In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing an efficient air pressurizer can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With various options available, understanding the nuances of air pressurizers—ranging from portable models to industrial-grade units—can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower decision-makers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Nigeria and Vietnam, by providing critical insights into the air pressurizer market.
Throughout this guide, you will explore the diverse types of air pressurizers available, their specific applications across different industries, and best practices for supplier vetting to ensure reliability and quality. We will also delve into cost considerations, helping you to align your budget with your operational needs. By addressing common challenges faced by B2B buyers, this resource aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions, enabling you to select the right air pressurizer that meets both your business requirements and compliance standards.
With a focus on practical advice and actionable insights, this guide serves as an essential tool for navigating the complexities of the global air pressurizer market. By leveraging this information, you can streamline your procurement process, enhance productivity, and ultimately drive your business success.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Air Compressors | Lightweight, easy to transport, small tank sizes | DIY projects, small workshops, automotive repairs | Pros: Highly mobile, ideal for varied locations. Cons: Limited air supply for larger jobs. |
| Stationary Air Compressors | Larger tanks, higher PSI, designed for fixed locations | Manufacturing, construction, heavy-duty applications | Pros: Continuous air supply, suitable for extensive use. Cons: Less portable, requires dedicated space. |
| Electric Air Compressors | Operated via electric power, quieter operation | Indoor tasks, woodworking, spray painting | Pros: Quiet operation, no fuel costs. Cons: Limited by electrical outlets, may require extension cords. |
| Gas-Powered Air Compressors | Operates on gasoline, high PSI capabilities | Outdoor construction, remote locations | Pros: High mobility, powerful for heavy tasks. Cons: Fuel costs, noisier operation. |
| Oil-Free Air Compressors | No oil required for operation, lower maintenance | Medical applications, food processing, automotive | Pros: Cleaner air output, minimal maintenance. Cons: Generally lower durability than oil-lubricated models. |
Portable air compressors are designed for mobility and convenience, making them ideal for smaller tasks or DIY projects. They typically feature smaller tank sizes ranging from 1 to 6 gallons, providing sufficient power for tools like nail guns and inflators. Businesses in sectors such as automotive repair or home improvement often find these compressors valuable due to their ease of transport and setup. Buyers should consider their specific project requirements, as these compressors may not sustain prolonged use or support heavy-duty applications.
Stationary air compressors are built for durability and continuous operation, featuring larger tanks (often 20 gallons or more) and higher PSI ratings. These compressors are commonly utilized in manufacturing, construction, and other industrial settings where a reliable and constant air supply is crucial. While they require a designated space and are less portable, they excel in powering multiple air tools simultaneously. B2B buyers should assess their operational needs and facility layout to determine if a stationary compressor meets their requirements.
Electric air compressors are favored for indoor applications due to their quieter operation and lower maintenance needs. They are ideal for tasks like woodworking, spray painting, or running pneumatic tools in confined spaces. With most models designed to connect to standard electrical outlets, they eliminate the need for fuel, making them a cost-effective option for businesses focused on indoor projects. Buyers should consider their power availability and the compressor’s decibel rating to ensure compliance with workplace noise standards.
Gas-powered air compressors are essential for outdoor projects or remote job sites where electrical access is limited. They offer high PSI capabilities and the ability to run continuously, making them suitable for construction and heavy-duty applications. However, they come with higher operational costs due to fuel consumption and may produce more noise. B2B buyers should evaluate the nature of their work environment and the necessity for mobility versus the convenience of electric models when considering gas-powered options.
