In today’s fast-paced global marketplace, sourcing reliable solutions for vehicle maintenance, such as portable tire inflators, is crucial for B2B buyers across various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Flat tires can disrupt operations, leading to costly downtime and logistical challenges. Understanding how to effectively use a portable tire inflator not only mitigates these risks but also enhances overall fleet management and operational efficiency. This comprehensive guide covers everything from the different types of inflators available—such as 12-volt and battery-powered models—to their diverse applications in various industries.
Moreover, we delve into essential considerations for supplier vetting, ensuring that international buyers are equipped with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Factors such as cost, features, and compatibility with local vehicles will be examined, providing a holistic view of the market landscape. By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical steps, this guide enables businesses to maintain vehicle readiness and reliability, ultimately leading to improved safety and productivity on the road. Whether you’re a fleet manager or an automotive supplier, mastering the use of portable tire inflators is a valuable skill that can drive significant operational advantages.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12-Volt Tire Inflators | Connects to vehicle’s power outlet; compact design | Automotive repair shops, fleets | Pros: Convenient; Cons: Limited by vehicle battery. |
| Battery-Powered Tire Inflators | Operates independently; can double as a power bank | Remote service operations, outdoor events | Pros: Portable; Cons: Requires charging. |
| Digital Tire Inflators | Features digital pressure gauges and automatic shut-off | Tire service centers, logistics | Pros: Precise; Cons: May be pricier. |
| Heavy-Duty Tire Inflators | Designed for larger vehicles; higher pressure capacity | Construction, agriculture | Pros: High performance; Cons: Bulkier and more expensive. |
| Multi-Function Inflators | Includes attachments for various inflatables | Sports facilities, event organizers | Pros: Versatile; Cons: May lack tire-specific features. |
12-volt tire inflators are designed to plug into a vehicle’s power outlet, making them highly accessible for on-the-go tire inflation. These inflators are compact and lightweight, ideal for automotive repair shops and fleet operations where quick, efficient service is essential. Buyers should consider the inflator’s power draw and maximum pressure output, as these factors can influence performance, especially in high-demand environments.
Battery-powered tire inflators offer the advantage of portability, operating independently of a vehicle’s power source. This feature is particularly useful for businesses involved in remote service operations or outdoor events, where access to power may be limited. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate battery life, charging time, and whether the inflator can double as a power bank, enhancing its utility.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Digital tire inflators are equipped with advanced features like digital pressure gauges and automatic shut-off functions, ensuring precise inflation. These inflators are particularly suited for tire service centers and logistics companies, where accuracy in tire pressure is critical for vehicle safety and efficiency. Buyers should assess the ease of use and reliability of the digital components, which can justify a higher price point.
Heavy-duty tire inflators are engineered for larger vehicles such as trucks and construction equipment, offering higher pressure capacities. These inflators are essential for industries like construction and agriculture, where downtime due to tire issues can be costly. B2B buyers should consider the inflator’s size, weight, and durability, as these factors can impact portability and performance in demanding environments.
Multi-function inflators come with various attachments for inflating not just tires but also sports balls, air mattresses, and other inflatables. This versatility is advantageous for businesses in sports facilities and event organizing, where different types of equipment may need inflation. When selecting a multi-function inflator, buyers should ensure that it meets the necessary tire-specific requirements while providing the flexibility needed for additional tasks.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to use a portable tire inflator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair Shops | Quick tire inflation for customer vehicles during service | Enhances customer satisfaction by reducing wait times for tire service | Reliability and ease of use; compatibility with various vehicle types |
| Logistics and Transport | On-site tire maintenance for delivery and transport vehicles | Minimizes downtime and ensures fleet vehicles are always roadworthy | Portability, power source options, and inflation speed |
| Construction and Heavy Machinery | Inflation of tires on construction equipment and vehicles | Increases productivity by reducing equipment downtime due to flat tires | Durability for rugged environments and high-pressure capabilities |
| Agricultural Sector | Inflating tires on farm equipment and vehicles | Ensures operational efficiency and reduces the risk of delays in farming activities | Adaptability to various tire types and ease of transport |
| Sports and Recreation | Quick inflation for recreational vehicles, bicycles, and sports equipment | Improves user experience and safety during outdoor activities | Lightweight design, additional attachments for diverse inflatables |
In automotive repair shops, portable tire inflators are invaluable for providing quick service to customers experiencing tire issues. Repair technicians can rapidly inflate tires during routine maintenance or after repairs, significantly reducing customer wait times. For B2B buyers in this sector, reliability and compatibility with a variety of vehicle types are essential. The inflators should be durable enough to withstand daily use and easy to operate, ensuring that technicians can assist customers efficiently.
In the logistics and transport industry, portable tire inflators are crucial for maintaining the operational readiness of delivery vehicles. Fleet managers can ensure that their vehicles are always roadworthy by addressing tire pressure issues promptly, minimizing downtime. For international buyers, considerations such as the inflator’s portability, power source options, and inflation speed are vital. A lightweight and efficient inflator can be a game-changer for companies operating in regions with limited access to repair facilities.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
The construction sector relies heavily on portable tire inflators for maintaining the tires of heavy machinery and vehicles. Quick inflation capabilities can prevent costly delays on job sites caused by flat tires. B2B buyers in this field should focus on inflators that are robust and capable of handling high-pressure applications. Additionally, the inflators must be designed to perform well in rugged environments, ensuring they can withstand the demands of construction sites.
In agriculture, portable tire inflators are essential for maintaining the tires of various farming equipment and vehicles. Quick inflation ensures that farmers can continue their work without unnecessary interruptions, which is vital during critical planting and harvesting seasons. Buyers in this sector should look for inflators that can adapt to different tire types and are easily transportable across fields. The ability to operate in remote locations without the need for a power source can also be a significant advantage.
