Navigating the complexities of correct tire inflation is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing for fleets across diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A key challenge faced by these buyers is ensuring that tires are properly inflated to enhance safety, optimize fuel efficiency, and prolong tire lifespan, all while managing varying local regulations and climate conditions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of tire inflation, covering essential topics such as recommended pressure levels, the impact of temperature fluctuations, and the differences between maximum and minimum pressure guidelines.
In addition to technical specifications, the guide delves into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for maintenance. By equipping buyers with this critical knowledge, we empower them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs. Whether you are in Nigeria, Germany, or anywhere in between, understanding the nuances of tire inflation can lead to significant cost savings and improved safety for your fleet. This resource is designed not just to inform but also to support strategic procurement decisions that enhance overall efficiency and reliability in tire management.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Tire Pressure | Measured when tires are cold, typically before driving. | Fleet management, logistics companies | Pros: Ensures safety and optimal performance. Cons: Requires regular monitoring. |
| Maximum Tire Pressure | The highest pressure a tire can safely hold. | Heavy-duty vehicles, construction | Pros: Useful for heavy loads. Cons: Can impair handling and safety if used regularly. |
| Recommended Tire Pressure | Manufacturer’s optimal pressure for performance. | Automotive dealerships, service centers | Pros: Enhances fuel efficiency and tire lifespan. Cons: Misunderstandings can lead to under- or over-inflation. |
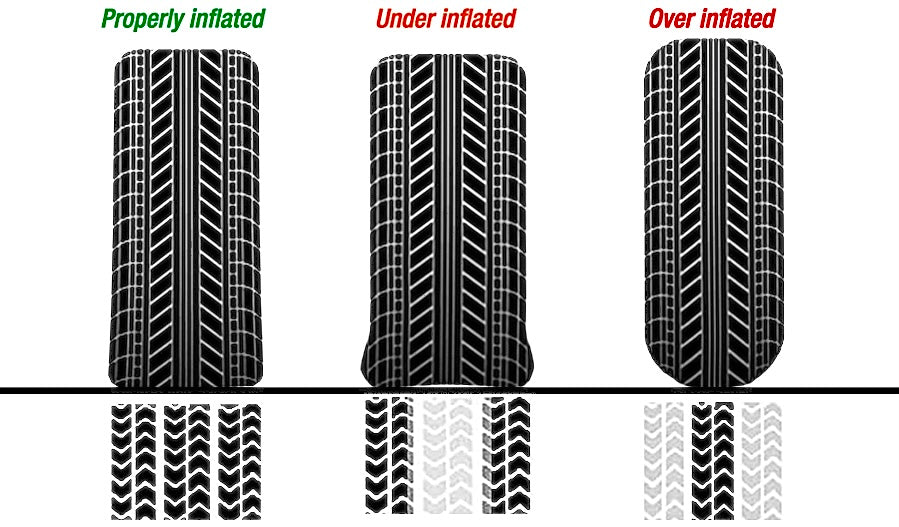
| Under-Inflation | Pressure below the recommended level, often due to leaks or neglect. | Transportation, delivery services | Pros: Low initial cost. Cons: Increases risk of blowouts and reduces fuel efficiency. |
| Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) | Automated systems that alert users to pressure changes. | Automotive manufacturing, fleet services | Pros: Enhances safety and reduces manual checks. Cons: Potential for system failure and false alerts. |
Cold tire pressure refers to the optimal tire inflation level measured when the tire is not heated from driving. This is crucial for fleet management and logistics companies, where safety and performance are paramount. Regular monitoring of cold tire pressure helps in maintaining vehicle efficiency and longevity, thereby reducing operational costs. B2B buyers should invest in accurate gauges and establish protocols for routine checks to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Maximum tire pressure indicates the highest inflation level a tire can withstand without failure. This is particularly relevant for heavy-duty vehicles in construction and industrial sectors, where tires are subjected to extreme loads. While inflating to maximum pressure can enhance load capacity, it may compromise vehicle handling and safety during regular operations. Buyers should consider the trade-offs and only use maximum pressure in specific, controlled scenarios.
