In the fast-paced world of logistics and transportation, ensuring optimal truck tire inflation pressure is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of fleet management. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets like Nigeria and Brazil, the challenge of sourcing reliable and efficient tire inflation solutions can significantly impact safety, fuel efficiency, and overall operational costs. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by providing in-depth insights into various tire inflation systems, their applications across different vehicle types, and best practices for maintaining tire pressure under varying conditions.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the types of tire inflation systems available, including manual and automated options, and delve into supplier vetting processes to help you identify reputable manufacturers. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations and the long-term benefits of maintaining proper tire pressure, such as improved fuel efficiency and reduced wear and tear on tires. By equipping buyers with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance the safety and sustainability of your fleet operations. Whether you are navigating the complexities of the African market or seeking solutions in Europe and the Middle East, understanding truck tire inflation pressure is essential for optimizing your logistics strategy and achieving competitive advantage.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Inflation Pressure | Based on vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. | General freight transport, logistics. | Pros: Ensures safety and performance. Cons: May not account for load variations. |
| Load-Specific Inflation | Adjusted based on the weight of the load being carried. | Heavy-duty hauling, construction. | Pros: Optimizes tire life and performance. Cons: Requires regular monitoring and adjustment. |
| Temperature-Adjusted Pressure | Considers ambient and operating temperatures affecting PSI. | Long-haul trucking, seasonal operations. | Pros: Enhances safety and fuel efficiency. Cons: Complexity in monitoring temperature changes. |
| Nitrogen Inflation | Uses nitrogen instead of air, reducing pressure loss. | Specialty fleets, high-performance transport. | Pros: Longer tire life, less frequent inflation. Cons: Higher initial cost and availability. |
| TPMS-Integrated Inflation | Utilizes Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems for real-time data. | Fleet management, safety-focused operations. | Pros: Immediate alerts for pressure changes. Cons: Can be costly to implement and maintain. |
Standard inflation pressure refers to the recommended tire pressure set by the vehicle or tire manufacturer. This baseline ensures optimal performance and safety for general freight transport and logistics operations. Buyers should consider the manufacturer’s specifications as a starting point; however, this method may not address variations in load or road conditions, potentially leading to inefficiencies.
Load-specific inflation adjusts tire pressure according to the weight being carried. This approach is crucial for heavy-duty hauling or construction applications, where loads can significantly fluctuate. By tailoring tire pressure to the actual load, businesses can enhance tire longevity and performance. Buyers must monitor load weights consistently to ensure proper inflation, adding a layer of complexity to tire management.
Temperature-adjusted pressure takes into account the effects of ambient and operating temperatures on tire inflation. This method is particularly relevant for long-haul trucking and seasonal operations, where temperature variations can be significant. Properly managing tire pressure according to temperature can enhance safety and fuel efficiency. Buyers need to implement processes to regularly check and adjust tire pressure as temperatures change, which may require additional training for staff.
Nitrogen inflation involves filling tires with nitrogen rather than regular air, which helps reduce pressure loss over time. This technique is beneficial for specialty fleets or high-performance transport, as it can lead to longer tire life and less frequent inflation needs. However, the higher initial cost and limited availability of nitrogen filling stations could deter some buyers, making it essential to evaluate the long-term savings versus initial investment.
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) integrate technology to provide real-time tire pressure data, alerting fleet managers to any changes. This approach is vital for safety-focused operations and enhances fleet management efficiency. While the immediate alerts help prevent issues before they escalate, the cost of installation and maintenance can be significant. Buyers must weigh the benefits of improved safety and reduced downtime against the financial implications of implementing such systems.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of truck tire inflation pressure | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Freight | Monitoring and adjusting tire pressure for fleet vehicles | Enhanced safety and reduced fuel consumption | Compatibility with various tire types and sizes |
| Agriculture | Maintaining tire pressure for agricultural trucks | Improved efficiency in transporting goods | Ability to withstand varying load conditions |
| Construction | Ensuring proper tire inflation on heavy machinery | Minimization of downtime and operational costs | Availability of inflation monitoring systems |
| Mining | Tire pressure management for off-road vehicles | Increased tire lifespan and reduced maintenance | Robustness to handle harsh environments |
| Public Transport | Regular tire pressure checks for buses and coaches | Enhanced passenger safety and comfort | Compliance with local safety regulations |
In the logistics and freight industry, maintaining proper tire inflation pressure is crucial for fleet efficiency. Regular monitoring can prevent tire blowouts, which can lead to costly delays and accidents. Businesses must ensure that their tire pressure management systems are compatible with various tire types and sizes to accommodate different vehicles in their fleet. This is particularly important for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can vary significantly.
Agricultural trucks often carry heavy loads over uneven terrain, making accurate tire inflation essential for optimal performance. Proper inflation helps in maintaining traction and stability, which is vital for transporting goods efficiently. Buyers in this sector should consider tires that can handle varying load conditions and ensure that their inflation systems are robust enough to manage the demands of agricultural operations in diverse climates, particularly in regions like Brazil and Nigeria.
In the construction sector, heavy machinery relies on proper tire inflation to function effectively. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased wear and tear, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. Ensuring that tires are adequately inflated can minimize operational costs and enhance productivity. Buyers should look for comprehensive tire pressure monitoring systems that provide real-time data, which is essential for maintaining equipment in the field, especially in remote locations.
In mining, the harsh environment places significant stress on vehicles, making tire pressure management critical. Correct inflation extends tire lifespan and reduces the frequency of maintenance, which is crucial in an industry where equipment reliability is paramount. Buyers must source durable tires designed for off-road conditions and invest in pressure monitoring systems that can withstand rugged environments, ensuring consistent performance in challenging terrains.