In the sports and recreation sector, portable tire inflators are used to quickly inflate tires on recreational vehicles, bicycles, and sports equipment. This capability enhances user experience and safety, particularly during outdoor activities where access to traditional air pumps may be limited. For B2B buyers, lightweight design and the availability of additional attachments for various inflatables are key considerations. Ensuring that the inflator is user-friendly and portable can significantly improve customer satisfaction in this industry.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those managing fleets or logistics, encounter issues with ensuring that tires are inflated to the correct pressure. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased fuel consumption, higher maintenance costs, and decreased safety on the road. The challenge becomes acute when drivers lack familiarity with how to properly use a portable tire inflator, risking over-inflation or misreading the pressure gauge. This can lead to significant operational inefficiencies and increased downtime, ultimately affecting the bottom line.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
The Solution: To tackle this issue, businesses should invest in portable tire inflators that come equipped with digital pressure gauges and automatic shut-off features. These advanced inflators allow users to set the desired pressure level based on the manufacturer’s specifications, which can usually be found on the driver’s door jamb or in the vehicle’s manual. Training sessions on the use of these inflators can be highly beneficial. Ensuring that all personnel understand how to read the gauge accurately and set the desired pressure before inflating can drastically reduce the likelihood of mismanagement. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can help to confirm that the inflators are functioning correctly and that all employees are equipped with the knowledge to use them effectively.
The Problem: For B2B buyers operating in regions with unreliable power sources, such as remote areas in Africa or South America, using a portable tire inflator can become a frustrating experience. Many inflators require a direct connection to a vehicle’s 12V outlet, and if the vehicle’s battery is low or the inflator draws too much power, it may fail to operate. This situation can lead to prolonged vehicle downtime and increased reliance on external roadside assistance services, which can be both costly and time-consuming.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, businesses should consider investing in battery-powered portable tire inflators that come with built-in rechargeable batteries. This flexibility allows for operation without relying on the vehicle’s power supply. When sourcing these inflators, it’s essential to look for models with a robust battery life and sufficient power output to ensure they can handle a range of tire sizes and pressures. Additionally, having a backup power solution, such as a portable jump starter or solar charger, can further enhance operational reliability in remote locations. Regular training on the maintenance and charging of these devices will also ensure they remain functional when needed most.
The Problem: Safety is a significant concern when using portable tire inflators, especially for businesses that have employees working in potentially hazardous environments, such as roadside assistance or transport logistics. Users may be unsure about the safety protocols when inflating tires, which could lead to accidents, such as blowouts or injuries from improperly handled equipment. The stress of operating in high-traffic areas can further exacerbate these safety issues, making it imperative that users are well-informed.
The Solution: To enhance safety when using portable tire inflators, businesses should develop comprehensive safety protocols that outline best practices for tire inflation. This includes training on inspecting tires for damage before inflation, choosing safe locations away from traffic, and ensuring that all personnel are aware of how to operate the inflator correctly. Providing personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety vests and cones can help create a safer working environment. Additionally, investing in inflators that have built-in safety features, such as automatic shut-off mechanisms and heat-resistant materials, can further protect users from accidents. Regular safety drills can also reinforce the importance of adhering to these protocols, ultimately promoting a culture of safety within the organization.
When selecting materials for portable tire inflators, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of materials directly impacts the performance, durability, and overall user experience of the inflator. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the construction of portable tire inflators: plastic, aluminum, rubber, and steel.
Key Properties: Plastic is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be molded into complex shapes. It typically has a moderate temperature tolerance, making it suitable for various environments.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Pros & Cons: The main advantages of plastic include its low cost and ease of manufacturing, which allows for mass production. However, plastic can be less durable than metal alternatives, especially under high-pressure conditions. Over time, exposure to UV light may cause degradation, particularly in outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are often used for housings and non-structural parts of inflators. They are generally compatible with air and other non-corrosive gases but may not withstand high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with regulations regarding plastic materials, such as REACH in Europe, which governs chemical safety. In regions like Africa and South America, local standards may also apply.
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. It can handle moderate pressures and is often used in high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its durability, which extends the lifespan of the inflator. However, aluminum can be more expensive than plastic and may require more complex manufacturing processes, leading to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is frequently used for the body of the inflator and components that require strength and heat dissipation. Its compatibility with air and non-corrosive gases makes it a suitable choice for tire inflation.
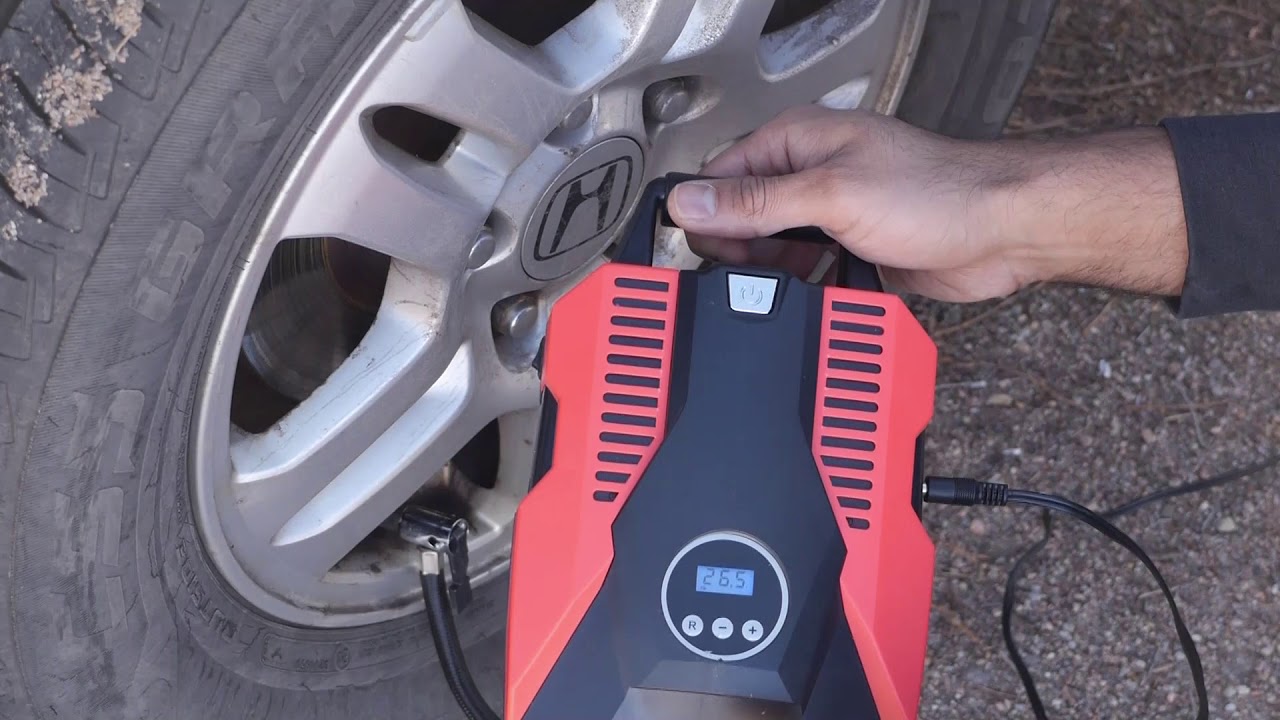

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum used in inflators meets international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, particularly regarding pressure ratings and safety. In markets like Germany, adherence to strict regulations is essential.