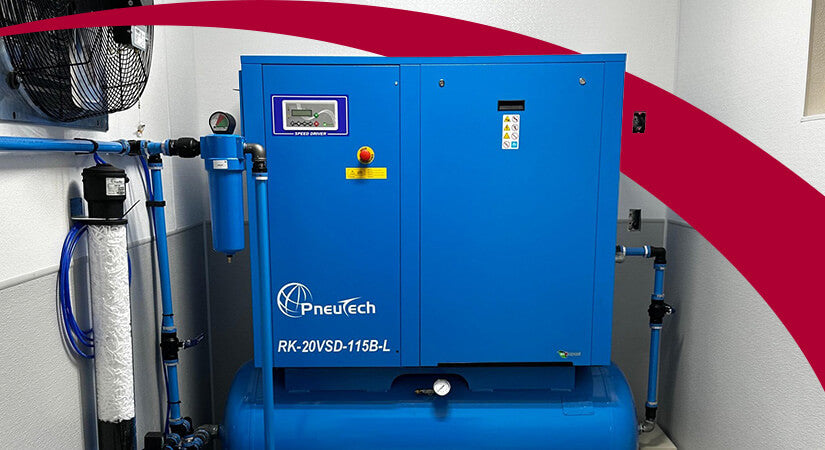

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Oil-free air compressors are designed for applications requiring clean air, such as in the medical or food processing industries. They eliminate the need for oil, resulting in lower maintenance and cleaner air output. While they may not offer the same durability as oil-lubricated models, they are often lighter and easier to handle. Businesses focused on hygiene and air quality should prioritize oil-free options, while also considering the compressor’s performance specifications to ensure it meets their operational demands.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of air pressurizer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Pneumatic Tool Operation | Increased productivity and efficiency | Energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, noise levels |
| Automotive | Tire Inflation and Maintenance | Enhanced safety and reduced downtime | Portability, pressure capacity, and durability |
| Construction | Concrete Spraying and Finishing | Improved quality and faster project completion | Tank capacity, mobility, and compatibility with tools |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and Sealing Processes | Ensured product integrity and extended shelf life | Compliance with safety standards, air quality, and reliability |
| Agriculture | Crop Spraying and Pest Control | Enhanced crop yield and reduced labor costs | Versatility, tank size, and ease of use |
In the manufacturing sector, air pressurizers are integral for operating pneumatic tools such as drills, wrenches, and hammers. They provide a consistent air supply, which is essential for maintaining high productivity levels. By using air pressurizers, manufacturers can significantly reduce the time spent on repetitive tasks, allowing for a more streamlined workflow. Buyers should consider energy efficiency and maintenance requirements when sourcing equipment, particularly in regions where operational costs are a concern.
In automotive contexts, air pressurizers are crucial for tire inflation and routine maintenance tasks. They ensure that tires are inflated to the optimal pressure, enhancing vehicle safety and performance. This application minimizes downtime in service stations and enhances customer satisfaction. For international buyers, key considerations include the portability of the units, pressure capacity to meet various vehicle requirements, and the durability of the compressors in different environmental conditions.
Air pressurizers are extensively used in construction for concrete spraying and finishing processes. They enable contractors to apply materials evenly and efficiently, which results in higher-quality finishes and faster project completion times. This application also reduces manual labor, leading to cost savings. Buyers in the construction sector should prioritize tank capacity and the mobility of the air pressurizers, as projects often require equipment to be moved between sites.
In the food and beverage industry, air pressurizers are utilized in packaging and sealing processes, ensuring that products remain uncontaminated and have an extended shelf life. This application is critical for maintaining product integrity and meeting safety regulations. Buyers should focus on sourcing equipment that complies with industry safety standards, ensures air quality, and offers reliability, especially in regions with stringent food safety regulations.
Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Air pressurizers are increasingly being used in agriculture for crop spraying and pest control applications. They allow for precise application of pesticides and fertilizers, leading to enhanced crop yields and reduced labor costs. This technology enables farmers to cover large areas quickly and efficiently. For international buyers, versatility, tank size, and ease of use are critical factors to consider, as they can significantly impact the effectiveness of agricultural practices in varying climates and terrains.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in manufacturing and assembly industries face the challenge of inconsistent air pressure from their air pressurizers. This inconsistency can lead to subpar product quality, wasted materials, and increased operational costs. For example, in a paint spraying application, fluctuating pressure levels can result in uneven finishes, requiring additional labor and materials to rectify the defects. Such issues not only delay production timelines but also impact customer satisfaction and overall profitability.