For public transport systems, maintaining the correct tire inflation pressure is vital for passenger safety and comfort. Regular checks can prevent accidents caused by tire failure and improve fuel efficiency, which is a significant operational cost. Buyers in this sector should ensure compliance with local safety regulations and invest in tire pressure monitoring systems that can provide alerts for immediate action, particularly in regions with fluctuating weather conditions.
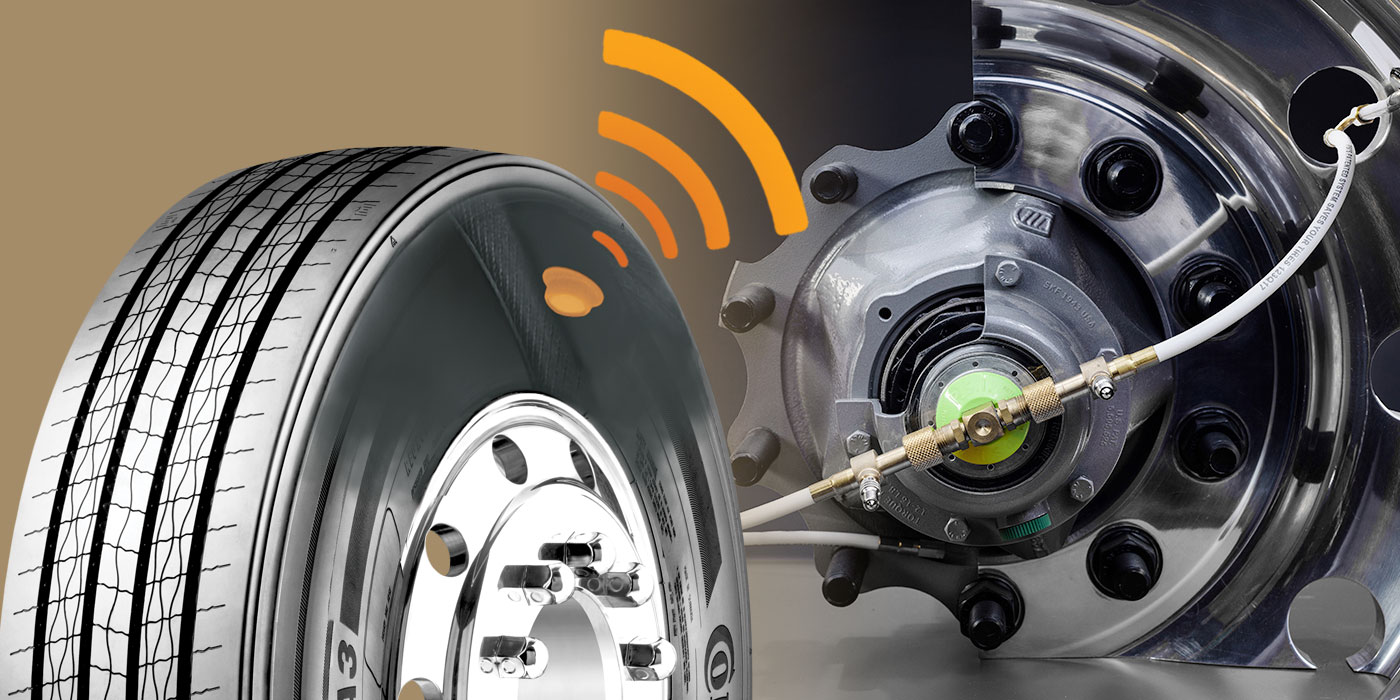

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the trucking industry face the challenge of inconsistent tire pressure monitoring across their fleet. This inconsistency often results from relying solely on manual checks, which can be infrequent and prone to human error. Without accurate, real-time tire pressure data, companies may experience increased fuel consumption, higher maintenance costs, and a greater risk of tire blowouts. This not only affects operational efficiency but can also lead to delays in deliveries and dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To combat this issue, B2B buyers should invest in Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) that provide real-time data and alerts. Implementing a TPMS can ensure that all tires are regularly monitored, allowing fleet managers to make informed decisions about tire maintenance. Furthermore, training staff to understand the importance of tire pressure and how to interpret TPMS data can enhance operational efficiency. Regularly reviewing and calibrating the system according to manufacturer guidelines will ensure its reliability, thereby reducing the likelihood of costly tire-related incidents.
The Problem: Buyers often struggle with the impact of temperature fluctuations on tire performance, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions. For example, a fleet operating in Brazil may face soaring temperatures during the day, leading to increased tire pressure, while cooler nights can cause pressure to drop. This inconsistency can lead to either over-inflation or under-inflation, both of which compromise safety and efficiency. Over-inflated tires can wear unevenly and increase the risk of road damage, while under-inflated tires significantly reduce fuel efficiency.
The Solution: A proactive approach involves educating fleet managers about the relationship between temperature and tire pressure. Buyers should establish a routine for checking tire pressures at different times of the day, ideally when tires are cold. Additionally, utilizing a tire pressure adjustment system that accounts for temperature variations can greatly enhance tire longevity. Fleet operators should also consider investing in nitrogen inflation systems, which are less affected by temperature changes compared to regular air. This can help maintain optimal tire pressure more consistently.