Recommended tire pressure is the manufacturer’s specified inflation level for optimal vehicle performance. This standard is essential for automotive dealerships and service centers, as it directly impacts fuel efficiency and tire lifespan. Misunderstandings about recommended pressure can lead to costly maintenance and safety issues. B2B buyers should prioritize training and resources that ensure accurate tire inflation practices among their staff to enhance customer satisfaction and vehicle reliability.
Under-inflation occurs when tire pressure falls below the recommended level, often due to leaks or neglect. This situation is particularly risky for transportation and delivery services, where operational safety is critical. Tires that are under-inflated can lead to increased rolling resistance, resulting in higher fuel consumption and an elevated risk of blowouts. B2B buyers should implement regular maintenance checks and educate drivers on the importance of monitoring tire pressure.
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) provide real-time alerts regarding tire pressure changes, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. This technology is increasingly adopted in automotive manufacturing and fleet services, where timely information can prevent accidents and reduce maintenance costs. While TPMS offers significant advantages, buyers should be aware of potential system failures and ensure they have backup procedures in place to maintain tire safety.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of correct tire inflation | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Fleet Management | Improved safety, reduced fuel costs | Reliability of tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS), supplier reputation, and availability of tire gauges. |
| Construction | Heavy Equipment Operations | Enhanced equipment performance and longevity | Compatibility with various machinery, local regulations, and service support. |
| Agriculture | Agricultural Machinery | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Access to specialized tire inflation systems, local climate considerations, and tire durability. |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Delivery Vehicles | Lower operational costs and improved delivery times | Availability of bulk purchasing options and tire pressure management solutions. |
| Automotive Services | Tire Retail and Maintenance Services | Customer satisfaction through enhanced safety and performance | Quality of tire pressure gauges, training for staff on proper inflation techniques, and aftermarket support. |
In the transportation industry, particularly in fleet management, maintaining correct tire inflation is critical for ensuring safety and efficiency. Fleet operators must regularly monitor tire pressure to prevent blowouts and enhance fuel economy. Under-inflated tires lead to increased rolling resistance, resulting in higher fuel consumption and operational costs. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing reliable tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and high-quality tire gauges to facilitate regular checks, ensuring compliance with safety regulations across various regions, including Africa and Europe.
In construction, heavy equipment relies heavily on correct tire inflation for optimal performance. Properly inflated tires enhance traction and stability, reducing the risk of accidents on job sites. Equipment downtime due to tire issues can significantly impact project timelines and budgets. Buyers must consider the compatibility of tire pressure management systems with different machinery types and ensure that suppliers offer robust service support and comply with local safety regulations, especially in regions with diverse operating conditions, such as South America and the Middle East.
For agricultural machinery, maintaining correct tire inflation is essential for operational efficiency and reducing downtime during critical planting and harvesting seasons. Properly inflated tires improve traction and reduce soil compaction, which is vital for crop health. Buyers in the agricultural sector should look for durable tires that can withstand varied terrain and climate conditions. Additionally, access to specialized tire inflation systems that can handle large volumes and varying tire sizes is crucial for maximizing productivity.
In logistics and warehousing, delivery vehicles must maintain correct tire inflation to ensure timely deliveries and minimize operational costs. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased fuel consumption and reduced vehicle handling, impacting delivery schedules. Businesses should focus on sourcing bulk purchasing options for tires and tire pressure management solutions that enable efficient monitoring across fleets. Understanding regional fuel costs and regulatory requirements will also help logistics companies optimize their operations in diverse markets like Africa and Europe.
For automotive service providers, correct tire inflation is a key aspect of customer service and vehicle maintenance. Proper tire inflation enhances vehicle safety and performance, leading to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business. Service providers should invest in high-quality tire pressure gauges and ensure that their staff is trained in proper inflation techniques. Offering tire pressure checks as part of routine maintenance can differentiate service providers in competitive markets, particularly in regions with varying consumer expectations, such as Germany and Nigeria.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers managing fleets of vehicles face the challenge of inconsistent tire pressure monitoring. In regions with varying climates, such as Africa and the Middle East, temperature fluctuations can cause tire pressure to change significantly. This inconsistency often leads to under- or over-inflation, which can compromise safety, increase fuel consumption, and accelerate tire wear. Fleet managers may struggle to implement a standardized process for checking and maintaining tire pressure, risking vehicle performance and operational costs.