The Solution: To tackle this problem, it is crucial to invest in high-quality air pressurizers that offer reliable and adjustable pressure settings. Buyers should look for models equipped with pressure regulators and gauges to monitor and maintain consistent output. Additionally, implementing a routine maintenance schedule, including regular checks on filters and hoses, can prevent pressure drops caused by blockages. It’s also beneficial to train staff on the importance of maintaining consistent air pressure and how to adjust settings based on specific job requirements. By ensuring a stable air supply, businesses can enhance product quality and operational efficiency.
The Problem: Noise pollution from air pressurizers is a significant concern for many businesses, especially those operating in enclosed spaces or near customer-facing areas. Excessive noise not only creates a discomforting work environment but can also lead to reduced employee productivity and potential hearing damage over time. For instance, in a workshop setting, the constant hum of high-decibel air compressors can distract workers, making it difficult for them to communicate effectively or concentrate on their tasks.
The Solution: To mitigate noise levels, buyers should consider investing in low-noise or ultra-quiet air pressurizers designed specifically for quieter operations. Models with sound-dampening features, such as insulated cabinets or advanced motor designs, can significantly reduce noise output. Additionally, placing air pressurizers in soundproof enclosures or designated areas away from the main work zone can further minimize disruption. Implementing regular noise assessments and providing employees with noise-canceling headphones can enhance their comfort and productivity. By prioritizing a quieter workplace, companies can improve employee morale and maintain a conducive environment for operations.
The Problem: Frequent breakdowns of air pressurizers are a common pain point for B2B buyers, leading to costly downtime and disrupted workflows. This issue often arises from inadequate maintenance, incorrect usage, or the selection of unsuitable equipment for specific applications. For instance, a construction company relying on portable air pressurizers may find that their equipment fails during critical tasks, resulting in project delays and increased labor costs.
The Solution: To reduce the frequency of breakdowns, businesses should conduct thorough assessments of their air pressurizer needs before purchase. This includes evaluating the specific applications, required air pressure, and volume needs. Sourcing equipment from reputable manufacturers that offer warranties and customer support can also provide peace of mind. Establishing a comprehensive maintenance program, including regular inspections and timely replacements of wear-and-tear parts, can prolong the lifespan of air pressurizers. Training operators on best practices for usage and maintenance can further enhance reliability. By taking these proactive steps, companies can minimize downtime, ensuring smooth operations and cost-effectiveness.
When selecting materials for air pressurizers, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly impact performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in air pressurizers: aluminum, steel, composite materials, and stainless steel.
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity. It typically has a pressure rating of up to 150 PSI, making it suitable for various applications.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Pros: Aluminum is easy to manufacture, which can reduce production costs. Its lightweight nature allows for easy handling and installation, particularly beneficial in portable air pressurizers.
Cons: While aluminum is corrosion-resistant, it may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as other materials. Additionally, it can be more expensive than some other options, particularly when high-strength alloys are required.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, including air and inert gases, making it a versatile choice for many applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN is crucial. Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet the necessary specifications for their region, especially in markets like Africa and the Middle East, where environmental factors may affect material performance.
Steel is a robust material with high tensile strength and excellent durability, making it ideal for high-pressure applications. It can handle pressures exceeding 200 PSI, depending on the grade.
Pros: Steel’s strength and durability make it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is generally less expensive than aluminum, particularly in bulk purchases.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion, requiring protective coatings or treatments, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage for portable applications.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for various media, including air and gases, but may require additional treatment when used with corrosive substances.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as JIS and DIN, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations. The availability of corrosion-resistant coatings may also be a factor in regions with high humidity or saline environments.
Composite materials, often a combination of polymers and reinforcing fibers, are increasingly used in air pressurizers due to their unique properties. They can offer pressure ratings similar to metals while being lightweight and resistant to corrosion.