Key Properties: Rubber is flexible, has excellent sealing properties, and can withstand a wide range of temperatures. It is also resistant to abrasion and wear, making it ideal for components that experience friction.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of rubber is its ability to create airtight seals, which is critical for maintaining pressure. However, rubber can degrade over time due to exposure to heat and ozone, which may limit its lifespan.
Impact on Application: Rubber is commonly used for seals, hoses, and gaskets within the inflator. Its compatibility with air and other non-corrosive media makes it an ideal choice for tire inflation applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for rubber materials that comply with international standards, such as JIS in Japan and ISO standards globally. In regions with high temperatures, like parts of Africa and the Middle East, heat-resistant rubber is essential.
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high strength and durability, with excellent resistance to deformation under pressure. It can withstand high temperatures and is often used in heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of steel is its robustness, making it suitable for high-performance inflators. However, steel is heavier and more expensive than other materials, which may not be ideal for portable applications.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Impact on Application: Steel is typically used for high-pressure components, such as the inflator’s cylinder or housing. Its compatibility with air makes it a reliable choice for tire inflators.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that steel components meet relevant safety and performance standards, such as ASTM and ISO. In regions like Europe, compliance with environmental regulations regarding steel production is also critical.
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to use a portable tire inflator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Housing and non-structural parts | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under high pressure | Low |
| Aluminum | Body and heat-dissipating components | Durable and corrosion-resistant | Higher manufacturing costs | Medium |
| Rubber | Seals, hoses, and gaskets | Excellent sealing properties | Degrades over time with heat exposure | Medium |
| Steel | High-pressure components | High strength and durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the material selection process for portable tire inflators, considering performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
The manufacturing process of portable tire inflators involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Here’s a detailed breakdown of these stages:
The manufacturing of portable tire inflators begins with material selection. Common materials include high-grade plastics for the body, metals such as aluminum for the housing, and rubber for hoses and seals. Suppliers of these raw materials must adhere to strict quality standards to ensure durability and performance.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
During this stage, materials undergo rigorous inspections to verify their quality. This may involve checking for consistency in size, weight, and physical properties. Any discrepancies are addressed before the materials proceed to the next stage, ensuring that only the best materials are used in production.
The forming stage typically includes processes such as injection molding for plastic components and stamping for metal parts. For instance, the body of the inflator may be produced using injection molding, which allows for complex shapes and designs while maintaining uniform thickness.
Key techniques in this phase also include die casting for metal components and extrusion for rubber hoses. Each method is chosen based on the specific requirements of the inflator’s design and functionality. Precision in this stage is critical, as any flaws in forming can lead to issues in the assembly stage.
Once all components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage involves integrating the electrical systems, such as the motor and pressure gauge, with the mechanical parts.
Automated assembly lines are increasingly common in this phase to enhance efficiency and accuracy. However, manual assembly is still prevalent, especially for quality-sensitive components. Workers are trained to follow strict assembly protocols to minimize defects and ensure all parts fit together seamlessly.
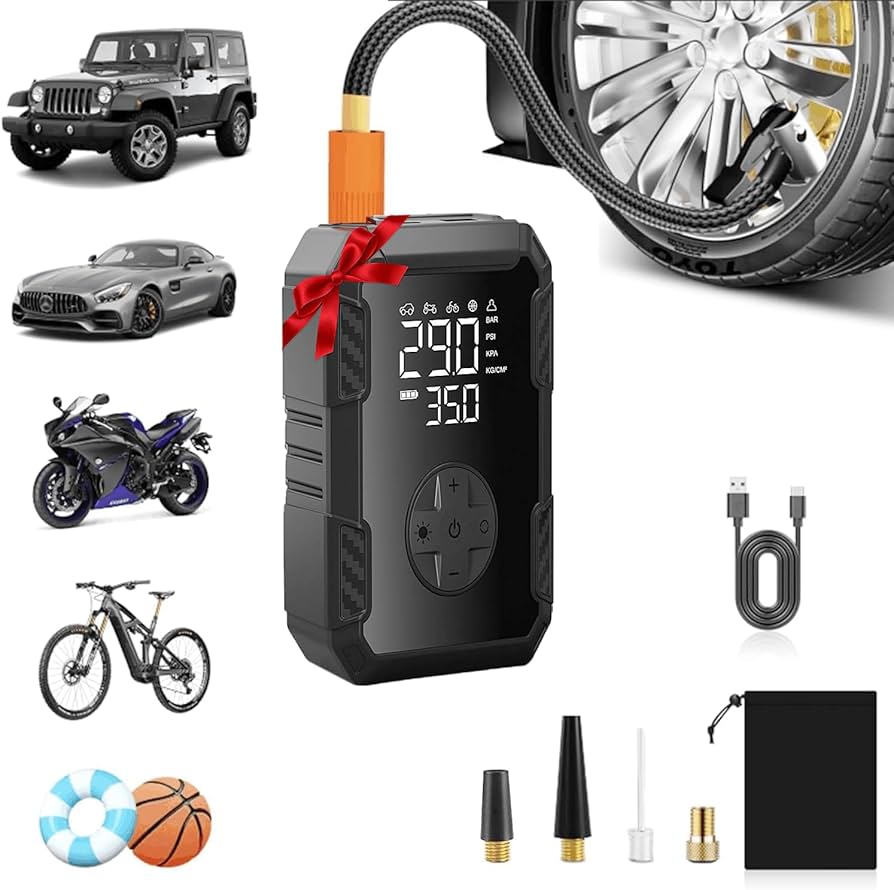

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
The finishing stage involves several processes, including painting, surface treatment, and quality checks. This stage not only enhances the aesthetics of the product but also improves durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Finishing processes may include powder coating or anodizing metal parts to prevent corrosion. Additionally, the final assembly is subjected to quality control inspections to ensure all components are functioning correctly and meet the specified standards.