The Solution: To address this issue, fleet managers should invest in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) that provide real-time data on tire pressure across all vehicles. Opt for systems that integrate with fleet management software, allowing for centralized monitoring and alerts when tire pressure deviates from the recommended levels. Additionally, establish a routine maintenance schedule where tire pressure is checked and adjusted monthly. Providing training for drivers on the importance of maintaining correct tire pressure can further enhance compliance and awareness. By creating a culture of proactive maintenance, fleet operators can significantly improve vehicle safety and efficiency.
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those in regions with less access to automotive education, often lack knowledge about the correct tire pressures for their vehicles. This gap in understanding can lead to improper inflation, resulting in increased operational costs and safety hazards. For example, businesses in South America may find it challenging to locate the manufacturer’s recommended tire pressure, leading to trial-and-error approaches that can be costly and dangerous.
The Solution: To overcome this knowledge gap, businesses should prioritize education by developing comprehensive guides on tire maintenance that include clear instructions on how to find and interpret the recommended tire pressures. These resources can be distributed as part of onboarding materials for new employees or shared through workshops. Companies should also ensure that tire pressure information is readily available on vehicle stickers and in manuals, and consider using mobile apps that provide reminders for tire pressure checks based on the vehicle’s usage patterns. Implementing these educational strategies will empower employees to make informed decisions regarding tire inflation, ultimately improving safety and reducing costs.
The Problem: A common issue for B2B buyers is the misunderstanding of the difference between cold and hot tire pressure readings. Many fleet operators may check tire pressure after driving, resulting in inflated readings due to heat. This misunderstanding can lead to under-inflation if adjustments are made based on incorrect data, compromising vehicle safety and performance, particularly in European markets where regulatory standards for tire maintenance are stringent.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, organizations should implement strict protocols for checking tire pressure. Emphasize that tire pressure should be checked when tires are cold—ideally, first thing in the morning or after the vehicle has been parked for at least three hours. Provide training sessions to educate staff on how temperature affects tire pressure and the importance of following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Additionally, consider equipping vehicles with digital tire pressure gauges that can store previous readings, allowing users to compare cold and hot pressures easily. By fostering an understanding of these concepts, businesses can enhance the safety and efficiency of their fleet operations.
Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
When selecting materials for tire inflation systems, it is essential to consider properties such as temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in tire inflation systems, focusing on their advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Key Properties: Rubber is flexible, resilient, and can withstand a range of temperatures. It typically has a pressure rating that aligns with standard tire inflation requirements, making it suitable for most vehicles.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of rubber is its excellent sealing properties, which prevent air loss. It is also relatively inexpensive and widely available. However, rubber can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and ozone, leading to potential leaks. Additionally, its performance can be affected by extreme temperatures, which may not be suitable for all environments.
Impact on Application: Rubber is compatible with air and nitrogen, commonly used in tire inflation. However, in regions with extreme temperatures, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, the degradation of rubber may be a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Germany should ensure that the rubber used meets local standards, such as DIN or ASTM, to ensure safety and performance.
Key Properties: Metals, such as aluminum and steel, are often used in tire valves and inflation tools. They possess high strength and corrosion resistance, particularly when treated or coated.
Pros & Cons: The durability of metal components makes them suitable for repeated use, and they can withstand high pressures without deforming. However, metal can be more expensive than rubber and may require additional treatments to prevent corrosion, especially in humid or coastal environments.