Pros: Composites are highly customizable, allowing manufacturers to tailor material properties for specific applications. They also provide excellent resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for harsh conditions.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly, especially for high-performance composites. Additionally, they may not be suitable for all types of media, particularly those that can degrade polymers.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials, particularly in portable pressurizers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that composite materials meet relevant standards, as regulations vary significantly across regions. In markets like South America and Africa, understanding local material preferences and availability is essential for successful procurement.
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It is capable of handling high pressures, often exceeding 300 PSI, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: Stainless steel offers excellent longevity and requires minimal maintenance. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for use in various environments, including those with moisture or chemicals.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Cons: The primary drawback of stainless steel is its cost, which can be significantly higher than other materials. Additionally, its weight may be a concern for portable applications.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive gases, making it a versatile option for industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is vital. Buyers should also consider the availability of different grades of stainless steel, as preferences may vary by region.
| Material | Typical Use Case for air pressurizer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable air pressurizers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Composite | Lightweight portable applications | Customizable and corrosion-resistant | Complex manufacturing | High |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure industrial applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | High cost | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for air pressurizers, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
The manufacturing process of air pressurizers involves several critical stages to ensure the final product meets performance and safety standards. The main stages include:
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection and preparation of high-quality raw materials, typically metals such as aluminum or steel for the casing and components. These materials are sourced from certified suppliers who adhere to international standards. The preparation stage may also include cutting, machining, and treating the materials to enhance durability.
Forming: This stage involves shaping the raw materials into the required components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and extrusion are commonly employed. For instance, the casing of an air pressurizer may be stamped from a sheet of metal, while internal components like pistons may be forged for strength and precision.
Assembly: Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage may include the integration of mechanical parts, electrical components, and safety features. Automated assembly lines are often used to increase efficiency and consistency, although skilled technicians are also involved to ensure quality workmanship.
Finishing: After assembly, the air pressurizer undergoes finishing processes such as painting, coating, or polishing. These not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also provide protection against corrosion and wear. Final inspections are performed to ensure that all components fit correctly and that the product meets design specifications.
Quality assurance (QA) is a pivotal aspect of the manufacturing process for air pressurizers, ensuring that products are safe, reliable, and meet customer expectations. Key elements of QA include:
International Standards Compliance: Manufacturers often adhere to international quality management standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement, which is crucial for gaining trust in international markets.
Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the application of the air pressurizer, additional certifications may be required. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply for products intended for oil and gas applications.
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints designed to catch defects early. Common QC checkpoints include:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This involves checking for compliance with specifications, ensuring that materials are free from defects and meet the required standards.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various inspections and tests are conducted at different stages to identify any deviations from quality standards. This may include checking the dimensions of formed parts, ensuring proper assembly techniques, and verifying that machinery is functioning correctly.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, the air pressurizer undergoes a final inspection. This includes functional testing, pressure testing, and safety checks to ensure that the product operates correctly and meets all specifications. Documentation of test results is often maintained for traceability.
To ensure that air pressurizers perform reliably and safely, manufacturers employ various testing methods, including:
Pressure Testing: This is a critical test to verify that the air pressurizer can withstand operational pressures without leaking or failing. It typically involves filling the unit with air or water and measuring for any loss of pressure over time.
Performance Testing: This assesses the efficiency and output of the air pressurizer under different conditions. It evaluates factors such as airflow rate, pressure output, and energy consumption to ensure that the product meets performance specifications.
Durability Testing: This involves subjecting the air pressurizer to stress tests that simulate real-world usage. It helps identify potential failure points and ensures that the product can withstand the rigors of daily operation.
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential. Here are actionable steps:
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards. This allows buyers to assess the supplier’s capabilities and commitment to quality firsthand.
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports can provide transparency regarding the supplier’s quality assurance practices and help identify any recurring issues.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections typically include assessments of manufacturing practices, compliance with international standards, and product testing.