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for portable tire inflators, where safety and reliability are paramount. Here are key QA practices and standards relevant to this industry.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Manufacturers of portable tire inflators often comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. This certification ensures that companies maintain high standards in their manufacturing processes and customer service.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) for products used in petroleum contexts may apply. These certifications indicate that products have been tested and meet rigorous safety and performance standards.
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial phase focuses on raw materials. Suppliers are evaluated based on their ability to deliver materials that meet specifications. Random sampling and testing are common practices to ensure quality.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. This includes checking dimensions, functionality, and assembly accuracy.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each portable tire inflator undergoes a final inspection. This includes functional testing, where the inflator is checked for performance against specified pressure levels and operational features.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are some strategies:

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers provides insight into their manufacturing practices and quality assurance protocols. Audits should focus on evaluating compliance with international standards, examining production processes, and reviewing record-keeping practices.
Buyers should request comprehensive documentation from suppliers, including quality control reports, test results, and certifications. This documentation provides evidence of the supplier’s commitment to maintaining high-quality standards.
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These services can perform inspections at various stages of production, ensuring that products meet the required standards before they are shipped.
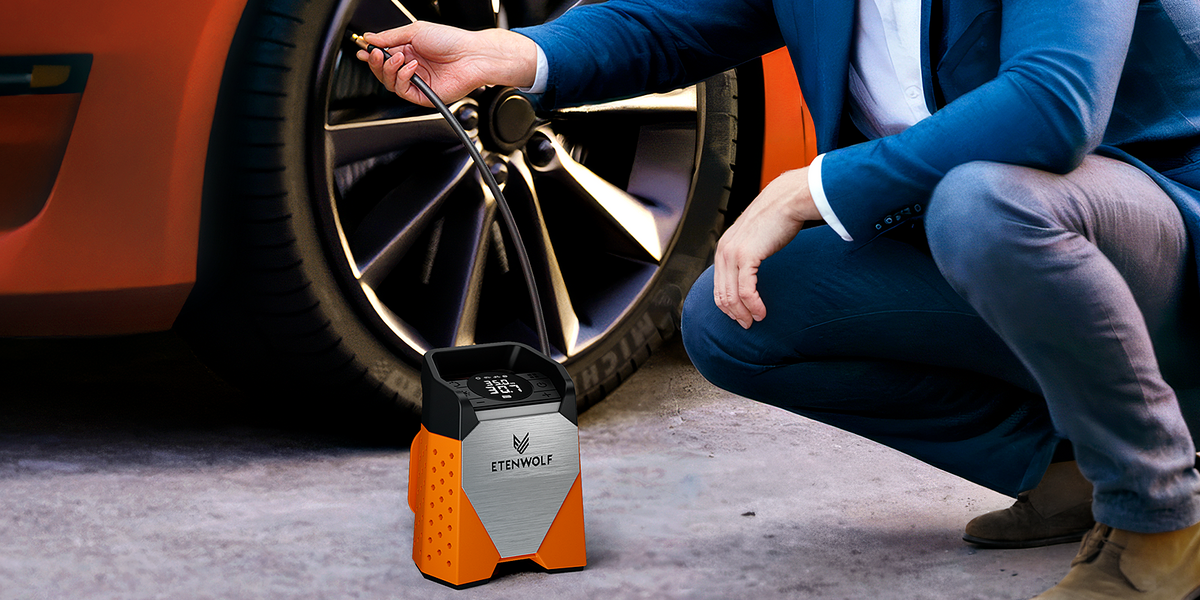

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
B2B buyers from different regions face unique challenges when it comes to quality control in portable tire inflators. Here are some nuances to consider:
Different countries may have specific regulations regarding product safety and quality. Buyers must be aware of these regulations to ensure that the products they import comply with local laws. For instance, products sold in the European market must meet CE marking requirements, while those in the United States may require compliance with the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS).
Cultural differences can impact communication and the understanding of quality expectations. It’s essential for buyers to establish clear lines of communication with suppliers and ensure that quality requirements are thoroughly understood and documented.
Logistical challenges, such as shipping delays and customs inspections, can also affect product quality upon arrival. Buyers should consider these factors when planning their procurement strategies and set realistic timelines for product delivery.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with portable tire inflators, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure product reliability and safety for their customers.
This guide aims to equip B2B buyers with essential steps to effectively utilize a portable tire inflator. Understanding how to operate this tool not only ensures optimal tire performance but also enhances vehicle safety and efficiency. By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process and maximize the utility of portable tire inflators in your fleet or service offerings.
Before using a portable tire inflator, it’s crucial to know the specific tire pressure required for your vehicles. This information can typically be found in the owner’s manual or on the driver’s door jamb. Understanding these specifications is vital to avoid over-inflation or under-inflation, both of which can lead to safety issues and increased operational costs.