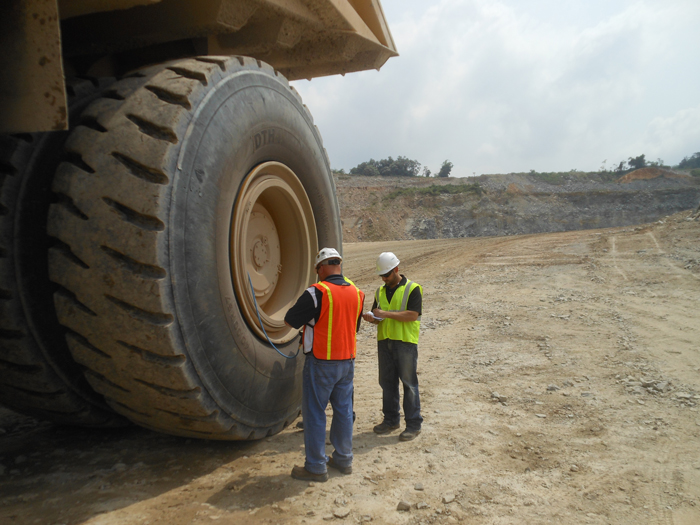

Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
Impact on Application: Metal valves and fittings are essential for maintaining the integrity of the tire inflation system, particularly in heavy-duty applications. They are compatible with various gases, including air and nitrogen.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the local availability of treated metals and compliance with international standards to ensure longevity and reliability in diverse climates.
Key Properties: Plastics, including polyamide and polypropylene, are lightweight and can be engineered for specific pressure ratings. They often exhibit good chemical resistance and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of plastics makes them ideal for portable tire inflation tools. They are generally less expensive than metals and can be produced in various colors and designs. However, some plastics may not withstand high temperatures and pressures as effectively as metals or rubber.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) and inflation nozzles. They are compatible with air and nitrogen, making them versatile for various tire inflation needs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the plastics used comply with local regulations and standards, particularly in Europe, where material safety is strictly regulated.
Key Properties: Composite materials combine the benefits of different substances, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent resistance to environmental factors.
Pros & Cons: Composites can be tailored for specific applications, providing superior performance in harsh conditions. However, they tend to be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for high-performance tire inflation systems, particularly in motorsports or heavy-duty applications where weight and durability are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the availability of composite materials and their compliance with international standards, especially in regions where advanced materials are required for competitive performance.

Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
| Material | Typical Use Case for correct tire inflation | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Tire seals and valves | Excellent sealing properties | Degrades under UV exposure | Low |
| Metal | Tire valves and inflation tools | High strength and durability | Higher cost and potential corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | TPMS and inflation nozzles | Lightweight and versatile | Limited high-pressure capabilities | Low |
| Composite | High-performance tire inflation systems | Tailored performance in harsh conditions | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This comprehensive analysis of materials used in tire inflation systems provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions, ensuring safety, performance, and compliance in their respective markets.
The manufacturing process of tires is intricate, involving several stages that ensure not only the structural integrity of the tire but also its ability to maintain correct inflation levels. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages involved in tire production:
The initial stage involves sourcing and preparing materials such as natural rubber, synthetic rubber, fabric, steel, and various chemicals. Each component is critical for achieving the desired performance characteristics of the tire. High-quality materials are essential for durability and inflation retention. Key techniques in this stage include:
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming the tire components. This includes the inner liner, belts, and tread. Key techniques include:
In the assembly stage, the various components are brought together to form the tire. This involves:
The final stage in manufacturing involves curing the tire through a process called vulcanization, where heat and pressure are applied to set the rubber structure. Key techniques include:
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of tire manufacturing, ensuring that every tire produced meets safety and performance standards. Here’s how QA processes are structured in tire production:
Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as:
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that tires can maintain proper inflation and meet safety standards:
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s QC processes is crucial:
International buyers must navigate various certification requirements that can differ by region:
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for tire inflation is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality tires. By focusing on the details of production and the robustness of QC measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers capable of meeting their needs for safety, performance, and longevity.
Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to ensure correct tire inflation for their fleet or commercial vehicles. Proper tire inflation is essential for safety, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity. By following these steps, organizations can streamline their procurement process and enhance overall vehicle performance.
Understanding the specific tire pressure recommendations for your vehicles is crucial. Each vehicle model has unique requirements, typically found in the owner’s manual or a sticker inside the driver’s door. Proper adherence to these specifications ensures optimal handling, safety, and performance.
Investing in reliable tire pressure gauges is essential for accurate measurements. This equipment allows for consistent monitoring of tire pressure, which should be checked monthly and before long trips. A quality gauge will provide precise readings and help maintain the recommended pressure.

Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
Create a regular schedule for checking tire pressure as part of your fleet maintenance program. Consistency in monitoring helps prevent issues related to under- or over-inflation, which can lead to accidents and increased fuel costs.