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification, particularly when sourcing from manufacturers in different regions:
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. For instance, while CE marking is essential in Europe, other regions may prioritize different certifications. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the relevant standards in their target markets.
Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices may vary significantly across regions. Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance collaboration and ensure that quality expectations are clearly understood and met.
Logistics and Compliance: Buyers should consider the logistics involved in importing products, including compliance with local regulations and tariffs. Understanding these factors can help mitigate risks associated with product quality and delivery.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of air pressurizers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations. This diligence not only supports operational efficiency but also enhances the overall success of their business endeavors in a competitive global market.
To ensure a successful procurement process for air pressurizers, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help international B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions.
Start by clearly outlining the technical requirements for the air pressurizer you need. Consider factors such as pressure ratings, tank capacity, power source (electric or gas), and intended applications. This step is critical because having precise specifications helps streamline the selection process and ensures that you acquire a product that meets your operational needs.
Stay informed about the latest trends and innovations in air pressurization technology. Look for advancements that enhance efficiency, reduce noise levels, or improve portability. Understanding market dynamics allows you to make informed decisions and could lead to cost savings or improved performance in your applications.
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and customer references. It’s beneficial to seek feedback from other businesses in your industry or region to assess reliability and service quality. A robust vetting process reduces risks associated with quality and delivery issues.
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with international standards. Look for ISO certifications or compliance with local regulations specific to air pressurizers. This step is vital to guarantee product safety, efficiency, and environmental compliance, which are increasingly important in today’s market.
Inquire about after-sales services and warranty options offered by suppliers. Reliable support can include maintenance services, spare parts availability, and technical assistance. A strong warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind, ensuring that you have access to support if issues arise after purchase.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Once you have identified a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Compare these quotes not only on price but also on the value offered, including product features and support services. This thorough comparison will help you identify the best overall deal.
Engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms, including price, payment conditions, and delivery schedules. Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing or additional benefits such as extended warranties. Once terms are agreed upon, finalize the purchase with a clear contract that outlines all agreed-upon details to avoid misunderstandings.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for air pressurizers with confidence, ensuring they select the right product and supplier for their specific needs.
When sourcing air pressurizers, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
Materials typically account for a significant portion of the total cost. Common materials used in air pressurizers include aluminum, steel, and various plastics, which can vary widely in price based on quality and availability.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Labor costs can fluctuate based on the region where production occurs. In countries with higher labor costs, the overall price of air pressurizers may be elevated.
Manufacturing overhead includes expenses related to the production environment, equipment maintenance, and utilities. This cost can be minimized by choosing suppliers with efficient production processes.
Tooling costs may also be significant, especially for custom designs or specialized equipment. These costs are typically amortized over the volume of units produced, making them a critical consideration for buyers looking to negotiate pricing based on order volume.
Quality control is essential for ensuring that the air pressurizers meet the required specifications. Investing in rigorous QC processes may increase upfront costs but can lead to long-term savings by reducing returns and warranty claims.
Logistics encompasses shipping, handling, and any duties or tariffs that may apply. International buyers must account for these additional costs in their total budget.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Several factors can influence the pricing of air pressurizers. Volume and minimum order quantity (MOQ) are critical; larger orders typically yield better pricing due to economies of scale. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate lower unit prices for bulk purchases.
Specifications and customization also play a significant role in determining price. Custom features or specific certifications may lead to higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
Material quality and certifications can significantly affect pricing. High-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) often justify a premium price, but they also enhance reliability and performance, leading to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over time.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Supplier factors such as reputation, reliability, and service level can also impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but offer better warranties and customer support, which can be invaluable in the long run.
Incoterms determine the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements. Understanding the chosen Incoterm (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial as it affects the total landed cost, which includes shipping and insurance.
