility with your existing equipment and the environmental conditions where the gauges will be used. Additionally, evaluate the durability and build quality, especially for rugged applications in industries like automotive or manufacturing.
2. What are the key features to look for in a high-quality air pressure reader?
A high-quality air pressure reader should offer accuracy within ±1 PSI, a clear and easy-to-read display, and a robust design for longevity. Features like backlighting, automatic shut-off, and a rubberized grip can enhance usability. Consider additional functionalities such as dual pressure readings (e.g., PSI and bar) and the ability to measure both high and low pressures, particularly if your operations require versatility.
3. What is the typical lead time for air pressure reader orders in international trade?
Lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location, manufacturing capabilities, and shipping logistics. Typically, for international orders, you should expect a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks. This timeframe accounts for production, quality assurance, and shipping. Always confirm lead times with the supplier to align your inventory needs and operational timelines accordingly.
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for air pressure readers?
Minimum order quantities can differ by supplier and product type. For air pressure readers, MOQs typically range from 50 to 500 units, depending on the manufacturer and specific model. Higher MOQs may be negotiable, especially for repeat orders or long-term contracts. Communicate your needs clearly to suppliers to explore potential flexibility in MOQs.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
5. How can I vet suppliers for air pressure readers effectively?
To vet suppliers, conduct thorough research to assess their reputation and reliability. Look for certifications like ISO and reviews from other B2B clients. Request samples to evaluate product quality firsthand. Additionally, consider their capacity for customization, response times, and willingness to communicate. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who have a proven track record in your region can also enhance trust and reliability.
6. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing air pressure readers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of your business relationship. Common terms include advance payments, letters of credit, or net 30 to 60 days after shipment. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as partial payments upon order confirmation and the remainder upon receipt of goods. Ensure clarity on currency exchange rates and potential fees involved in international transactions.
7. What quality assurance measures should I consider when sourcing air pressure readers?
Quality assurance is crucial in ensuring the reliability of air pressure readers. Look for suppliers who conduct rigorous testing, including calibration and durability assessments. Request documentation of quality control processes and any third-party certifications. It’s also beneficial to establish a returns policy for defective products and to inquire about warranty terms to safeguard your investment.
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing air pressure readers?
Logistics are vital in international trade, impacting both cost and delivery timelines. Evaluate shipping methods (air vs. sea) based on urgency and budget. Understand customs regulations and potential duties in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Collaborate with freight forwarders or logistics companies experienced in your region to streamline the import process, ensuring that you can efficiently manage the supply chain from the supplier to your location.
Domain: autometer.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: AutoMeter offers a variety of professional-grade tire pressure gauges, including heavy-duty analog and digital options. These gauges provide accurate readings in small increments of 0.5 PSI, with a maximum measurement of 150 PSI. They are essential for maintaining proper tire inflation, improving handling, fuel economy, and tire durability for vehicles such as cars, bikes, trucks, SUVs, and motorc…
Domain: jacosuperiorproducts.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘ElitePro™ Tire Pressure Gauge – 60 PSI’, ‘price’: ‘$22.95’, ‘original_price’: ‘$49.99’, ‘features’: “Rated the ‘Easiest To Read’ Tire Pressure Gauge by Road & Track Magazine. Accurate. Durable. Reliable.”}, {‘name’: ‘ElitePro™ Tire Pressure Gauge – 100 PSI’, ‘price’: ‘$22.95’, ‘original_price’: ‘$49.99’, ‘features’: “Rated the ‘Easiest To Read’ Tire Pressure Gauge by Road & Track Magazi…
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, strategic sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking reliable air pressure readers. By prioritizing quality, accuracy, and durability, companies can ensure they invest in tools that not only meet their operational needs but also enhance overall productivity. The growing demand for precise measurement tools in diverse markets—including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—underscores the importance of sourcing from reputable manufacturers known for innovation and quality assurance.
Moreover, understanding regional specifications and compliance standards can significantly impact procurement success. Engaging with suppliers who offer versatile product ranges, such as digital and analog gauges tailored for various applications, can lead to better inventory management and reduced operational downtime.
As you look to strengthen your supply chain, consider leveraging strategic partnerships with trusted brands that provide comprehensive support and after-sales services. This proactive approach not only secures high-quality products but also fosters long-term collaboration.
Moving forward, seize the opportunity to enhance your sourcing strategies and ensure your business is equipped with the best air pressure readers available. Invest in tools that empower your operations and position your company for future growth in a competitive marketplace.

Illustrative image related to air pressure reader
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Illustrative image related to air pressure reader