The Problem: Many buyers lack a comprehensive understanding of how tire load capacities affect inflation pressure, leading to incorrect tire specifications. This is particularly common among fleets operating in diverse terrains and with varying load requirements. Without adequate knowledge, buyers may either over-inflate or under-inflate tires based on the wrong assumptions, resulting in tire damage, safety hazards, and increased operational costs.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
The Solution: To address this knowledge gap, B2B buyers should prioritize training programs that focus on tire specifications, including load capacities and the corresponding inflation pressures. It is essential to understand the manufacturer’s guidelines as well as to weigh each vehicle’s load accurately. Buyers can also utilize load and inflation tables provided by tire manufacturers to ensure proper tire selection and inflation based on specific load conditions. Regular consultations with tire experts can further enhance understanding and ensure that the fleet operates at maximum efficiency, ultimately reducing costs and improving safety.
When considering materials for truck tire inflation pressure systems, several options stand out due to their unique properties and performance characteristics. Below, we analyze four common materials: rubber, steel, aluminum, and composite materials. Each material has distinct advantages and drawbacks that can significantly impact the overall performance and suitability for specific applications.
Rubber is the most widely used material in tire manufacturing due to its excellent elasticity and flexibility. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various operating conditions. Rubber’s inherent properties allow it to maintain a tight seal, which is crucial for preventing air loss.
Pros: Rubber is durable and can handle extreme conditions, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, which keeps costs low for bulk buyers.
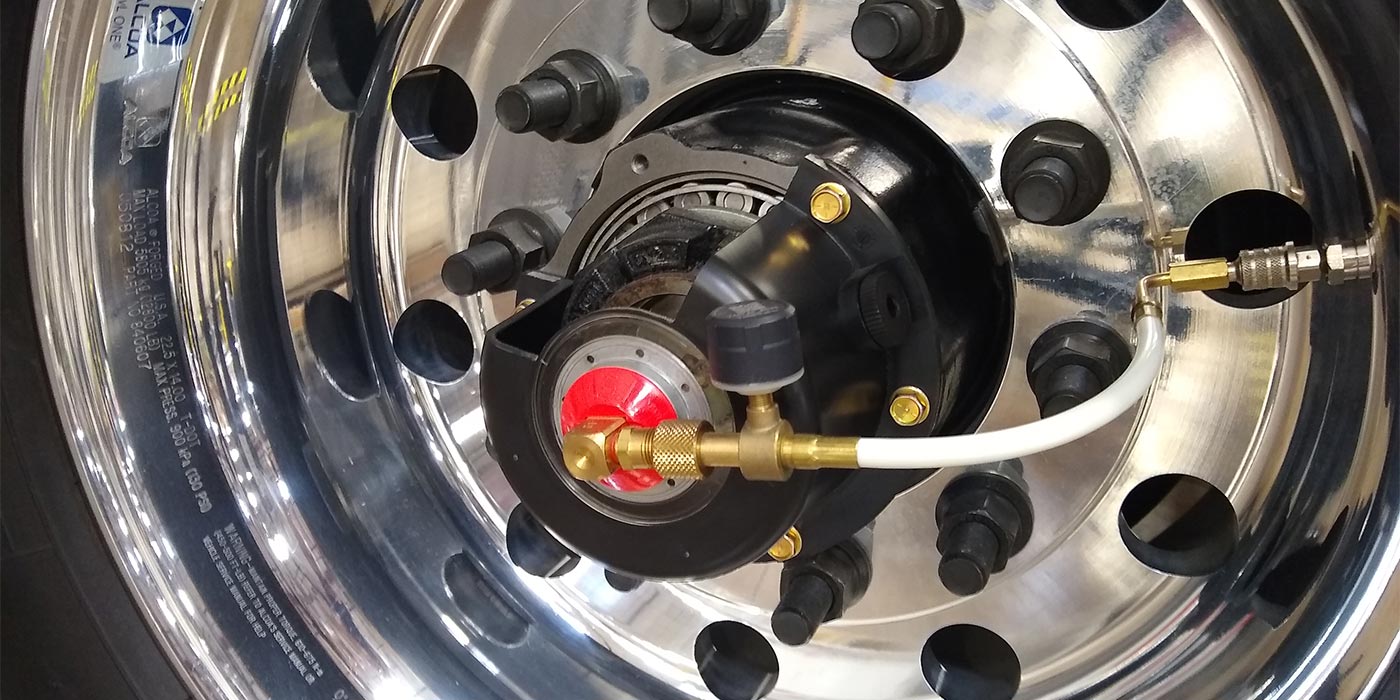

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Cons: The primary limitation of rubber is its susceptibility to degradation from ozone and UV exposure, which can lead to premature failure. Additionally, rubber may not perform as well in extremely high temperatures compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: Rubber is compatible with most tire inflation media, including air and nitrogen. However, it requires regular inspection to ensure it remains in good condition.
Steel is often used in tire rims and pressure monitoring systems due to its high strength and durability. It can withstand significant mechanical stresses and is resistant to deformation under load.
Pros: Steel provides excellent pressure retention and is highly resistant to punctures and tears. Its strength makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, particularly in commercial trucking.
Cons: The main drawback of steel is its weight, which can affect fuel efficiency. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which can compromise its integrity over time.