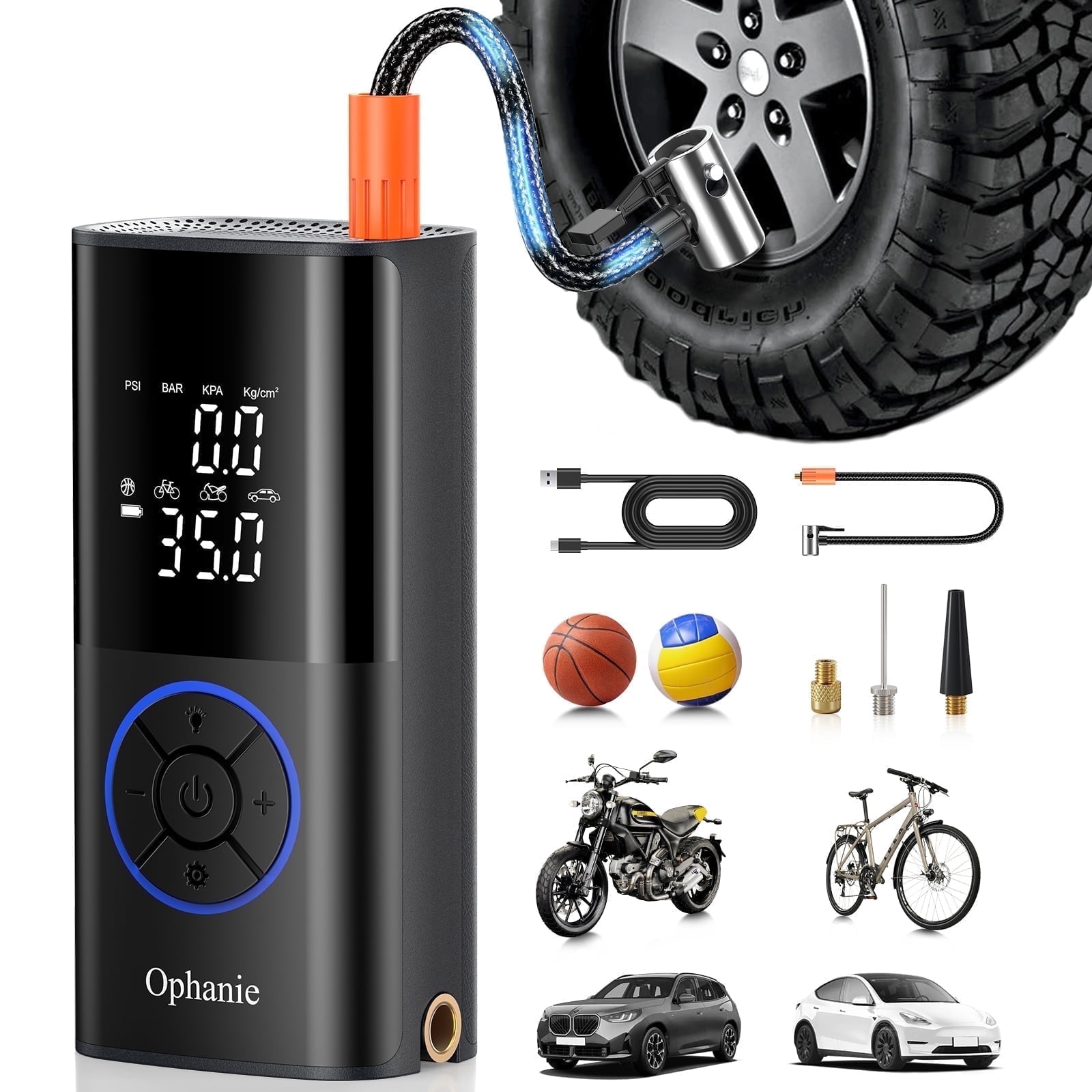
Choose between 12-volt inflators that plug into the vehicle’s power outlet and battery-powered models that offer more flexibility. Each type has its pros and cons, depending on your operational needs. For instance, battery-powered inflators can be used without relying on the vehicle’s power, which is beneficial in remote locations.
Look for essential features that enhance usability and efficiency. Key features may include:
– Digital pressure gauge for accurate readings.
– Automatic shut-off functionality to prevent over-inflation.
– Built-in LED lights for use in low-light conditions.
These features not only improve the user experience but also ensure safety during operation.
Ensure that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality assurance processes in place. This can include ISO certifications or compliance with international safety standards. Valid certifications can provide peace of mind regarding product reliability and performance.
Before finalizing a purchase, request demonstrations or samples of the inflators. This allows your team to assess the ease of use and functionality in real-world scenarios. Testing the product can also highlight any potential issues that may not be evident from specifications alone.
Review the warranty and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A strong warranty reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in their product and provides a safety net for your investment. Additionally, ensure that the supplier offers responsive customer service to assist with any issues that may arise post-purchase.
When procuring portable tire inflators for a fleet or multiple locations, inquire about bulk purchase discounts. Many suppliers are willing to offer reduced rates for larger orders, which can significantly lower overall costs. This is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to standardize their tools across various vehicles.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing portable tire inflators, ultimately contributing to improved vehicle maintenance and operational efficiency.
When sourcing portable tire inflators, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing portable tire inflators significantly impact costs. High-grade plastics and metals, along with advanced electronic components, will increase material costs but often result in better durability and performance.
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Asia and Latin America, can offer competitive pricing. However, quality assurance and skilled labor might come at a premium.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers.
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for manufacturing specialized or customized inflators can be significant. For mass production, these costs are amortized over larger volumes, making per-unit costs lower.
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures that the inflators meet safety and performance standards, which is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction. Higher QC costs can lead to better products and fewer returns.
Logistics: Shipping costs, which can vary widely based on the destination and shipping method, are a critical component of total costs. International buyers should consider freight charges, customs duties, and handling fees, particularly when sourcing from overseas suppliers.
Margin: The manufacturer’s profit margin will affect the final price. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge whether a quote is competitive.
Several factors can influence the pricing of portable tire inflators:
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on order volume. Larger orders can significantly reduce the per-unit price, making it beneficial for businesses to consolidate purchases.
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as unique design elements or additional functionalities, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the added expense.
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects pricing. High-quality, durable materials may come at a higher price but can result in lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to longevity and reduced maintenance needs.
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international safety and quality standards typically command higher prices. Certifications can also enhance marketability, particularly in regions with stringent regulations.
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their brand equity, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipping can affect total costs. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risks during transit.