B2B buyers should employ several strategies to negotiate favorable pricing. Start by conducting thorough market research to understand the typical price range for the desired air pressurizer specifications. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
Focus on total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider long-term operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment in a quality product may lead to significant savings over its lifespan.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Be transparent about your needs and order quantities. Suppliers may offer better pricing for larger volumes or long-term contracts, so it’s beneficial to establish a solid relationship with potential vendors.
Consider alternative suppliers to create competition, which can drive down prices. However, ensure that these suppliers meet your quality and service expectations to avoid compromising your operational efficiency.
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several pricing nuances must be considered. Currency fluctuations can impact pricing, so it’s wise to negotiate terms that account for potential changes.
Import duties, tariffs, and shipping logistics can significantly affect the final cost. Ensure that you fully understand these factors before committing to a supplier.
Additionally, cultural differences in negotiation styles may influence outcomes. Familiarizing yourself with the local business customs can enhance communication and foster better relationships with suppliers.
Prices for air pressurizers can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier relationships, and specific buyer requirements. The prices referenced in this analysis are indicative and subject to change. Always verify current pricing and terms with suppliers to ensure the best deal possible.
When evaluating the effectiveness of air pressurizers, it is essential to consider alternative solutions that can fulfill similar roles in various industrial applications. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and budget constraints. Below, we compare air pressurizers with two viable alternatives: traditional air compressors and gas-powered air systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Air Pressurizer | Traditional Air Compressor | Gas-Powered Air System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High pressure delivery; suitable for precise applications | Versatile, good for various tasks | High power output for heavy-duty applications |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower operating costs | Varies widely; generally higher operational costs | Higher initial and ongoing fuel costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively simple setup; minimal infrastructure required | Requires space and installation of tanks | Complex setup; requires fuel storage and safety measures |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; minimal wear | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance | High maintenance; fuel systems can be complex |
| Best Use Case | Precision tasks in confined spaces | General-purpose tasks in workshops | Heavy-duty industrial applications requiring high mobility |
Traditional air compressors have long been a staple in many industries due to their versatility. They can handle a wide range of applications, from powering pneumatic tools to inflating tires. However, they often come with higher operational costs due to energy consumption and maintenance requirements. Additionally, they may require considerable space for installation and use, which can be a drawback in environments with limited space.
Gas-powered air systems are ideal for heavy-duty applications where high mobility is required. These systems can operate in remote locations without access to electricity, making them suitable for construction sites and outdoor work. However, they have higher initial costs and ongoing fuel expenses, which can be a significant factor for B2B buyers. Maintenance is also more demanding due to the complexities of the fuel systems and the need for regular checks to ensure safety and reliability.
Selecting the appropriate air pressurizer or its alternatives hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your operations. Consider factors such as the intended application, available budget, and maintenance capabilities. If precision and low maintenance are critical, an air pressurizer may be the best choice. Conversely, for versatile and general-purpose applications, a traditional air compressor might serve better. For high-demand situations where mobility and power are paramount, a gas-powered air system could be the most effective solution. By carefully weighing these aspects, B2B buyers can make a well-informed decision that aligns with their operational goals.
When evaluating air pressurizers, several critical specifications significantly impact performance, reliability, and suitability for various applications. Understanding these properties is crucial for B2B buyers making informed purchasing decisions.
The material grade of an air pressurizer determines its durability and resistance to corrosion. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and composite materials. For example, aluminum is lightweight and resistant to rust, making it ideal for portable applications, while steel offers strength and longevity for stationary units. Choosing the right material ensures that the pressurizer can withstand the intended operating environment, thus minimizing replacement costs over time.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
The pressure rating, usually measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the maximum pressure the air pressurizer can handle safely. This specification is vital for applications requiring specific pressure levels to operate tools or machinery effectively. Understanding the required PSI for your projects helps avoid equipment failure and ensures optimal performance.
Tank capacity, measured in gallons, refers to the volume of air the pressurizer can store. Larger tanks can supply compressed air for extended periods without frequent cycling, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. Conversely, smaller tanks are more portable and ideal for DIY or light commercial use. Selecting the appropriate tank size aligns with operational demands and efficiency.