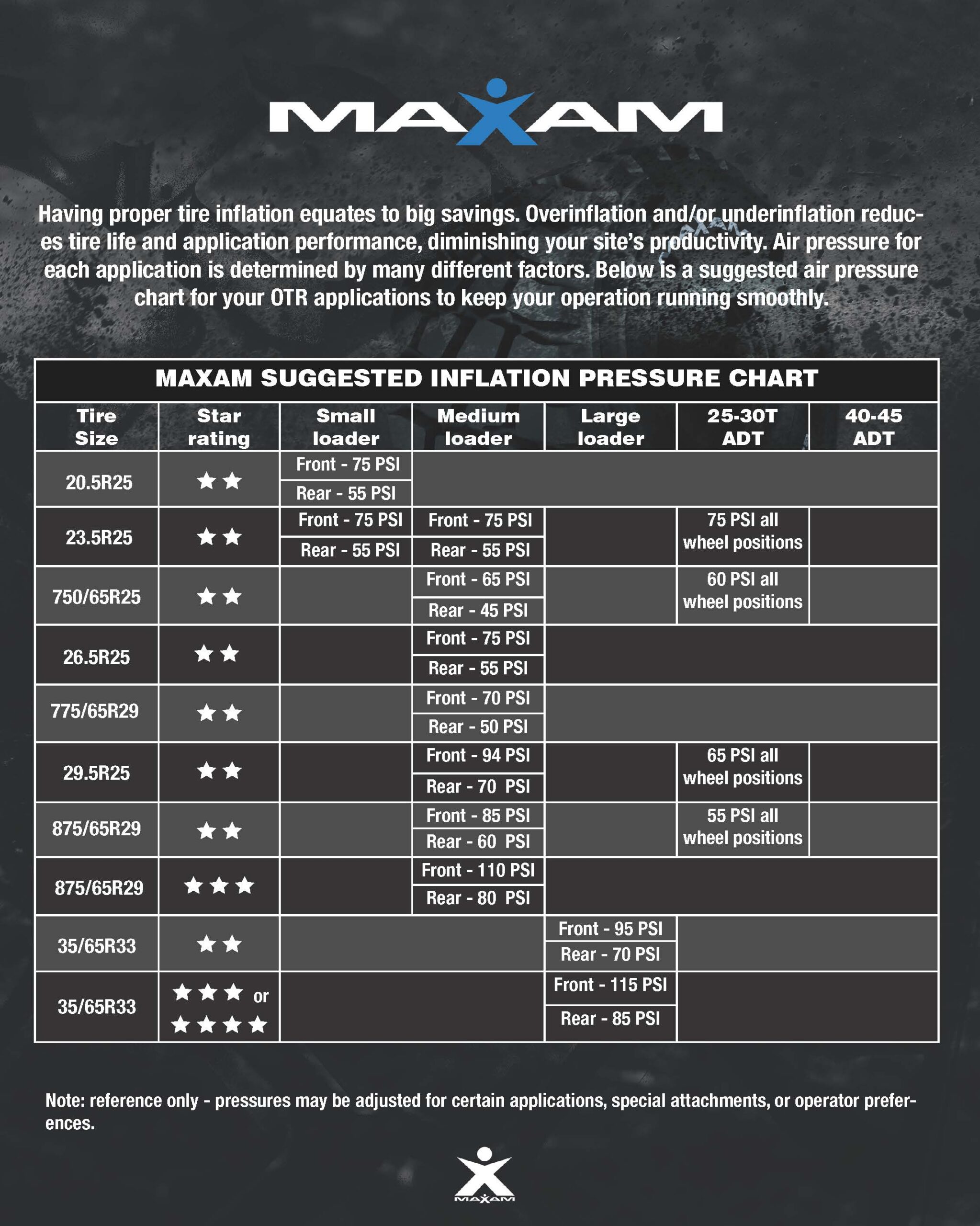
Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Impact on Application: Steel components can handle high-pressure conditions and are compatible with various inflation media. However, proper maintenance is essential to prevent corrosion, especially in humid or coastal environments.
Aluminum is increasingly being used for tire rims and inflation systems due to its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance. It offers a good balance between strength and weight, making it a popular choice for modern trucking applications.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which can enhance fuel efficiency. It is also resistant to corrosion, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is not as robust as steel, making it more susceptible to deformation under extreme loads. Additionally, aluminum components can be more expensive than their steel counterparts.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various inflation media and is particularly beneficial in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments. Buyers should consider the trade-off between weight savings and potential strength limitations.
Composite materials, which combine different substances to achieve desirable properties, are gaining traction in tire inflation systems. They can be engineered to provide specific performance characteristics, such as enhanced strength-to-weight ratios.
Pros: Composites can be tailored for specific applications, offering excellent resistance to environmental factors and fatigue. They are often lighter than metals, contributing to improved fuel efficiency.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, not all composites are suitable for high-pressure applications, and careful selection is necessary.
Impact on Application: Composites can be designed for specific media compatibility, making them versatile for various inflation systems. However, buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards to guarantee safety and performance.
| Material | Typical Use Case for truck tire inflation pressure | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Tire seals and inner linings | Excellent elasticity and flexibility | Susceptible to ozone and UV degradation | Low |
| Steel | Rims and pressure monitoring systems | High strength and durability | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight rims and inflation components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less robust under extreme loads | High |
| Composite | Specialized inflation components | Tailored performance characteristics | Complex and potentially costly to produce | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the various materials used in truck tire inflation pressure systems, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
The manufacturing of truck tires involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets rigorous performance standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess suppliers and their capabilities.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
The first stage of tire manufacturing involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. Key components include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, fabric (such as polyester or nylon), and steel for the belts. These materials must meet specific quality standards to ensure durability and performance.
In this phase, manufacturers often conduct tests for material integrity and composition. This is vital, as variations in material quality can directly impact tire performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. B2B buyers should inquire about suppliers’ sourcing practices and material certifications to ensure adherence to international standards.
The next stage is the forming process, where raw materials are shaped into the tire structure. This involves creating the inner liner, body plies, belts, and tread. Advanced techniques such as extrusion and calendering are commonly used to ensure precise dimensions and uniformity.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
During this stage, manufacturers also perform in-process quality checks (IPQC) to monitor the consistency of the tire components. B2B buyers should ask about the machinery used and the precision of the forming techniques, as these factors affect the overall quality and reliability of the tires.