When sourcing tires or tire maintenance services, ensure that suppliers possess the necessary certifications and adhere to industry standards. This not only guarantees quality but also compliance with safety regulations, which is paramount for operational safety.
Consider equipping your fleet with TPMS technology. These systems provide real-time data on tire pressure, alerting drivers to any deviations from the recommended levels. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of tire-related incidents.
Invest in training programs for your maintenance team to ensure they understand the importance of correct tire inflation and how to check pressures properly. Educated staff can identify issues early, which can save costs and enhance safety.

Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
Regularly assess the performance metrics of your tires, including tread wear and fuel efficiency. Monitoring these indicators can help identify inflation issues early and inform decisions about tire replacements or adjustments.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure that their tire inflation processes are optimized, contributing to safer and more efficient vehicle operations.
When sourcing solutions for correct tire inflation, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The quality of materials used in tire inflation systems, such as pressure gauges, inflation tools, and monitoring systems, can significantly impact costs. Durable materials that resist wear and tear are often more expensive but provide long-term savings.
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely by region. In Europe and North America, labor costs are generally higher than in regions like Africa or South America. Additionally, skilled labor may be required for installation and maintenance of tire inflation systems.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility expenses. High overhead can arise from advanced manufacturing technologies used to produce more accurate and reliable tire inflation systems.
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized tire inflation solutions can add to initial costs. However, investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better long-term efficiency and product quality.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that products meet safety and performance standards. While this adds to production costs, it can reduce liability and improve customer satisfaction.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, especially for international transactions. These costs can vary based on the shipping method, distance, and destination. Understanding Incoterms is vital to avoid unexpected expenses.
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin that reflects their brand value, market demand, and the competitive landscape. This margin can vary significantly based on the supplier’s reputation and the uniqueness of their offering.
Several factors influence pricing when sourcing tire inflation solutions:
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide better pricing for bulk purchases or minimum order quantities (MOQs). Negotiating for higher volumes can yield significant savings.
Specifications/Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific vehicle types or industrial applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of customization against potential benefits.
Materials: The choice of materials can greatly impact pricing. For instance, high-performance materials may be more expensive but can offer longer service life and efficiency, ultimately lowering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or have certifications can command higher prices. However, they often provide better performance and reliability, justifying the investment.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to perceived reliability and service levels.
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (such as FOB, CIF, etc.) is crucial for cost management. Different Incoterms can result in varying levels of responsibility for shipping costs and risks, impacting the overall price.
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies for effective negotiation and cost management:
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the long-term benefits of products rather than just initial purchase prices. A higher upfront cost may lead to reduced maintenance and longer service life.
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a solid relationship may yield better deals and terms.
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations. Knowledge of competitor pricing can empower buyers in negotiations.
Evaluate Logistics Options: Consider various shipping methods and logistics partners to find the most cost-effective solutions. This may involve looking at different freight forwarders or exploring consolidated shipping options.
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Recognize that pricing can vary significantly across regions. For instance, sourcing from local suppliers in Africa may offer cost advantages due to lower shipping expenses compared to sourcing from Europe or North America.
Prices for tire inflation solutions can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors, including regional market conditions, supplier agreements, and specific product requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes before making purchasing decisions.
In the realm of tire management, correct tire inflation is crucial for safety, performance, and cost efficiency. However, businesses may seek alternative methods or technologies that can help achieve similar outcomes, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis compares correct tire inflation with two viable alternatives: Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) and Automatic Tire Inflation Systems (ATIS).

Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
| Comparison Aspect | Correct Tire Inflation | Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) | Automatic Tire Inflation System (ATIS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Optimizes fuel efficiency and tire life | Provides real-time pressure alerts, enhancing safety | Maintains optimal pressure automatically, reducing manual checks |
| Cost | Low-cost solution (manual checks) | Moderate initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Higher initial investment; potential long-term savings on tire wear |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple manual checks; requires user diligence | Requires installation; user-friendly interfaces available | Professional installation needed; generally seamless operation post-installation |
| Maintenance | Requires regular manual checks | Low maintenance; alerts for pressure drops | Minimal maintenance; relies on system functionality and monitoring |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for businesses with smaller fleets and lower operational costs | Suitable for medium to large fleets needing enhanced safety | Best for large fleets or high-value vehicles where uptime is critical |
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS)
TPMS are designed to monitor tire pressure in real-time and alert drivers when pressure falls below a specified threshold. This technology enhances safety by preventing under-inflation, which can lead to accidents. The moderate cost associated with TPMS includes both initial installation and periodic maintenance. While TPMS improves safety, it does not replace the need for manual checks, as it primarily functions as a warning system. Businesses with medium to large fleets benefit significantly from TPMS, as it reduces the risk of tire-related incidents while improving overall fleet management.
Automatic Tire Inflation Systems (ATIS)
ATIS automatically adjusts tire pressure, ensuring that tires are always inflated to optimal levels. This system eliminates the need for regular manual checks, providing significant convenience for fleet operators. Although the initial installation cost is higher compared to TPMS, ATIS can lead to long-term savings by reducing tire wear and improving fuel efficiency. This system is particularly beneficial for large fleets or vehicles that operate under heavy loads, where maintaining tire pressure can be critical for operational efficiency and safety. However, ATIS requires professional installation and may involve ongoing monitoring costs.
When selecting a tire management solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, fleet size, and budget constraints. Correct tire inflation remains a fundamental practice, especially for smaller operations. However, for businesses aiming for enhanced safety and efficiency in larger fleets, investing in TPMS or ATIS may provide substantial long-term benefits. Analyzing the performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
When engaging in the tire industry, understanding the essential technical properties related to correct tire inflation is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity of tire performance. Below are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
The recommended tire pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), is a vital specification provided by the vehicle manufacturer. Maintaining tires at this pressure optimizes handling, fuel efficiency, and tire lifespan. For B2B buyers, ensuring compliance with these specifications is essential for fleet safety and operational costs.
Maximum pressure is the highest PSI that a tire can safely withstand, as indicated on the tire sidewall. While it may exceed the recommended PSI, filling tires to this level can impair vehicle handling and increase the risk of blowouts. Understanding this distinction helps buyers avoid over-inflation, which can lead to costly tire replacements and safety issues.
Cold tire pressure refers to the pressure measurement taken when the tires are not heated from driving. This is the most accurate time to check tire pressure, as heat can artificially inflate the reading. B2B buyers should emphasize routine checks of cold tire pressure to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear.
TPMS is a safety feature that alerts drivers when tire pressure falls below a certain threshold, typically 25% below the recommended PSI. For businesses with vehicle fleets, investing in vehicles equipped with TPMS can enhance safety and reduce liability by proactively addressing under-inflation issues.
The load index indicates the maximum weight a tire can support when properly inflated. Each tire’s load index must align with the vehicle’s specifications to ensure safe operation. B2B buyers should verify that the load index meets or exceeds the demands of their specific applications, particularly in industries involving heavy loads.
In addition to technical specifications, familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in the manufacturing of vehicles. For tire suppliers, understanding OEM specifications ensures that the tires meet original performance criteria, which is critical for fleet operations and vehicle resale value.
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their inventory and budget effectively. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to optimize procurement processes for tire purchases.
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is crucial for B2B buyers to gather competitive bids and make informed purchasing decisions regarding tire inflation systems and related components.
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping, insurance, and delivery obligations, which are vital when sourcing tires from overseas manufacturers.
These are small raised sections on the tire tread that indicate when a tire has worn down to an unsafe level. Recognizing treadwear indicators is essential for maintaining tire safety and performance. B2B buyers should ensure that their procurement includes tires with visible treadwear indicators for compliance with safety regulations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their tire management practices align with safety, regulatory, and operational standards.
The global market for correct tire inflation is influenced by several key drivers, including safety regulations, fuel efficiency concerns, and advancements in tire technology. Increasing awareness about vehicle safety and fuel economy is prompting B2B buyers to prioritize proper tire inflation as a crucial factor in operational efficiency. As fuel prices remain volatile, maintaining optimal tire pressure can significantly reduce fuel consumption, making it a vital consideration for logistics and transportation companies across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Emerging technologies such as Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) are becoming standard in many vehicles, enabling real-time monitoring of tire pressure. These systems not only enhance safety but also streamline maintenance processes for fleet operators, reducing downtime and repair costs. Moreover, the rise of mobile applications that provide tire pressure monitoring and management solutions is reshaping how B2B buyers interact with tire maintenance services.