Noise level, measured in decibels (dBA), is a crucial consideration, particularly in environments where noise regulations are in place or where operator comfort is a concern. Low-noise models, typically rated below 70 dBA, provide a more pleasant working environment and can be used in residential areas without disturbing nearby activities. Evaluating noise levels can enhance workplace safety and compliance with local regulations.
Air pressurizers can be powered by electricity or gas. Electric models are often quieter and require less maintenance, making them suitable for indoor use. In contrast, gas-powered models provide mobility and higher output for outdoor applications. Understanding the operational context helps in selecting the right power source, ensuring efficiency and convenience.
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some key terms you should know:
An OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of air pressurizers, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they receive quality components that meet industry standards.
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers, especially small businesses or those testing a new product line, as it affects budget and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases and avoiding excess stock.
An RFQ is a document that buyers use to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It is an essential step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers, negotiate terms, and make informed decisions based on pricing and specifications.
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in global trade transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations. This knowledge aids in negotiating contracts and ensuring smooth transactions across borders.
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory planning and project scheduling. Buyers should consider this factor to align procurement with operational timelines effectively.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the air pressurizer market more effectively, ensuring they make well-informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
The air pressurizer market is currently experiencing significant growth driven by a surge in industrial automation, increased demand for compressed air in various applications, and technological advancements. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Vietnam, the adoption of energy-efficient and compact air compressors is rising. This shift is largely influenced by the need for reliable and cost-effective solutions in manufacturing, construction, and automotive sectors.
One of the most significant trends is the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology in air pressurizers. Smart air compressors equipped with sensors and connectivity features enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which can significantly reduce downtime and operational costs. This trend is particularly appealing to international B2B buyers looking to optimize their operational efficiency and minimize maintenance expenses.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a central focus within the industry. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices, such as producing low-emission air compressors or utilizing recyclable materials. As regulations tighten globally, especially in Europe, compliance with environmental standards is crucial for suppliers aiming to capture market share in these regions.
In summary, international B2B buyers should be aware of the technological advancements in air pressurizers, the growing emphasis on sustainability, and the importance of sourcing from suppliers that align with these trends to remain competitive in their respective markets.
Sustainability is reshaping the air pressurizer sector as businesses increasingly recognize the environmental impact of their operations. Air compressors are often energy-intensive, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, there is a growing demand for energy-efficient models that minimize energy consumption while maintaining performance. Buyers are encouraged to look for products that carry certifications such as Energy Star or ISO 14001, which indicate compliance with rigorous environmental standards.
Ethical sourcing is another critical consideration. International buyers are now more inclined to partner with manufacturers who maintain transparent supply chains and adhere to ethical labor practices. This focus not only enhances brand reputation but also reduces risks associated with supply chain disruptions and compliance issues.
Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of air pressurizers is gaining traction. Manufacturers are increasingly exploring the use of recyclable and biodegradable components, which can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of their products. By prioritizing suppliers who commit to sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility initiatives while meeting the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.

Illustrative image related to air pressurizer
The evolution of the air pressurizer sector can be traced back to its early mechanical origins in the 19th century, where steam-driven compressors laid the groundwork for modern air compression technology. Over the decades, innovations such as the introduction of electric compressors and advancements in materials science have significantly enhanced efficiency and reliability. The 20th century saw the rise of portable and compact models, making air pressurizers accessible to a broader range of industries and applications.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards automation and smart technology, reflecting broader trends in industrialization. The integration of IoT capabilities has transformed traditional air compressors into smart devices, capable of providing real-time data and analytics. This evolution not only improves operational efficiency but also aligns with the increasing demand for sustainability and ethical sourcing in today’s market. As the industry continues to advance, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these developments to capitalize on new opportunities and ensure their sourcing strategies remain competitive.
How do I solve issues with inconsistent air pressure in my operations?