The assembly stage brings together all the components to form the final tire. This process involves layering the inner liner, body plies, belts, and tread in a specific order. The tire is then molded and cured in a press to achieve its final shape and characteristics.
The curing process is particularly crucial, as it determines the tire’s performance attributes, including elasticity and heat resistance. Manufacturers typically adhere to strict temperature and pressure guidelines during curing, and B2B buyers should verify that suppliers utilize modern, calibrated curing equipment.
After curing, tires undergo various finishing processes, including trimming, inspection, and marking. Quality control checks are performed at this stage to ensure that the tires meet the specified dimensional and performance standards. Tires are also marked with their specifications, including load capacity and inflation pressure.
B2B buyers should consider asking for detailed reports on the finishing processes, including any final quality checks that were conducted. This will provide insight into the level of care and precision taken in the manufacturing process.
Quality assurance in tire manufacturing is governed by several international standards, including ISO 9001, which focuses on maintaining a quality management system. Additionally, specific industry standards such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) apply to particular tire types and uses.
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with these international standards, as this compliance reflects a commitment to quality and safety. It is advisable to request documentation that verifies adherence to these standards.
Manufacturers typically implement a multi-tiered quality control system that includes several checkpoints:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. This step is crucial for ensuring that only high-quality materials are used.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various tests are conducted to monitor the quality of components as they are formed and assembled. This includes checks on dimensions, weights, and material properties.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the tires are finished, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure they meet all specifications. This includes visual inspections, pressure tests, and performance assessments.
B2B buyers should inquire about the frequency and rigor of these quality checks, as well as the specific testing methods employed.
Several common testing methods are employed to ensure tire quality:
Uniformity Testing: This assesses the tire’s roundness and balance, which are critical for safe and efficient performance.
Durability Testing: Tires undergo various stress tests to evaluate their performance under extreme conditions, including high speeds and heavy loads.
Inflation Pressure Testing: This measures how well the tire maintains its specified inflation pressure over time. It is essential for ensuring safety and performance.
Tread Wear Testing: This assesses how the tire wears over time under typical operating conditions. It helps predict the tire’s lifespan and performance characteristics.
B2B buyers should ask for documentation of these tests, including any certifications from third-party testing organizations.
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can take several steps:
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can include site visits and evaluations of their quality management systems.
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality assurance practices. This is especially important for international transactions where standards may vary.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider in quality control:
Compliance with Local Regulations: Ensure that suppliers are compliant with both international and local regulations governing tire manufacturing and safety.
Adaptability to Local Conditions: Tires may need to be adapted to meet local road conditions and climate variations. Discussing these needs with suppliers can ensure that the tires are fit for purpose.
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is key to understanding quality control processes. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication with suppliers to address any concerns promptly.
By paying close attention to these aspects of the manufacturing process and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing truck tires, ensuring safety, performance, and compliance with relevant standards.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring effective truck tire inflation pressure solutions. Proper tire inflation is crucial for safety, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity, making it essential for fleet managers and procurement specialists to understand the steps involved in sourcing the right products and services.
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of effective procurement. Consider factors such as the types of trucks in your fleet, the typical loads they carry, and the operating conditions they encounter (e.g., temperature, terrain). This will help you identify the right tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) or inflation solutions that align with your operational needs.
Understanding the local regulations regarding tire inflation and maintenance is essential, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Ensure that the products you consider comply with both international standards and local laws. This not only mitigates legal risks but also ensures the safety and efficiency of your fleet.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Before committing to a supplier, thorough vetting is crucial. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies. Look for suppliers who have experience in your specific market and ask for references from other businesses that operate under similar conditions. This helps ensure that the supplier can meet your expectations and provide reliable support.
Investigate how potential tire inflation solutions integrate with existing fleet management systems. Advanced TPMS can provide real-time data on tire pressure and temperature, which is vital for proactive maintenance. Ensure that the technology aligns with your operational goals and that your team is trained to utilize it effectively.
Whenever possible, request demonstrations or samples of the tire inflation solutions you are considering. This hands-on experience can provide valuable insights into the ease of use, accuracy, and reliability of the products. Evaluate how the solutions perform under different conditions that are relevant to your fleet.
A strong after-sales support system is vital for any procurement decision. Ensure that the supplier offers comprehensive training, maintenance, and warranty options for their products. This will not only enhance your operational efficiency but also protect your investment over time.
Finally, analyze the pricing structure and total cost of ownership associated with the tire inflation solutions. While initial costs are important, consider long-term factors such as maintenance, potential fuel savings from proper tire inflation, and the lifespan of the products. This holistic view will help you make a more informed purchasing decision.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure they make well-informed decisions regarding truck tire inflation pressure solutions, ultimately enhancing fleet safety and efficiency.
Understanding the cost structure of sourcing truck tire inflation pressure solutions is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The quality of materials used directly impacts the performance and longevity of tire inflation systems. High-grade rubber and advanced inflation systems made from durable materials typically result in higher upfront costs but can lead to significant savings over time through reduced tire wear and improved fuel efficiency.
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control. Countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to balance this with the skill level and experience of the workforce.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs necessary for production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
Tooling: Initial costs for specialized tools and molds can be substantial, especially for custom tire pressure solutions. However, these costs are often amortized over large production runs, making it essential for buyers to consider their expected order volumes.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the products meet industry standards and regulations. While this can increase costs, it ultimately protects against costly returns and safety liabilities.