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to maximize cost efficiency when sourcing portable tire inflators:
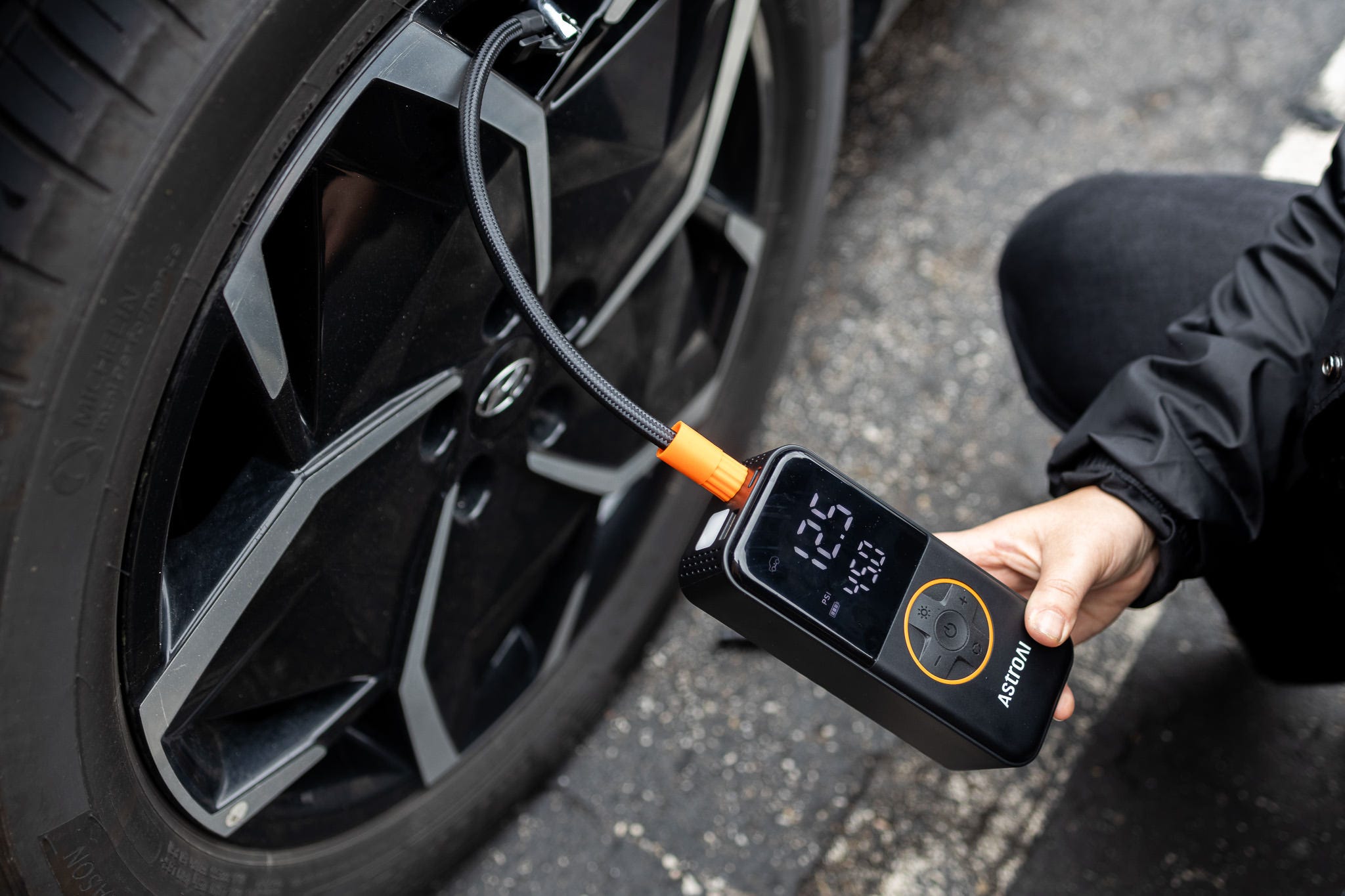

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially when dealing with larger orders. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing that they are willing to share for committed buyers.
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, warranty, and potential savings from using high-quality inflators that require fewer repairs.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import tariffs is vital. These factors can significantly impact the final cost.
Supplier Research: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Assess their production capabilities, quality control measures, and past performance. This diligence can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
Trial Orders: Before committing to large quantities, consider placing smaller trial orders to evaluate product quality and supplier reliability.
By understanding the cost components and price influencers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies for portable tire inflators, ensuring they receive quality products at competitive prices.
In the realm of tire maintenance, having reliable solutions is paramount for ensuring safety and efficiency. While portable tire inflators are popular for their convenience and ease of use, there are alternative methods that can also effectively address tire inflation needs. This section compares the use of portable tire inflators with two other viable solutions: traditional air compressors and manual hand pumps. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | How To Use A Portable Tire Inflator | Traditional Air Compressor | Manual Hand Pump |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Quick inflation, limited by power source | High power, suitable for heavy-duty tires | Labor-intensive, slower inflation |
| Cost | $30 – $200, varies by features | $100 – $500, typically higher | $10 – $50, budget-friendly |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, plug-and-play operation | Requires setup and often a power outlet | Requires physical effort and technique |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; check for leaks | Moderate; regular checks needed | Minimal; occasional cleaning |
| Best Use Case | Emergency tire inflation on the go | Regular maintenance for multiple vehicles | Light use for bicycles or sports equipment |
Traditional air compressors provide a powerful alternative for tire inflation, especially for commercial fleets or larger vehicles. These devices typically offer a higher airflow rate, making them suitable for heavy-duty tires and quicker inflation times. However, they often require a dedicated power source and may involve more complex setup processes. Additionally, traditional compressors can be more expensive to purchase and maintain compared to portable inflators. They are ideal for businesses that frequently service multiple vehicles or require robust tire maintenance solutions.
Manual hand pumps are the most budget-friendly option for inflating tires. They are simple to use and portable, making them an excellent choice for light applications such as inflating bicycle tires or sports equipment. However, they require significant physical effort and time, making them less suitable for larger vehicle tires or situations requiring quick inflation. While maintenance is minimal, the effectiveness of a manual pump significantly decreases with larger tires or when high pressure is needed. This method is best for businesses with limited budgets or those that need an occasional inflation solution without relying on power sources.
When selecting a tire inflation solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the types of vehicles they manage. Portable tire inflators offer convenience and ease of use, making them suitable for emergency situations. In contrast, traditional air compressors provide higher performance for regular maintenance of larger fleets, while manual hand pumps serve as a cost-effective option for light-duty applications. By evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their tire maintenance processes and contribute to overall operational efficiency.