Furthermore, international trade dynamics and sourcing trends are shifting towards local suppliers who can offer quicker turnarounds and better support. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that provide comprehensive tire maintenance solutions, including inflation systems and regular monitoring services. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions with growing automotive markets, where the demand for reliable tire inflation products and services is on the rise.

Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the tire industry, particularly as environmental regulations tighten globally. The production and disposal of tires can have significant environmental impacts, including pollution and resource depletion. As such, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as utilizing eco-friendly materials in tire manufacturing and ensuring responsible disposal and recycling methods.
The adoption of ‘green’ certifications, such as those provided by the Global Sustainability Council or the Tire Industry Association, can enhance a supplier’s credibility and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. These certifications often indicate that the products meet specific environmental standards, which can be a deciding factor for companies looking to align their procurement processes with their corporate social responsibility goals.
Moreover, incorporating sustainable practices in tire inflation solutions—such as using energy-efficient compressors or offering services that promote tire longevity—can further reduce the carbon footprint of logistics operations. This focus on sustainability not only helps businesses comply with regulations but also resonates with consumers who prioritize environmentally responsible practices.
The evolution of the correct tire inflation sector has been marked by technological advancements and increased consumer awareness. Historically, tire inflation was a largely manual process, often neglected by drivers, leading to widespread issues of under-inflation and over-inflation. The introduction of tire pressure monitoring systems in the late 20th century revolutionized the industry by providing real-time feedback and alerts, significantly enhancing safety and efficiency.

Illustrative image related to correct tire inflation
In recent years, the integration of smart technologies has further transformed tire management. Innovations such as mobile apps for tire monitoring and automated inflation systems are making it easier for businesses to maintain optimal tire pressure. As the sector continues to evolve, B2B buyers must stay informed about technological advancements and sustainability practices that can enhance their operational efficiency while promoting safety and reducing environmental impact.
This evolution underscores the importance of selecting suppliers who are not only knowledgeable about these advancements but also committed to ethical and sustainable practices in the tire inflation sector.
How do I solve issues with tire under-inflation for my fleet?
To address tire under-inflation, implement a routine tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) across your fleet. Conduct regular checks at least once a month and before long trips. Educate your drivers about the importance of maintaining proper tire pressure and provide them with reliable tire pressure gauges. Additionally, consider using centralized inflation systems that automatically adjust tire pressure based on real-time data, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
What is the best tire pressure monitoring system for commercial vehicles?
The best tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) for commercial vehicles should include features such as real-time alerts, temperature monitoring, and remote access. Look for systems that offer compatibility with multiple vehicle types and easy integration with existing fleet management software. Brands like TireBoss and Michelin offer robust solutions tailored for commercial use, providing insights that help reduce downtime and improve fuel efficiency.
How can I ensure compliance with international tire safety regulations?
To comply with international tire safety regulations, familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the regions where your vehicles operate. This includes understanding the recommended tire pressures, load ratings, and safety standards set by authorities such as the European Union and local regulations in countries like Nigeria and Brazil. Work with suppliers who are knowledgeable about regional compliance and provide tires that meet or exceed these standards.
What should I consider when vetting tire suppliers for my business?
When vetting tire suppliers, evaluate their certifications, product quality, and track record in the industry. Request references and check for compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications. Assess their ability to meet your specific needs, including minimum order quantities (MOQs) and customization options. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery and responsiveness to your inquiries.
What are the typical payment terms offered by tire suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among tire suppliers, but common arrangements include net 30, net 60, or even letter of credit for larger orders. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and financial planning. It’s prudent to establish a clear understanding of payment schedules, potential discounts for early payments, and the consequences of late payments to avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
How do temperature fluctuations affect tire pressure in different climates?