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary significantly based on the destination. Factors such as shipping routes, packaging, and customs duties should be factored into the total cost of ownership.
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their business costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market competition and the perceived value of the product.
Several factors can influence the pricing of truck tire inflation pressure solutions, including:
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on order volume. Larger orders can lead to lower per-unit costs, making it advantageous for buyers to negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs.
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific fleet requirements can lead to higher prices. Buyers should assess whether the customization justifies the additional cost compared to standard solutions.
Materials and Quality Certifications: Products that meet or exceed international quality standards (such as ISO certifications) may command higher prices but offer greater reliability and performance, reducing long-term operational costs.
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge a premium for their products. However, these suppliers often provide added value through superior customer service and product support.
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect the final price. Buyers should be clear about who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance to avoid unexpected costs.
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage bulk purchasing to negotiate better terms. Present data on your purchasing history and projected needs to strengthen your position.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating options, consider not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, fuel efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A higher upfront cost may result in lower TCO.
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Different regions may have varying pricing strategies influenced by local market conditions, economic factors, and regulatory environments. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct thorough market research to identify competitive suppliers.
Monitor Market Trends: Stay informed about global supply chain issues, material shortages, and technological advancements that can impact pricing. This knowledge can help buyers make timely and informed purchasing decisions.
Request for Proposals (RFPs): Utilize RFPs to solicit competitive bids from multiple suppliers, ensuring a transparent process that can lead to better pricing and terms.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure, pricing influences, and effective negotiation strategies can empower international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions regarding truck tire inflation pressure solutions.
In the realm of truck tire management, maintaining the correct inflation pressure is crucial for safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. However, several alternative solutions can complement or even replace traditional tire inflation monitoring methods. This analysis explores these alternatives to help B2B buyers identify the best approach for their specific operational needs.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
| Comparison Aspect | Truck Tire Inflation Pressure | Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) | Nitrogen Inflation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Essential for safety and fuel efficiency; directly affects tire longevity. | Continuously monitors pressure; alerts for deviations, enhancing safety. | Reduces pressure loss over time; maintains consistent pressure. |
| Cost | Minimal ongoing costs; primarily involves occasional checks and adjustments. | Initial investment in technology; potential subscription fees for advanced systems. | Higher initial cost for nitrogen filling; ongoing costs similar to air. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to implement with basic tools; requires regular manual checks. | More complex installation and integration; requires training for staff. | Straightforward filling process but needs specialized equipment for nitrogen. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks and adjustments; prone to human error. | Low maintenance; automatic alerts reduce manual checking requirements. | Minimal maintenance once filled; however, periodic checks are still necessary. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for fleets managing standard tire pressures manually; cost-effective for small operations. | Best for large fleets needing real-time monitoring and safety assurance. | Suitable for fleets operating in extreme conditions; provides longer intervals between pressure adjustments. |
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) are advanced electronic systems that monitor tire pressure in real-time. They provide alerts to drivers when tire pressure deviates from recommended levels. The primary advantage of TPMS is its ability to enhance safety by preventing under-inflation, which can lead to accidents or tire blowouts. Additionally, TPMS can improve fuel efficiency and tire life by ensuring optimal pressure. However, the initial investment can be significant, and proper training is necessary for effective implementation.
Nitrogen inflation is an alternative that utilizes nitrogen gas instead of regular air to fill tires. One of the main benefits of nitrogen is its reduced permeability, which leads to less pressure loss over time. This can be particularly advantageous for fleets operating in harsh conditions or environments where temperature fluctuations are common. Nitrogen inflation also helps maintain tire pressure longer, potentially improving fuel efficiency. However, the initial cost of nitrogen filling and the need for specialized equipment can be a drawback for some operations.
Selecting the right tire inflation solution depends on various factors, including fleet size, operational conditions, and budget constraints. For smaller fleets or those with limited resources, maintaining traditional tire inflation pressure might be the most cost-effective approach. In contrast, larger fleets or those operating in demanding environments may benefit from investing in TPMS or nitrogen inflation systems for enhanced safety and efficiency. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of each alternative’s pros and cons, alongside the specific operational requirements, will guide B2B buyers to the most suitable tire management strategy.
Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Understanding the technical specifications of tire inflation pressure is crucial for B2B buyers in the trucking industry. These specifications not only influence the safety and performance of vehicles but also impact operational costs and efficiency. Here are several critical properties to consider:
The inflation pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), is the primary specification for tire performance. Correct PSI ensures optimal tire contact with the road, which enhances traction, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity. For fleets, maintaining the correct PSI can significantly reduce operating costs, as under-inflated tires lead to increased rolling resistance and fuel consumption.
Each tire is designed to carry a specific load, which is crucial for maintaining safety and performance. The load capacity is usually indicated on the tire sidewall and varies based on tire size and construction. Understanding load limits is essential for fleet managers to avoid overloading tires, which can lead to premature wear, blowouts, and accidents.
Tire pressure can fluctuate with temperature changes, affecting overall performance. For every 10°F increase in temperature, tire pressure can rise by approximately 2 PSI. Fleet operators need to account for temperature variations in different regions and adjust tire pressures accordingly, especially in extreme climates. This understanding helps in maintaining tire integrity and safety.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Tread wear indicators are built into tires to help assess their remaining tread depth. Monitoring tread wear is vital for ensuring safety, as inadequate tread can increase the risk of hydroplaning and reduce traction. Regularly checking these indicators allows fleet managers to schedule timely replacements, thereby avoiding costly downtime.
The materials used in tire construction, such as rubber compounds and steel belts, play a significant role in performance characteristics like durability and fuel efficiency. Understanding the composition helps in selecting tires that best suit specific operational requirements, such as terrain and load type, leading to optimized performance and cost savings.