Understanding the technical specifications of portable tire inflators is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting products that meet specific operational needs. Here are some key properties to consider:
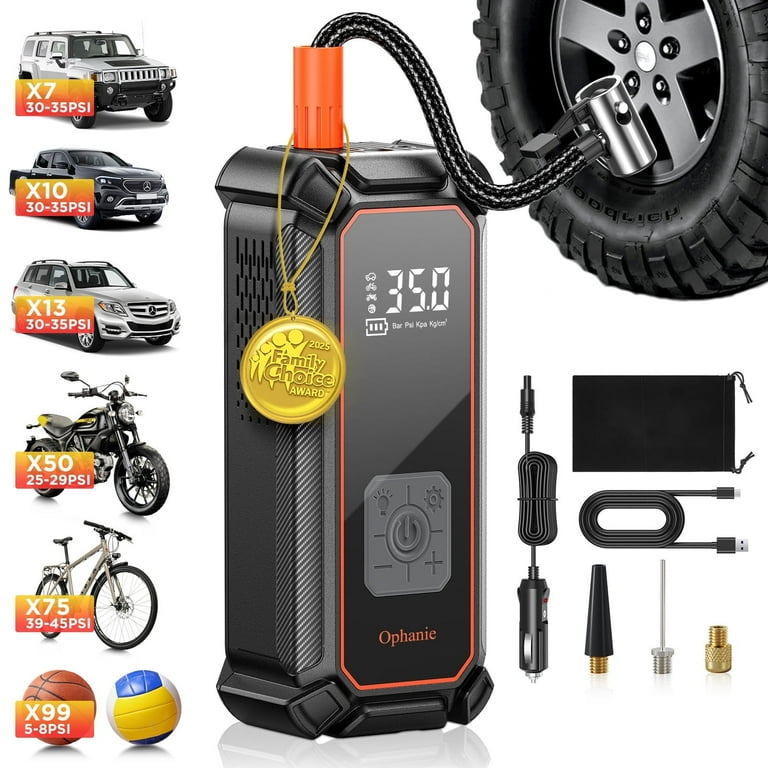
Portable tire inflators typically operate on either a 12-volt power supply (from a vehicle) or a rechargeable battery. The choice of power source affects the inflator’s portability and usability in various situations. B2B buyers should consider the intended use; for frequent roadside assistance, a 12-volt model may be more suitable, while battery-powered options provide greater flexibility in remote locations.
The maximum pressure capacity, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates how much air the inflator can deliver. Most passenger car tires require a pressure of around 30-35 PSI, but larger vehicles may need higher pressures. Selecting an inflator with an appropriate PSI rating is critical to ensure it can handle the demands of different tire types, particularly in regions with diverse vehicle usage.
The inflation speed, often measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), determines how quickly the inflator can fill a tire. Faster inflation speeds are advantageous for businesses that may need to service multiple vehicles quickly. Buyers should evaluate this specification based on their operational volume and urgency of service.
The length of the hose and the type of fittings included can significantly affect usability. A longer hose provides more flexibility in reaching the tire valve, especially for larger vehicles. Additionally, compatibility with various tire valve types is essential to avoid the need for additional adapters, which can complicate the inflation process.
The materials used in the construction of a tire inflator affect its longevity and reliability. Durable plastics and metal components can withstand the rigors of frequent use, making them ideal for businesses that rely on these tools. Understanding material grades helps buyers choose products that offer the best value and performance over time.
Safety features such as automatic shut-off mechanisms and overheat protection are vital for preventing accidents and equipment damage. These features ensure that the inflator stops working once the desired pressure is reached, minimizing the risk of over-inflation. B2B buyers should prioritize inflators that incorporate these safety measures to protect both their investment and the end-users.
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms that buyers should know:
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of tire inflators, understanding which components are OEM can assure buyers of the quality and compatibility of the products they are purchasing.
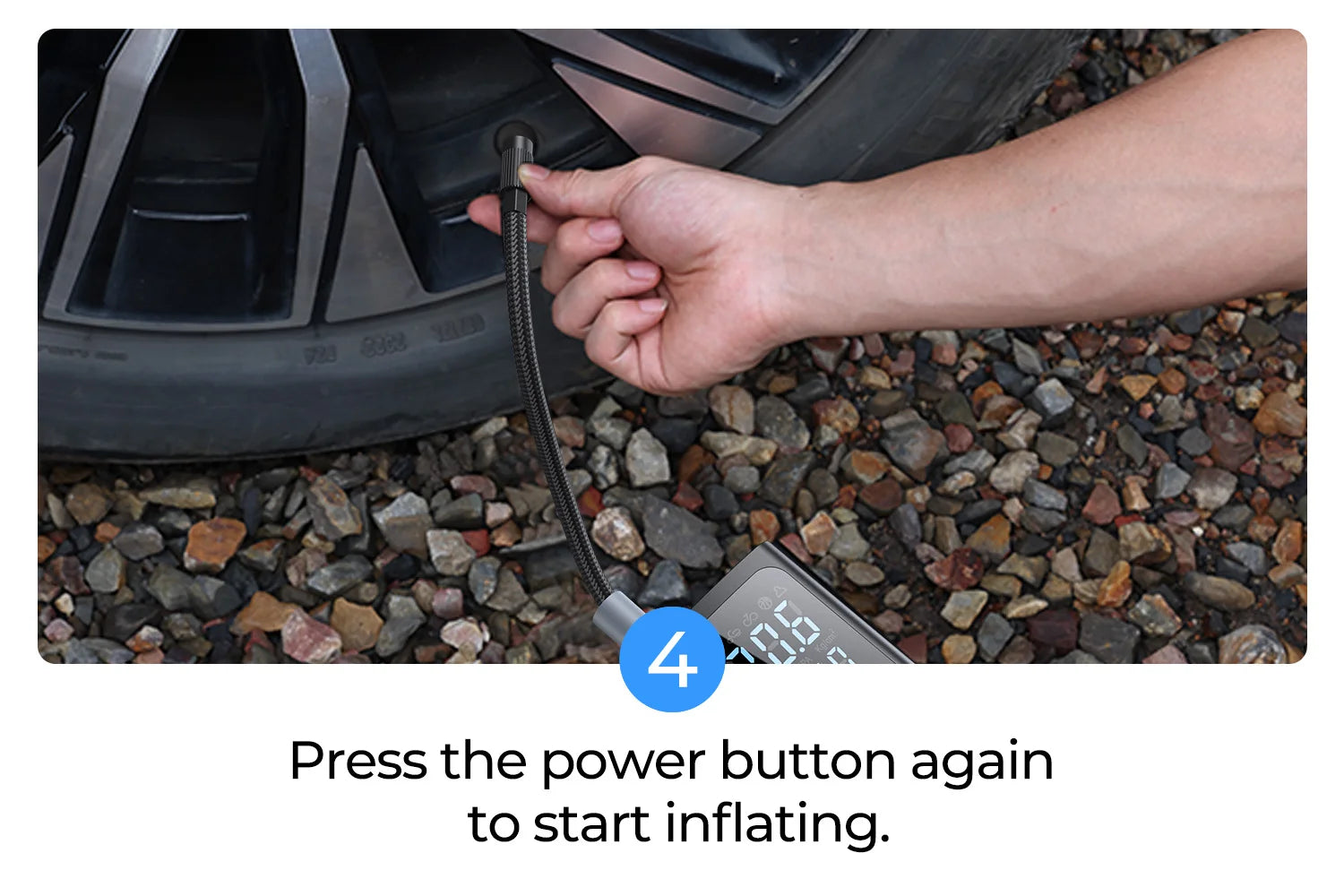
Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their operational needs and storage capabilities.