Inconsistent air pressure can hinder production efficiency and equipment performance. To address this, first, ensure that your air pressurizer is properly sized for your application, as an undersized unit may not meet demand. Regular maintenance, including checking for leaks in hoses and fittings, is crucial. Additionally, consider installing pressure regulators and storage tanks to stabilize pressure fluctuations. If problems persist, consult with suppliers about upgrading to a more robust system or incorporating advanced technologies such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) for better control.
What is the best air pressurizer for industrial applications?
The best air pressurizer for industrial applications typically features a higher capacity, robust build quality, and advanced technology for efficiency. Look for units with a tank capacity of at least 20 gallons, high PSI ratings (above 100 PSI), and features such as oil-free pumps for lower maintenance. Brands with proven reliability in heavy-duty environments should be prioritized. It’s also essential to assess the specific requirements of your operations, such as the types of tools you’ll be using, to choose the most suitable model.
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for air pressurizers?
When vetting suppliers, consider their reputation, experience, and customer feedback. Check for certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate quality assurance. It’s beneficial to request references from previous clients in your industry. Evaluate their ability to provide technical support and service, as well as warranty options. Additionally, inquire about their production capabilities to ensure they can meet your order volume and customization needs, especially for specific applications.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for air pressurizers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for air pressurizers can vary widely by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs can range from one unit for smaller, portable models to several units for larger, industrial-grade systems. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your business requirements. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or bulk orders, so it’s advantageous to communicate your intended volume clearly.
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing air pressurizers internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions typically include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or net terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). The choice of terms often depends on the supplier’s policies, your business relationship, and the risk involved. Ensure to clarify these terms before finalizing any agreements. It’s also wise to consider the currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees that might apply when dealing with international suppliers.
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when purchasing air pressurizers?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing air pressurizers, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Conduct factory audits if possible, or rely on third-party inspection services to verify manufacturing practices. Establish clear quality standards and testing procedures in your purchase agreement. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer trial periods or satisfaction guarantees, allowing you to assess the product’s performance in your operational environment before committing to larger orders.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing air pressurizers?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, transit times, and customs regulations. Choose between air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your timeline and budget. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes applicable in your country, as these can significantly impact total costs. Collaborate with a logistics partner experienced in international shipping to navigate documentation and compliance requirements efficiently.
Can air pressurizers be customized to fit specific operational needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for air pressurizers to meet specific operational requirements. Custom features may include tailored tank sizes, specific PSI ratings, or unique control systems that align with your workflow. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and discuss potential impacts on lead times and costs. Engaging with suppliers early in the design phase can facilitate smoother integration of customized solutions into your operations.
Domain: lowes.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Air Tools & Compressors at Lowe’s include a variety of options such as Portable Air Compressors, Stationary & Industrial Air Compressors, Electric Air Compressors, Gas Air Compressors, and Quiet Air Compressors. Portable models are suitable for various locations and come in styles like pancake, hot dog, twin stack, and wheelbarrow. They are ideal for DIY projects and tire inflation. Stationary air…
In the evolving landscape of air pressurizers, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for B2B buyers looking to optimize their procurement processes. By understanding the diverse offerings—ranging from portable to stationary compressors—businesses can align their needs with the right products, ensuring operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Key considerations such as power source, noise levels, and tank size directly impact the selection process, influencing both short-term project outcomes and long-term sustainability.
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should leverage local market insights and supplier capabilities to enhance their sourcing strategies. Building relationships with reputable manufacturers can not only secure competitive pricing but also foster innovation through tailored solutions that meet specific market demands.
As we move forward, the importance of strategic sourcing in the air pressurizer market cannot be overstated. Embrace this opportunity to refine your procurement strategy and invest in technologies that drive efficiency. Engage with trusted suppliers and stay informed on emerging trends to ensure your business remains at the forefront of operational excellence. The future of your projects depends on the decisions you make today—take action now to enhance your sourcing strategy.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.