Knowledge of industry-specific terminology is essential for B2B buyers to facilitate effective communication and negotiations. Here are several key terms:
OEM refers to the original manufacturer of the tire or vehicle. Understanding OEM specifications is critical for ensuring compatibility and performance when replacing tires. B2B buyers should always seek OEM recommendations to maintain vehicle integrity and warranty compliance.
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for fleet operators when budgeting for tire purchases, as it can affect overall procurement costs. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to better pricing and inventory management.
An RFQ is a formal request issued to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing RFQs for tire purchases can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing, ultimately leading to cost-effective purchasing decisions.
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities associated with tire procurement, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers.
TPMS refers to electronic systems that monitor tire pressure in real-time. These systems enhance safety and efficiency by alerting drivers to pressure changes, allowing for immediate corrective action. Understanding TPMS is vital for modern fleet management, as it aids in proactive maintenance and reduces the risk of tire-related incidents.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize tire performance and enhance fleet efficiency.
The truck tire inflation pressure market is experiencing significant transformation driven by several global factors. Increasing fuel prices and the urgent need for operational efficiency are pushing fleet operators toward technologies that optimize tire performance. Advanced tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are gaining traction, allowing real-time monitoring and adjustments to tire pressure, which can enhance fuel efficiency and safety. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions may vary significantly, necessitating adaptable tire management solutions.
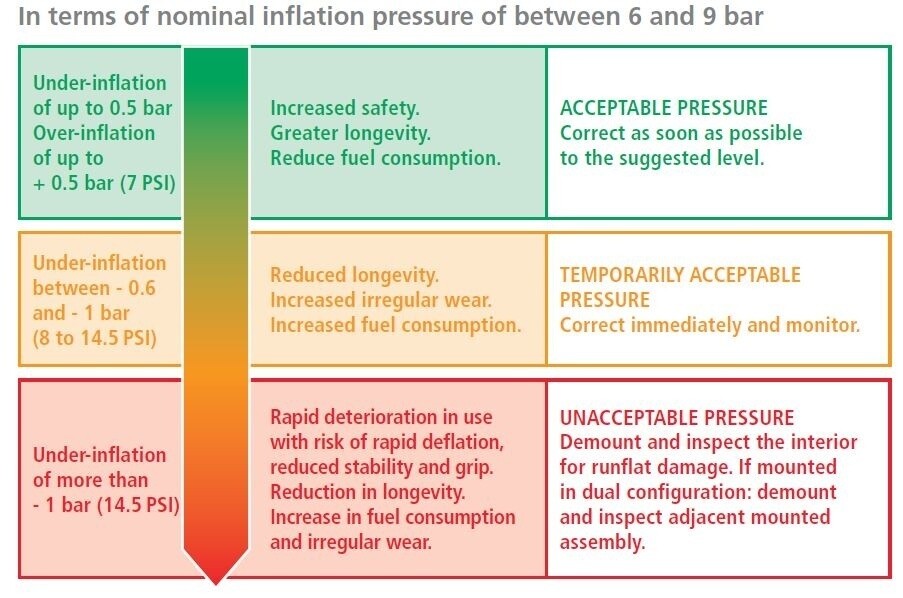
Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Emerging technologies such as predictive analytics and artificial intelligence are also influencing sourcing strategies. These technologies enable fleets to analyze tire performance data, predict maintenance needs, and optimize tire life, ultimately reducing total cost of ownership. For B2B buyers, understanding these trends is essential for making informed procurement decisions that align with both operational efficiency and sustainability goals.
Furthermore, regional market dynamics play a crucial role. In the Middle East and Europe, stringent regulations regarding emissions and safety standards are driving demand for high-quality tires that meet these requirements. Buyers from these regions must stay informed about compliance standards while also considering the advancements in tire manufacturing that support enhanced performance and reduced environmental impact.
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of procurement strategies, particularly in the truck tire inflation pressure sector. The environmental impact of tire production and disposal is significant, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and processes, as well as initiatives aimed at reducing waste through tire recycling programs.

Illustrative image related to truck tire inflation pressure
Ethical sourcing is equally critical, as it fosters transparency and accountability in the supply chain. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers with verified ethical certifications, ensuring that the materials used in tire production meet social responsibility standards. This is particularly important for international buyers from regions such as Africa and South America, where the socio-economic implications of sourcing practices can be profound.
Investing in ‘green’ certifications and materials not only enhances a company’s brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products. As regulations around sustainability tighten globally, B2B buyers must prioritize partnerships with suppliers committed to environmental stewardship and ethical practices to remain competitive in the marketplace.
The evolution of truck tire inflation pressure management can be traced back to the early days of commercial trucking. Initially, tire pressure was monitored manually, leading to frequent under-inflation and associated risks such as blowouts and reduced fuel efficiency. As the trucking industry grew, so did the awareness of tire maintenance’s critical role in operational safety and efficiency.
In the 1990s, the introduction of tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) revolutionized the sector. These systems allowed for real-time monitoring, significantly reducing the incidence of tire-related accidents. Over the years, advancements in technology have continued to shape tire management practices, with data analytics and predictive maintenance becoming standard in modern fleets.
Today, the focus has shifted toward integrating sustainability and efficiency in tire management practices. With the ongoing developments in materials science and manufacturing processes, the future of truck tire inflation pressure management will likely center around optimizing performance while minimizing environmental impact. This historical context highlights the importance of staying informed about both technological advancements and sustainability trends for B2B buyers looking to enhance their procurement strategies.