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price proposals from suppliers. This term is crucial for B2B buyers looking to compare costs and features across different manufacturers. An effective RFQ can streamline the purchasing process and lead to better pricing.
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers involved in cross-border trade, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
A warranty is a promise from the manufacturer regarding the repair or replacement of defective products. Buyers should be aware of the warranty terms to assess the risk associated with their purchase. Additionally, service agreements can provide ongoing support and maintenance for tire inflators, ensuring long-term reliability.
By grasping these essential properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
The portable tire inflator market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. As vehicle ownership rises in developing regions such as Africa and South America, the demand for convenient automotive solutions is on the rise. The increasing awareness of vehicle maintenance and safety is leading to a heightened focus on proper tire care, making portable inflators essential tools for both individual consumers and businesses in the automotive sector. Furthermore, the integration of technology in these devices, such as smart pressure monitoring and digital displays, is appealing to tech-savvy consumers and businesses alike.
Current trends indicate a shift towards battery-powered inflators, which offer greater versatility and ease of use. These models are not only used for car tires but also for bicycles and sports equipment, broadening the potential market. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices and materials in the production of portable tire inflators, responding to consumer demand for sustainable products. As B2B buyers explore sourcing options, they must consider suppliers that align with these emerging trends, ensuring they can meet the evolving needs of their customers.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern supply chain strategies, and the portable tire inflator sector is no exception. Environmental impact concerns are prompting manufacturers to seek ‘green’ certifications and utilize sustainable materials in their products. The production of inflators that minimize energy consumption and use recyclable materials not only caters to eco-conscious consumers but also enhances the brand reputation of B2B buyers.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction, as businesses are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. Buyers should look for suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and ethical labor practices. Collaborating with manufacturers who prioritize sustainability can help businesses reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more responsible marketplace. This shift not only meets consumer expectations but also aligns with global initiatives aimed at reducing waste and promoting sustainable practices.
The evolution of portable tire inflators can be traced back to the early days of automotive development. Initially, tire inflation was performed using manual pumps, which required significant physical effort and time. As vehicles became more widespread, the need for convenient and efficient inflation solutions led to the introduction of electric and battery-operated inflators in the late 20th century.
The modern portable tire inflator has transformed into a compact, user-friendly device that incorporates advanced features such as digital pressure gauges and automatic shut-off mechanisms. This evolution has not only improved consumer convenience but has also opened new avenues for B2B applications, allowing businesses in various sectors—such as automotive repair, rental services, and logistics—to offer enhanced services. As technology continues to advance, the future of portable tire inflators will likely include even more innovative features, catering to the changing demands of both consumers and businesses.
How do I solve a problem with my portable tire inflator not turning on?
If your portable tire inflator fails to turn on, first check the power source. Ensure that the inflator is securely connected to the vehicle’s 12V outlet or that the battery is charged if it’s a battery-operated model. Inspect the power cord for any visible damage. If the inflator still does not power on, consult the user manual for troubleshooting tips or consider contacting the manufacturer for support.
What is the best portable tire inflator for heavy-duty vehicles?
When sourcing a portable tire inflator for heavy-duty vehicles, look for models that offer a high PSI capacity, ideally above 150 PSI, and a robust motor for efficient inflation. Ensure the inflator has a long power cord or hose to reach the tire easily. Additionally, consider inflators with durability features, such as rugged housing or thermal overload protection, to withstand heavy use in various environments.
How do I choose the right supplier for portable tire inflators?
Selecting the right supplier involves evaluating their product range, quality certifications, and customer service reputation. Request samples to assess the inflators’ performance and durability. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes, compliance with international safety standards, and after-sales support. It’s beneficial to read reviews from other buyers and check for any partnerships or certifications that indicate reliability.
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for portable tire inflators?
MOQs for portable tire inflators can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific model. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units for bulk orders. It’s important to discuss your needs with the supplier and negotiate terms that suit your business requirements, especially if you’re testing a new product line or entering a new market.
What payment terms are typically available for international purchases of tire inflators?
Payment terms for international purchases can include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may also accept partial payments with a balance due upon shipment. It’s crucial to clarify these terms in advance and ensure that they align with your cash flow capabilities to avoid any disruptions in the transaction process.
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for portable tire inflators?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and quality control processes from the supplier. Ask for certifications such as ISO or CE, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Consider implementing a third-party inspection before shipment to verify the inflators meet your quality expectations, especially if sourcing from overseas manufacturers.
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing tire inflators?
When importing portable tire inflators, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Evaluate the supplier’s shipping methods and whether they can handle logistics or if you need to arrange it separately. Additionally, ensure that all import documentation is correctly prepared to avoid delays at customs. Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding product imports to ensure compliance.
Can portable tire inflators be customized for branding purposes?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for portable tire inflators, such as adding your company logo or specific color schemes. Customization may require a minimum order quantity and could affect the production timeline. Discuss your branding needs with the supplier early in the negotiation process to understand the available options and any additional costs involved.
Could not verify enough suppliers for how to use a portable tire inflator to create a list at this time.

Illustrative image related to how to use a portable tire inflator
In summary, understanding how to effectively use a portable tire inflator is essential for businesses that rely on vehicle fleets or logistics operations. By ensuring that tires are properly inflated, companies can enhance fuel efficiency, extend tire lifespan, and improve overall safety on the road. The strategic sourcing of high-quality inflators tailored to your operational needs can lead to significant cost savings and operational reliability.
As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to evaluate not only the features of portable tire inflators—such as power source, pressure capacity, and portability—but also the after-sales support and warranty options from suppliers. Investing in reliable inflators is a step towards a proactive maintenance strategy that minimizes downtime and enhances productivity.
Looking ahead, consider establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide consistent access to the tools necessary for maintaining your fleet. Take action today to secure the best portable tire inflators for your business needs, ensuring that your operations remain efficient and your vehicles safe on the road.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.