Temperature fluctuations can significantly impact tire pressure, as air expands when heated and contracts when cooled. In warmer climates, tire pressure can increase, leading to over-inflation, while in cooler areas, it may drop, causing under-inflation. To mitigate these effects, regularly check tire pressures and adjust accordingly based on seasonal changes. This is particularly important for businesses operating in regions with extreme temperature variations, such as parts of Africa and South America.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for tire procurement?
When procuring tires, consider the logistics of transportation, warehousing, and distribution. Evaluate shipping options, including costs, delivery times, and the reliability of carriers. Ensure that your supplier can efficiently handle customs clearance if importing tires, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Additionally, assess the storage facilities for tires to prevent damage and ensure they remain in optimal condition until installation.
Can I customize tires to meet specific operational needs?
Yes, many tire manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific operational needs, such as tread patterns, load capacities, and materials. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options. Customizing tires can enhance performance and safety, especially for specialized applications like off-road vehicles or heavy-duty transport. Be prepared to meet minimum order quantities and timelines for custom tire production.
Domain: pirelli.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Recommended tire pressure is established by the vehicle manufacturer and typically falls between 28 and 36 PSI. The correct pressure can be found in the car’s operator manual or on a sticker inside the driver’s door. It’s important to check tire pressure when tires are cold. Maximum tire pressure is stated on the tire’s sidewall and should not be used for everyday driving, as it can impair handlin…
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The correct tire pressure for your car is located on a sticker in the driver’s doorjamb, not on the tire itself. The pressure printed on the sticker is typically about 32 PSI +/- 4 PSI, depending on the vehicle. The ‘max pressure’ on the tire sidewall is the absolute maximum, not the operating pressure. Overinflated tires can increase brake distance, reduce traction, decrease tire lifespan, and ri…
Domain: bridgestoneamericas.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Proper tire inflation is crucial for maximizing tire performance and lifespan. It is recommended to check tire pressure at least once a month, as tires lose approximately 1 PSI per month. Tire pressure can also change with temperature, losing about 1 PSI for every 10 degrees F change. The correct tire pressure is not indicated on the tire’s sidewall; instead, the maximum inflation pressure is list…
Domain: tirereview.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Proper tire inflation is influenced by temperature, altitude, and load weight. For every 10-degree Fahrenheit change, tire pressure shifts by about 2 PSI. A hot tire can show 10 to 20 PSI higher than normal; if it’s below recommended pressure, inflate it to the recommended PSI plus an extra 10 PSI. Altitude affects tire pressure, increasing by about 0.48 PSI for every 1,000 feet gained. The maximu…
Domain: toyotires.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Load and Inflation Tables provide assistance for replacing tires with optional sizes, including plus sizes not listed on the vehicle’s tire information placard (T.I.P) or owner’s manual. For original equipment (OE) size inflation pressure, refer to the T.I.P., commonly found on the vehicle door jam, glove compartment, or near the gas cap. Important to consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual for speci…
Domain: generaltire.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: General Tire offers a range of tires including performance tires (G-MAX AS 07, G-MAX RS), touring tires (Alti MAX 365 AW, Alti MAX RT 45), all-terrain/mud-terrain tires (Grabber H/T, Grabber A/T X, Grabber X 3), and winter tires (Alti MAX Arctic 12, Grabber Arctic LT, Grabber Arctic). Proper tire pressure is crucial for vehicle performance, affecting driving comfort, stability, cornering, braking …
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of tires, adhering to the recommended tire inflation pressure is crucial. For B2B buyers, understanding the implications of tire maintenance extends beyond safety; it significantly impacts operational efficiency and cost management. Proper tire inflation improves fuel economy, enhances vehicle handling, and reduces the risk of premature tire wear, ultimately lowering replacement costs.
Strategic sourcing of tire maintenance solutions, including accurate gauges and monitoring systems, enables businesses to maintain compliance with safety standards while optimizing fleet performance. Regular tire pressure checks should be integrated into standard operating procedures, fostering a culture of proactive maintenance that can yield substantial cost savings.
Looking ahead, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with reliable tire suppliers and service providers. By investing in quality tire management solutions and training, businesses can ensure safety and efficiency in their operations. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your fleet’s performance through strategic sourcing—your bottom line will thank you.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.