How do I determine the correct tire inflation pressure for my truck?
To determine the correct tire inflation pressure for your truck, refer to the vehicle’s owner’s manual or the Tire Information Placard (T.I.P.), typically located in the driver’s door jamb. Additionally, weigh your truck fully loaded on a scale to accurately assess axle weights, as inflation pressure varies based on load. Consult the manufacturer’s tire data book to match the actual load with the recommended pressure. Regularly checking and adjusting tire pressure, particularly in response to temperature and load changes, is essential for safety and efficiency.
What is the best tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) for fleet management?
The best TPMS for fleet management is one that offers real-time monitoring, alerts for pressure changes, and data analytics to track tire performance across the fleet. Systems like those endorsed by leading tire manufacturers provide comprehensive solutions, including temperature readings and predictive maintenance alerts. Look for systems that integrate seamlessly with existing fleet management software and offer mobile access for on-the-go monitoring. A reliable TPMS can significantly reduce tire-related downtime and enhance overall fleet safety.
How can improper tire pressure affect fuel efficiency?
Improper tire pressure can drastically reduce fuel efficiency. For example, under-inflation of just 22 PSI can lead to a 10% loss in fuel yield and a 1% increase in fuel consumption. This is primarily due to increased rolling resistance, which forces the engine to work harder. Regularly monitoring and maintaining the correct tire pressure not only improves fuel economy but also extends tire life, ultimately saving costs for your fleet.
What are the implications of international shipping on tire procurement?
International shipping introduces complexities such as customs regulations, tariffs, and varying standards for tire specifications across countries. Buyers must ensure compliance with local regulations in the destination country, which can affect tire design and labeling. Additionally, consider logistics costs, lead times, and the reliability of shipping partners. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers who understand these intricacies can help mitigate risks and ensure timely delivery of tires.
How do I vet suppliers for truck tire inflation products?
When vetting suppliers for truck tire inflation products, consider their reputation, certifications, and industry experience. Request references from other B2B clients and assess their financial stability. Evaluate their ability to meet your specific needs, including customization options and adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales support and warranty policies to ensure a reliable partnership.
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect from tire suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly among tire suppliers based on product type and supplier policies. For bulk purchases, MOQs may be lower, while specialized or custom tires may require higher quantities. Always clarify the MOQ during negotiations to ensure it aligns with your purchasing capabilities. Some suppliers may be open to flexibility based on your purchasing frequency or long-term contracts.
What payment terms are common in international tire trade?
Common payment terms in international tire trade include letters of credit, advance payments, and open account terms, depending on the trust level between buyer and supplier. Letters of credit provide security for both parties, while advance payments may be requested for new relationships. Always negotiate payment terms that suit your cash flow needs while ensuring supplier confidence. Additionally, consider currency exchange rates and payment processing fees when finalizing agreements.
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I expect from tire suppliers?
Reputable tire suppliers should have robust quality assurance (QA) measures in place, including adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001. Expect suppliers to conduct routine inspections and testing of tires for performance, durability, and safety. Inquire about their quality control processes, including certifications and documentation provided with shipments. Regular audits and feedback mechanisms can also help maintain product quality over time, ensuring you receive reliable tires for your fleet.
Domain: business.michelinman.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: The text emphasizes the importance of selecting the correct tire pressure for trucks and buses to maintain tire performance, safety, and fuel efficiency. It highlights that tire pressure is often one of the least monitored maintenance issues. Proper inflation is crucial, and trucks should be weighed fully loaded to determine the correct tire pressure based on the manufacturer’s tire data. Insuffic…
Domain: toyotires.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Load and Inflation Tables provide assistance for replacing tires with optional sizes, including plus sizes not listed on the vehicle’s tire information placard (T.I.P) or in the owner’s manual. For original equipment (OE) size inflation pressure, refer to the T.I.P. found on the vehicle door jam, glove compartment, or near the gas cap. Important: Consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific s…
Domain: yournexttire.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Tire Inflation Chart: The formula for load capacity is Tire Weight / Tire Pressure = Load Capacity Pounds per PSI. Example: A 265/75R16 10-ply tire at 80 psi carries 3,085 pounds; at 60 psi, it carries 2,314 pounds; at 65 psi, it carries 2,507 pounds. A 265/75R16 6-ply tire at 50 psi carries 2,470 pounds, which is more than a 10-ply at 60 psi.
Domain: tirereview.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Proper tire inflation is influenced by temperature, altitude, and load weight. For every 10-degree Fahrenheit change, tire pressure shifts by about 2 PSI. Technicians should not lower a hot tire’s pressure to match cold inflation recommendations. If a hot tire reads below the recommended pressure, inflate it to the recommended PSI plus an extra 10 PSI. Altitude affects tire pressure as well; for e…
In conclusion, the significance of precise truck tire inflation pressure cannot be overstated for international B2B buyers. Maintaining the correct tire pressure is essential for safety, efficiency, and sustainability, directly impacting fuel consumption and overall operating costs. Strategic sourcing of high-quality tires, complemented by a robust tire maintenance program, ensures that fleets can maximize their performance while minimizing environmental footprints.
For companies operating across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the local climates and load conditions is crucial. Variations in temperature and altitude necessitate tailored tire inflation strategies to optimize performance. Regular monitoring and adjustments based on these factors will not only prolong tire life but also enhance vehicle safety and reliability.
As you navigate your sourcing strategies, prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive support and resources for tire management. Collaborating with experts in the field can yield significant benefits, ensuring that your fleet operates at peak efficiency. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operations through strategic tire sourcing and management, positioning your business for future growth and success.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.